Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rheumatic Fever Ок
Hochgeladen von
Ali Baker AlgelaneCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rheumatic Fever Ок
Hochgeladen von
Ali Baker AlgelaneCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Rheumatic
fever
Rheumatic fever
is acute systemic disease of
the connective tissue immune
inflammatory genesis,
characterised mainly by
arthritis, carditis, chorea,
subcutaneous nodules and
erythema marginatum.
Rheumatic fever (RF)
is common world-wide and is
responsible for many causes
of damage heart valves.
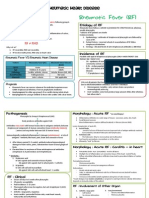
Etiology:
Group A, hemolytic streptococcus
(strains 3,5,18,24,28,49 ) is the maine
etiologycal factor. RF occurs about 2
weeks after exudative tonsilitis
(quinsy,soa throat), scarlet
fever,streptodermia or other
streptococcus infections, if it goes
without treatment.
Person who has high hyperensitivity to
immune system on streptococcus
suffered more frequently. This
hypersensibility of immune system
genotype determinate with HLA system
antigen A
11
, B
27
, B
35
, CW
2
, CW
5
, DR
5
,
DR
7
.
Pathogenesis:
On the basis of pathogenesis RF is
immunoinflamatory reaction
(reaction antigen-antibody) with
edema,
hyperemia,
lymphocyte infiltration of
connective tissue heart (valvule,
endocardium, myocardium,
pericardium), brain, vessels,
synovial membrane of joints,skin,
other organ and formatione
rheumatic granuloma (Aschoffs
nodule) in connective tissue.
Immunoinflamatory reaction (reaction
antigen-antibody) is always
accompanied by elimination of
inflammatory mediators: histamine,
bradikinin, prostaglandin E2 and
other.Histamin is dilated capillares and
bring on oedema, hyperemia,
infiltratione connective tissue with
cells of immune response
(lymphocytes, plasmatic cells, mast
cells, eosinophils, basophils).
Prostaglandin E2 - cause
increase t
o
C.
Cluster circulate immune
complex in connective tissue
is cause formation of
pointing necroses in
particular area.
during immunoinflamatory
reaction morphologically we are
different 4 stages:
mucoid swelling;
fibrinoid swelling;
granulomatosis;
sclerosis and hyalinosis.
Outcome of the
immunoinflammatory reaction
are sclerosis,hialinosis,
deformation,calcification
valvulas and formatione
anatomical defects (valvula
heart disease) .
Sclerosis of myocardium -
myocardiosclerosis (cardiac
insufficiency heart failure,
arrhythmias, blockades).
Clinical PICTURE
symptoms and signs arise 2 weeks
after pharyngitis or tonsillitis (soa
throat) or scarlet fever.
major criteria (manifestation)
of RF are:
1.Migratory polyarthritis
2.Carditis
3.Chorea
4.Subcutaneous nodules
5.Erythema marginatum
minor criteria of RF are:
high t
o
C;
abdominal pain, anorexia;
heart failure;
epistaxis;
pneumonia;
asthenia;
malaise;
fatigue.
Migratory polyarthritis is the most
common clinical manifestation,
monoarthritis can also occur. Joints
become painful and tender ,red, hot,
swollen, sometimes with effusion.
Knees, elbows or wrists are most
commonly involved. It leaves no
permanent joint deformility.
Carditis
(involves 2 or 3 wall of heart)
endocarditis+myocarditis=
rheumocarditis:
Rheumatic myocarditis, mature Aschoff nodule
CLINICAL SIGNS OF CARDITIS:
Cardiac failure
Changes heart sounds
Cardiac enlargement
Murmurs;
1. systolic myocardial murmur;
2. murmurs of VS, MI, AS, AI.
pericardial rub.
Chorea
SydenhamS chorea
emotional instability,
muscular weakness and
rapid, uncoordinated jerky
movements affecting
primarily the face, foot and
hands.
Subcutaneus nodules
These are firm,
colorless, painless
nodules 1-2 cm in size,
near the tendens or
bony prominences of
joints, especially elbow.
Subcutaneous nodules (rheumatic fever
nodules/Aschoff nodules)
Erythema marginatum
This is a nonpruritic, flat,
circular or serpigious rash
on thoraxic trunk and near
joints.
