Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bohr Diagram Lesson
Hochgeladen von
ibrahim_s0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten26 Seitenpresentation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenpresentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten26 SeitenBohr Diagram Lesson
Hochgeladen von
ibrahim_spresentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 26
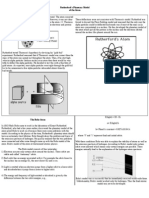
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr (1913):
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr (1913):
-studied the light produced when atoms
were excited by heat or electricity
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr (1913):
-studied the light produced when atoms
were excited by heat or electricity
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr (1913):
-studied the light produced when atoms
were excited by heat or electricity
Rutherford's model couldn't explain why
unique colours were obtained by atoms of
different elements
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Niels Bohr (1913):
-studied the light produced when atoms
were excited by heat or electricity
Rutherford's model couldn't explain why
unique colours were obtained by atoms of
different elements
Bohr proposed that electrons are in orbits &
when excited jump to a higher orbit. When
they fall back to the original they give off light
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Bohr's model:
-electrons orbit the nucleus like planets
orbit the sun
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Bohr's model:
-electrons orbit the nucleus like planets
orbit the sun
-each orbit can hold a specific maximum
number of electrons
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Bohr's model:
-electrons orbit the nucleus like planets
orbit the sun
-each orbit can hold a specific maximum
number of electrons
orbit
maximum #
electrons
1
2
3
4
2
8
8
18
Bohr's Model of the Atom
Bohr's model:
-electrons orbit the nucleus like planets
orbit the sun
-each orbit can hold a specific maximum
number of electrons
-electrons fill orbits closest to the nucleus
first.
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P =
#e- =
#N =
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = atomic #
=9
#e- =
#N =
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = # P
=9
#N =
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = atomic mass - # P
= 10
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
9P
10N
#N = 10
draw the nucleus with
protons & neutrons
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
9P
10N
#N = 10
how many electrons can
fit in the first orbit?
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
9P
10N
#N = 10
how many electrons can
fit in the first orbit?
2
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = 10
9P
10N
how many electrons are left?
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = 10
9P
10N
how many electrons are left?
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = 10
9P
10N
how many electrons are left?
how many electrons fit in the
second orbit?
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = 10
9P
10N
how many electrons are left?
how many electrons fit in the
second orbit?
7
8
Bohr's Model of the Atom
e.g. fluorine:
#P = 9
#e- = 9
#N = 10
9P
10N
Bohr's Model of the Atom
try these:
hydrogen
boron
magnesium
Bohr's Model of the Atom
try these:
hydrogen
1P
0N
Bohr's Model of the Atom
try these:
boron
5P
6N
Bohr's Model of the Atom
try these:
12P
12N
magnesium
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Bohr Model LessonDokument22 SeitenBohr Model LessonRoss Adrales GeleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr Diagram LessonDokument26 SeitenBohr Diagram Lessonjanice alquizarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr Diagram LessonDokument26 SeitenBohr Diagram LessonGlenn ClementeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure: Prepared by Mr. Peter H. MammbaDokument95 SeitenAtomic Structure: Prepared by Mr. Peter H. MammbaRIZIKI BONIFACENoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic TheoryDokument1 SeiteAtomic TheoryAnnaoj SalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niels Bohr Model of An AtomDokument5 SeitenNiels Bohr Model of An AtomAnecito Gemida Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr Atom: The Planetary Model of The AtomDokument12 SeitenBohr Atom: The Planetary Model of The AtomShekhar RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic-Structure G8Dokument13 SeitenAtomic-Structure G8Jaco GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excitation by Absorption of Light and De-Excitation by Emission of LightDokument8 SeitenExcitation by Absorption of Light and De-Excitation by Emission of LightqueencieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bohr ModelDokument42 SeitenThe Bohr Modelsteodoro012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Frances John Salo 9-Aguho ScienceDokument5 SeitenName: Frances John Salo 9-Aguho ScienceHelloItsXp TiongsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PowerPoint - Models of The Atom - A Historical PerspectiveDokument25 SeitenPowerPoint - Models of The Atom - A Historical PerspectivedemplelugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rutherford's Al-WPS OfficeDokument13 SeitenRutherford's Al-WPS Officesudha guruprasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr's Model of The AtomDokument7 SeitenBohr's Model of The AtomsantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Estructura Atomica-2011Dokument85 Seiten04 Estructura Atomica-2011FranciscoTestaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 - The QuantumMechanical Model Q2 Wk1 1Dokument82 SeitenScience 9 - The QuantumMechanical Model Q2 Wk1 1Fianna GalleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Niels Bohr: Electrons Travel in Separate OrbitsDokument3 SeitenAbout Niels Bohr: Electrons Travel in Separate OrbitsAadarshini ShreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Model TheoriesDokument6 SeitenAtomic Model Theoriesjustforbuznes1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 (Semester-1)Dokument16 SeitenUnit-1 (Semester-1)Afsar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelDokument17 SeitenAtomic ModelSuperUserNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Science: Atomic PhysicsDokument24 SeitenGeneral Science: Atomic PhysicshelperforeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Atom Project by Aditi RaiDokument13 SeitenStructure of Atom Project by Aditi RaiAnamika RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models of The Atom: Prepared By: Therese Anne G. CababarrosDokument12 SeitenModels of The Atom: Prepared By: Therese Anne G. CababarrosTherese Anne CababarrosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsKaizerani FatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2022-11-28 at 4.34.42 PMDokument4 SeitenScreenshot 2022-11-28 at 4.34.42 PMBaneen HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr's Atomic ModelDokument3 SeitenBohr's Atomic ModelMamidanna SashankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rutherford Atomic ModelDokument2 SeitenRutherford Atomic ModelRichillo OliverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic TheoryDokument7 SeitenAtomic TheoryChelsea Reyna TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awais Assignment QM 2Dokument31 SeitenAwais Assignment QM 2Awais YousafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Scale StructuresDokument3 SeitenAtomic Scale StructuresErish Brylle G. MañalacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rutherford Atomic ModelDokument5 SeitenRutherford Atomic ModelDevank RajvanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 2 ModDokument16 SeitenChap 2 ModM Zia DogarNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of The Atoms and Atomic StructureDokument38 SeitenHistory of The Atoms and Atomic StructureAndy RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- General ChemistryDokument14 SeitenGeneral ChemistryEduardo BasonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project File School WorkDokument15 SeitenChemistry Project File School WorkNaman Gupta100% (1)
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsJoyae Chavez100% (1)
- Physical Science SHS 2.3 Bohr Model of The AtomDokument18 SeitenPhysical Science SHS 2.3 Bohr Model of The AtomMaricris Jane PeranteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomos: Not To Be CutDokument34 SeitenAtomos: Not To Be Cutemo mHAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryDokument4 SeitenPrince Harold Silvania 12-Eleazar: Dalton's TheoryAllen AcojidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planetary Model of An AtomDokument4 SeitenPlanetary Model of An AtomTeresa100% (1)
- Emission SpectraDokument14 SeitenEmission SpectraAli MakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Students Version 01 - Atomic ModelsDokument26 SeitenStudents Version 01 - Atomic ModelsENSANO, RHYNS G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of RadioactivityDokument143 SeitenBasic Principles of RadioactivityBulu Chandra MahantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure: Atom:Atoms Are The Smallest Particle of Element That ContainDokument12 SeitenAtomic Structure: Atom:Atoms Are The Smallest Particle of Element That ContainAbdul AwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Niels Bohr Atomic Theory BohrDokument1 SeiteNiels Bohr Atomic Theory BohrAyessa AnchetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Plum Pudding Model:: Philosophical MagazineDokument2 SeitenThe Plum Pudding Model:: Philosophical MagazinevcespecialistmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models of The AtomDokument38 SeitenModels of The AtomKC TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bohr TheoryDokument10 SeitenThe Bohr TheoryManP13Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Atomic ModelDokument4 SeitenThe Atomic ModelElia SilvestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsherniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDokument5 SeitenDalton's Atomic TheoryKeanneMarieJandusayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atom's AssignmentDokument12 SeitenAtom's Assignmentbihaishak_268311918Noch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsPedi ApriansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- BohrDokument7 SeitenBohrDesita Tri ArifienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsDr Siva Kumar0% (1)
- Atomic Theory ExpierimentsDokument8 SeitenAtomic Theory Expierimentsapi-323082319Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr's Planetary ModelDokument8 SeitenBohr's Planetary ModelClarissa MuliawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic ModelsDokument12 SeitenAtomic ModelsPedi ApriansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
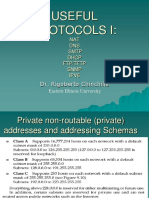
