Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Monopoly - Indian Railways
Hochgeladen von
vrj1091Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Monopoly - Indian Railways
Hochgeladen von
vrj1091Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Monopoly - Introduction
Primary characteristics of a monopoly
Single Sellers
No Close substitutes
Price Maker
Blocked Entry
Profit Maximization for Monopoly
Costs and
Revenue
Monopoly
price
2. ...and then the
demand curve shows
the price consistent
with this quantity.
B
1. The intersection
of the marginalrevenue curve and
the marginal-cost
curve determines
the profitmaximizing
quantity...
Average
total cost
A
Demand
Marginal
cost
0
QMAX
Marginal revenue
Quantity
Background Information - Evolution
Railways Zone
Background Information - Evolution
Railways Zones
Sr.
No.
Name
Abbr.
1 Central
CR
2 East Central
3 East Coast
4 Eastern
5 North Central
6 North Eastern
ECR
ECoR
ER
NCR
NER
7 North Western
8 Northeast Frontier
9 Northern
NWR
NFR
NR
10 South
11 South
12 South
13 South
Central
East Central
Eastern
Western
SCR
SECR
SER
SWR
14 Southern
15 West Central
SR
WCR
16 Western
WR
Date
Headquarters Established Divisions
November 5,
1951
Mumbai
Mumbai, Bhusawal, Pune, Solapur, Nagpur
October 1,
Danapur, Dhanbad, Mughalsarai, Samastipur,
2002
Hajipur
Sonpur
April 1, 2003
Bhubaneswar Khurda Road, Sambalpur, Visakhapatnam
April, 1952
Kolkata
Howrah, Sealdah, Asansol, Malda
April 1, 2003
Allahabad
Allahabad, Agra, Jhansi
1952
Gorakhpur
Izzatnagar, Lucknow, Varanasi
October 1,
2002
Jaipur
Jaipur, Ajmer, Bikaner, Jodhpur
1958
Guwahati
Alipurduar, Katihar, Lumding, Rangia, Tinsukia
April 14, 1952 Delhi
Delhi, Ambala, Firozpur, Lucknow, Moradabad
October 2,
Secunderaba Secunderabad, Hyderabad, Guntakal, Guntur,
1966
d
Nanded, Vijayawada
April 1, 2003
Bilaspur, CG Bilaspur, Raipur, Nagpur
1955
Kolkata
Adra, Chakradharpur, Kharagpur, Ranchi
April 1, 2003
Hubli
Hubli, Bangalore, Mysore
Chennai, Madurai, Palakkad, Salem,
April 14, 1951 Chennai
Tiruchchirapalli, Thiruvanathapuram
April 1, 2003
Jabalpur
Jabalpur, Bhopal, Kota
November 5,
Mumbai Central, Vadodara, Ratlam, Ahmedabad,
1951
Mumbai
Rajkot, Bhavnagar
Background Information - Services
Passenger Services
Operates over 9000 trains and
transports over 5 billion annually across
India.
Preferred mode of transport in most of
the country.
Overcrowding is a widely faced problem
Ticket-less travel is also an additional
problem faced.
Background Information - Services
Production Services
Name
Diesel Locomotive Works
Chittaranjan Locomotive
Works
Diesel-Loco Modernisation
Works
Headquar
ters
Purpose
Manufacture mainline diesel-electric for passenger and freight
Varanasi
traffic
Chittaranja Manufacture electric locomotives using DC traction as well as ACn
AC transmission
Patiala
Manufactures key sub-assemblies for Diesel Locomotives
Integral Coach Factory
Chennai
Make coaches for the Indian Railways
Rail Coach Factory
Kapurthala Modern plant and has a much more flexible automation
Wheel & Axle Plant
Bengaluru Makes cast wheels for wagons
In addition, Central Organisation for Railway Electrification
(CORE) headquartered at Allahabad is also headed by a GM.