DIAGTOSTICS
For diagnostic we use:
* major and minor rheumatic criterias
* rheumatic anamnesis
* markers of streptococcus infection
* laboratory findings
* ECG
* Doppler USG of heart.
2 major criteria or one major criteria
and 2 minor criteria with markers of
streptococcus infection are basement
for support the diagnosis of RF.
NB!
LABORATORY FINDINGS:
General blood analysis (blood test)
anemia, leycocytosis, shift in leycocyt formula
left, accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate
(ESR);
biochemical blood analysis:
reumoprobs:
Level of C-reactive protein;
Level of Seromucoids
Level of Glycoproteins
positive throat culture;
elevated level of antistreptolisin O,
antistreptokinaze or other streptococcal
antibody.
ECG findings:
PQ prolongation more than 0,18-0,20 sec;
Signs of enlargement of atria or
ventricules;
Signs of pericarditis.
Doppler USG heart:
Thickening of walls
Patological blood flows
(regurgitatione)
Enlargement atrium or ventricles;
Signs of effusion in pericardium.
Treatment
regimen the patient must take rest
before normalizaton of his temperature ;
Diet N10;
Ethyologycal treatment: :
- antistreptoccocal antibiotics
- Benzilpenicillini-natrii 1,2 1,5 million U
per day,
- Benzathine penicillini G 1,2 million U per
day
Or Amoxicillin 0,5 - 4 times per day;
Ampicillin 0,5 - 4 times per day
If the patient have allergic to penicillin
we use:
Erytromicinum
Cephalexin 50mg/kg
Cephadroxil 50mg/kg
2 times per day
Azithromycin 15mg/kg
Clarithromicin 15mg/kg
One of this antibiotics administer
during 10 day, than we change
antibiotic and prescribe prolongate
antibiotics:
Bicillinum-3 (1,5 million U for
one injection weeks;
Or Bicillinum-5 (1,5 milliom U
one jnjectione for 3 weeks
during the year)
4. Anti-inflammatory drugs: (NON
STEROID ANTI INFLAMMATORY
DRUGS) NSAID This drugs
blocked Pr a
2
.NONSELECTIVE:
1) Salicylic Acid:
Acetylsalicylic acid;
Sodium salicylate; Mg salicylate.
2) Antraylic acid
- Mefenamic acid 0,25 0,5;
- Flufenamic acid;
- Meclofenamic acid.
3) Arylbenzene acids
-Diclofenac Sodium ( Voltaren,
ortofen ) - tablets 0,025 0,05;
-ampules 0,075; suppository 0,05;
gel 1 %;
-Alclofenac;
-Fenclofenac;
- Fentiazak.
4) Propionic acids:
Ibuprofen ( brufen ) Dragee 0,2;
Florbiprofen Dragee 0,05;
Ketoprofen;
Naproxen;
Fenoprofen;
Fenbufen;
Piridofen.
INDOL DERIVATIVES :
Indomethacin ( Metindol, Indosid )
Dragee 0,025 Suppository 0,05;
Sulindac Tablets 0,2.
PYRAZOLE DERI VATI VES :
Butadion ( Phenylbutazone );
Analgin;
Amidopirin.
SELECTIVE COX2
BLOKERS:OXICAMS
Piroxicam ( Felden ) Tablets 0,01
Izoxicam
Sudoxicam
Meloxicam ( Movalis )
COXI BS :
Celecoxib ( Celebrex, Rancelex
Rofecoxib ( Rofica )
5. Corticosteroid therapy:
Prednizoloni 0,5-1 mg/kg orally 3
times daily(during 3-5 week) with
decrease dose step by step on
regime 5 mg for weeks.
6. Symptomatical therapy:
If the patient have signs of carditis and
heart failure we administrate:
diuretic drugs:
furosemid 20-40 mg orally daily in the
morning before meal;
Hypothyazidi 50-100 orally daily.
- Cardiotonic drugs such as
Digoxin 0,0001 1-2 times orally
daily.
If the patient has arrhythmias
ahtiarrhythmic drugs.
If the patient has signs vasculitis we
are administed ac. Ascorbinici 0,5 3
times orally daily.
