Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Respiratory System: By: Carter Paquette, Ethan Eldridge, Brendan Marusiak, Nik Brading
Hochgeladen von
Junje Hbb0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten15 SeitenRespiratory Presentation.pptx
Originaltitel
Respiratory Presentation.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenRespiratory Presentation.pptx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
18 Ansichten15 SeitenThe Respiratory System: By: Carter Paquette, Ethan Eldridge, Brendan Marusiak, Nik Brading
Hochgeladen von
Junje HbbRespiratory Presentation.pptx
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 15
By: Carter Paquette, Ethan Eldridge, Brendan Marusiak,
Nik Brading
THE RESPIRATORY
SYSTEM
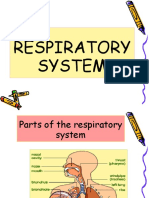
The Structure
Trachea- Tracheal rings (tracheal cartilages).
Bronchi- Bronchi are air tubes that spring out like roots into the
lungs and transport air.
Mouth/Nose- Both are passages that allow air to enter the lungs
and circulate the air.
Lungs- Are sponge like organs filled with air.
Diaphragm- Is the muscular structure that expands the cavity.
Pharynx- is a tubular structure placed behind the oral and nasal
cavity.
Larynx- Is made of bone like cartilages.
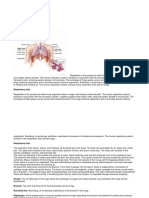
The Roles of each Organ
Lungs- provides oxygen to capillaries so they can oxygenate blood.
Bronchi- are the 2 main airways to the lungs. Allows the air into the
lungs through the nose or mouth.
Diaphragm- is the main muscle used to process the inspiration or
breathing in.
Trachea- known as the wind pipe.
Mouth/Nose- are the main access passages to the lungs to
transport air.
Pharynx- is a tubular structure placed behind the oral and nasal
cavity.
Larynx- from the pharynx, air enters the larynx, part of the upper
respiratory tract.
How does the respiratory system
react to a stimuli?
If the heart rate changes drastically the amount of
oxygenated blood will increase to keep your muscles
moving.
When exercising your adrenal gland produces
adrenaline and noradrenaline that directly affects the
heart and the ability to transport oxygen and carbon
dioxide throughout the body.
When you are scared the adrenal gland does the
same thing, releases adrenaline and noradrenaline
(reaction) to make your heart beat faster then the
oxygenated blood gets to your muscles faster than
normal and that makes you react to a scare (stimuli)
How does the respiratory system
react to a stimuli?
If the heart rate changes drastically the amount of
oxygenated blood will increase to keep your muscles
moving.
When exercising your adrenal gland produces
adrenaline and noradrenaline that directly affects the
heart and the ability to transport oxygen and carbon
dioxide throughout the body.
When you are scared the adrenal gland does the
same thing, releases adrenaline and noradrenaline
(reaction) to make your heart beat faster then the
oxygenated blood gets to your muscles faster than
Respiratory System Video
normal and that makes you react to a scare (stimuli)
By Nik
RESPIRATORY
SYSTEM: COMMON
DISEASES
Table and Graphs
Asthma
The airways are persistently inflamed,
and may occasionally spasm, causing
wheezing and shortness of breath.
Symptoms: Wheezing
Coughing that won't stop
Shortness of breath
Tightness in the chest
In severe cases, an untreated asthma
attack can be life-threatening.
Allergies
infections or pollution can trigger
asthma's symptoms.
The airways are persistently inflamed,
and may occasionally spasm, causing
wheezing and shortness of breath.
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD: Blocks the
airway and makes it difficult to exhale air.
Symptoms: Inside the lungs, COPD can clog the airways and
damage the tiny, balloon-like sacs (alveoli) that absorb
oxygen. These changes can cause the following symptoms:
Shortness of breath in everyday activities
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Constant coughing
Producing a lot of mucus (sputum)
Feeling tired
Frequent colds or flu
Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis: A form of COPD
characterized by a chronic productive
cough.
Emphysema
Lung damage allows air to be trapped in
the lungs in this form of COPD. Difficulty
blowing air out is its hallmark.
Acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis: A sudden infection of
the airways, usually by a virus.
Cystic fibrosis
A genetic condition causing poor
clearance of mucus from the bronchi.
The accumulated mucus results in
repeated lung infections.
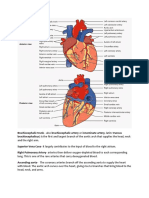
Respiratory system
The human respiratory is a group
of organs and tissues that enables
your body to breathe. Its primary
function is to supply oxygen to all
the parts of your body.
The respiratory system is made up
of airways (your nose, mouth,
voice box, windpipe and bronchial
tubes) and the lungs and the
muscles and blood vessels
connected to them.
The lungs exchange gasses and
when you inhale you breath the
alveoli exchanges gasses so
oxygen comes in and pushes
carbon dioxide out and that
causes you to breathe.