Its job is to undertake electrification projects of IR & monitor
their progress across the country.
Background Information - Services
Freight
Carries variety of goods
Contributes to 70% of revenues
Last 2 decades, shifted to large
container movement.
Majority of earnings comes from
carrying bulk goods like iron ore, coal.
Introduced CONRAJ for high priority
freight
Background Information - Services
Suburban Rail
Many cities have dedicated suburban
networks.
Cities include Mumbai, Chennai, Delhi,
Hyderabad, Kolkata, Lucknow & Pune.
Only Mumbai, Pune & Hyderabad share tracks
with long distance trains.
Trains are mostly electric multiple units.
Only in Mumbai trains run on Direct Current,
rest run on Alternating Current.
Background Information Organizational
Services
Background Information Organizational
Structure
Other PSUs under the control of Ministry of Railways
Indian Railways Catering and Tourism Corporation
Konkan Railway Corporation
Indian Railway Finance Corporation
Mumbai Rail Vikas Corporation
Railtel Corporation of India Telecommunication Networks
RITES Ltd. Consulting Division of Indian Railways
IRCON International Ltd. Construction Division
Rail Vikas Nigam Limited
Centre for Railway Information Systems is an
autonomous society under Railway Board, which is
responsible for developing the major software
required by Indian Railways for its operations.
Indian Railways - Present
Worlds third largest railway network
Prime movers to the nation
Approximately 65,000 km of rail tracks and over
7,151 railway stations.
IR owns a fleet of
2,22,379 wagons
42,441 coaches
7,910 locomotives
Operates 1,60,251 trains including 9,550
passenger trains, carrying about 1.6 million tonnes
of freight and about 18 million passengers daily
Indian Railways - Present
Prime infrastructural sector
World's largest commercial or utility employer,
with more than 1.5million employees on its
payrolls
Commercial Organization
Perform the dual role
Vehicle for fulfillment of social obligations
Part and parcel of the total receipts and
expenditure of the Government of India.
Contributes to 1% of GDP of INDIA.
Indian Railways The Mayhem
In 2002-03, 'social service obligation' of
Indian Railways worked out Rs 37.87 billion.
A 2001-02 review of all "branch lines"
disclosed that 115 trains had become
uneconomical, accounting for an annual loss
of Rs 434 crore.
In 2001, the ratio of net revenue to capital
declined to 2.5
In 1999-2000, fund balances had touched a
low of Rs. 1.49 billion.
Operating ratio reached 98.8 percent in the
year ending March 2001.
Indian Railways Problems faced
Surplus manpower1.6 million in FY
2001.
Poor staff productivity.
Loss of market share in the profitable
freight business.
Lack of flexibility in pricing.
Lack of accountability.
Politicization of the decision-making
processes
Indian Railways Cost Structure
Indian Railways Corrective Measures
modernization
safety and security of passengers
replacement and renewal of assets
track renewal & improvement in passenger
amenities
increase in productivity and reduction in operating
ratio.
computerization of railway systems.
induction of new technologies for signalling and
telecom.
prevention of leakages of revenue.
Indian Railways Strategic
Performance Enhancement Initiatives
Capacity Enhancement
increasing wagon loading capacity
reducing wagon turnaround time
increasing length of wagon
sidings(platforms)
reducing loading/unloading time
avoiding frequent train examination
Indian Railways Strategic
Performance Enhancement Initiatives
Capacity Utilization
Dynamic pricing policy
Tariff Rationalization
Non-peak Season Incremental Freight
Discount
Loyalty Discount Scheme
Long-term Freight Discount Scheme
Multiple Unloading
Indian Railways Strategic
Performance Enhancement Initiatives
Revenue Enhancement
Focusing on low-cost high-volume
operations
Revision in freight rates
Increasing number of coaches in popular
trains
Reducing AC class fares
Introducing Garib Raths to attract volumes
Indian Railways Favourable Factors
Change in the macro-economic
conditions
Rise in demand
Change in the legal position
Changes in organisational culture
Human resources initiatives
Downsizing
Decentralising
Indian Railways The Recovery
In FY 2006-2007, IR registered profits of Rs. 200 billion.
