Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
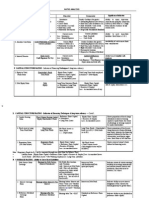
Shares, Debentures & Term Loans
Hochgeladen von
sshreyas0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten22 SeitenThis document discusses various types of financial instruments used by companies to raise capital, including ordinary shares, debentures, and term loans. It describes share capital structures and rights of shareholders. It also covers debentures and term loans as sources of long-term financing, and the roles of financial markets and intermediaries in facilitating capital raising and allocation of funds between savers and borrowers.
Originalbeschreibung:
Financial management -3
Originaltitel
FM 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document discusses various types of financial instruments used by companies to raise capital, including ordinary shares, debentures, and term loans. It describes share capital structures and rights of shareholders. It also covers debentures and term loans as sources of long-term financing, and the roles of financial markets and intermediaries in facilitating capital raising and allocation of funds between savers and borrowers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten22 SeitenShares, Debentures & Term Loans
Hochgeladen von
sshreyasThis document discusses various types of financial instruments used by companies to raise capital, including ordinary shares, debentures, and term loans. It describes share capital structures and rights of shareholders. It also covers debentures and term loans as sources of long-term financing, and the roles of financial markets and intermediaries in facilitating capital raising and allocation of funds between savers and borrowers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
Shares, Debentures & Term Loans
Ordinary shares/Common shares represent
the ownership position in a company
Shareholders are holders of ordinary
shares
Ordinary shares are permanent capital
Entitled to dividends; amount not fixed
Also called variable income security
Shareholders bear risk: residual value
ownership after meeting claims of others
Authorised 250000000 equity shares of Rs.10
each
Rs.2500000000
Issued 148565000 equity shares of Rs10 each
1485650000
Subscribed & fully paid up 146476214 equity
shares of Rs.10 each
1464762140
Reserves & Surplus
5837739000
Net worth
7302501140
Authorised share capital is the maximum
amount of capital permitted by the Registrar
of Companies to be raised from shareholders
Issued share capital is the portion offered to
shareholders out of authorised share capital
Subscribed share capital is the portion
accepted by shareholders
Paid up capital is the amount of subscribed
share capital actually paid up by
shareholders
Issue price may include par value &
premium value
If issue price is in excess of par value, it is
shown separately as share premium
Undistributed earnings are called reserves &
surplus
Shareholder equity=Net Worth=paid up
share capital + share premium + reserves &
surplus
Book value/share=Net worth/Number of
ordinary shares
Residual ownership claim
Residual claim on assets upon liquidation
Right of control
Voting rights
Pre-emptive rights
Limited liabilty
Permanent capital
Borrowing base
Dividend payment discretion
Cost: dividends not tax deductible
Risk: uncertainty about dividends/capital
gain
Ownership dilution: follow up issue
Public issue: raising capital directly from
public
Underwriting: guarantee by underwriter
to buy shares not fully subscribed by
public
Private placement: sale to few selected
investors, esp. institutional investors.
Small size; less expensive than public
issue; is faster than public issue
Sale of ordinary shares to existing
shareholders
Value: No. of new shares=Desired funds
Subscription
price(Ps)
No. of rights=Existing shares/New shares
N=S0/s
Share price cum-rights =Pc=NxR+Ps
Share price ex-rights issue=Px=S0P0+sPs
S0 + s
Shareholder control maintained pro rata
Cheaper than public issue
Issue likely to succeed as subscription
price below market price
Shareholders not exercising rights lose
value
Shareholding concentration among
financial institutions thru conversion of
loans to shares
Hybrid security: features of ordinary
shares as well as debentures
Like shares: Non-payment of dividends
does not cause insolvency; dividends not
tax deductible; no fixed maturity dates in
some cases
Like debentures: Dividend fixed; no share
in residual earnings; claim on
assets/income prior to ordinary
shareholders; usually no voting rights
Claims on incomes/assets: senior security
Fixed dividend
Cumulative dividends
Redemption: maturity date; sinking fund
Call feature: buy-back at specific price
Participation feature: share in
extraordinary profit
Voting rights: contingent/conditional rights
Convertibility: fully/partly into shares;
debentures
Riskless leverage
Dividend postponabilty
Fixed dividend
Limited/no voting rights: dividend arrears
Dividends not tax deductible
Commitment to pay dividends
Long-term fixed-income financial security;
debenture holders creditors s/us of company
Fixed interest rate: contractual rate of interest
Fixed maturity: period specified
Redemption: mostly redeemable; buyback/call
Buyback: redemption before maturity at sp.pr.