Healthy vs unhealthy
Healthy- your cells are fully
functioning. Then they exchange
gasses properly. Which makes you
able to breath. And that makes you
live. A healthy respiratory system is
really important because it causes
you to breath/live.
unhealthy- your cells are dying and
aren't functioning properly. When
that happens your lungs and other
organs to not function properly. If
that happens it can cause other
systems to shut down. And possibly
kill the body. Because what
happens is your alveoli's get
plugged up from your own body
fluid helps the infected area so that
fluid in the alveolis fills up and
causes your lungs to not
exchanges gasses properly so it
slows your breathing
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fourth Periodical Test in EnglishDokument3 SeitenFourth Periodical Test in EnglishJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of Exercise On The Cardiorespiratory SystemDokument15 SeitenThe Effect of Exercise On The Cardiorespiratory SystemBASAVARAJ100% (1)
- The Human Breathing SystemDokument5 SeitenThe Human Breathing SystemHarry Cianne Luther Sayon100% (1)
- Earth As A PlanetDokument60 SeitenEarth As A PlanetR AmravatiwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perioperative Care For CABG PatientsDokument32 SeitenPerioperative Care For CABG PatientsAya EyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hippocrates OathDokument6 SeitenHippocrates OathSundary FlhorenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Api 579-2 - 4.4Dokument22 SeitenApi 579-2 - 4.4Robiansah Tri AchbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDokument4 Seiten3.6 - The Respiratory SystemDjej100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory SystemxoxosvwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Cholecystectomy ReportDokument7 SeitenOpen Cholecystectomy ReportjosephcloudNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPD Case ICUDokument19 SeitenCOPD Case ICUKim Vizcarra100% (1)
- Case Study CopdDokument7 SeitenCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter II - Respiratory SystemDokument3 SeitenChapter II - Respiratory SystemIndranil SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDokument15 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav May100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)Dokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Handouts)bluecindy87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised List of Maharashtra HospitalsDokument16 SeitenRevised List of Maharashtra Hospitalsdummy data100% (1)
- ISBAR For Clear CommunicationDokument6 SeitenISBAR For Clear Communicationmehara1920Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASSURE Model Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenASSURE Model Lesson PlanJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path FitDokument21 SeitenPath FitChris Timothy TurdanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument23 SeitenRespiratory Systemjimboy baddiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- LungsDokument5 SeitenLungsTishonna DouglasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: What Is Respiration?Dokument25 SeitenRespiratory System: What Is Respiration?Perla AlejandresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System AssignmentDokument3 SeitenRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System AssignmentDokument3 SeitenRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 025735919Dokument3 Seiten025735919Vinz JaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Respiratory SystemDokument5 SeitenAnatomy Respiratory SystemSusanne Seynaeve95% (20)
- Respiratory System: Nose and NostrilsDokument8 SeitenRespiratory System: Nose and NostrilsKabang MoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument5 SeitenRespiratory Systemruben diwasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: Agatha Babyet A. Alabata, Bsn-Iii StemDokument31 SeitenRespiratory System: Agatha Babyet A. Alabata, Bsn-Iii StemJay VillasotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: A. NormalDokument10 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System: A. NormalCherrie CatingubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Physiology - MelaneeDokument5 SeitenAnatomy Physiology - MelaneeNikkoBacasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Covid Ana - Phy DiscussionDokument3 SeitenCovid Ana - Phy DiscussionFrance Llana CueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation: Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenOxygenation: Anatomy and PhysiologyMark Elen100% (1)
- Science Week 1 (Bil)Dokument6 SeitenScience Week 1 (Bil)shashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems Module 12Dokument40 SeitenSystems Module 12Richiel Angulo SungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breathtaking Lungs: Their Function and Anatomy: Bronchial Tree BronchiDokument6 SeitenBreathtaking Lungs: Their Function and Anatomy: Bronchial Tree BronchiRatnaPrasadNalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDokument33 SeitenLesson 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemIgnacio MarLiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Document 14Dokument2 SeitenDocument 14Avighna Reddy DargulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Dokument12 SeitenRespiratory: Email: Phone No. 07703123038Wria AbdulrahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hercor CollegeDokument7 SeitenHercor CollegeRodrinerBillonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5678 Human BodyDokument20 Seiten5678 Human BodysuryohandokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance)Dokument17 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance)Michelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDokument3 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument10 SeitenReviewerMaybelyn Rivera PagkatotohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDokument15 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 ReviewerDokument7 SeitenScience 9 ReviewerArgie MabagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System 3Dokument26 SeitenRespiratory System 3fel izNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory SystemDokument7 SeitenRespiratory SystemxoxogeloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research PaperDokument14 SeitenResearch PaperAlicia ValverdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDokument7 SeitenRespiratory and Circulatory SystemElle MateoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDokument44 SeitenCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKlaudette Collin PaynorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sience