Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
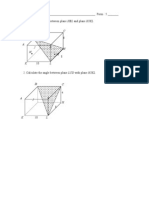
Form 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 Dimensions
Hochgeladen von
soonsiewleeOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Form 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 Dimensions
Hochgeladen von
soonsiewleeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
LINES AND PLANES
IN
3-DIMENSIONS
CHAPTER 11
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
3 Different types of dimensions
One surface
length and width
more than one surface
length, width and height
A line
Only has length
Two- Dimensional Three- Dimensional One- Dimensional
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Pythagoras Theorem
Trigonometric Ratios
c
b
a
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
A. Identify Plane
PLANE: is a flat surface
Plane
Not a
Plane
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
3 types of plane
Vertical plane Inclined plane Horizontal plane
Horizontal plane
Vertical plane
Vertical plane
Inclined plane
Activity 1
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1. According to the prism below. Name the specific
plane.
A
E
H
D
G
C
B
F
Horizontal plane
ABFE
DHGC
Vertical plane
ABCD
EFGH
ADHE
Inclined plane
BFGC
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
B. Identify Lines
A
B
C
D
Lines that lie on a plane
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Lines that intersect with a plane
A
B
C
D
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Normal to a plane
Y
P Q
R
S
X
Definition:
Normal to a plane is a perpendicular straight line
to the intersection of any lines on the plane.
Normal to a plane
Activity 2
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1. Identify the normal(s) to each of the given planes.
A
E
H
D
G
C
B
F
Example:
Normal to the plane ADHE are
Answer:
AB, DC, EF and HG
Activity 2
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
A
E
H
D
G
C
B
F
(a) Normal to the plane CDHG are
AD and HE
(b) Normal to the plane BCGF are
No normal line
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN LINES AND PLANES
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Orthogonal Projection
Definition:
Is a perpendicular projection of the object on a plane.
P
Q
R S
B
A
Orthogonal projection
of line AB on the plane
PQRS
Plane at bottom
Plane at top
Plane at right hand side
Plane at left hand side
Plane at the back
Plane in front
REMEMBER THIS
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Imagine
Screen=PLANE
Object=LINE
Activity 3
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1. Find the orthogonal projection of a given line on a
specific plane given.
A
B
C D
P Q
R
S
Line Plane Orthogonal
Projection
a) AC ADSP AD
b) BD DCRS CD
c) AR PQRS PR
d) PC ABCD AC
e) QC DCRS RC
f) DQ PQRS SQ
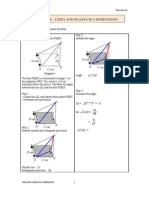
Angle between a line and a plane
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
P
Q
R S
B
A
Orthogonal projection
of line AB on the plane
PQRS is line AC
C
BC is normal to the
plane PQRS
Angle between the line AB and the plane PQRS is the angle form between
the line AB and the orthogonal projection on the plane.
ANSWER:
TECHNIQUE
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
__ __ __
Point
NOT TOUCH
on plane
Point
TOUCH
on plane
NORMAL
of not touch
point on plane
Angle between a line and a plane
P
Q
R S
B
A
__ __ __
Identify the angle between the line AB
and the plane PQRS
NOT TOUCH TOUCH NORMAL
C
A B
C
Based on the diagram, name the
angles between the following:
Answers
Activity 4
NOT
TOUCH
TOUCH NORMAL
B A
C
D
P Q
R
S
(a) Line BR and plane ABCD
(b) Line AS and plane ABCD
(c) Line AR and plane CDSR
(d) Line BS and plane PQRS
__ __ __
B R C
__ __ __
A S D
__ __ __
R A D
__ __ __
S B Q
Activity 5
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1. Identify the angle of the line and the plane given.
A
B
C D
P Q
R
S
Line Plane Angle
a) AC ADSP CAD
b) BD DCRS
BDC
c) AR PQRS
ARP
d) PC ABCD
PCA
e) QC DCRS
QCR
f) DQ PQRS
DQS
Based on the diagram,
(a)Identify the angle between the
line PB and the plane ABCD.