Sinking fund: cash set aside for redemption
Indenture/Debenture trust deed
Yield = Annual interest/Market price
Prior claim on assets/income
Non-convertible debentures repayable on
maturity
Fully-convertible: converted into shares
as per terms of issue wrt price & time
Partly-convertible: features of both above
Less costly: less risky; lower ror acceptable
Interest payment tax deductible
Ownership not diluted
Fixed interest payment
Inflation reduces real cost of interest; but
Obligatory payment
Increases financial leverage
Must be paid on maturity
May contain restrictive terms & conditions
Non banking/non financial companies: up
to 25% of paid-up capital & free reserves
from public; up to 10% of paid-up capital
& free reserves from shareholders
Maximum 35% of paid-up capital & free
reserves from public and shareholders
Period: 6 months to 36 months; 3 months
up to 10% of paid-up capital & free
reserves
Liquid assets with banks: 15% of deposits
maturing by 31st March of following year
Annual return to Registrar of Companies
on/before 30th June
Payment before maturity after 6months
Tax deduction at source
Failure to repay deposit on maturity leads
to action by Company Law Board
Savings in economy: domestic savings;
remittances from abroad
Kinds of financial instruments:
ADR/GDR/FCCB apart from instruments
mentioned earlier
Kinds of financial intermediaries
Price discovery: time preference, risk
return trade-off
Liquidity: transferabilty & negotiability
Low transaction costs: search &
information, buying & selling, advertising
& marketing, time & effort, and
evaluation costs
Credit rating agency: Moodys, S&P,
CRISIL, CARE, FITCH
Allocate funds between savers &
borrowers
Primary & secondary, OTC, derivative
markets
SEBI
Merchant banks
Mutual funds
Development banks, commercial banks,
insurance companies, and pension funds
RBI & IRDA
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Series 6 Study GuideDokument8 SeitenSeries 6 Study GuideelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buyback of SharesDokument22 SeitenBuyback of SharesJagruti Surve100% (1)
- Seminar On SOurces of FinanceDokument35 SeitenSeminar On SOurces of FinanceBrinda AsokanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 - Long Term Sources of FinanceDokument28 SeitenChapter 6 - Long Term Sources of FinanceCiara CrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Long Term FinanceDokument11 SeitenSources of Long Term FinanceParth BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of FinanceDokument28 SeitenSources of FinanceShalini Jain0% (1)
- Equity CapitalDokument9 SeitenEquity CapitalPiyush AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics o O: LiabilitiesDokument10 SeitenCharacteristics o O: Liabilitiesmilkie fernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFA FlashcardsDokument258 SeitenCFA FlashcardsBrook Rene Johnson71% (7)
- Long Term Sources of FinanceDokument21 SeitenLong Term Sources of Financevivek patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShareholdersDokument7 SeitenShareholderszhutilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cfas Quizlet Final Part 1Dokument9 SeitenCfas Quizlet Final Part 1LINXQUANTUM5ACENoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented by - Parikshit Saha Pankaj Lokesh Randeep Garg Sahil Aggarwal Nishant AdlakhaDokument70 SeitenPresented by - Parikshit Saha Pankaj Lokesh Randeep Garg Sahil Aggarwal Nishant AdlakhaRandeep Garg100% (1)
- Traditional Investing InstrumentDokument3 SeitenTraditional Investing InstrumentIndranilGhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dealings in Property NotesDokument6 SeitenDealings in Property NotesLinrhay RicohermosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting: The Importance of AccountingDokument22 SeitenAccounting: The Importance of AccountingsidhanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin 304 Notesfdfhwefudvg Fdre Financial Markets and InstitutionDokument89 SeitenFin 304 Notesfdfhwefudvg Fdre Financial Markets and InstitutionAhmed YousufzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dividend Decisions: Dividend: Cash Distribution of Earnings Among ShareholdersDokument33 SeitenDividend Decisions: Dividend: Cash Distribution of Earnings Among ShareholdersKritika BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIMA F2 SummaryDokument21 SeitenCIMA F2 SummaryFederico BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationDokument12 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Power Point PresentationmathadbhjNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOS 3311 Midterm Notes: Chapter 1: Review of Corporate FinanceDokument8 SeitenMOS 3311 Midterm Notes: Chapter 1: Review of Corporate FinanceUdbhav KambojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting StandardDokument93 SeitenAccounting Standardsiddhi1234pedNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIMA F2 Summary - v1Dokument28 SeitenCIMA F2 Summary - v1Federico BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of FinanceDokument85 SeitenSources of Financeyashchauhan100% (1)
