Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tonsillitis and Adenoids
Hochgeladen von
FilbertaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tonsillitis and Adenoids
Hochgeladen von
FilbertaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
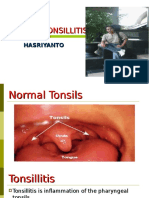
Definition:
Is an inflammation of the
tonsils.
Types:
Acute tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis
Classification:
acute catarrhal or superficial
tonsillitis: Here tonsillitis is a
part of generalized
pharyngitis and seen in viral
infections
acute follicular tonsillitis: In
which tonsillar crypts become
filled with purulent materials
acute parenchymatous
tonsillitis: Here tonsils are
uniformly enlarged and red
acute membranous
tonsillitis: The exudates in
the crypts coalesces to form
membrane on the surface
Affects school-age children
but adults can also be
affected. It is rare in infants
(< 1 year age) and persons
above 50 years.
Group A beta hemolytic
streptococci
Haemophilus influenzae
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Staphylococci
Tuberculosis (in
immunocompromised)
Viruses: adenovirus, Epstein-Bar
virus and herpes simplex virus
sore throat
difficulty in swallowing + pain
fever (can be accompanied
by rigors and chills)
ear ache
headache
generalized body fatigue
breath is foetid and tongue is
coated
hyperaemia of the pillars, soft palate
and uvula
red and swollen tonsils with
yellowish spots in the crypts
(follicular tonsillitis) , whitish
membrane on the medial surface of
the tonsils (membranous tonsillitis)
or enlarged and congestive tonsils
with swollen uvula (acute
parenchymatous tonsillitis)
enlarged and tender jugulodigastric
lymph nodes
bed rest + plenty of fluids
analgesia (Aspirin or
Paracetamol)
antimicrobial (Penicillin is the
drug of choice) should be
continued for 7 -10 days
chronic tonsillitis with recurrent
acute attacks
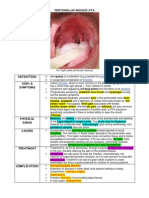
peritonsillar abscess (quinsy)
parapharyngeal abscess
cervical abscess
acute otitis media
rheumatic fever
acute golomerulonephritis
sub acute bacterial endocarditis
Diphtheria
Infectious mononucleosis
malignancy (lymphoma,
leukemia)
recurrent infections (> 6
times per year)
peritonsilar abscess
possibility of malignancy
sleep apnoea
febrile convulsions
Types:
chronic follicular tonsillitis
chronic parenchymatous
tonsillitis
chronic fibroid tonsillitis
may be a complication of
acute tonsillitis
subclinical infection of tonsils
without acute attack
chronic infection of sinuses
or teeth may be a
predisposing factor
recurrent attacks of acute
tonsillitis
chronic irritation in throat
and cough
bad taste in mouth and foul
breath (halitosis)
conservative treatment:
attention to diet, general
health and treatment of
coexisting infections of teeth,
sinuses and nose.
tonsillectomy: if tonsils
interfere with deglutition,
speech, respiration or there is
recurrent attacks of tonsillitis
situated
at the junction of the
posterior wall and roof of the
nasopharynx
composed of lymphoid tissues
covered by columnar epithelium
it is present at birth
physiologically enlarged up to 6
years then regress and
completely disappears by the
age of 20
Recurrent attacks of rhinitis,
tonsillitis and sinusitis cause
adenoid infection and
hyperplasia
nasal obstruction
mouth breathing
nasal discharge
adenoid face:
elongated face, dull expression,
nasal discharge, open mouth,
hitched-up upper lip, prominent
and overcrowded upper teeth,
high-arched palate
pulmonary hypertension
nasopharyngoscopy
X-ray nasopharynx lateral
view
When symptoms are not
severe, decongestant nasal
drops + antihistamines is the
treatment of choice
Marked symptoms,
treatment is adenoidectomy
Thank You
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Adenotonsillar Diseases: Becky ChepngenoDokument37 SeitenAdenotonsillar Diseases: Becky ChepngenoKIBET ERNEST MUTAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Hoarse Voice (Laryngitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandHoarse Voice (Laryngitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenotonsillar DiseasesDokument36 SeitenAdenotonsillar DiseasesKIBET ERNEST MUTAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Ludwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandLudwig’s Angina, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Gets Tonsillitis?Dokument3 SeitenWho Gets Tonsillitis?Mounir ChadliNoch keine Bewertungen
- TonsilDokument60 SeitenTonsilShabiela Mafazah100% (1)
- Pharygitis AND TonsillitisDokument29 SeitenPharygitis AND Tonsillitisstara123Noch keine Bewertungen
- TonsillitisDokument3 SeitenTonsillitisVina MuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis FACT SheetDokument3 SeitenTonsillitis FACT SheetSiska SitumorangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscessDokument19 SeitenTonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscesszayNoch keine Bewertungen
- TonsillitisDokument6 SeitenTonsillitisAnonymous UzWZrQU2kNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenotonsillar Diseases DrbugnahDokument37 SeitenAdenotonsillar Diseases DrbugnahDr.Sherif Bugnah100% (8)
- Chapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDokument7 SeitenChapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPeej Reyes100% (2)
- Pharyngitis TonsilitisDokument23 SeitenPharyngitis TonsilitisJessa BorreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute TonsillitisDokument22 SeitenAcute Tonsillitisg0ldz21100% (10)
- Tonsil, Small Mass of Lymphatic Tissue Located in The Wall of The Pharynx at The Rear of The ThroatDokument13 SeitenTonsil, Small Mass of Lymphatic Tissue Located in The Wall of The Pharynx at The Rear of The Throatbai2222Noch keine Bewertungen