B
A
C
D
P
Q
R S
3 cm
4 cm
Example 1
(b) Hence, calculate the angle
between the line PB and the
plane ABCD.
__ __ __
B P
A
Not
Touch
Touch
Normal
of P
4 cm
B
P
A
3cm
tan PBA =
PBA = tan
-1
PBA = 3652
A
B
C D
P Q
R S
(a) Find the angle between the line
SB and the plane ABCD.
(b) Calculate the angle between the
line SB and the plane ABCD if
SB = 19cm and BD= 13 cm.
D B
13 cm
19 cm
S
Example 2
__ __ __
B S
D
Not
Touch
Touch
Normal
of S
H
A
cos SBD =
SBD = cos
-1
SBD= 4650
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
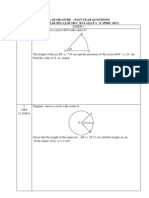
Example 3 (SPM 2006 PAPER 2)
Diagram shows a right prism. The base PQRS is
a horizontal rectangle. The right angled triangle
UPQ is the uniform cross section of the prism.
Identify and calculate the angle between the
line RU and the base PQRS. [3 marks]
__ __ __
R U P Identify angle
P R
9 cm
U
S
T
U
P Q
R
5 cm
9 cm
Calculate
angle
tan URP=
URP = tan
-1
URP= 3442
13 cm
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Example 4(SPM 2008 PAPER 2)
E
H
A
B
C
G
D
F
M
8cm
Diagram shows a cuboid. M is the midpoint of
the side EH and AM = 15 cm.
a) Name the angle between the line AM and
the plane ADEF
b) Calculate the angle between the line AM
and the plane ADEF
[3 marks]
(a) __ __ __
A M E Name angle
(b)
E
A
M
4cm
15 cm
sin MAE=
MAE= sin
-1
MAE= 1528
H
O
T
U
P
Q
R
S
V
5 cm
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Example 5 (SPM 2007 PAPER 2)
Diagram shows a right prism. The base PQRS
Is a horizontal rectangle. Right-angled triangle
QRU is the uniform cross section of the prism.
V is the midpoint of PS.
Identify and calculate the angle between the
line UV and the plane RSTU. [3 marks]
__ __ __
U V S
S
U
8cm
V
Identify angle
Calculate
angle
13 cm
tan VUS=
VUS= tan
-1
VUS= 3136
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
11.2 ANGLE BETWEEN PLANES AND PLANES
Identify the angle between the plane ABCD and the plane BCEF.
A B
C
D
E
A B
C D
__ __ __
E D C
E
F
F
__ __ __
F A B
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN PLANES AND PLANES
Identify the angle between the plane ABCD and the plane BCF.
A B
C
D
A B
C D
__ __ __
A F B
F
F
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN PLANES AND PLANES
Identify the angle between the plane ABC and the plane BCD.
A B
C
A B
C
__ __ __
F A B
F
F
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
11.1 ANGLE BETWEEN PLANES AND PLANES
Identify the angle between the plane ABCD and the plane BCE.
A B
C
D
E
A B
C D
E
__ __ __
G E F
F
G
F G
SPM 2006 (PAPER 1)
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
1) Name the angle between the plane PQWT and the
plane SRWT.
Q
P
R
S
V
U
W
T
__ __ __
S P T
__ __ __
R Q W
OR
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
2) Vertex P is vertically above T. Name the angle
between the plane PTS and the plane PTQ.
SPM 2007 (PAPER 1)
Q
P
R
S
T
__ __ __
S Q T
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
3) What is the angle between the plane STU and the
base QSTV.
SPM 2008 (PAPER 1)
__ __ __
V U T
S
T
U
P
Q
V
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
3) Given M and N is the midpoint of the line QR and PS. Name
the angle between the plane VQR and the base PQRS.
SPM 2009 (PAPER 1)
__ __ __
N V M
Q
R
U
S
P
V
M
N
SPM 2010 (PAPER 2)
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Diagram in the answer space shows a right prism. The base CDHG is a horizontal
rectangle. Trapezium ABCD is the uniform cross section of the prism.