- Sources of FinanceDokument26 SeitenSources of FinanceKanav GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2bsources of Long Term FinanceDokument19 Seiten2bsources of Long Term FinancetamannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aman MathurDokument31 SeitenAman MathursajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing Decisions Creditors and InvestorsDokument35 SeitenFinancing Decisions Creditors and InvestorsPramod KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2871f Ratio AnalysisDokument24 Seiten2871f Ratio AnalysisHaseeb KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet SolutionDokument18 SeitenBalance Sheet SolutionRabia RabiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity and DebtDokument30 SeitenEquity and DebtsandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Disadvantages of The Perpetual and Period Inventory System?Dokument4 SeitenWhat Are The Disadvantages of The Perpetual and Period Inventory System?Siwei TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary For Capital IQDokument26 SeitenGlossary For Capital IQHimanshu RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2871f Ratio AnalysisDokument24 Seiten2871f Ratio Analysisumar321Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Preferential Issue? Select Group of People Private Placement Basis Does Not IncludeDokument6 SeitenWhat Is A Preferential Issue? Select Group of People Private Placement Basis Does Not IncludeShashank EashwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interest: Financial Assets Cash and Cash Equivalents Prepaid Receivables Investments Cash Surrender Value Sinking FundDokument2 SeitenInterest: Financial Assets Cash and Cash Equivalents Prepaid Receivables Investments Cash Surrender Value Sinking FundAngela ViernesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Long Term FinanceDokument30 SeitenSources of Long Term FinanceManu Mallikarjun NelagaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CF & FM Ch. SOURCES OF FINANCEDokument48 SeitenCF & FM Ch. SOURCES OF FINANCEJignaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Finance by Jasveen KaurDokument4 SeitenSources of Finance by Jasveen KaurJasveen SawhneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Long Term Finance 1194352169348636 3Dokument21 SeitenSources of Long Term Finance 1194352169348636 3murugasugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment Management: Course Instructor: Dr. Jasbir Singh MatharuDokument26 SeitenInvestment Management: Course Instructor: Dr. Jasbir Singh MatharuAmit JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- If Possible Feel Free To Add Any Relevant Material Including Real Life Example or Examples On BD Perspective To Enrich Your PresentationDokument4 SeitenIf Possible Feel Free To Add Any Relevant Material Including Real Life Example or Examples On BD Perspective To Enrich Your Presentationraju01723031884Noch keine Bewertungen
- RatioDokument27 SeitenRatioHumair ShaheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data DictionaryDokument6 SeitenData DictionarySecret PsychologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial RatiosDokument5 SeitenFinancial RatioszarimanufacturingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Debt MarketDokument32 SeitenIndian Debt MarketProfessorAsim Kumar Mishra0% (1)
- Finance For Non FinanceDokument146 SeitenFinance For Non Financehithr1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RSM230 Chapter NotesDokument15 SeitenRSM230 Chapter NotesJoey LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- S F L - T F: Ources AND Orms OF ONG ERM InancingDokument21 SeitenS F L - T F: Ources AND Orms OF ONG ERM InancingRk BainsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shares: Presentation BY Mahender VijaypalDokument24 SeitenShares: Presentation BY Mahender VijaypalHemant AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing NotesDokument10 SeitenFinancing NotesAmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources of Finance: Section: ADokument32 SeitenSources of Finance: Section: AAhmad NaseerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing ActivitiesDokument41 SeitenFinancing ActivitiesZahoor Ul HaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sources OF BUSINESS FINANCEDokument28 SeitenSources OF BUSINESS FINANCENeeraj BabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Bank Financial InstitutionsDokument15 SeitenNon-Bank Financial InstitutionsGaurav DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionVon EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (8)
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 46, Urgent Care Center FinancingVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 46, Urgent Care Center FinancingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Standard-Iso 14000Dokument1 SeiteEnvironmental Standard-Iso 14000sshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- E RecruitmentDokument11 SeitenE RecruitmentsshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovative Motivational Techniques in 10 CompaniesDokument28 SeitenInnovative Motivational Techniques in 10 CompaniessshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Individual BehaviorDokument10 SeitenFoundation of Individual BehaviorsshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Interpersonal Relations OrientationDokument8 SeitenFundamental Interpersonal Relations OrientationsshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation of TQMDokument2 SeitenOperation of TQMsshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing PeopleDokument62 SeitenDeveloping Peoplesshreyas100% (1)
