Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jcby1101 Tutorial5 2013
Hochgeladen von
ana_06_9Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jcby1101 Tutorial5 2013
Hochgeladen von
ana_06_9Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
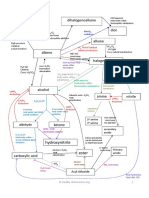
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Tutorial for module BY1101:
Chromatography
Joe Colgan (tcolgan@tcd.ie)
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Tutorial objectives
Describe chromatography
Describe the different types and why
they were used in the BY1101
practicals
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Column chromatography
What is chromatography?
Column
chromatography
A set of lab techniques to separate mixtures
Mobile phase:
Fluid that houses the mixture to be separated
(e.g. Cell lysate, haemoglobin, mould extract)
Stationary phase:
Structure holding another material that
interacts with and aids in separation of mixture
(e.g. Sepharose, sephadex, DEAE-cellulose)
Mobile
Stationar
y
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Three types of column chromatography
used in the BY1101 practicals. What are
they?
Practical 2
Practical 3
Experiment 1
Practical 3
Experiment 2
Affinity
chromatography
Gel filtration
chromatography
Ion exchange
chromatography
Separates
molecules based
on biological
specificity
Separate molecules
based on size
Separates
molecules based
on charge
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
What do we use affinity chromatography for?
Purpose
Purification and concentration of
biomolecules, such as proteins, on the
basis of their biological specificity
Applications
Purification of antibodies
Purification of enzymes
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
What was the purpose of Practical 2
Experiment One?
Glutathione S-transferase (GST):
Catalyzes conjugations of the substrate
glutathione (GSH)
GST is an enzyme and binds GSH in an
enzyme-substrate complex
Enzyme (E) + Substrate (S) Enzymesubstrate complex
Substrate
GSH
Interaction is dynamic and GST will bind
reversibly
Enzyme
Enzymesubstrate
complex
GST
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
What is the source
of the GST?
Natural source
Recombinant protein
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
What is a recombinant protein?
A protein encoded for by a gene recombinant DNA that has
been cloned into a system that supports its transcription and
translation
l
Transcripti
on
gst gene
mRNA
Translation
Represso
r protein
l= lac
operon
P=
Promoter
O=
Operator
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
How do we get overexpression of a
protein?
Isopropyl-beta-D-thio-galactoside (IPTG):
IPTG binds to the repressor protein and inactivates it
l
gst gene
mRNA
Transcription of
mRNA
l= lac
IPT
operon
Represso
G
P=
r protein
Promoter
Within the present experiment, what
would be the purpose of
O=
adding IPTG to the bacterial
culture?
Operator
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Molecule of interest
Mobile phase
Stationary phase
Escherichia coli
(bacterial) lysate
Sepharose beads
coated with
glutathione
Glutathione Stransferase
Are the proteins present in the cell lysate in their native
(active) state or are they denatured?
Would you expect the proteins present in the lysate to exhibit
their natural biological activity?
Why was it important to keep the cell lysate on ice?
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity
chromatography
Sepharo
Glutathione
se
(GSH)
Cell
lysate
Glutathione Stransferase
(GST)
SepharoseGlutathione
Stationary phase
Mobile phase
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Mobile
Stationa
ry
1. Pour the column
(Sepharose Beads-Stationary
phase)
2. Wash the column
(Phosphate buffered saline)
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
3. Run the column
(E. coli lysate) Contains enzyme of
interest
- GST within lysate binds to
glutathione-sepharose beads
Would
you expect GST to be
complex
Mobile
in fraction one?
Stationa
ry
4.(PBS) Washes the column
- Other bacterial proteins are
washed out of the column leaving
only GST
bound
sepharose
Why
does
GSTtoremain
in the
beads
column after the PBS
washes?
