Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Module 3 L&D
Hochgeladen von
Ganesh Kumar. ROriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Module 3 L&D
Hochgeladen von
Ganesh Kumar. RCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
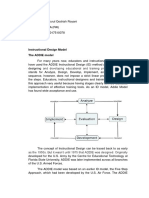
Design and Development
Modul
e
Design and Development
Design and Development
Design is a planning activity which
in the context of training, refers to
the framework for analyzing a
training problem, defining the
intended outcome, determining how
to present the content to learners to
achieve
those
outcomes,
developing the training course
according
to
the
design,
implementing
the
course,
evaluating its effectiveness and
devising follow-up activities.
Training Process
Step 1
Identify the Needs
Step 4
Evaluate the
Training
Step 2
Design the
Training
Step 3
Implement the
Training
Cont.
Design and Development
(1) What materials will be
required to implement the
programme in a particular
way,
Organizational
strategies and needs
(2) what media will be
used and
(3)
what
specialized
expertise will be required
for implementation of this
design (Warren, 1969).
Knowledge, skills and
attitudes required for
the job
Training
Context
Environmental
compliance and
competition
Context of training design
Existing knowledge,
skills and attitudes of
the employee
Design and Development
Principles of training design
Gane has suggested six principles of training design as under:
1. The objectives should be expressed in performance terms as far as
possible.
2. Learners should respond pro-actively to the material in a way that is
relevant to the training purpose.
3. Learners should receive immediate and unambiguous feedback as to how
correct their responses are.
4. Training systems must be validated and then modified if they do not
achieve the intended objectives.
5.
Training system must adapt to the individual needs of the trainees.
6. Learners must be involved by having the material expressed in a way
which they see as directly relevant to their interest and needs.
Cont.
Design and Development
Nilson (1992) has suggested 10 guidelines for designing training
programmes which are as under:
1. Spend a lot of time identifying the target audience (trainees) for this
particular training.
2. Think of those trainees as customers and know what they expect regarding
quality and suitability.
3. Break the design and development process into activities with beginnings
and ends.
4. Hold a design review of each product.
5. Identify errors and eliminate them.
6. Build broad ownership by involving stakeholders.
7. Define objectives for learners not trainers.
8. Remember the business reasons, why you are designing this course.
9. Let people know that this course is tied into the life and breadth of your
company.
10. Ask for feedback during design activities and incorporate the suitable
suggestions.
Cont.
Design and Development
Similarly, Abella (1986) has suggested some steps for design and
development process as under:
1. Gather information on training needs to precisely pinpoint the areas to be
addressed.
2. Prepare programme specification document and have it approved by the
HRD head. This will contain background of the programme, description of
the people to be trained, programme objectives, programme requirements
and constraints.
3. Conduct the design meeting with the stakeholders and experts to obtain
their inputs and involvement.
4.
Prepare the design document, which contains the overall structure,
individual units, methodologies, duration, learning conditions and possible
outcome.
5. Gather information on programme materials.
6. Write/develop the materials at the development stage.
7. Test the material for validity.
Cont.
8. Hold the pilot programme to see the outcome.
Design and Development
Analyzing the general characteristics of trainees for designing training programme
Name of the programme
Objective of the programme
Duration
Physical feature of trainees (like eyesight, hearing
impairment, physical strength)
Health conditions
Language preference
Gender
Age
Do trainees have any limitation or special needs to be
considered?
Previous work experience
Education qualification
Position in the organizational hierarchy
Learning styles
Personality types
Any other characteristics
Cont.
Trainee characteristics and training design
Design and Development
Issues for consideration
Available
Required
Time
Money
Expertise
Infrastructure facilities
Trainee characteristics
Objectives of the programme
Instructional activities to be
included
Methodologies to be us
ed
Likely obstacles and limitations
Contingency plans to be kept
ready
Safety aspects to be taken into
account
Inconvenience to daily operations/
customers
Strategies to overcome the
inconvenience
Barriers to transfer of learning
Strategies
barriers.
to overcome such
Generic issues to be considered for training design
Strategy to fill the
gap
Design and Development
Motivational Dynamics
Most trainees go through three phases of motivation as under:
1. Initial stage: At this stage, the trainee is a novice. Here, the trainees
primary learning goal is getting started and learning enough material to
proficiently handle the routine tasks. Trainees only need how-to do
instructions and supervision at this point. Do not overburden trainees with
too much content or overwhelm them with unnecessary choices.
2. Intermediate stage: Learners have mastered routine tasks and gained
confidence. Now they want to learn how to handle routine tasks more
efficiently and how to handle some less common tasks. Learners still want
instructions at this point, but some do not want supervision or practice.