- AdenotonsilitisDokument42 SeitenAdenotonsilitisELIA RICHARDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDokument45 SeitenUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionNatasha Abdulla100% (2)
- TonsilitisDokument23 SeitenTonsilitisatai-phin-4632100% (4)
- Chapter 73Dokument88 SeitenChapter 73Julian TaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- ON TONSILITIS (Autosaved)Dokument31 SeitenON TONSILITIS (Autosaved)kiran kumari yadav0% (1)
- PharyngitisDokument6 SeitenPharyngitisJeriel DelavinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenotonsillitis NewDokument100 SeitenAdenotonsillitis NewDrravikumar Bhandari100% (1)
- Disorder of ThroatDokument21 SeitenDisorder of ThroatSumit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angina (Streptococcal Diphtheria, Herpes, Mononucleosis) - MumpsDokument83 SeitenAngina (Streptococcal Diphtheria, Herpes, Mononucleosis) - MumpsBeni KelnerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of Upper Respiratory System (URTI) : DR Sarwar Hussain, Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, NBUDokument36 SeitenDiseases of Upper Respiratory System (URTI) : DR Sarwar Hussain, Assistant Professor Department of Pediatrics, NBUخالد مطرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Learning ModuleDokument38 SeitenOnline Learning ModuleMani SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Tonsillitis: Zhong Shixun PH.DDokument43 SeitenAcute Tonsillitis: Zhong Shixun PH.DEINSTEIN2DNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdenotonsilitisDokument35 SeitenAdenotonsilitisAriSugiharto100% (2)
- Acute Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsMB, BSDokument33 SeitenAcute Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsMB, BSibnbasheer83% (6)
- Mbbs Feb11Dokument22 SeitenMbbs Feb11Dr. T. Balasubramanian100% (2)
- Laporan Kasus Tonsilitis KronisDokument49 SeitenLaporan Kasus Tonsilitis KronisTabita P SNoch keine Bewertungen
- TonsilitisDokument32 SeitenTonsilitisFitriNajibahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peritonsillar AbscessDokument1 SeitePeritonsillar AbscessFatimah Az-ZahrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- TonsillitisDokument19 SeitenTonsillitisrosejoseph0777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding TonsillitisDokument2 SeitenUnderstanding TonsillitisMarjun JacosalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- URI-ppt 03Dokument111 SeitenURI-ppt 03tinsjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.acute PharyngitisDokument88 Seiten1.acute PharyngitisIhsan Hanif0% (1)
- Anesthesia For Tonsillectomy: Aau-Chs School of AnesthesiaDokument54 SeitenAnesthesia For Tonsillectomy: Aau-Chs School of AnesthesiaagatakassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adenoiditis With Tonsillitis (H)Dokument6 SeitenAdenoiditis With Tonsillitis (H)Ilyes FerenczNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9acutegingivalinfections Pdabscess 160503154630Dokument141 Seiten9acutegingivalinfections Pdabscess 160503154630kishore KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Respiratory InfectionsDokument50 SeitenAcute Respiratory InfectionsLinus PuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent Med RevisionDokument41 SeitenEnt Med RevisionswamysamsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Острые заболевания глотки - enDokument27 SeitenОстрые заболевания глотки - enMindy LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDokument27 SeitenNursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDody ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- History (One or More Required) : A. Gejala Dan TandaDokument4 SeitenHistory (One or More Required) : A. Gejala Dan TandaIkram HikmatyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDokument43 SeitenUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionNaresh JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Respiratory InfectionsDokument16 Seiten14 Respiratory InfectionsEsteban PrietoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharyngitis (Tonsillopharyngitis) : Principles of DiseaseDokument21 SeitenPharyngitis (Tonsillopharyngitis) : Principles of DiseaseefendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharyngeal Symptoms Acute &chronic Pharyngitits: Submitted By, Aravind RajanDokument11 SeitenPharyngeal Symptoms Acute &chronic Pharyngitits: Submitted By, Aravind RajanVictor EnachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscessDokument38 SeitenTonsillitis and Peritonsillar AbscessAyush PaudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Diseases of PharynxDokument72 SeitenCommon Diseases of PharynxPinak DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit X URTIDokument37 SeitenUnit X URTIdiadiaidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosen's Emergency Medicine Concepts and Clinical PracticeDokument15 SeitenRosen's Emergency Medicine Concepts and Clinical PracticeMusdal RahmatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 PharngitisDokument26 Seiten10 PharngitisCabdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023Dokument41 SeitenDiseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023dr MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- TonsillitisDokument7 SeitenTonsillitisjuicyprunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)Dokument7 Seiten18 Tonsil, Adenoid Notes Cumming Abd Key Topics (New Moe)osamaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Upper Airway InfectionsDokument45 Seiten1.0 Upper Airway InfectionsMariahNoch keine Bewertungen