Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
C2.3 How Much
Hochgeladen von
Denesha KaurOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C2.3 How Much
Hochgeladen von
Denesha KaurCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
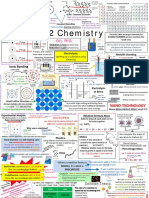
Additional Chemistry
3.1 The mass of atoms
C2.3 How Much
3.2 Masses of atoms & moles
3.3 Percentages & formulae
3.4 Equations & calculations
3.5 Making as much as we want
3.6 Reversible reactions
3.7 Analysing substances
3.8 Instrumental analysis
3.1 The mass of atoms
Sub atomic
particle
Mass
Proton
Neutron
Electron
protons & neutrons in an atom
Mass of proton and
neutron are about the
same. They have a
relative mass
Proton
Neutron
Mass is concentrated in the
tightly packed nucleus
Atomic mass (almost)
(Ar)
Atomic number
Proton number
Mass number: Number of
Li
Number of Neutrons =
atomic mass atomic number
Nucleus
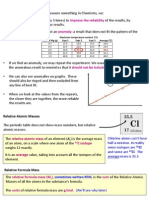
Isotope: The same element with some
atoms having different numbers of neutrons
76% of chlorine atoms are 35Cl whereas 24%
are as 37Cl. Its Relative atomic mass (RAM) is:
(76 x35) + (24x37)
100
RAM= 35.5
Lithium neutrons =
Relative atomic mass (RAM):
7-3 = 4 neutrons
The average value for all the isotopes of an element.
3.2 Masses of atoms & moles
RAM (Ar): The relative atomic mass.
Compares atomic mass to that of
a standard atom (carbon)
RFM (Mr): The relative formula mass.
What is the RFM of carbon dioxide CO2:
RAM C = 12
Formula (CO2 ) = C + O + O
RFM = 12 +16+16
Adds the relative atomic masses
of the elements present together.
1 mole of a substance
is its RAM or RFM
in grams
RFM = 44
Mole: The number of atoms present
in an element based on its RAM.
This number is always 6.02x1023
What is the mass of 1 mole of H2O:
RAM H = 1
RFM H2O = 18
RAM O = 16
RFM = 1 +1+16
so 1 mole = 18g
No units
for RAM or
RFM
What is the mass of 3 mole of H2O:
Formula (H2O ) = H + H + O
RFM = 18
RAM O = 16
Mass = Moles x RAM
mass
moles x RAM
= 3 x 18
= 54g
3.3 Percentages & empirical formulae
What percentage of carbon
dioxide is oxygen?
Calculate RFM of compound
RAM C = 12
RAM O = 16
% element = No. of atoms x RAM element
RFM
percentage element =
Formula (CO2 ) = C + O + O
2 x 16 = 0.73
44
x100 to get percentage = 73%
RFM = 12 +16+16 =
44
If 5.5g of manganese reacted with 3.2g of oxygen. What is the formula
of the oxide of manganese formed? (Atomic. Mass Mn=55: O=16)?
Known mass
element
RAM
Mn =
O=
5.5g
55
3.2g
16
= 0.1 moles
= 0.2 moles
Moles
= number
Lowest mole number
0.1 moles
0.1 moles
0.2 moles
0.1 moles
= 1
Formula
= 2
MnO2
3.4 Equations & calculations
What mass of aluminium & chlorine are needed to make aluminium chloride?
Balance symbol
equation
Using RAM work
out reacting
masses
Minimum reacting
masses needed
aluminium +
2Al
2 x 27
chlorine aluminium chloride
3Cl2
3 x (35.5)2
54g
213g
2AlCl3
2x (27+(3x35.5)
267g
So 27g of Al will react with 106.5g of Cl to give 133.5g of AlCl3.
How much NH3 is produced when 56g of nitrogen is reacted with hydrogen?
Symbol equation
must be balanced
Known mass
Total RFM
RAM
N = 14, H = 1
N2
+ 3H2
2NH3
56g
(14 x 2)
2 x(14 +1+1+1)
?
34
so amount of NH3 produced is 2 x 34 = 68g
3.5 The yield of a chemical reaction
Reactant A
Reactant B
Yield is rarely 100% because:
Reaction may be reversible
Some reactants produce unexpected product
Product being left behind in the apparatus
Difficulty separating product from mixture
Product C
waste product
Product D
useful product
Yield: The amount of useful
product a reaction produces.
CHEMICAL
PLANTS are
designed...
In a fermentation reaction, 36 g of ethanol
are produced. Lots of impurities mean that
the mass of ethanol that could have been
made was 120g. What is the % yield?