(a) On diagram in the answer space, mark the angle between the plane BCGF and
the base CDHG .
(b) Hence, calculate the angle between the plane BCGF and the base CDHG.
[3 marks]
Answer :
(a)
Mark
A
E
H
D
G
C
B
F
21 cm
13 cm
2 cm
(b)
X C
19 cm
13 cm
B
tan BCD =
BCD= tan
-1
BCD= 3423
SPM 2005 (PAPER 2)
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Diagram shows a right prism. Right-angled triangle PQR is the uniform cross
section of the prism.
(a) Name the angle between the plane RTU and
the plane PQTU.
(b) Hence, calculate the angle between
the plane RTU and the base PQTU.
[3 marks]
Answer :
(a)
(b)
Q R
12 cm
18 cm
T
tan RTQ=
RTQ= tan
-1
RTQ= 3341
__ __ __
T R Q
R
P
Q
S
U
T 12 cm
5 cm
18 cm
MATHEMATICS FORM 4
SPM 2009 (PAPER 2)
Diagram below shows a cuboid with horizontal base ABCD. J is the midpoint of the
side AF.
(a) Name the angle between the plane BCJ
and the base ABCD.
(b) Calculate the angle between the plane
BCJ and the base ABCD.
[3 marks]
Answer :
(a)
__ __ __
B J A
6 cm
8 cm
E
H
A
B
C
G
D
F
10 cm
J
(b)
A
B
10 cm
4 cm
J
tan JBA=
JBA= tan
-1
JBA= 2148
Example (PAPER 2)
__ __ __
N V M
Diagram shows a right pyramid. V is the vertex of the pyramid and the base PQRS is
a horizontal square. M and N is the midpoint of QR and PS. The height of the pyramid
is 11 cm.
Identify and calculate the angle between
the plane VQR and the base PQRS.
[3 marks]
Q
R
U
S
P
V
M
N
10 cm
5 cm
11 cm
V
M
X
tan VMX=
VMX= tan
-1
VMX= 6533
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Quadratic Equations Form 4 Topical ExerciseDokument6 SeitenQuadratic Equations Form 4 Topical ExerciseAyu Lil'princess100% (1)
- (Worksheet) Lines & Planes in 3DDokument21 Seiten(Worksheet) Lines & Planes in 3DAmir Faisal75% (4)
- Form 4 Add Maths Chapter 1Dokument25 SeitenForm 4 Add Maths Chapter 1Azhar GameMaster100% (1)
- Holka PolkaDokument69 SeitenHolka Polkasoonsiewlee100% (1)
- Vocology For The Singing Voice PDFDokument120 SeitenVocology For The Singing Voice PDFNathalia Parra Garza100% (2)
- Lim Lim: Marking Scheme For Mathematics T 2 Second Term STPM Trial Examination (2018)Dokument10 SeitenLim Lim: Marking Scheme For Mathematics T 2 Second Term STPM Trial Examination (2018)Michelles JimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)Dokument11 SeitenKuen Cheng High School Junior Two Physics Mid-Year Examination 2021 (Light)黑Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Component Notes Form 5Dokument16 SeitenLiterature Component Notes Form 5Nabila Abdul MukthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Force PressureDokument6 SeitenAnswer Force PressureCart KartikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Area & Perimeter: Name: DateDokument14 SeitenCalculating Area & Perimeter: Name: DateY6n6nNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Reduce PollutionDokument3 SeitenHow To Reduce Pollutionalyaa_haziraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buku Bina Ayat - Contoh Jawapan - PDFDokument4 SeitenBuku Bina Ayat - Contoh Jawapan - PDFong0625Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversiti: BiodiversityDokument9 SeitenBiodiversiti: BiodiversityAmmar SyahmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UEC Test Practice 7 8Dokument2 SeitenUEC Test Practice 7 8谢顺德Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Form 3Dokument24 SeitenMathematics Form 3Amal SufiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section A p3Dokument8 SeitenSection A p3Zunaidi JaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Geometry 2 AnswerDokument15 SeitenSolid Geometry 2 AnswerHazri Mohd HamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Idioms ExerciseDokument2 SeitenIdioms ExerciseQing Yi100% (1)
- Form 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017Dokument3 SeitenForm 4 Chemistry Calculation Practice Chapter 7: Acids and Bases 2017khangsiean89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upsr ScienceDokument30 SeitenUpsr ScienceShyweyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Expression Exercise 2Dokument2 SeitenSocial Expression Exercise 2poppy_90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Notes Form 2 (Science)Dokument11 SeitenQuick Notes Form 2 (Science)FishGlobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDokument2 SeitenTopical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeMei Yun LiewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doll Pencil Train Plane Monster Ball: Year 1 3 Assessment 2018 English Paper 2Dokument6 SeitenDoll Pencil Train Plane Monster Ball: Year 1 3 Assessment 2018 English Paper 2metalace777Noch keine Bewertungen