As of 2007, IR was India's second largest profit making PSU
after ONGC.
Revenue per staff witnessed a rise by 68 percent (2001
2006).
Operating Ratio was brought down to 78.7 percent by 2007.
Enhanced axle load and reduction in turnaround time of
wagons increased by 14%
IR increased wagon capacity available per day by 36 %
The number of employees reduced to 1.412 million by 2006
.
The number of accidents have been more than halved from
473 (2001) to 200 (2007)
Increase in the volume of passengers by approx 29 percent
over the period 2001 to 2007
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Increase in market share in freight traffic, both bulk and non-bulk,
was the important focus area.
Plan priorities for IR - building capacity for handling traffic growth
Up-gradation for heavy axle load movement
Modernization of freight and passenger terminals
Developing world class stations
Information Technology initiatives and technological up-gradations.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Amenities
Provision of on-line coach indication display board; on-line train arrival departure
information board; on-line reservation availability information board.
Provision of discharge-free green toilets in all 36,000 coaches in XI Plan period
at a cost of about Rs.4,000 cr.
LHB design coaches for all Rajdhani and Shatabdi trains over next few years.
Provision of LHB coaches with stainless steel bogies in Mail/Express trains.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Concessions
Senior citizen concession for women enhanced to 50% from existing 30%.
Free Monthly Seasonal Ticket to girl students up to graduation level in
place of 12th standard and for boys up to 12 th standard in place of 10th
standard.
Improvements in ticketing
Termination of queues at ticket counters targeted in two years.
Ticket booking on mobile phones; E-ticket for waitlisted passengers.
Increase in Unreserved Ticketing Systems counters to 15,000 and ATVMs
to 6000.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Reduction in passenger fares
One rupee discount per passenger for fares up to Rs.50 in non suburban
Second Class (ordinary and mail/express)
5% discount across the board for passenger fares beyond Rs.50 for all non
suburban Second Class (ordinary and mail/express).
Increase in discount for travel in new design high capacity reserved
coaches.
Reduction in fare AC-I : 7%; and AC-II : 4% (the reduction will be half for
popular trains and during peak period).
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Freight Business
Reductions & Concessions
5% reduction in freight rates for Petrol and
Diesel.
14% reduction in freight rate of Fly-ash.
Liberalisation of Traditional Empty Flow
direction incentive scheme
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Freight Business
Reductions & Concessions
30% discount on entire traffic in place of
incremental traffic booked from goods shed.
Increase in discount on incremental traffic
booked from private sidings from 30% to 40%.
6% freight concession for traffic booked from
other States for stations in North Eastern
States.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Initiatives
Target for loading fixed at 850 MT in 2008-09.
Blue - Print prepared for High Density Network.
Top priority being given to port rail connectivity
projects.
New and dedicated iron ore routes to be
upgraded/constructed.
Work on Eastern freight corridor from Ludhiana to
Dankuni (Kolkata) and Western freight corridor
from Delhi to JNPT to start in 2008-09.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Initiatives
Procurement of Rolling Stock: All time high
of 20,000 wagons, 250 diesel and 220
electric locomotives to be manufactured.
New Wagon Leasing Policy and Wagon
Investment Scheme formulated to increase
availability of wagons in the system.
Discounts for development of bulk and nonbulk goods terminals.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Safety & Security
Multi-pronged scheme to strengthen railway safety through various
automatic devices like anti-collision device etc.
Rail accidents have reduced remarkably despite substantial increase
in gross traffic volumes.
Fire resistant material to be used in coaches.
Unmanned level crossings at busy sections to be manned on a fast
track basis.