Prognosis:
In case of initial RF with advantage arthritis
and initial carditis prognosis will be favourable
if the patient receive adequate therapy.
In cases severe RF with arthritis, severe
carditis, chronic rheumatic disease, heart
valvule diseases are observed.
If RF is not treated, chronic rheumatic disease
and heart valvule diseases are always occur.
Arthritis, chorea, subcutaneous nodulus
erythema marginatum have favorable outcome.
Prophylaxis (prevention):
Primary prevention:is prevention from
streptococcal infection (tonsilitis,
pharingitis, scarlet fever).
Secondary prevention:
---Antistreptococcal prophylaxis should
be conducted after attack of acute RF in
order to prevent recurrence.
---Bicillini-5 1,5milliom U (or Benziline
penicillin 6 1,2 million) one injection for
month due to 3 month
---Aspirini 0,5 4 times daily
orally during 3 weeks or other
NSAID.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Alert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIIVon EverandAlert Medical Series: Emergency Medicine Alert I, II, IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever: DR: Yousif Adam AliDokument20 SeitenRheumatic Fever: DR: Yousif Adam AliÅbübâkêř Äbd-ëřhēēm BãřřîNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infectious Diseases of The HeartDokument84 SeitenInfectious Diseases of The HeartHarold DiasanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic - Fever - Internal Medicine 15 MarchDokument35 SeitenRheumatic - Fever - Internal Medicine 15 MarchLedia EssamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever and Heart DiseaseDokument37 SeitenRheumatic Fever and Heart Diseasejiregna eticha dakoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0002 Infectious Diseases of The HeartDokument35 Seiten0002 Infectious Diseases of The Heartmblanco.dchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument26 SeitenRheumatic Heart Diseasecandice_manuel_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio - InfectiveDokument13 SeitenCardio - InfectiveHgiel100% (1)
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument37 SeitenRheumatic Heart Diseasesalman hNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Romila Chimoriya Lecturer Department of Pediatrics: Acute Rheumatic FeverDokument27 SeitenDR Romila Chimoriya Lecturer Department of Pediatrics: Acute Rheumatic FeverDhiraj PantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac DisordersDokument80 SeitenCardiac Disordersscan1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Inflammatory ProblemsDokument11 SeitenCardiac Inflammatory ProblemsAnnalou Amadure JoaquinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument39 SeitenRheumatic Heart DiseaseSamarjeet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group A Streptococcal Infections: PatophysiologyDokument11 SeitenGroup A Streptococcal Infections: Patophysiologyrahma perwitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Emergencies in Rehabilitation MedicineDokument24 SeitenMedical Emergencies in Rehabilitation MedicineAzza El Awar100% (1)
- Sle SlidesDokument42 SeitenSle SlidesAzizan HannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel BakyDokument8 SeitenSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel Bakyahmed gabrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic FeverDokument27 SeitenRheumatic FeverFerrariRoche_14Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10rheumatic FeverDokument3 Seiten10rheumatic FeverKristina Ana ClaudioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoDokument37 Seiten2 - RH Fev, Inf EndoLobna ElkilanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvular Heart Disease: Cardiology Division, Medical Faculty Diponegoro UniversityDokument46 SeitenValvular Heart Disease: Cardiology Division, Medical Faculty Diponegoro UniversityChacha TasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Rheumatic Fever: Prof - Univ.Dr. Corina ZorilăDokument40 SeitenAcute Rheumatic Fever: Prof - Univ.Dr. Corina ZorilăGermanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio InfectionDokument6 SeitenCardio InfectionCindy Mae de la TorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic FeverDokument39 SeitenRheumatic FeverDharaneedhar AdepuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever 2Dokument4 SeitenRheumatic Fever 2Radin Nurulfathiah RSuleimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Cardiology: Ruby Ann L. Punongbayan, MDDokument51 SeitenPediatric Cardiology: Ruby Ann L. Punongbayan, MDsarguss14100% (3)
- Medically Compromised Pts PresentationDokument123 SeitenMedically Compromised Pts PresentationAhmed SaudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Rheumatic Fever UmeshDokument4 SeitenSeminar On Rheumatic Fever UmeshawasthiphothocopyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocarditis Blok 10Dokument50 SeitenEndocarditis Blok 10Dena Paramita RustandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Infections: (Outside To Inside)Dokument7 SeitenCardiac Infections: (Outside To Inside)Ashley MalsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever: &knee PainDokument49 SeitenFever: &knee PainJohn Christopher LucesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever: DR: Kaem Shir AliDokument24 SeitenRheumatic Fever: DR: Kaem Shir AliMwanja Moses100% (1)