- M Matrik Songsang Bagi A: PPR Maths NBK m3Dokument14 SeitenM Matrik Songsang Bagi A: PPR Maths NBK m3Adib AdwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foon Yew High School Kulai 2021 Junior Middle Two (Group A) Mathematics Final Examination (Question Sheet)Dokument2 SeitenFoon Yew High School Kulai 2021 Junior Middle Two (Group A) Mathematics Final Examination (Question Sheet)溫維華Noch keine Bewertungen
- SJK (C) Pu Sze Year 3 English Language Assessment (4) : Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenSJK (C) Pu Sze Year 3 English Language Assessment (4) : Paper 1Anonymous 7dHDP4jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansDokument14 SeitenBlood Circulation and Transport Learning Objective: 2.1 Understanding The Transport System in HumansJames WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument1 SeiteChapter 6cikguanuar100% (1)
- Answers: Topical Test 1Dokument5 SeitenAnswers: Topical Test 1Edwin Jesu DassNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 English Essay Example: TalkDokument2 SeitenPT3 English Essay Example: TalkNoor Harlina Jalil100% (2)
- Section A Choose and Circle The Correct Answer To Fill in The BlanksDokument9 SeitenSection A Choose and Circle The Correct Answer To Fill in The BlanksSoffea RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- F2 Science Chpt1Dokument24 SeitenF2 Science Chpt1Yong SiewkuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module Chapter 3-Gravitation2020 PDFDokument20 SeitenModule Chapter 3-Gravitation2020 PDFNoorleha Mohd Yusoff100% (1)
- Haze in Malaysia 2019Dokument21 SeitenHaze in Malaysia 2019farah6214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Form 5 Chapter 6Dokument44 SeitenScience Form 5 Chapter 6Ashwin Josiah Samuel100% (1)
- Bab 1 Nota RingkasDokument11 SeitenBab 1 Nota RingkasWAN HURUN AIN BINTI W. YANoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Sains SPM Section CDokument25 SeitenModul Sains SPM Section CJaaizah JaafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Y2 Paper 1Dokument8 SeitenEng Y2 Paper 1ntv_syukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kerja Kursus Matematik Tambahan 2011Dokument26 SeitenKerja Kursus Matematik Tambahan 2011voe_comigo100% (3)
- Quadrilaterals - MATHS - PRACHIDokument15 SeitenQuadrilaterals - MATHS - PRACHIPalakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCEDokument15 SeitenBody Coordination FORM 4 SCIENCESiti NorhayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBS Maths F1 Chapter 9Dokument10 SeitenPBS Maths F1 Chapter 9Ai LanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Dokument22 SeitenModul 2 Science Form 1 Chapter 2: Cell As A Unit of Life What Is Cell?Nurhuda MitieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3.2: Liquid PressureDokument22 SeitenTutorial 3.2: Liquid PressurePauling ChiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan BM Thn6Dokument28 SeitenSoalan BM Thn6NadarajahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science F3 Chapter 8 Generation of Electricity-Paper 2 AnswersDokument1 SeiteScience F3 Chapter 8 Generation of Electricity-Paper 2 AnswersRebecca Choong Xin HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3-DimensionsDokument44 SeitenForm 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3-DimensionsMing Fong Liaw75% (8)
- Form 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 DimensionsDokument44 SeitenForm 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 DimensionskwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 DimensionsDokument44 SeitenForm 4 Chapter 11 Lines and Planes in 3 Dimensionsliewqiying3354Noch keine Bewertungen