- Useful Protocols IDokument132 SeitenUseful Protocols Iibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- SiyasahkhilafahDokument18 SeitenSiyasahkhilafahibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEC62056Dokument5 SeitenIEC62056ibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uart DSPIC33F GuideDokument56 SeitenUart DSPIC33F Guideibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap2 PDFDokument16 SeitenChap2 PDFibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Gauss TestDokument10 SeitenGauss TestpudintekelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipschutz LinearAlgebraDokument340 SeitenLipschutz LinearAlgebradoidavarrida123Noch keine Bewertungen
- MM Ch06Dokument85 SeitenMM Ch06ibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- P SeriesDokument3 SeitenP Seriesibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Inner Ear - Structure and FunctionDokument17 SeitenThe Inner Ear - Structure and FunctionRose MerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taye Taye FishDokument276 SeitenTaye Taye FishSyed Zishan Haider NaqviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bohr's Model: Nucleus Electron OrbitDokument5 SeitenBohr's Model: Nucleus Electron Orbitibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- STEVAL-MKI108V1: L3G4200D and LSM303DLHC 9-Axis Module For A Standard DIL24 SocketDokument4 SeitenSTEVAL-MKI108V1: L3G4200D and LSM303DLHC 9-Axis Module For A Standard DIL24 Socketibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 82C84Dokument10 Seiten82C84ibrahim_sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrostatics : Fluid Mechanics 1, Lecture #1 Dr. Ir. Pieter C. RoosDokument45 SeitenHydrostatics : Fluid Mechanics 1, Lecture #1 Dr. Ir. Pieter C. RoosJohanna PilataxiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nso Sample Paper Class-6Dokument2 SeitenNso Sample Paper Class-6Ks ShamithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics by Hipolito Chapter 1Dokument10 SeitenThermodynamics by Hipolito Chapter 1Nash Fernandez100% (6)
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Dokument4 SeitenScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy and Exergy Analysis of A Steam Power Plant in EgyptDokument13 SeitenEnergy and Exergy Analysis of A Steam Power Plant in EgyptaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 1Oburu David KatandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- G4 Geology AssignmentDokument5 SeitenG4 Geology AssignmentAmanuel AlemayehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Mass and Atomic Number WorksheetDokument1 SeiteAtomic Mass and Atomic Number WorksheetGuayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioplastic Made With Jicama StarchDokument2 SeitenBioplastic Made With Jicama StarchTHE MONSTAAGAMERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report in Meteorology (Structure of Depressions)Dokument16 SeitenReport in Meteorology (Structure of Depressions)Cecilia PicayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Đề thi tuyển vào lớp 10 trường THPT Chuyên môn Tiếng Anh 2016-2017Dokument8 SeitenĐề thi tuyển vào lớp 10 trường THPT Chuyên môn Tiếng Anh 2016-2017Nguyen NhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Thompson ExperimentDokument8 SeitenGP Thompson ExperimentHemanth GoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Reflection PaperDokument2 SeitenFirst Reflection Paperapi-303052743Noch keine Bewertungen
- History of BiologyDokument3 SeitenHistory of BiologyJS DSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography ProjectDokument16 SeitenGeography ProjectJai KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force Calc - PSVDokument2 SeitenForce Calc - PSVChris DENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Virtual Cook - McGeeDokument7 SeitenThe Virtual Cook - McGeeJuan Van HalenNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPPM Unit 1 Study MaterialDokument46 SeitenDPPM Unit 1 Study MaterialJyothi GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamDokument13 SeitenChemistry f4 Mid-Year ExamWindy SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krishna Sie FPT 2000Dokument33 SeitenKrishna Sie FPT 2000Chia Sheng WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Biodiversity and The Interconnected Web of Life Are ImportantDokument3 SeitenWhy Biodiversity and The Interconnected Web of Life Are ImportantAzmi AlsayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank - Module 2Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Bank - Module 2Mohammed ElsheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Dokument14 Seiten7.e.c Evaporation Part 2Sumaya HammoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 02Dokument12 SeitenNotes 02PrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mud ConstructionDokument35 SeitenMud ConstructionPaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Passive HouseDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Passive HouseLeontin LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Thermodynamics Nov2004 NR 21030Dokument8 Seiten4 Thermodynamics Nov2004 NR 21030Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Corporation of Telangana LimitedDokument3 SeitenTransmission Corporation of Telangana LimitedBoddu ThirupathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 - Workbook 3 Updated PDFDokument276 SeitenA2 - Workbook 3 Updated PDFMaham Furqan 1737934Noch keine Bewertungen
- TurbinesDokument39 SeitenTurbinesHmaedNoch keine Bewertungen