- Acute Rheumatic Fever: DR Mohamed Rafa MSC PediatricsDokument6 SeitenAcute Rheumatic Fever: DR Mohamed Rafa MSC PediatricsPeace ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- CARDIO - Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument3 SeitenCARDIO - Rheumatic Heart DiseaseMoon KillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic FeverDokument87 SeitenRheumatic FeverFarida Mawaddah Husna100% (1)
- Acquired Heart DiseasesDokument41 SeitenAcquired Heart DiseasesSaman SarKoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro - CVS InfectionsDokument55 SeitenMicro - CVS InfectionsMahmoud hilmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument30 SeitenRheumatic Heart DiseaseABREHAM BUKULONoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument132 SeitenRheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDamie FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pericardial DiseaseDokument59 SeitenPericardial DiseaseGunawan Yoga100% (1)
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDokument37 SeitenIschemic Heart DiseaseAli100% (1)
- AHD Kulmag2009Dokument17 SeitenAHD Kulmag2009KevinDilianSugandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument14 SeitenRheumatic Heart Diseaseudaybujji100% (1)
- ARF PresentationDokument39 SeitenARF PresentationRichard SsenyondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carol Rivers'board Review FlashcardsDokument440 SeitenCarol Rivers'board Review FlashcardsJennelle CadoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Questions For A Lecture On Acute Rheumatic FeverDokument6 SeitenTest Questions For A Lecture On Acute Rheumatic FeverFiona CoutinhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infective EndocarditisDokument45 SeitenInfective EndocarditisReem 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Rheumatic Fever Kuliah TK 4Dokument47 SeitenAcute Rheumatic Fever Kuliah TK 4Marwah ChiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever & Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument87 SeitenRheumatic Fever & Rheumatic Heart DiseaseMarianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ААААаААААаААаААаАААААААААААааааАААААаАааААААААааааанггггггггггггггггггллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллDokument15 SeitenААААаААААаААаААаАААААААААААааааАААААаАааААААААааааанггггггггггггггггггллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллллSerhii TsomaiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatic Fever AND Rheumatic Heart Disease: Departemen Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK UsuDokument15 SeitenRheumatic Fever AND Rheumatic Heart Disease: Departemen Kardiologi Dan Kedokteran Vaskular FK UsuXeniel AlastairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Rhuematic Heart DiseaseDokument16 SeitenSeminar On Rhuematic Heart Diseasenaga maniNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS1 - K7 - Rheumatic Fever & Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDokument15 SeitenCVS1 - K7 - Rheumatic Fever & Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDumora FatmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- StrokeDokument34 SeitenStrokeMakojoa KatisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demam RematikDokument18 SeitenDemam RematikWonderCatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDokument20 SeitenAcute Rheumatic Feverfaizal samadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrugsDokument15 SeitenDrugsRomm JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infective EndocarditisDokument67 SeitenInfective EndocarditisDr. Rajesh PadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auscultation of The HeartDokument20 SeitenAuscultation of The HeartAli Baker Algelane100% (1)
- Pencil Drawing TechniquesDokument138 SeitenPencil Drawing TechniquesAyman Almorsy100% (1)
- Hemoblastosis in ChildrenDokument40 SeitenHemoblastosis in ChildrenAli Baker Algelane100% (3)
- Diaphragm: Anatomy Hernias TreatmentDokument15 SeitenDiaphragm: Anatomy Hernias TreatmentAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthyroidism: Co-Existing Diseases: The Endocrine SystemDokument32 SeitenHyperthyroidism: Co-Existing Diseases: The Endocrine SystemAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- GoiterDokument17 SeitenGoiterAli Baker Algelane100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsDokument46 SeitenLecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Neph Ropa ThyDokument18 SeitenDiabetic Neph Ropa ThyAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Achalasia: Prof. Dr. Faisal Ghani SiddiquiDokument18 SeitenAchalasia: Prof. Dr. Faisal Ghani SiddiquiAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Myocardial InfarctionDokument50 SeitenComplications of Myocardial InfarctionAli Baker Algelane50% (2)