- Line and Plan in 3DDokument31 SeitenLine and Plan in 3DMing Fong LiawNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Angles QuestionsDokument4 Seiten3D Angles QuestionsyddapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEDokument21 SeitenChapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENHANCEjuriah binti ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Between Line and Planes - 2008Dokument16 SeitenAngle Between Line and Planes - 2008Sean GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHDokument12 SeitenChapter 9 II Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lines & Planes in 3DDokument41 SeitenLines & Planes in 3Djuriah binti ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHDokument18 SeitenChapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE9 LinesandPlanein3DDokument15 SeitenMODULE9 LinesandPlanein3DSiva RajahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajah Di Bawah Menunjukkan Sebuah Kuboid. M Ialah Titik Tengah Bagi Sisi VW Dan QP 6cmDokument10 SeitenRajah Di Bawah Menunjukkan Sebuah Kuboid. M Ialah Titik Tengah Bagi Sisi VW Dan QP 6cmRoslan AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 DimensionsDokument12 Seiten3 DimensionsFauziah SallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9Dokument18 SeitenNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9funson123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Section 1 2Dokument6 SeitenGeometry Section 1 2api-262621710Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter11 - Lines and Planes in 3DDokument6 SeitenChapter11 - Lines and Planes in 3DHayati Aini AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exemplar Area of QuadDokument13 SeitenExemplar Area of QuadnNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Literature Titles Studied For Poems AreDokument10 SeitenThe Literature Titles Studied For Poems AreIzzuddin MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Mentor Mentee Add Math 2014Dokument3 SeitenModul Mentor Mentee Add Math 2014soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Essay: A Day Trip To An English Camp: Chartered Seventh's HeavenDokument1 SeiteReport Essay: A Day Trip To An English Camp: Chartered Seventh's HeavensoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report WritingDokument1 SeiteReport WritingsoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors: SMK Raja Jumaat, Port DicksonDokument31 SeitenVectors: SMK Raja Jumaat, Port DicksonsoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fun & Splash Package at RM 41.00/ StudentDokument1 SeiteFun & Splash Package at RM 41.00/ StudentsoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic EquationsDokument6 SeitenQuadratic EquationsCYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles: Points SBCDokument2 SeitenPrinciples: Points SBCsoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Circular MeasureDokument9 SeitenChapter 8: Circular MeasureHayati Aini AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add MathsDokument40 SeitenAdd MathsJoseph TingNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Dokument44 SeitenSPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Norman de Kattun100% (1)
- Monocular Vision Stereoscopic VisionDokument2 SeitenMonocular Vision Stereoscopic VisionsoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simultaneous Equations - Past Year Questions Program Bijak Belajar MGC Kulaijaya (9 April 2011)Dokument2 SeitenSimultaneous Equations - Past Year Questions Program Bijak Belajar MGC Kulaijaya (9 April 2011)soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ist Monthly Test 2013Dokument4 SeitenIst Monthly Test 2013soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 MatricesDokument6 SeitenChapter 5 MatricessoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kenali Diri Anda Melalui Sikap Anda Sebagai Pengguna ElektrikDokument1 SeiteKenali Diri Anda Melalui Sikap Anda Sebagai Pengguna ElektriksoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Trial 2012 Addmath A PahangDokument16 SeitenSPM Trial 2012 Addmath A PahangNg Imm KhuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optikal IlusiDokument3 SeitenOptikal IlusisoonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!Dokument18 SeitenMachine A PDF Writer That Produces Quality PDF Files With Ease!soonsiewleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths - Form 4 - Year-PlanDokument15 SeitenAdd Maths - Form 4 - Year-PlanFikrah ImayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT4400 STRG Flo Amp ValveDokument7 SeitenMT4400 STRG Flo Amp ValveBrian Careel0% (1)