ReviewerDokument6 SeitenSience ReviewerRish NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: (A Written Report)Dokument16 SeitenRespiratory System: (A Written Report)hellofrom theothersideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 Respiratory System1Dokument2 SeitenLesson 1 Respiratory System1Glaisa CudiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherDokument2 SeitenRespiratory and Circulatory Systems Working TogetherPsycho Kpop OtakuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologymalindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breathing Process PDFDokument3 SeitenBreathing Process PDFDianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDokument11 SeitenChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderOlivelhynn BernaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Case StudyDokument23 SeitenA Case StudyFritzie NagacNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory SystemDokument74 SeitenThe Respiratory SystemRaghu NadhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr. 9 Science LM (AG)Dokument33 SeitenGr. 9 Science LM (AG)Aizalonica GalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System: Done By: Daniella DhanesarDokument25 SeitenRespiratory System: Done By: Daniella DhanesarDaniellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory SystemDokument28 SeitenThe Respiratory SystemRoland Jacques AlconisNoch keine Bewertungen
- COPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, ChronicDokument13 SeitenCOPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, Chronicmaxmay07Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory SystemDokument28 SeitenThe Respiratory SystemJuma SammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument3 SeitenScienceVaughn Siegfried FuertezNoch keine Bewertungen
- RESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeDokument4 SeitenRESPIRATORY SYS-WPS OfficeRina Catubo100% (1)
- Respiratory AnatomyDokument35 SeitenRespiratory Anatomyapi-217919217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation in ZoologyDokument5 SeitenCompilation in ZoologyJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 354 361 PDFDokument8 Seiten354 361 PDFJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name of PupilsDokument1 SeiteName of PupilsJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Assessment: GRASPS: When Constructing Performance Assessment Tasks, It Helps To Use The Acronym GRASPSDokument1 SeitePerformance Assessment: GRASPS: When Constructing Performance Assessment Tasks, It Helps To Use The Acronym GRASPSJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Teaching Guide - Business Math - Fractions (ABM - BM11FO-Ia-1) - TEDokument20 Seiten01 Teaching Guide - Business Math - Fractions (ABM - BM11FO-Ia-1) - TEJunje Hbb50% (2)
- ASSURE Model Lesson Plan1Dokument6 SeitenASSURE Model Lesson Plan1Junje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deductive Approach: ExampleDokument1 SeiteDeductive Approach: ExampleJunje HbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- S:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Dokument19 SeitenS:/admin/mpi/MP1169 - Amaia Skies Samat/000 - ACTIVE DOCUMENTS/09 - SPECS/2013-07-23 - Design Development/04-Plumbing/15050Lui TCC BariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Slides SEMINAR 1 - 220606 - 142811 - 220606 - 223805Dokument32 SeitenBrain Slides SEMINAR 1 - 220606 - 142811 - 220606 - 223805pang pangNoch keine Bewertungen
- W2 - Fundementals of SepDokument36 SeitenW2 - Fundementals of Sephairen jegerNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.f.roof Beam & Slab DetailDokument1 SeiteG.f.roof Beam & Slab Detailahmad anasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kern County Sues Governor Gavin NewsomDokument3 SeitenKern County Sues Governor Gavin NewsomAnthony Wright100% (1)
- SET 2022 Gstr1Dokument1 SeiteSET 2022 Gstr1birpal singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Communities From Arid Environments On A Global Scale. A Systematic ReviewDokument12 SeitenMicrobial Communities From Arid Environments On A Global Scale. A Systematic ReviewAnnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Just Another RantDokument6 SeitenJust Another RantJuan Manuel VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Athletes Who Made Amazing Comebacks After Career-Threatening InjuriesDokument11 SeitenAthletes Who Made Amazing Comebacks After Career-Threatening InjuriesანაNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Hand Grip Strength: NormsDokument7 SeitenFor Hand Grip Strength: NormsPraneethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenStax - Psychology - CH15 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERSDokument42 SeitenOpenStax - Psychology - CH15 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERSAngelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Sheet - Parsys Cloud - Parsys TelemedicineDokument10 SeitenProduct Sheet - Parsys Cloud - Parsys TelemedicineChristian Lezama Cuellar100% (1)
- Laws and Regulation Related To FoodDokument33 SeitenLaws and Regulation Related To FoodDr. Satish JangraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachiocephalic TrunkDokument3 SeitenBrachiocephalic TrunkstephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depression List of Pleasant ActivitiesDokument3 SeitenDepression List of Pleasant ActivitiesShivani SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rahu Yantra Kal Sarp Yantra: Our RecommendationsDokument2 SeitenRahu Yantra Kal Sarp Yantra: Our RecommendationsAbhijeet DeshmukkhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imagine Unit 1 P 10 11Dokument1 SeiteImagine Unit 1 P 10 11נויה לבדובNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Composition and Organoleptic Attributes of Lesser-Known Vegetables As Consumed in Njikoka Local Government Area, Anambra State, NigeriaDokument4 SeitenThe Chemical Composition and Organoleptic Attributes of Lesser-Known Vegetables As Consumed in Njikoka Local Government Area, Anambra State, NigeriaEmri CynthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preservation and Collection of Biological EvidenceDokument4 SeitenPreservation and Collection of Biological EvidenceanastasiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RB Boiler Product SpecsDokument4 SeitenRB Boiler Product Specsachmad_silmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pet 402Dokument1 SeitePet 402quoctuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PaintballDokument44 SeitenPaintballGmsnm Usp MpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buddahism ReportDokument36 SeitenBuddahism Reportlaica andalNoch keine Bewertungen