3. Matured stage: At this stage, the learning attains a kind of maturity and
trainees feel humble to be learned people. This is a realization stage and
most trainees are aware of the limits of their capabilities.
Cont.
Design and Development
Some kinds of learning can occur at individual level, little more at the level of
dyads and groups and rest at the organizational level.
Dyads
Groups
Organizational
Learning Pyramid
Design and Development
Training design process
Write down the
training design
Identify goals
and objectives
Determine
training content
Identify follow
up activities
Decide
training
methodologies
Define
evaluation
criteria
Identify learning
activities
Design and Development
Identifying the training objective
A decision is required to be made on the learning objectives to match job
performance, job conditions and job standards (Roscoe, 1995).
Objectives should be set out from the learners perspective; they should
be specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and timebound
(Agochia,2002.p.95).
For example, the objective for a car driving training programme could
be; the trainees after successful completion of the programme:
should be able to drive any motor car on city or countryside roads;
during any time of the day or night;
safely in accordance with law, without causing injuries to others or to
themselves and
without causing damage to the vehicle or to any other property.
Design and Development
Determine the structure
Always keep in mind the training structure right from the design stage. In this
connection Gane (1972) has suggested the following measures:
1. Arrange the activities/concepts in the sequence of logical dependence. If
there is no/little logical dependence, then organize them in the order of easy
to difficult sequence.
2. Determine the training structure.
3.
Determine how much and which of the theoretical aspects are to be
incorporated into the course.
4. Determine the performance outcome expected on the successful completion
of each module.
5. Assess and estimate time requirements for successful completion of each
topic/level/ module.
6. Identify appropriate methodologies to be used for each of the topic.
7. Assemble all the information into a coherent plan which can be understood
Cont.
by trainers, trainees and organizers.
Design and Development
There are basically three kinds of training structures. They are linear, spiral and
modular. A linear structure is one in which the lessons are arranged logically
one after the other from beginning to conclusion or from simple to complex. Table
shows the linear training structure.
Linear training structure
Sl.No.
1
2
3
4
5
Topics to be covered
Introduction to training design
Objectives
Scope
Limitation
Conclusion
Cont.
Design and Development
A spiral structure is the one in which easier topics of all the interrelated subjects
are taught first, then to the next level of all interrelated subjects and then to the
final level and so on. Figure shows the spiral training structure.
Spiral training structure
Level 4
Level 3
Level 2
Level 1
Cont.
Design and Development
A modular structure is one in which a programme is divided into small
independent units with clear-cut beginning and ending. This helps the learner to
begin at any module any time without having to complete the initial modules
since they are independent from one another. Table 4 shows the modular training
structure.
Modular training structure
Module 1
Module 6
Module 11
Module 2
Module 7
Module 12
Module 3
Module 8
Module 13
Module 4
Module 9
Module 14
Module 5
Module 10
Module 15
Design and Development
Models of training design
There are various ways of building a training design. But the two important
among them are open model and closed model.
1. Open model is one which recognises that outside factors exist which can
have an impact on the design process. An open model is a working hypothesis. It
provides the designer with possible courses of action and anticipation of
outcomes.
Unstructured or open skills do not inherently have a single most way of
performance. Neither they can be taught exactly the way they have to be
practiced nor they can be practiced exactly the way they are taught.
Cont.
Design and Development
Worker level -----Managerial level
The closed model or structured model is based on the assumption that all inputs
can be identified. Closed models endeavour to build all the possible variables
into the model. When using a closed model, the designer is being assured that
the conclusions and outcomes are predetermined.
Mixed use of structured and unstructured
skills
More use of structured skills
More use of unstructured skills
Mixed use of structured and unstructured
skills
Nature of work
and skill types
Back office ----------Frontline
Closed models are also known as structured models. Structured skills are those
which have got a single most way of efficient performance all the time.
Design and Development
Selecting training methods
Appropriateness of the methodology is based on several factors like current level
of expertise; nature of learning outcome expected or course objective, time
available and required, trainee characteristics, infrastructure and expertise
available, funds available and estimated investment on training and so on.
Cont.
Design and Development
Training approaches and Learning contexts
Training
method
On the
job
methods
Advantages
Off the
job
methods
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
Disadvantages
Appropriate for and
when
Transfer of learning to
work is easier.
Less expensive.
Illiterates or
handicapped can also
learn.
Individualized attention.
Mandays at work are
not lost.
Instant evaluat ion
Risk of safety, quality, and
customer service.
No uniformity of learning.