Integrated security plan drawn up through installation of CCTVs, metal
detectors etc.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Welfare Measures
Social Welfare
99% backlog vacancies for SCs/STs filled up in special campaign launched
since 2004.
Appointment of candidates from SCs/STs/OBCs exceeded their respective
quotas inGroup D appointments.
Minorities welfare cells to be opened at Railway Board and Zonal Railways.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Welfare Measures
Social Welfare
One time exercise of appointing Railway Porters as gangmen and
to other Group D posts.
Mother-Child Health Express to be run on a pilot basis at
concessional fares in collaboration with Rajiv Gandhi Foundation
for providing medical facilities to mother and child.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Staff Welfare
Per-capita contribution to Staff Benefit Fund to be increased by ten
times from Rs.35 to Rs.350 for 2008-09.
Northern Railway Central Hospital at Delhi to be made centrally airconditioned.
Two divisional hospitals at Jaipur and Hubli to be upgraded to central
hospitals.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Staff Welfare
A new divisional hospital at Ranchi and an OPD block at
Integral Coach Factory to be constructed.
Employees who joined Railways from other
agencies/PSUs etc and are eligible for pensionary
benefits, would now be eligible for post retirement
complimentary passes as per the norms being set.
Way Forward for Indian Railways..
Vision 2025
Public-Private Partnership schemes to be launched for
attracting an investment of Rs.1,00,000 cr over the next
five years for developing world class stations, rolling stock
ad other logistics.
Commercial use of Railway land by Rail Land Development
Authority to give a boost to Railway Revenues.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Monopoly - Indian RailwaysDokument52 SeitenMonopoly - Indian RailwaysBinit GadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Railways at The Crossroads: Presentation by Group - 2 Mba - HRDokument14 SeitenIndian Railways at The Crossroads: Presentation by Group - 2 Mba - HRAditya KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Railways MacroeconomicsDokument28 SeitenIndian Railways MacroeconomicsVarun AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly of Indian RailwaysDokument52 SeitenMonopoly of Indian Railwayslostanand62% (21)
- Monopoly Case Study - Indian Railways and Its PerformanceDokument2 SeitenMonopoly Case Study - Indian Railways and Its PerformanceBivek BasumataryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly of Indian RailwayDokument16 SeitenMonopoly of Indian RailwayNawnit Kumar67% (3)
- 19 - InvBotDL - Adani Group Presentation Dec 14 - VFDokument23 Seiten19 - InvBotDL - Adani Group Presentation Dec 14 - VFSUKHSAGAR1969Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian RailwaysDokument12 SeitenIndian RailwaysZoya Siddiqui50% (2)
- Marginal Pricing of Indian RailwayDokument16 SeitenMarginal Pricing of Indian RailwayShobhan MeherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amonopoly Is An Enterprise That Is The Only Seller of A Good or ServiceDokument4 SeitenAmonopoly Is An Enterprise That Is The Only Seller of A Good or ServiceFarhat Abbas DurraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVR Swot AnalysisDokument3 SeitenPVR Swot AnalysisRishabh KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kapferer Model Brand Identity Prism 1228214291948754 9Dokument31 SeitenKapferer Model Brand Identity Prism 1228214291948754 9Saquib AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On MonopolyDokument6 SeitenCase Study On Monopolymiraadil0071% (14)
- 1306170498important Model Question Papers For Mba 1st SemisterDokument4 Seiten1306170498important Model Question Papers For Mba 1st SemisterraajsamalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Kolkata PortDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To The Kolkata PortgitmlifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3 - Consumer Behaviour - Dhonuk Case StudyDokument3 SeitenGroup 3 - Consumer Behaviour - Dhonuk Case StudyUshaman Sarkar100% (1)