- Oncology: Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical University Department of OncologyDokument41 SeitenOncology: Ivano-Frankivsk National Medical University Department of OncologyAli Baker AlgelaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acupuncture GuidelineDokument31 SeitenAcupuncture Guideline健康生活園Healthy Life Garden50% (2)
- Lesson Exemplar in Mapeh Grade Level Learning Area QuarterDokument8 SeitenLesson Exemplar in Mapeh Grade Level Learning Area QuarterErwin Balid GasconNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawsuit Against Small Smiles Dental Center Aka Alabany Access Dental Center Et. Al.Dokument52 SeitenLawsuit Against Small Smiles Dental Center Aka Alabany Access Dental Center Et. Al.DebHgnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender and Society 2Dokument27 SeitenGender and Society 2Kent Ian InfanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prolonged PregnancyDokument40 SeitenProlonged Pregnancyjan caraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nusing Skills Output (Nso)Dokument3 SeitenNusing Skills Output (Nso)leroux2890Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Casualty IncidentDokument41 SeitenMass Casualty IncidentCristel De TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Pre Principles in MLS 1Dokument12 Seiten1 Pre Principles in MLS 1Maria Faith Jeneen BisnarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy in Reducing PainDokument7 SeitenThe Effectiveness of Hypnotherapy in Reducing PainArie DwianggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root PlainingDokument10 SeitenRoot PlainingSooul MateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pearls of Wisdom Anesthesiology Board Review PDFDokument8 SeitenPearls of Wisdom Anesthesiology Board Review PDFAyman Mustafa0% (1)
- Learner'S Packet (Leap)Dokument6 SeitenLearner'S Packet (Leap)jennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herpes-Zoster Concept MapDokument5 SeitenHerpes-Zoster Concept MapElleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 11 2016.tanzania National Guideline For Management Hiv and Aids May 2015. TaggedDokument290 Seiten04 11 2016.tanzania National Guideline For Management Hiv and Aids May 2015. TaggedArdilah Dwiagus SafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Board of Veterinary Medical Examiners - Sample Questions-NAVLEDokument2 SeitenNational Board of Veterinary Medical Examiners - Sample Questions-NAVLEPapu Lahoria50% (2)
- Network Lists in UAE - Mar 2015Dokument93 SeitenNetwork Lists in UAE - Mar 2015Kamran KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROCEDURE On AmniocentesisDokument2 SeitenPROCEDURE On AmniocentesisMansiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question NurseDokument240 SeitenQuestion NurseKaye PatanindagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Pyloromyotomy?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Pyloromyotomy?Adrian John DecolongonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Mangement Flyer Word Document.-1Dokument2 SeitenPain Mangement Flyer Word Document.-1atifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flu Medical ExemptionDokument1 SeiteFlu Medical Exemptionplayboi501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dahlin Et al-2016-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyDokument9 SeitenDahlin Et al-2016-BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & GynaecologyPrima Hari PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Venous Access DevicesDokument6 SeitenCentral Venous Access DevicesAllan MacacapagalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPCR NewDokument30 SeitenCPCR NewPhil PhilipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying InfectionDokument2 SeitenNCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying InfectionNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANoch keine Bewertungen
- COURSE OBJECTIVES or NursingDokument5 SeitenCOURSE OBJECTIVES or NursingFil AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DineshPonraj 1808165 - 05 00 - 1Dokument4 SeitenDineshPonraj 1808165 - 05 00 - 1revanth kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 1edited With ConstiDokument3 SeitenNCP 1edited With ConstiKizza SaavedraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Sexuality Education: Education For A Healthy FutureDokument8 SeitenComprehensive Sexuality Education: Education For A Healthy FutureCristina AguinaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring TDMDokument33 SeitenConcept of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring TDMWalaa YousefNoch keine Bewertungen