Time consuming
Benefit of experts is
minimal
Disturbances and
distractions while learning.
Minimum use of learning
aids.
More trainees and fewer
trainers.
Learn by interaction with
group members.
Multiple learning aids
and approaches.
Experts can be invited.
Distracti ons can be
controlled.
Non-threatening
environment.
Time bound.
No risk of safety, quality
and productivity.
Expensive
Transfer of learning is
difficult.
Loss of mandays.
Evaluation difficult
Not ideal for skill focused
outcomes.
Learning practical
skills.
Minimizing training
cost.
Enhancing transfer of
learning.
Easier evaluation.
Training illiterates
and handicapped.
Generic and
knowledge f ocused
outcomes.
Larger trainee
groups.
Time bound
outcomes.
Few trainers and
many trainees.
Avoiding work place
distractions.
Trainees want safe
and non -threatening
environment.
Cont.
Design and Development
Self
paced
training
Anytime anywhere
learning.
No loss of mandays.
Less expensive.
Can be on the job or off
the job.
Can be full-time or parttime.
Manual or
computerized.
Learner-controlled.
Cost of training per
head is minimum
Control and monitoring is
difficult.
Development cost is high.
Not having an expert for
instant advice.
Learning by interacting with
cannot be fixed for
all.
group of trainees is not
Common timetable
possible.
Finding time to learn may
be difficult.
Requires high degree of
self motivation.
Trainee must be capable of
learning correctly by self
study independently.
Not ideal for illiterates and
the handicapped.
Not ideal for novice.
Mandays cannot be
wasted.
Trainees are high on
self monitoring.
Trainees are capable
of learning on their
own.
Trainees are literates
and able bodied.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Dennis Tan Caballed Beed Iv: Instructional DesignersDokument6 SeitenDennis Tan Caballed Beed Iv: Instructional DesignersDennis Tan CaballesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ADDIE Model Why Use ItDokument4 SeitenThe ADDIE Model Why Use ItMuhammad Arif IzzudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Addie Model - Article ReviewDokument7 SeitenThe Addie Model - Article ReviewMuhd Hafiz B Bidi100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - The ADDIE ModelDokument4 SeitenLesson 1 - The ADDIE ModelJustine Jerk BadanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar 1A - Topics (Module 1)Dokument19 SeitenSeminar 1A - Topics (Module 1)Khy Renz BajajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument14 SeitenUnit 2Raveena SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument31 SeitenAddie Modelshazlinazanudin100% (1)
- The ADDIE Instructional Design Model: A Structured Training MethodologyDokument7 SeitenThe ADDIE Instructional Design Model: A Structured Training MethodologyJessica ObertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContentDokument12 SeitenContentjeyabairaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie Model of Instructional DesignDokument8 SeitenAddie Model of Instructional Designfariez79Noch keine Bewertungen
- The ADDIE ModelDokument14 SeitenThe ADDIE ModelPaul De Las Alas100% (1)
- The ADDIE Instructional Design ModelDokument8 SeitenThe ADDIE Instructional Design Modelflorence.beraud4348100% (4)
- Design of A Training Program CorrectDokument13 SeitenDesign of A Training Program CorrectJusy Bingura100% (1)
- ADDIE ModelDokument12 SeitenADDIE ModelMel Bautista DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument11 SeitenAddie ModelPanis RyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Level 5 Project Management FinalDokument8 SeitenLevel 5 Project Management FinalDr Kerry GoughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructional Design Model The ADDIE ModelDokument8 SeitenInstructional Design Model The ADDIE ModelUyungndutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cia3 HRMDokument18 SeitenCia3 HRMPriyanshu ChhabariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument6 SeitenAddie ModelIrene Balane AranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADDIE Model: Instructional DesignDokument10 SeitenADDIE Model: Instructional DesignJames ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwi Pradnyani (ADDIE MODEL)Dokument2 SeitenDwi Pradnyani (ADDIE MODEL)Dwi PradnyaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie Model LABONIDokument4 SeitenAddie Model LABONILaboni patraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Course DevelopmentDokument18 Seiten8 Course DevelopmentNhial AbednegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- INFS2605 S2 2015 Course Outline - v1.5Dokument11 SeitenINFS2605 S2 2015 Course Outline - v1.5mounica_veraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramDokument12 SeitenADDIE Instructional Design Certificate ProgramJoeManikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business GuideDokument37 SeitenBusiness Guidevivi_15o689_11272315Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course Design and DevelopmentDokument18 SeitenCourse Design and Developmentsharareh2010100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Designing Training ProgramDokument40 SeitenChapter 15 Designing Training Programanik mostafa100% (1)