- Exploring Consumer Perception About Premium Watches in The Indian ContextDokument8 SeitenExploring Consumer Perception About Premium Watches in The Indian ContextYuktarth NagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Project Report On Haldiram SDokument64 SeitenMarketing Project Report On Haldiram SDhruv Dang100% (1)
- Ghari - From No One To No.1Dokument32 SeitenGhari - From No One To No.1Dr Amit Rangnekar100% (3)
- Strategic Market Segmentation: Prepared By: Ma. Anna Corina G. Kagaoan Instructor College of Business and AccountancyDokument33 SeitenStrategic Market Segmentation: Prepared By: Ma. Anna Corina G. Kagaoan Instructor College of Business and AccountancyAhsan ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Research Question AresDokument4 SeitenMarket Research Question Aressaurabh242000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Influencing Market and Entry Mode SelectionDokument11 SeitenFactors Influencing Market and Entry Mode SelectionAndres Felipe FigueredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management 1 Case Study On Indian RailwaysDokument19 SeitenStrategic Management 1 Case Study On Indian RailwaysGaurav ModiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic AlliancesDokument23 SeitenStrategic AlliancesViraj DhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer Imagery: by Anagha DasDokument36 SeitenConsumer Imagery: by Anagha DasMariya RESHMI T.JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forms of Market PDFDokument32 SeitenForms of Market PDFADITYA BANSALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic Management Project On Tata SteelDokument18 SeitenStrategic Management Project On Tata SteelRonak GosaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- People, Service, and Profit At: Jyske BankDokument12 SeitenPeople, Service, and Profit At: Jyske BankArushiRajvanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group2 NAM SensoryBranding PaperBoatdocxDokument12 SeitenGroup2 NAM SensoryBranding PaperBoatdocxJuhi Gahlot SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Consumer Perception Towards Multiplex Theatre - With Special Reference To Coimbatore CityDokument4 SeitenA Study On Consumer Perception Towards Multiplex Theatre - With Special Reference To Coimbatore Cityabhishek jamwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report 2 TatasteelDokument2 SeitenProject Report 2 TatasteelOperation KoldamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modes of TransportationDokument8 SeitenModes of Transportationshashi singh100% (1)
- Jio PriocingDokument4 SeitenJio PriocingNarinder SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNCs Are They DevilsDokument26 SeitenMNCs Are They DevilsMekhla MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1906 Heet General Management Project ReportDokument65 SeitenM1906 Heet General Management Project ReportSatish WagholeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liberalisation, Privatisation and GlobalisationDokument15 SeitenLiberalisation, Privatisation and GlobalisationShruti KurupNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Production: A Decade of Transformation AheadDokument60 SeitenInternational Production: A Decade of Transformation AheadSunil ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1) - Introduction: A) - Introduction of The Automobile IndustryDokument12 Seiten1) - Introduction: A) - Introduction of The Automobile IndustryRohit AswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDP, GNP, SavDokument108 SeitenGDP, GNP, SavAshish ParidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 009 103 209 Cold-Chain-LogisticsDokument29 Seiten009 103 209 Cold-Chain-Logisticsshebin_abdsajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio Revision 16Dokument9 SeitenPortfolio Revision 16ramunagatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GUCCIDokument21 SeitenGUCCIvictor xauNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Tyre Market Forecast and Opportunities, 2017 - SampleDokument10 SeitenIndia Tyre Market Forecast and Opportunities, 2017 - SampleTechSciResearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindustan UnileverDokument34 SeitenHindustan UnileverBindu VeerabhadrappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Sudarshana Bhat Asst General Manager Corporation Bank: Exchange Rate MechanismDokument42 SeitenBy Sudarshana Bhat Asst General Manager Corporation Bank: Exchange Rate MechanismUmesh ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 CTDokument19 SeitenCh2 CThiteshgbhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Boat Case StudyDokument9 SeitenPaper Boat Case StudyManoj RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reliance Fresh Channel DesignDokument6 SeitenReliance Fresh Channel Designvishalsoni2933% (3)
