Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Heat Treatment Processes Explained
Hochgeladen von
sandhu31janOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Heat Treatment Processes Explained
Hochgeladen von
sandhu31janCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GURJANT SINGH
PE-1104
HEAT TREATMENT
The process of heat treatment is carried out first by heating the material
and
then cooling it in the brine, water and oil. The purpose of heat treatment
is to
soften the metal, to change the grain size, to modify the structure of the
material
and to relieve the stress set up in the material after hot and cold working
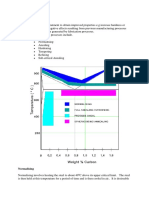
ANNEALING:-
Spherodizing:-
Spherodite forms when carbon steel is heated to
approximately 700 for over 30 hours. The purpose is to
soften higher carbon steel and allow more formability. This
is the softest and most ductile form of steel. Here cementite
is present.
HARDENING:-
The process of hardening consist of heating the metal to a
temperature of 30-50 c above the upper critical point for
hypo-eutectoid steels and by the same temperature above
the lower critical temperature for hyper-eutectoid steels. It
is held this temperature for some time and then quenched.
The purposes of hardening are to increase the hardness of
the metal and to make suitable cutting tools.
AUSTEMPERING:-
It is a hardening process. it is also known as isothermal
quenching. In this process, the steel is heated above the
upper critical temperature at about 875 c where the
structure consists entirely of austenite. It is then suddenly
cooled by quenching it in a salt bath maintained at a
temperature of about 250 c to 525 c.
MARTEMPERING:-
This process is also known as steeped quenching or
interrupted quenching. It consists of heating steel above
the upper critical temperature and quenching it in a salt
bath kept at a suitable temperature.
TEMPERING:-
This process consists of reheating the hardened steel to
some temperature below the lower critical temperature,
followed by any desired rate of cooling. The purpose is to
relive internal stress, to reduce brittleness and to make
steel tough to resist shock and fatigue.
SURFACE HARDENING
In many engineering applications, it is desirable that steel
being used should have a hardened surface to resist wear
and tear. At this time, it should have soft and tough interior
or core so that it can absorb any shocks. Case hardening is
the process of hardening the surface of metal, often a low
carbon steel by infusing elements into the metal surface
forming a hard, wear resistance skin but preserving a tough
and ductile interior. This type of treatment is applied to
gears, ball bearings, railway wheels
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Annealing, Normalizing, Quenching, Martensitic TransformationDokument22 SeitenAnnealing, Normalizing, Quenching, Martensitic TransformationAboo BackerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creep and Shrinkage Analysis in Strand7 R2.4Dokument18 SeitenCreep and Shrinkage Analysis in Strand7 R2.4caojin259Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Process GuideDokument67 SeitenHeat Treatment Process GuidebassamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Heat TreatmentDokument59 SeitenUnit 2 Heat TreatmentAmutha PSGRKCWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minitab 16 Full Version - Download Full Version Software Key Serial Number Patch - Available-CrackDokument8 SeitenMinitab 16 Full Version - Download Full Version Software Key Serial Number Patch - Available-Cracksandhu31jan75% (4)
- Inergen SpecDokument19 SeitenInergen SpecMargaret DaughertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Flag Pavements Design GuideDokument31 SeitenConcrete Flag Pavements Design GuideNguyễn Hoàng Bảo100% (2)
- Heat Treatment of Ferrous MetalsDokument8 SeitenHeat Treatment of Ferrous Metalsarchangeluriel06Noch keine Bewertungen
- AnnealingDokument11 SeitenAnnealingsourabhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Complete Guide to Watch Repair - Barrels, Fuses, Mainsprings, Balance Springs, Pivots, Depths, Train Wheels and Common Stoppages of WatchesVon EverandA Complete Guide to Watch Repair - Barrels, Fuses, Mainsprings, Balance Springs, Pivots, Depths, Train Wheels and Common Stoppages of WatchesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelVon EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Catalog PDFDokument979 SeitenProduct Catalog PDFa7mos0% (1)
- Presentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningDokument37 SeitenPresentation Heat Treatment-Induction HardeningRizwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agriculture Notes PDFDokument37 SeitenAgriculture Notes PDFRohit GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument22 SeitenHeat Treatmentansh_k9250% (2)
- PCI 6th Edition OverviewDokument36 SeitenPCI 6th Edition Overviewandrej2112Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bim Module EpflDokument105 SeitenBim Module EpflMúÑír PåhôrêNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Design Verification InspectionsDokument20 SeitenEngineering Design Verification InspectionsixoteeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Car Park DesignDokument71 SeitenCar Park DesignAlf Horseman100% (1)
- Shaft Sinking: Department of Mining Engineering Muet Jamshoro (11-04-2014)Dokument21 SeitenShaft Sinking: Department of Mining Engineering Muet Jamshoro (11-04-2014)Carlos Arturo Casas HuamánNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silt Control GuideDokument32 SeitenSilt Control GuidePcEngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping HandbookDokument78 SeitenPiping HandbookAurinho9292% (12)