- Training With Focus On Training DesignDokument55 SeitenTraining With Focus On Training Designswetha23rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument48 SeitenAddie Modelmarkespino100% (3)
- Model Addie 5Dokument7 SeitenModel Addie 5Egan-Ash ArijenanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soalan 1 Abu Ubaidah Amir Bin Abdul Aziz (2021.2.edu02.0002) April 2021 0187029086Dokument13 SeitenSoalan 1 Abu Ubaidah Amir Bin Abdul Aziz (2021.2.edu02.0002) April 2021 0187029086Abu UbaidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Comprehensive Training PlanDokument26 SeitenStandard Comprehensive Training PlanAlicia PearlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training & DevelopmentDokument22 SeitenTraining & DevelopmentJannatul JerinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eco 448 Economic Planning IIDokument135 SeitenEco 448 Economic Planning IIprincessprecious013Noch keine Bewertungen
- ADDIEDokument3 SeitenADDIEつづ くNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of TrainingDokument18 SeitenHandbook of Trainingkalyani_iyer63504Noch keine Bewertungen
- Training Delivery and EvaluationDokument7 SeitenTraining Delivery and EvaluationRoman PanditNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESP. GROUP 4. ADDIE Model For Instructional DesignDokument15 SeitenESP. GROUP 4. ADDIE Model For Instructional DesignSyf IsmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Employee Training and DevelopmentDokument14 SeitenI. Employee Training and DevelopmentCLAUDIA RIVERA GARCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- ADDIE MODEL - Instructional Design ModelDokument9 SeitenADDIE MODEL - Instructional Design ModelEnz OgnillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Training and Development Programs: Using The ADDIE MethodDokument5 SeitenCreating Training and Development Programs: Using The ADDIE MethodYayan NadzriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Techniques and MethodologiesDokument32 SeitenTraining Techniques and MethodologiesAlmario SagunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing WorkshopsDokument82 SeitenDesigning WorkshopsGucciGrumps100% (1)
- AddieModel VoicenotesDokument45 SeitenAddieModel VoicenotesJunel Lapinid100% (1)
- 4 AsDokument6 Seiten4 AsWeljunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online ReferencesDokument13 SeitenOnline ReferencesHarvey AlapadNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Instructional Design Models?: Branch and MerrillDokument4 SeitenWhat Are Instructional Design Models?: Branch and MerrillarastuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arredondo FinalDokument10 SeitenArredondo Finalapi-269601467Noch keine Bewertungen
- Training and DDokument8 SeitenTraining and DAkshay BadheNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Training DesignDokument6 SeitenWhat Is A Training DesignSai Krishna67% (3)
- 5 Elements of ISDDokument9 Seiten5 Elements of ISDHari MudzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Manual Tle 7-8Dokument11 SeitenSubject Manual Tle 7-8Rhayan Dela Cruz DaquizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uw Stout Instructional Design Program OverviewDokument4 SeitenUw Stout Instructional Design Program Overviewapi-309468587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument2 SeitenAddie ModelPutra AftusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addie ModelDokument5 SeitenAddie Modelmansor201250% (4)
- Subject Manual Tle 9-10Dokument12 SeitenSubject Manual Tle 9-10Rhayan Dela Cruz DaquizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.4 Designing A Training Program - Human Resource ManagementDokument21 Seiten8.4 Designing A Training Program - Human Resource Managementkumarsaurabhverma100% (1)
- MKTG 392-Brand Management-Sarah Suneel SarfrazDokument8 SeitenMKTG 392-Brand Management-Sarah Suneel SarfrazAbdullahIsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Scholarship Rates in AICTE Supported QIP Centers (W.e.f. Academic Session 2016-17)Dokument1 SeiteRevised Scholarship Rates in AICTE Supported QIP Centers (W.e.f. Academic Session 2016-17)Ganesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCMDokument3 SeitenSCMGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012: (CHEP) (IAP) (MA) (PHY)Dokument4 SeitenIndian Institute of Science Bangalore 560012: (CHEP) (IAP) (MA) (PHY)Ganesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOI 2019 FinalDokument253 SeitenSOI 2019 FinalGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Marketing Channels and Supply Chains: HapterDokument20 SeitenManaging Marketing Channels and Supply Chains: HapterGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2 Training Need AnalysisDokument36 SeitenMODULE 2 Training Need AnalysisGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrialpolicy From 1948-1991Dokument33 SeitenIndustrialpolicy From 1948-1991Ganesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi-View Video: Get Ready For Next-Generation Television: From The