- JK Tyre Sales Promotion (Repaired)Dokument42 SeitenJK Tyre Sales Promotion (Repaired)VinodDubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindustan Lever'S Project: Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Rural ConsumerDokument27 SeitenHindustan Lever'S Project: Shakti - Marketing FMCG To The Rural ConsumerShamoeel Khan100% (1)
- 14 Monopolistic CompetitionDokument37 Seiten14 Monopolistic CompetitionSIDDHANT KATARIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction Towards Cab Service Providers in CoimbatoreDokument4 SeitenService Quality and Customer Satisfaction Towards Cab Service Providers in CoimbatoreInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1402754455 - 17018 - 5 - 2020 - MKT201 Ca3Dokument2 SeitenA1402754455 - 17018 - 5 - 2020 - MKT201 Ca3Shubham Saurav SSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Konkan RailwaysDokument11 SeitenKonkan RailwaysSandeshChandrashekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- McDonalds Food Supply Chain PDFDokument7 SeitenMcDonalds Food Supply Chain PDFabishek reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arshiya International LTDDokument21 SeitenArshiya International LTDBharathi RajaramanNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Marketing StrategyDokument37 SeitenInternational Marketing StrategyAkanksha SonkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monopoly - Indian Railways: - Anand Dube - Darshna Chande - Karan Sobti - Sriaditya Kasula - Vinay ChaudhariDokument52 SeitenMonopoly - Indian Railways: - Anand Dube - Darshna Chande - Karan Sobti - Sriaditya Kasula - Vinay ChaudhariKristamRajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway SystemDokument23 SeitenRailway SystemtusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noble - Indian RailwaysDokument16 SeitenNoble - Indian Railwaysnoble_josephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrtu & PulpDokument23 SeitenMrtu & Pulpvrj109150% (2)
- Conditions & Warranties: Doctrine of Caveat EmptorDokument22 SeitenConditions & Warranties: Doctrine of Caveat Emptorvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Useful Charts For Tax ComplianceDokument24 Seiten21 Useful Charts For Tax Compliancevrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resort Hotel Ski Lodge Business PlanDokument26 SeitenResort Hotel Ski Lodge Business Planvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- InductionMOVIENAME 1435746779809Dokument24 SeitenInductionMOVIENAME 1435746779809vrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Induction Games - Bba (Ca)Dokument25 SeitenInduction Games - Bba (Ca)vrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Penalties Chart For Companies Act 2013 CA FinalDokument7 SeitenPenalties Chart For Companies Act 2013 CA Finalvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Paper On The Role of Fdi inDokument13 SeitenResearch Paper On The Role of Fdi invrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning:-: Ntroduction of ArketingDokument10 SeitenMeaning:-: Ntroduction of Arketingvrj1091100% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Instant Platter Very Nice ReceipesDokument2 SeitenInstant Platter Very Nice Receipesvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Encana FinalDokument15 SeitenEncana FinalSushant Rajputra100% (3)
- Jones Income StatementDokument4 SeitenJones Income Statementvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communications All Case StudiesDokument12 SeitenCommunications All Case Studiesvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jennifer Gaston HRMDokument9 SeitenJennifer Gaston HRMvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- TestbankDokument33 SeitenTestbankBhavneet Sachdeva100% (2)
- DVR Ritevision 16v 4a RV9016ZADokument2 SeitenDVR Ritevision 16v 4a RV9016ZAvrj1091Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haborco Teaching GuideDokument14 SeitenHaborco Teaching Guidevrj1091100% (2)