- Himachal Pradesh Staff Selection Commission Hamirpur - 177001Dokument2 SeitenHimachal Pradesh Staff Selection Commission Hamirpur - 177001Verma JagdeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centralized PurchasingDokument2 SeitenCentralized PurchasingbiyyamobulreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contractor Hse Management ProgramDokument12 SeitenContractor Hse Management ProgramAhmed IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual: Slit Lamp Bon SL-EDokument20 SeitenInstruction Manual: Slit Lamp Bon SL-EVladimir LevchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Research ZoomDokument51 SeitenRevised Research ZoomAubrey Unique EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Aerodynamics of ParachutesDokument78 SeitenThe Aerodynamics of Parachutesstevehuppert50% (2)
- Cusps: Ramesh 04-Jun-1976 12:30:00 PM Krishnagiri 78:14:0 E, 12:32:0 N Tzone: 5.5 KP (Original) Ayanamsha 23:26:2Dokument1 SeiteCusps: Ramesh 04-Jun-1976 12:30:00 PM Krishnagiri 78:14:0 E, 12:32:0 N Tzone: 5.5 KP (Original) Ayanamsha 23:26:2Suresh NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alignment Technique - The Steam TurbineDokument2 SeitenAlignment Technique - The Steam TurbineRajeswar KulanjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pepperl KFD2 STC4 EX1.20 DatasheetDokument2 SeitenPepperl KFD2 STC4 EX1.20 DatasheetAhmed HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evs ManualDokument24 SeitenEvs ManualJoseph TuckerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ground Vehicle Operations ICAODokument31 SeitenGround Vehicle Operations ICAOMohran HakimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02.certificate of Compliance FM UkDokument10 Seiten02.certificate of Compliance FM Ukmyatthura870Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hilfswerk Wien-Salzburg - 11. Meio 2018Dokument9 SeitenHilfswerk Wien-Salzburg - 11. Meio 2018FreieEnergieNoch keine Bewertungen
- A C Engines and Jet Propulsion1Dokument16 SeitenA C Engines and Jet Propulsion1Mukesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FMS 427 BusinessPolicy1Dokument279 SeitenFMS 427 BusinessPolicy1Adeniyi Adedolapo OLanrewajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Plan Student 1Dokument7 SeitenOne Plan Student 1api-465826207Noch keine Bewertungen
- Avinash Uttareshwar MeherDokument6 SeitenAvinash Uttareshwar MeheravinashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Da Insem AllDokument217 SeitenDa Insem AllTECOA136TejasJadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry (CHM111) Laboratory ManualDokument73 SeitenAnalytical Chemistry (CHM111) Laboratory ManualKatrina BucudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1991 - Defect Chemistry of BaTiO3Dokument20 Seiten1991 - Defect Chemistry of BaTiO3Beh NaatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thursday / January 2019 Thursday / January 2019Dokument572 SeitenThursday / January 2019 Thursday / January 2019Zie EikinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staad 4Dokument37 SeitenStaad 4saisssms9116100% (2)
- SOL-Logarithm, Surds and IndicesDokument12 SeitenSOL-Logarithm, Surds and Indicesdevli falduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation DelcorteDokument15 SeitenPresentation Delcortecarlos2685Noch keine Bewertungen
- Focus On Teaching - Jim KnightDokument213 SeitenFocus On Teaching - Jim KnightFernando TeixeiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitalis 2000Dokument26 SeitenVitalis 2000ARLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3: Literature Review and CitationDokument3 SeitenModule 3: Literature Review and CitationLysss EpssssNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIMMS Modeling Guide - Linear Programming TricksDokument16 SeitenAIMMS Modeling Guide - Linear Programming TricksgjorhugullNoch keine Bewertungen