... to work as safely and economically as possible.
... to waste as little energy as possible
... to use as many reactants particles up as possible to make as much
useful product as possible, (this is called the ATOM ECONOMY).
OVERALL the plant needs to maximise yield & minimise energy costs.
3.6 Reversible reactions
Forwards:
The reactants N2 and H2 form
the product ammonia (NH3)
N2
+ 3H2
2NH3
Reversible reaction examples
Ammonium chloride
heat
NH4Cl
ammonium
chloride (g)
Backwards:
Ammonia (NH3) breaks down
into the reactants N2 & H2
hydrogen ion
hydrogen
chloride (g)
NH3 +
cool
Symbol for a reversible reaction.
Has both a forward &
backward reaction.
HCl
ammonia(g)
Heating ammonium chloride is a
thermal decomposition reaction
alkali
HLit
red
litmus
H+
acid
Litblue
litmus
Litmus paper
3.7 Analysing substances
Paper chromatography
Used to separate & identify chemicals,
usually food colours, in a mixture.
The solvent moves up the paper with the
colours. These are deposited depending how
soluble they are. (the more soluble the higher
up the paper they are deposited.
Rf = distance moved by the compound
distance moved by the solvent
Blue
4
=
= 0.4
dots
10
The sample has to be compared against
a data bank of known samples Rf values.
Instrumental methods
Advantages:
Quick
Highly accurate and sensitive
A very small amount of a
sample can be analysed.
Disadvantages:
Usually expensive
Takes special training to use
Can only interpret data when
compared against a data base
of known compounds.
3.8a Instrumental analysis
Gas chromatography
More sensitive than paper chromatography
and allows to detect amounts present
Sample is vaporised and moves into
the column by the carrier gas.
Materials with stronger attraction to the
beads in the column take longer to get
through the column (the retention time)
Interpreting data
A has the shortest retention
time.
A is present in the smallest
amount.
F has the greatest affinity
for the solid column
substrate (stationary
The
sample has to be compared against
phase).
a data bank of known samples.
F has the longest retention
This is called fingerprinting.
time.
3.8b Instrumental analysis
Mass spectrometry
Used with gas chromatography as the
sample has been separated.
Sample passes through an electron
beam which turns molecules into ions.
Ions are accelerated and pass through a
magnetic field to bend the ions pathway.
Ions with a small mass curve the most.
Ions with a large mass curve the least.
Interpreting data
Molecul
ar ion
peak
The molecular ion peak
is the relative formula
mass of that compound.
This compound has a
RFM of 72.
The sample has to be compared against
a data bank of known samples.
This is called fingerprinting.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Anthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsDokument23 SeitenAnthony Robbins - Time of Your Life - Summary CardsWineZen97% (58)
- IGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsDokument27 SeitenIGCSE Chemistry - CalculationsChemistryKlipz100% (14)
- Pharmacology TerminologiesDokument8 SeitenPharmacology TerminologiesDenesha Kaur100% (1)
- As Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDokument71 SeitenAs Chemistry Unit 1 NotesUmer Mohammed100% (2)
- Chemical Calculations Workbook NewDokument29 SeitenChemical Calculations Workbook NewVarshLokNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATTER - KMTPHDokument206 SeitenMATTER - KMTPHMohamad Firdaus HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATDokument29 SeitenTopic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATKhubaib Khan100% (1)
- Fluoride - Wide Range of Serious Health Problems"Dokument29 SeitenFluoride - Wide Range of Serious Health Problems"zataullah100% (2)
- Zumdahl Chapter 3Dokument4 SeitenZumdahl Chapter 3drzachcross100% (1)
- AP Chemistry: Chapter 3 - StoichiometryDokument7 SeitenAP Chemistry: Chapter 3 - StoichiometryS. Green100% (1)
- ACS Review: - Quick Refresher of Materials - Some Sample Questions and Short CutsDokument31 SeitenACS Review: - Quick Refresher of Materials - Some Sample Questions and Short Cutsjhhjjh100% (1)
- Cosmic Handbook PreviewDokument9 SeitenCosmic Handbook PreviewnkjkjkjNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFDokument50 Seiten20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFShah100% (1)
- 16 Personalities ResultsDokument9 Seiten16 Personalities Resultsapi-605848036Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSDokument8 SeitenCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 3 CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND EQUATIONSJay Bee94% (18)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Dokument15 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Chapter 3Helene_mbbt100% (9)
- Strategic Audit of VodafoneDokument35 SeitenStrategic Audit of VodafoneArun Guleria89% (9)