- RESPOD To A DISTRESS SIGNAL at SEA-1Dokument4 SeitenRESPOD To A DISTRESS SIGNAL at SEA-1octavian ekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd PU English Model QP 4 PDFDokument8 Seiten2nd PU English Model QP 4 PDFPrasad C M100% (8)
- The General Directory and Guide Book 1886Dokument575 SeitenThe General Directory and Guide Book 1886kwik tempoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CITIMAXDokument2 SeitenCITIMAXAgustin FinciNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 AutoDokument6 Seiten07 Auto2791957Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Design Loads On Bridges - Highway & Rail Bridge - Miscellaneous LoadsDokument3 Seiten10 Design Loads On Bridges - Highway & Rail Bridge - Miscellaneous LoadsfaridullahNoch keine Bewertungen
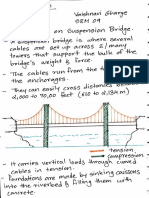
- TOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9Dokument3 SeitenTOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9VAISHNAVI GHARGENoch keine Bewertungen
- FH12 6x2 Tractor Rear Air Susp. - Volvo Truck CorporationDokument2 SeitenFH12 6x2 Tractor Rear Air Susp. - Volvo Truck Corporationeantphone kyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- ItineraryDokument5 SeitenItineraryKajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021Dokument21 SeitenTRIP Moving South Carolina Forward Report September 2021WMBF NewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome Aboard Kingfisher AirlinesDokument4 SeitenWelcome Aboard Kingfisher AirlinesAakriti WatalNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTSB Preliminary Report On NASCAR Plane Crash in Sanford, FLDokument5 SeitenNTSB Preliminary Report On NASCAR Plane Crash in Sanford, FLdaytonapost.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts Manual NDR 030 AE, NR 035 AE, NR 040 AE, NR 045 AE (C815) NS 040 AF, NS 050 AF (C816)Dokument232 SeitenParts Manual NDR 030 AE, NR 035 AE, NR 040 AE, NR 045 AE (C815) NS 040 AF, NS 050 AF (C816)Erisson100% (5)
- Reinforced Concrete Bridges PDFDokument93 SeitenReinforced Concrete Bridges PDFAlin SalageanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawworks MaintenanceOK enDokument46 SeitenDrawworks MaintenanceOK envichusega_809319337100% (1)
- Fiches 1 Et 2 Comprehension Orale Traveling-1Dokument2 SeitenFiches 1 Et 2 Comprehension Orale Traveling-1annemenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGU Annual Report 2019 - 23 Loresfinal PDFDokument66 SeitenIGU Annual Report 2019 - 23 Loresfinal PDFLong Nguyễn HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- SB1012 Fresh Air Duct Sutrak AC 35 Rooftop UnitDokument6 SeitenSB1012 Fresh Air Duct Sutrak AC 35 Rooftop UnittchernserNoch keine Bewertungen
- River Based Creative EconomyDokument52 SeitenRiver Based Creative EconomyS DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afghanistan Constructionpres PDFDokument10 SeitenAfghanistan Constructionpres PDFAsif Iqbal DawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Act 1 1 1historycivilengineeringarchitecureDokument3 SeitenAct 1 1 1historycivilengineeringarchitecureapi-247437088Noch keine Bewertungen
- Econ - Article1Dokument3 SeitenEcon - Article1Nicah AcojonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flying FordDokument24 SeitenFlying Fordanupam singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caab Atpl Requirement PamphletDokument5 SeitenCaab Atpl Requirement PamphletblessedbuddhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Satisfaction Level of Maruti Four Wheeler"Dokument54 SeitenCustomer Satisfaction Level of Maruti Four Wheeler"sumesh894100% (4)
- Hyundai Manual de Taller Hyundai h100Dokument124 SeitenHyundai Manual de Taller Hyundai h100Gustavo Carvajal Contreras100% (7)
- Environment and EcologyDokument36 SeitenEnvironment and EcologyNikhil RastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-5 GSKDokument13 SeitenCh-5 GSKDeepu RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHE ChecklistDokument7 SeitenMHE ChecklistJesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automated Toll Gate System Using Rfid and Arduino: Research PaperDokument5 SeitenAutomated Toll Gate System Using Rfid and Arduino: Research PaperKarthik DmNoch keine Bewertungen