- Heat Treatment Processes Powerpoint PresentationDokument14 SeitenHeat Treatment Processes Powerpoint PresentationDaniel Dowding100% (1)
- Villa Ottolenghi by Carlo ScarpaDokument6 SeitenVilla Ottolenghi by Carlo ScarpaOana ZavoianuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Processes ExplainedDokument31 SeitenHeat Treatment Processes ExplainedJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenUggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gvbhvjhbhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenGvbhvjhbhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jhbhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenJhbhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hjbjjnkjkjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjh Bhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenHjbjjnkjkjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjh Bhkuggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Processes for Improving Steel PropertiesDokument31 SeitenHeat Treatment Processes for Improving Steel PropertiesJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjhbhkugg Silla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenKjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjhbhkugg Silla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jnkjkjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjhbhk Uggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenJnkjkjklnhjhytguythjbhgvbhvjhbhk Uggsilla Ki Heat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEAT TREATMENT PROCESSESDokument31 SeitenHEAT TREATMENT PROCESSESJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uhergihnheat TreatmentDokument31 SeitenUhergihnheat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 54tuhergihnheat TreatmentDokument31 Seiten54tuhergihnheat TreatmentJackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Objectives and ProcessesDokument6 SeitenHeat Treatment Objectives and ProcessesAdaitaChowdhury100% (1)
- Material Science For CTTC BBSR 11oct 2022Dokument68 SeitenMaterial Science For CTTC BBSR 11oct 2022Nishant ThapliyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amt 611 Heat TreatmentDokument44 SeitenAmt 611 Heat TreatmentJhalbert BelmonteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument19 SeitenHeat TreatmentESABEL 15bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument28 SeitenHeat TreatmentHASHINI PABODHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment ProcessDokument31 SeitenHeat Treatment ProcessAbhishek IndalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Heat TreatmentDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Heat TreatmentAbdulbar kelilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument13 SeitenHeat Treatmentmissing wonderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annealing Heat Treatment: Mohit Kumar USN-1SI17ME059Dokument8 SeitenAnnealing Heat Treatment: Mohit Kumar USN-1SI17ME059mohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem ManufacturingDokument11 SeitenCHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem Manufacturingkaranragav12Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 - Heat Treatment & Engineering ApplicationDokument24 Seiten3 - Heat Treatment & Engineering ApplicationHussein SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of Plain Carbon SteelDokument12 SeitenHeat Treatment of Plain Carbon Steelweda walata heduwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Heat Treatment?: Written By: Johnsinit - Edited By: Lamar Stonecypher - Updated: 1/8/2011Dokument2 SeitenWhat Is Heat Treatment?: Written By: Johnsinit - Edited By: Lamar Stonecypher - Updated: 1/8/2011విష్ణువర్ధన్రెడ్డిNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument21 SeitenHeat TreatmentChernet MerknehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument33 SeitenHeat TreatmentIsrael HailuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Processes for SteelDokument5 SeitenHeat Treatment Processes for SteelRhoven MagbanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsDokument24 SeitenUnit 2: Heat Treatment of Iron and SteelsRahul kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment: Unit - 2Dokument75 SeitenHeat Treatment: Unit - 2reza chamanfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of Carbon SteelDokument23 SeitenHeat Treatment of Carbon SteelArielle Joyce de JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 7Dokument6 SeitenDocument 7Roy mugendi100% (1)
- Literature ReviewDokument23 SeitenLiterature ReviewRISHAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment: Definition: Heat Treatment Can Be Defined As TheDokument120 SeitenHeat Treatment: Definition: Heat Treatment Can Be Defined As TheBharath Agarwal100% (1)
- Heat TreatmentDokument30 SeitenHeat TreatmentDr-Bharath Vedashantha MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument18 SeitenChapter 5Ermias GuragawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment (Slide)Dokument13 SeitenHeat Treatment (Slide)Afiq SaimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matreial Lab PDFDokument14 SeitenMatreial Lab PDFNedaa AbboushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatments PDFDokument2 SeitenHeat Treatments PDFJhony BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment Effects on Material PropertiesDokument5 SeitenHeat Treatment Effects on Material PropertiesArgha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument6 SeitenHeat TreatmentHarsh SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment DefinitionsDokument2 SeitenHeat Treatment DefinitionsmrajaygNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeattreatmentDokument29 