Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Entamoeba Coli
Hochgeladen von
Hanisha Erica100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
781 Ansichten14 SeitenEntamoeba coli
Originaltitel
Entamoeba coli
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenEntamoeba coli
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
781 Ansichten14 SeitenEntamoeba Coli
Hochgeladen von
Hanisha EricaEntamoeba coli
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 14
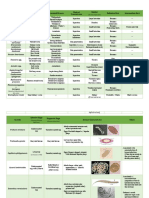
• Considered a non-pathogen
• Cyst and trophozoite are larger than E.
histolytica
• A stained smear is required to
differentiate E. coli and E. histolytica
trophs
• Cysts contain 8 nuclei
• Hyper nucleation is possible resulting to
16 or more nuclei
• trophozoites possess a single nucleus
with a characteristically large, eccentric
karyosome and coarse, irregular
peripheral chromatin
Trophozoites possess a single
nucleus with a characteristically
large, eccentric karyosome and
coarse, irregular peripheral
chromatin
The only species in the genus
encountered in humans with more
than four nuclei in the cyst stage
CYST TROPHOZOITE
TROPHOZOITE IN
CYST IN TRICHROME TRICHROME
Non pathogenic
Known to be the first amoeba in
humans to be described
Found in the mouth between the
gingival pockets
Found in 95% of people with gum
disease and 50% with healthy gums
Cyst stage is not present therefore
transmission is through kissing or
sharing utensils
Troph are between 10-20 micrometer
Pseudopodia present
Troph may be coughed up; should be
differentiated from E. histolytica which
can be found in sputum from pulmonary
abscess
Morphologically identical with E. histolytica
Different DNA and ribosomal RNA
Differentiated through PCR or genome
sequencing
Cysts have 4 nuclei that characteristically
have centrally located karyosomes and
fine, uniformly distributed peripheral
chromatin
Usually measure 12 to 15 µm
Important in studies concerning E.
histolytica pathogenicity
Killing of host cells yet it is non-
pathogenic, the molecular reason for
this is still in question
Three nuclei are
visible in the focal
plane (black
arrows), and the
cyst contains a
chromatoid body
with typically
blunted ends (red
arrow)
• Trophozoites have a single nucleus
• Centrally placed karyosome and uniformly
distributed peripheral chromatin
• Erythrophagocytosis (ingestion of red blood
cells by the parasite) is the only
morphologic characteristic that can be used
to differentiate E. histolytica from the
nonpathogenic E. dispar. However,
erythrophagocytosis is not typically
observed on stained smears of E. histolytica
Troph of E. Troph of E.
histolytica/E. histolytica with
dispar erythrophagocytosis
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Dokument14 Seiten3 SEMR421 Bacteriology Part 3Micah Daniel TapiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Diagnostic Parasitology: (Specimen Collection and Handling)Dokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Diagnostic Parasitology: (Specimen Collection and Handling)RIC JOSEPH PONCIANONoch keine Bewertungen
- TrematodesDokument30 SeitenTrematodesJezzah Mae CañeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestode SDokument79 SeitenCestode SVincent Manganaan67% (3)
- Outline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesDokument73 SeitenOutline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesAsxe CeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ameba ReportingDokument49 SeitenThe Ameba ReportingALLISON PAMITTANNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrematodesDokument9 SeitenTrematodesLewis P. SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitic AmoebaDokument23 SeitenParasitic AmoebaJethrö MallariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostDokument5 SeitenNematode Common Name Associated Disease Mode of Transmission Habitat Definitive Host Intermediate HostAnjelo PerenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology, Vector Studies, and CultureVon EverandPathology, Vector Studies, and CultureJulius P. KreierBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Medical ProtozoologyDokument6 SeitenMedical ProtozoologyRaymund MontoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epydemiologi AmebiasisDokument6 SeitenEpydemiologi AmebiasisRizal FajriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology - Lec - FinalDokument69 SeitenParasitology - Lec - FinalJannah Monaliza BambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me EnterobacteriaceaeDokument72 SeitenMe Enterobacteriaceaewimarshana gamage100% (1)
- Protozoans and Intestinal Helminths StagesDokument18 SeitenProtozoans and Intestinal Helminths StagesStephen YorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CestodesDokument83 SeitenCestodesveralynn2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andDokument4 SeitenAccurate Diagnosis of Parasitic Infections Is Important To Decrease The Prevalence andManulat VicaiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomphalaria&Aus Tralorbis Onchomelania Bulinus&PhysopsisDokument4 SeitenBiomphalaria&Aus Tralorbis Onchomelania Bulinus&PhysopsisOlib OlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Medical ParasitologyDokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Medical Parasitologyamrokhalidyousif77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haemophilus SPPDokument109 SeitenHaemophilus SPPJamie CañebaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 05. Normal Flora of The Human BodyDokument16 SeitenChapter 05. Normal Flora of The Human BodyChino Isiah CañeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rabies Virus, Disease, and PreventionDokument25 SeitenRabies Virus, Disease, and PreventionAdindapauliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TREMATODESDokument31 SeitenTREMATODESKen Mark ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coccidia 10 - 11Dokument40 SeitenCoccidia 10 - 11microperadeniya100% (1)