Editor: Distributed Multimedia CommunityDokument6 SeitenMulti-View Video: Get Ready For Next-Generation Television: From The Editor: Distributed Multimedia CommunityGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amma's CanteenDokument17 SeitenAmma's CanteenGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Market SegmentationDokument13 SeitenRetail Market SegmentationGanesh Kumar. RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Planning For All Learners Applying Universal Design For Learning UDL To A High School Reading Comprehension ProgramDokument11 SeitenCurriculum Planning For All Learners Applying Universal Design For Learning UDL To A High School Reading Comprehension ProgramFabiana PiokerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Speech DeliveryDokument27 SeitenTypes of Speech Deliverykevin kovhgNoch keine Bewertungen
- K 2 Unit2 SitesilikeDokument8 SeitenK 2 Unit2 Sitesilikeapi-288620311Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rationale/Reflection of Previous Practice: During Last SemesterDokument4 SeitenRationale/Reflection of Previous Practice: During Last Semesterapi-317358702Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edu 208 Reflection 3Dokument2 SeitenEdu 208 Reflection 3api-302040928Noch keine Bewertungen
- CI 402 Class Simulation MLK Lesson PlanDokument2 SeitenCI 402 Class Simulation MLK Lesson Plankklemm89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final PPT ANNDokument30 SeitenFinal PPT ANNWishal NandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Internship Observation #1Dokument3 SeitenTeaching Internship Observation #1api-342045486Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing EducationDokument18 SeitenNursing EducationMakhanVermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment ReportDokument1 SeiteAccomplishment ReportCathyren Capizonda Teves94% (16)
- Mary Manning ResumeDokument4 SeitenMary Manning Resumeapi-291339548Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Should Be Observe in Making and Use of Scoring RubricsDokument23 SeitenWhat Should Be Observe in Making and Use of Scoring RubricsCezLuzarraga100% (2)
- Text PreviewingDokument2 SeitenText Previewingyehezkil sitorusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talk2Me Video: Before WatchingDokument1 SeiteTalk2Me Video: Before Watchinglolita digiacomo0% (1)
- Test of English Communication Skills For Graduating StudentsDokument5 SeitenTest of English Communication Skills For Graduating StudentsPohhui Lam100% (2)
- Fall 2015 I2 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenFall 2015 I2 Syllabusapi-285916855Noch keine Bewertungen
- Action Plan in Mathematics SY 2019-2020: Prepared By: Approved byDokument2 SeitenAction Plan in Mathematics SY 2019-2020: Prepared By: Approved byAldrin Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- IntegersDokument4 SeitenIntegersmcdahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hofstedes Cultural Dimensions in The Educational RomaniaDokument9 SeitenHofstedes Cultural Dimensions in The Educational RomaniaDoinita MusteataNoch keine Bewertungen
- ID Deskripsi Kesalahan Struktur Berpikir Si PDFDokument10 SeitenID Deskripsi Kesalahan Struktur Berpikir Si PDFJulita WindayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test4 Answer Key PDFDokument1 SeiteTest4 Answer Key PDFTamer SaiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Making Tag Strategy LessonDokument13 SeitenDecision Making Tag Strategy Lessonapi-281411240Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Intercultural Communicative Competence in FL Education - A Survey On EFL Teachers' Perception and Practice in ChinaDokument21 SeitenAssessment of Intercultural Communicative Competence in FL Education - A Survey On EFL Teachers' Perception and Practice in ChinaMarjorie TovarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training and Development Program Design & Proposal: In-Service Training For Teachers 2020Dokument5 SeitenTraining and Development Program Design & Proposal: In-Service Training For Teachers 2020Precious Idiosolo100% (1)
- Internal Auditing: Assurance and Advisory Services.3Dokument10 SeitenInternal Auditing: Assurance and Advisory Services.3Alex ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooperative Learning Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenCooperative Learning Lesson Planapi-528696912Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arnis' Thesis Complete Chapters 1-5Dokument52 SeitenArnis' Thesis Complete Chapters 1-5Deyeck Verga67% (3)
- DLL Abegail C. Estacio EditedDokument80 SeitenDLL Abegail C. Estacio EditedAbegail Castaneda EstacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Method: Cumulative Frequency Distribution: Differentiate An Ungrouped Data From Grouped DataDokument4 SeitenResearch Method: Cumulative Frequency Distribution: Differentiate An Ungrouped Data From Grouped DataAilyn Guibao MamacNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 12 Roles and Competencies of School Heads3Dokument15 SeitenCHAPTER 12 Roles and Competencies of School Heads3mnbv vbnm60% (5)