SeitenHeattreatmentUJJWAL PRAKASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Heat Treatment of Carbon SteelDokument26 SeitenChapter 7 Heat Treatment of Carbon SteelTeptep GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Class Heat TreatmentDokument19 Seiten3rd Class Heat TreatmentPROMISE JULIUSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of MetalsDokument23 SeitenHeat Treatment of MetalsKevin HeraldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatment of MetalsDokument14 SeitenHeat Treatment of MetalsDawood AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Treatments of SteelsDokument7 SeitenHeat Treatments of SteelsBianca MihalacheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annealing, Normalizing, Quenching, Martensitic TransformationDokument22 SeitenAnnealing, Normalizing, Quenching, Martensitic TransformationAboo Backer100% (1)
- Heat Treatment: Unit - IiDokument94 SeitenHeat Treatment: Unit - Iisenthilkumar tsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TreatmentDokument9 SeitenHeat TreatmentsvsddsdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Track Consignment DMM MeradoDokument1 SeiteTrack Consignment DMM Meradosandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monad University DataDokument12 SeitenMonad University Datasandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davinder Sharma Education CertificateDokument6 SeitenDavinder Sharma Education Certificatesandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre RDC 2 Ropar 2017Dokument1 SeitePre RDC 2 Ropar 2017sandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- PunDokument1 SeitePunwert21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pune to Mumbai CST Deccan Express timetable and scheduleDokument1 SeitePune to Mumbai CST Deccan Express timetable and schedulesandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture3 Introduction To Solid ModelingDokument64 SeitenLecture3 Introduction To Solid Modelingsandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Grip Size For PistolsDokument2 SeitenHand Grip Size For Pistolssandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agenda 37 TH NCVTDokument16 SeitenAgenda 37 TH NCVTsandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPC Technq.Dokument6 SeitenSPC Technq.sandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Tu Be Tu Dilgiram by Noziya KaromatulloDokument2 SeitenBe Tu Be Tu Dilgiram by Noziya Karomatullosandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Do It Yourself+BLACKENING+at+Room+TemperatureDokument2 SeitenDo It Yourself+BLACKENING+at+Room+Temperaturesandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Force Common Admission Test (Afcat) : Scheme of Syllabus & Example of QuestionsDokument6 SeitenAir Force Common Admission Test (Afcat) : Scheme of Syllabus & Example of QuestionsUma ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual Bluetooth Pen-SpyepDokument2 SeitenUser Manual Bluetooth Pen-Spyepsandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO Tolerances For HolesDokument5 SeitenISO Tolerances For Holessandhu31janNoch keine Bewertungen
- Useful ECBC Tables and TermsDokument17 SeitenUseful ECBC Tables and TermsAnoop SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dual Phase SteelsDokument26 SeitenDual Phase SteelsharieduidNoch keine Bewertungen
- BH ECV HawthornDokument2 SeitenBH ECV HawthornMuhammad AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Branch Supply Duct As Far As Practical From The OutletDokument11 SeitenThe Branch Supply Duct As Far As Practical From The OutletKevinNavidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canadian Foundation ManualDokument10 SeitenCanadian Foundation Manualbenchowdry9615Noch keine Bewertungen
- KENCO CHEMICAL INJECTORS for Natural Gas & Oil IndustriesDokument2 SeitenKENCO CHEMICAL INJECTORS for Natural Gas & Oil IndustriesMEHDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. D. Y. Patil School of Engineering & Technology Department of Civil Engineering Be Project Phase Ii Sheet (Ay2019-20) Sem IiDokument3 SeitenDr. D. Y. Patil School of Engineering & Technology Department of Civil Engineering Be Project Phase Ii Sheet (Ay2019-20) Sem IiRao SahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster-Septic Tanks Dos and Donts PDFDokument1 SeitePoster-Septic Tanks Dos and Donts PDFRavi TejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Schools Guide PDFDokument181 SeitenGreen Schools Guide PDFMary KristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive Architecture of Shekhawati HavelisDokument6 SeitenPassive Architecture of Shekhawati HavelisShriya RajwadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting: Aim of The ExperimentDokument7 SeitenCasting: Aim of The Experimentsanskar mittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEP Specification for Raceways and FittingsDokument8 SeitenMEP Specification for Raceways and FittingsBala Krishna GallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Presentation On Doors & WindowsDokument45 SeitenA Presentation On Doors & WindowsFarheen BanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VILLA 430: Hyderabad, TelanganaDokument27 SeitenVILLA 430: Hyderabad, TelanganaH A I K U S T U D I ONoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection Board PDFDokument2 SeitenProtection Board PDFmilanbrasinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Control The Warping of Parts in Thin SheetDokument6 SeitenHow To Control The Warping of Parts in Thin SheetNeil WayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaxxShot & MaxxShot Plus Extend Die LifeDokument4 SeitenMaxxShot & MaxxShot Plus Extend Die LifeDhinesh DftNoch keine Bewertungen