- Entamoeba SPPDokument21 SeitenEntamoeba SPPragnabulletinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDokument5 SeitenBlood and Tissue FlagellatesChristine BuenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paragonimus WestermaniDokument3 SeitenParagonimus WestermaniHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Dokument20 SeitenPara-Transes Prelim Exam - Unit 2Aysha AishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParasitologyDokument3 SeitenParasitologyKCSotelo_xxviiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestode NotesDokument26 SeitenCestode NotesJOSEPH NDERITUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trichuris Trichiura: Lecture By: Maha Gamal AldeinDokument20 SeitenTrichuris Trichiura: Lecture By: Maha Gamal AldeinMohammad DweibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nematode NotesDokument2 SeitenNematode Notesapi-247084136100% (1)
- HookwormDokument10 SeitenHookwormAmelyalesmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To ParasitologyDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To ParasitologyRIC JOSEPH PONCIANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Virulence Factors & Pathogenesis of Fungal InfectionsDokument28 SeitenVirulence Factors & Pathogenesis of Fungal InfectionsNipun ShamikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables - CestodesDokument8 SeitenTables - CestodesSid Loverholic50% (4)
- Trematode Characteristics and Life CyclesDokument2 SeitenTrematode Characteristics and Life CyclesGougle MuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amoeba Characteristics and PathologyDokument3 SeitenAmoeba Characteristics and PathologyRuel Antiola Mateo100% (1)
- Antigens: Immunogenic Factors & Types in 40 CharactersDokument24 SeitenAntigens: Immunogenic Factors & Types in 40 CharactersUhjafwnuijhnfa KmerkgoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taenia Saginata Taenia Solium: "Beef Tapeworm"Dokument6 SeitenTaenia Saginata Taenia Solium: "Beef Tapeworm"Gela ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmoebaDokument5 SeitenAmoebasarguss14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gram-Negative Rods in Gut FloraDokument2 SeitenGram-Negative Rods in Gut FloraJohn TerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giardia lamblia in the Small IntestineDokument16 SeitenGiardia lamblia in the Small IntestineRahul ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NematodaDokument96 SeitenNematodaPurplesmilezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology TableDokument9 SeitenParasitology TablehumanupgradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parasitology Table ProtozoaDokument10 SeitenParasitology Table ProtozoaMae Rose Charlene MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PECOMADokument25 SeitenPECOMAAnan JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CestodesDokument39 SeitenCestodesNachiket Vijay PotdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestodes and TrematodesDokument48 SeitenCestodes and TrematodesFort SalvadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDokument23 SeitenAscaris LumbricoidesKay CeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics and Life Cycles of Common Flatworms (CestodesDokument73 SeitenCharacteristics and Life Cycles of Common Flatworms (CestodesEliza May BarrettoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Examination of UrineDokument4 SeitenPhysical Examination of UrineIceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cestode SDokument38 SeitenCestode SJang JangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTLBE Internship Assessment QuizDokument2 SeitenMTLBE Internship Assessment QuizAngela LaglivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupDokument14 Seiten1.entamoeba Histolytica - Is The Major Pathogen in This GroupJoseph De JoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- pm2 TREMATODESDokument39 Seitenpm2 TREMATODESshastaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nematodes and Their Life CyclesDokument18 SeitenNematodes and Their Life Cyclesnicole syNoch keine Bewertungen
- Helicobacter Pylori: Dr.B.BoyleDokument35 SeitenHelicobacter Pylori: Dr.B.BoyleTammy AdjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesDokument3 SeitenTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warm and Cold Type of IHADokument2 SeitenWarm and Cold Type of IHAHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParasitologyDokument5 SeitenParasitologyHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Pa Tho Physiology Ms1Dokument4 SeitenSchematic Pa Tho Physiology Ms1Hanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Hygiene and The Prevalence and Intensity of AscariasisDokument19 SeitenHand Hygiene and The Prevalence and Intensity of AscariasisHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schematic Pathophysiology Predisposing FactorsDokument7 SeitenSchematic Pathophysiology Predisposing FactorsHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of and Attitudes and Knowledge About Pap Smears Among Women in KuwaitDokument18 SeitenUse of and Attitudes and Knowledge About Pap Smears Among Women in KuwaitHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Para ReportDokument21 SeitenPara ReportHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Assessment: Vital SignsDokument8 SeitenPhysical Assessment: Vital SignsHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX Test ms1Dokument4 SeitenDX Test ms1Hanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- March 30Dokument4 SeitenMarch 30Hanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phylum Sarcomas Ti Gop HoraDokument38 SeitenPhylum Sarcomas Ti Gop HoraHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fasciolopsis BuskiDokument2 SeitenFasciolopsis BuskiHanisha Erica100% (1)
- Entamoeba HistoDokument25 SeitenEntamoeba HistoHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge of Selected Nurses and Clinical InstructorsDokument13 SeitenKnowledge of Selected Nurses and Clinical InstructorsHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterophyid FlukesDokument2 SeitenHeterophyid FlukesHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echinostoma IlocanumDokument2 SeitenEchinostoma IlocanumHanisha EricaNoch keine Bewertungen