- Employee RemunerationDokument55 SeitenEmployee Remunerationsshreyas100% (2)
- Various Building Blocks of TQMDokument2 SeitenVarious Building Blocks of TQMsshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of TQMDokument2 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of TQMsshreyas100% (3)
- Swot Analysis of All FMCG Companies in IndiaDokument8 SeitenSwot Analysis of All FMCG Companies in Indiasshreyas100% (2)
- Unilever'S "Real Beauty" DoveDokument17 SeitenUnilever'S "Real Beauty" DovesshreyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 360 Degree FeedbackDokument3 Seiten360 Degree FeedbackPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wallstreetjournal 20180531 TheWallStreetJournalDokument34 SeitenWallstreetjournal 20180531 TheWallStreetJournalMadhav BhattaraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 1 Presentation China Yunan Vs Yunus ModelDokument14 SeitenCase 1 Presentation China Yunan Vs Yunus ModelRaja Fahd Sultan0% (1)
- Trust Deed - Poverty Eradication Movement Foundation TrustDokument15 SeitenTrust Deed - Poverty Eradication Movement Foundation TrustANSY100% (2)
- f7sgp 2010 Jun QDokument9 Seitenf7sgp 2010 Jun Q2010aungmyatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Residential Rent AgreementDokument4 SeitenResidential Rent AgreementArnisha DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Memory AidDokument10 SeitenBanking Memory AidEdz Votefornoymar Del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Regulation Review PDFDokument35 SeitenBanking Regulation Review PDFMikeTampengcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial AccountingDokument4 SeitenFinancial AccountingManish KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derivatives: Greeks and Black-Scholes: Call PutDokument7 SeitenDerivatives: Greeks and Black-Scholes: Call PutSAITEJA DASARINoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision My Sbi My Customer First My SBI First in Customer Satisfaction MissionDokument4 SeitenVision My Sbi My Customer First My SBI First in Customer Satisfaction MissionAnandJollyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben & JerryDokument6 SeitenBen & JerrySachin SuryavanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Small Business Loans Work?Dokument3 SeitenHow Do Small Business Loans Work?Soumyajit Das MazumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revitalization of Shahjahanabad (Walled City of Delhi) : - Project Concept ProposalDokument98 SeitenRevitalization of Shahjahanabad (Walled City of Delhi) : - Project Concept ProposalVismay WadiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea 2.1 Acco 1050Dokument8 SeitenTarea 2.1 Acco 1050Caroline ClassNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Standards of Professional ... Ecommendations, and ActioDokument15 Seiten06 Standards of Professional ... Ecommendations, and ActioIves LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RocketDokument5 SeitenRocketFariha Mehzabin NoshinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market IntegrationDokument36 SeitenMarket IntegrationJessa CapuchinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rahul K. Gupta Profit and LossDokument4 SeitenRahul K. Gupta Profit and LossVivek Nnrr0% (1)
- The Sales ProcessDokument19 SeitenThe Sales ProcessHarold Dela FuenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krm8 Ism Ch11Dokument34 SeitenKrm8 Ism Ch11Saif Ullah Qureshi100% (2)
- P1 Day1 RM2020Dokument5 SeitenP1 Day1 RM2020P De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRLP (A) 17169 2014Dokument51 SeitenCRLP (A) 17169 2014Akshay DhawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Henry C K LiuDokument158 SeitenHenry C K Liuantix8wnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathoot Finanace ProjectsDokument32 SeitenMathoot Finanace ProjectsMayank Jain NeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxation - Defined - August 22, 2013Dokument93 SeitenTaxation - Defined - August 22, 2013Asdqwe ZaqwsxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch09.doc (2) Joint CostingDokument37 SeitenCh09.doc (2) Joint CostingAnna CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caps W 9Dokument4 SeitenCaps W 9api-215255337Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sector Grant and Budget Guidelines 2017/18Dokument152 SeitenSector Grant and Budget Guidelines 2017/18NsubugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pinturas Unidas FINALDokument60 SeitenPinturas Unidas FINALAlejandro MoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pta Financial StatementDokument2 SeitenPta Financial StatementDecember Cool100% (1)