- As Chemistry Note1 FinalDokument56 SeitenAs Chemistry Note1 Finaltej786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled 1Dokument5 SeitenUntitled 1Franco Luis C. MapuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry PowerpointDokument13 SeitenStoichiometry Powerpointapi-241764779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms Molecules Stoch 1Dokument31 SeitenAtoms Molecules Stoch 1jakelakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Calculations Workbook IgcseDokument29 SeitenChemical Calculations Workbook IgcsehannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1b - The MoleDokument16 Seiten1b - The Moleapi-227549282Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Stoichiometry PDFDokument41 SeitenChapter 3 Stoichiometry PDFAbou WalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Stoichiometry CHEM 107Dokument43 SeitenChemical Stoichiometry CHEM 107AhmedAdelIbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 - Chemical QuantitiesDokument44 SeitenChapter 10 - Chemical Quantitiesapi-256257174Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative ChemistryDokument76 SeitenQuantitative ChemistryTris WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch-03 Mass Relations in Formulas and Chemical Reactions 1Dokument34 Seitench-03 Mass Relations in Formulas and Chemical Reactions 1api-182809945Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 1 3 FollowalongnotesDokument15 SeitenCHP 1 3 FollowalongnotesToby JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 7 StoichiometryDokument59 SeitenPart 7 Stoichiometryjasumin91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Quantitative ChemistryDokument30 SeitenTopic 1 Quantitative ChemistrybaterbeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 - RecoverDokument13 SeitenExperiment 1 - RecoverChristina ApriliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument104 SeitenChapter 1Sarathy Hari KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating A and Percent Abundance Example 1: Boron Has Two Naturally Occurring IsotopesDokument9 SeitenCalculating A and Percent Abundance Example 1: Boron Has Two Naturally Occurring IsotopesJessica DobrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - ChemistryDokument48 SeitenModule 1 - ChemistryShapnil FinneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Mole ConceptDokument24 SeitenApplication of Mole ConceptVenkatesh MkNoch keine Bewertungen
- StoichiometryDokument53 SeitenStoichiometryNoorSabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F321 CalculationsDokument21 SeitenF321 CalculationsDoc_CrocNoch keine Bewertungen
- c2 Exam Revision PosterDokument3 Seitenc2 Exam Revision Posterapi-320022467Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mole MoleDokument4 SeitenMole Moleshaikha_77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokument12 SeitenChemical Formulae and EquationsJelitaAnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Chapter 3 - CombineDokument178 SeitenAP Chapter 3 - CombinesawgrassfunNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Relative Atomic MassDokument42 SeitenThe Relative Atomic MassMorris KariukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bab 3 StoikiometriDokument28 SeitenBab 3 StoikiometriM Nur M. Mahmud0% (1)
- Chemistry SPM Module Form 4 Chapter 3 PDFDokument14 SeitenChemistry SPM Module Form 4 Chapter 3 PDFShobanaKumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Principle of ChemistryDokument5 SeitenChapter 1 - Principle of ChemistryYouwer WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 108 Chapter 3 StoichiometryDokument29 Seiten108 Chapter 3 Stoichiometryzabdullahstud1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Chemical CalculationsDokument31 SeitenChapter 3 - Chemical Calculationsswethac100% (1)
- The Basicsof Stoichiometryand MolecalculationsDokument31 SeitenThe Basicsof Stoichiometryand MolecalculationsTracy LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1: Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceDokument15 SeitenTopic 1: Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceleenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry and Mole ConceptDokument45 SeitenStoichiometry and Mole ConceptYasser AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDokument31 SeitenMass Relationships in Chemical ReactionspussysweeperNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT 2. UNIT 1 - Chemistry NotesDokument9 SeitenPT 2. UNIT 1 - Chemistry NotesJB - 10SS 731765 Harold M Brathwaite SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Dan 05 StoichiometryDokument53 Seiten04 Dan 05 StoichiometryDarliati Ayu 'putri'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Form 4 ChemistryDokument3 SeitenChapter 3 Form 4 ChemistryEinstein PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - CHE 218 - 2021.2022Dokument7 SeitenModule 1 - CHE 218 - 2021.2022Emmy OlabosipoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 IM Chang 11eDokument7 SeitenChapter 3 IM Chang 11eSelma MeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole, Molar Mass, Formular MassesDokument20 SeitenMole, Molar Mass, Formular MasseshahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokument7 SeitenSPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsJedidah JongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations QuestionssDokument42 SeitenCalculations QuestionssAlluringcharmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 - The Mole (Part-1)Dokument3 SeitenChapter 9 - The Mole (Part-1)Mihika ShethNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceDokument40 Seiten01 Formulae, Equations and Amount of SubstanceM BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Relations in Chemistry Stoichiometry: William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. NethDokument73 SeitenMass Relations in Chemistry Stoichiometry: William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. NethRezel C. PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionVon EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Febrile Fit: Foong Wei Jian Denesha KaurDokument19 SeitenFebrile Fit: Foong Wei Jian Denesha KaurDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Febrile Fit: Foong Wei Jian Denesha KaurDokument19 SeitenFebrile Fit: Foong Wei Jian Denesha KaurDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDokument21 Seiten3010 Adrenal and Parathyroid HormonesDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacologic Principles: - Additive EffectsDokument8 SeitenPharmacologic Principles: - Additive EffectsDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- C7 Revision Earth and AtmosphereDokument2 SeitenC7 Revision Earth and AtmosphereDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: C4 Revision: Atomic StructureDokument1 SeiteChemistry: C4 Revision: Atomic StructureDenesha KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pautas Anatómicas para La Inserción de Minitornillos: Sitios PalatinosDokument11 SeitenPautas Anatómicas para La Inserción de Minitornillos: Sitios PalatinosValery V JaureguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mangement of Shipping CompaniesDokument20 SeitenMangement of Shipping CompaniesSatyam MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uts Cmo Module 5Dokument31 SeitenUts Cmo Module 5Ceelinah EsparazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisDokument15 SeitenIce 3101: Modern Control THEORY (3 1 0 4) : State Space AnalysisBipin KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- San Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionDokument28 SeitenSan Mateo Daily Journal 01-28-19 EditionSan Mateo Daily JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nikasil e AlusilDokument5 SeitenNikasil e AlusilIo AncoraioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)Dokument8 SeitenISO-3046-4-2009 (Gobernador de Velocidad)David GastelumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Tax Planning AY 2020-21 Sem V B.ComH - Naveen MittalDokument76 SeitenCorporate Tax Planning AY 2020-21 Sem V B.ComH - Naveen MittalNidhi LathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunDokument40 SeitenCatalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunHà Văn TiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3g Node B On Ip MediaDokument79 Seiten3g Node B On Ip MediaBsskkd KkdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetism WorksheetDokument3 SeitenElectromagnetism WorksheetGuan Jie KhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grasa LO 915Dokument2 SeitenGrasa LO 915Angelo Carrillo VelozoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specimen Signature FormDokument27 SeitenSpecimen Signature FormnandukyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epistemology and OntologyDokument6 SeitenEpistemology and OntologyPriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Dokument36 SeitenSRS Document Battle Royale Origins - V2Talha SajjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vishal: Advanced Semiconductor Lab King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) Thuwal, Saudi Arabia 23955Dokument6 SeitenVishal: Advanced Semiconductor Lab King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) Thuwal, Saudi Arabia 23955jose taboadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beer Pilkhani DistilleryDokument44 SeitenBeer Pilkhani DistillerySunil Vicky VohraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Percentage and Profit & Loss: Aptitude AdvancedDokument8 SeitenPercentage and Profit & Loss: Aptitude AdvancedshreyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspection Report For Apartment Building at 1080 93rd St. in Bay Harbor IslandsDokument13 SeitenInspection Report For Apartment Building at 1080 93rd St. in Bay Harbor IslandsAmanda RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbas Ali Mandviwala 200640147: Ba1530: Information Systems and Organization StudiesDokument11 SeitenAbbas Ali Mandviwala 200640147: Ba1530: Information Systems and Organization Studiesshayan sohailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitrol 900 910Dokument6 SeitenQualitrol 900 910chennupati999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Motor Steady-State Model (Squirrel Cage) : MEP 1422 Electric DrivesDokument21 SeitenInduction Motor Steady-State Model (Squirrel Cage) : MEP 1422 Electric DrivesSpoiala DragosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ose Sample QuotationDokument37 SeitenOse Sample Quotationrj medelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 12 Health Management Information SystemDokument14 SeitenLecture 12 Health Management Information SystemKamran SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study To Find Tank Bulging, Radial Growth and Tank Settlement Using API 650Dokument15 SeitenCase Study To Find Tank Bulging, Radial Growth and Tank Settlement Using API 650Jafer SayedNoch keine Bewertungen