1
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
3. Run the column
(E. coli lysate) Contains enzyme of
interest
- GST within lysate binds to
glutathione-sepharose beads
complex
Mobile
Stationa
ry
4. (PBS) Washes the column
- Other bacterial proteins are
washed out of the column leaving
only GST bound to sepharose
beads
5. (Glutathione) Substrate of enzyme
- High concentration of glutathione
displaces GST from the beads,
out
2 binds
3 to GST
4 and
5 is eluted
6
7 of
the column
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Affinity chromatography
GST binds to
GSH-Sepharose
beads
Free GSH bind
GST and elutes
Non-bound
proteins
removed
Column
is
washed
All proteins in
lysate except
GST
Addition
of free
GSH
Purifie
dGST
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
SDS-PAGE preparation
Precipitation of protein with trichloroacetic acid (TCA)
Pellet the precipitated protein by centrifugation
Dissolve precipitated protein in sodium-dodecyl sulphate
(SDS)
Boil the protein samples
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Gel filtration
chromatography
Practical 3- Experiment One
Purpose
Separation of macromolecules based
on size
Applications
Determination of relative molecular
size
Separation of molecules on the basis
of size
Removal of inorganic ions from
preparation of protein
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Gel filtration
chromatography
Direction of
flow
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Gel filtration chromatography
Practical 3- Molecule of
interest
Haemoglobin
Purple/red colour
Oxygen-depleted
blood
Venous blood
Oxyhaemoglobin
Scarlet/red colour
Oxygen-rich blood
Arterial blood
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Gel filtration chromatography
Practical 3- Molecule of
interest
Haemoglobin
Methaemoglobin
Oxidatio
n
Haemoglobin
Reducti
on
Oxidation: Potassium ferricyanide + Haemoglobin Oxidised haemoglobin
(methaemoglobin)
Reduction: Ferrous sulphate + methaemoglobin Reduced haemoglobin
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Mobile
Stationa
ry
1. Pour the column
(G-25 Sephadex beads-Stationary
phase)
2. Wash the column
(20mM PBS, pH 7)
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
3. Add the reducing agent
(40mM FESO4 + 80mM Na2EDTA)
4. Add methaemoglobin
Mobile
Stationa
ry
Methaemoglobin
Reducing agent
Haemoglobin
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Gel filtration chromatography
Addition of
reducing agent
Addition of
methaemoglobin
Reduction of
methaemoglobin
to haemoglobin
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange
chromatography
Purpose
Separation of molecules on the basis
of charge
Applications
Water softening, purification and
decontamination
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Direction of fow
Ion exchange
chromatography
Separation of molecules on the basis of charge
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Molecules of
interest
Ion exchange
chromatography
Mobile phase
Stationary phase
Aspergillus niger
(fungal) extract
Glucose oxidase
Catalase
DEAE- Cellulose
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange chromatography
Stationary phase:
Diethylaminoethyl (DEAE) cellulose
Positively charged (protonated)
Interacts with negatively charged molecules (anions)
Anion exchanger: Stationary phase is positively charged
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange chromatography
Separation of molecules on the basis of charge
Glucose oxidase:
Oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide
and glucono-1,5-lactone, which hydrolyzes
to gluconic acid
Glucose oxidase (GO) requires cofactor
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
Glucose oxidase
Substrate
Glucose
Glucose + GO:FAD Glucono-1,5-lactone +
GO:FADH2
GO:FADH2 + O2 GO:FAD + H2O2
Enzyme
Enzymesubstrate
complex
Glucose oxidase
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange chromatography
Separation of molecules on the basis of charge
Catalase:
Catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen
peroxide (H2O2) into water (H2O) and
oxygen (O2)
Catalase
2H2O2 2H2O +
O2
Substrate
Enzyme
Hydrogen
peroxide
Catalase
Enzymesubstrate
complex
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Mobile
Stationa
ry
1. Pour the column
(DEAE-Cellulose-Stationary phase)
2. Wash the column
(PBS)
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Mobile
Stationa
ry
3. Run the column
(Mould extract-Aspergillus niger)
4. Wash the column
(Buffer 1- 20mM NaOAc,
5mM
acetic acid)
How do we get our enzymes of
interest out of the column?
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
3. Run the column
(Mould extract-Aspergillus niger)
4. Release the bound molecules
(Buffer 1- 20mM NaOAc,
5mM
acetic acid)
(Buffer 2- 40mM NaOAc, 40mM
acetic acid)
(Buffer
Lowering
pH neutralizes
3-100mM
NaOAc, negative
100mM
charge
on the protein molecules
acetic
acid)
Increase anionic molecules for
competition
Mobile
Stationa
ry
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange
chromatography
Buffer I
20mM sodium
acetate
5mM acetic acid
Buffer II
Buffer III
Buffer II elutes
catalase
Buffer III elutes glucose
oxidase
40mM sodium
acetate
100mM sodium acetate
40mM acetic acid
Catalase
100mM acetic acid
Glucose
oxidase
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Ion exchange chromatography
Add molecules of
varying ionic
charge
Negatively charged
molecules bind to
beads
Addition of
different buffers
changes charge
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Functional assays
In biological studies, what is the role of
control samples?
Catalase
Control
Glucose
Glucose oxidase
Hydroge
n
peroxide
(H2O2)
Control
Glucose
Hydroge
n
peroxide
(H2O2)
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Summary
Chromatography: Used to
separate out mixtures
Affinity
chromatography
Gel filtration
chromatography
Ion exchange
chromatography
Separates
molecules based
on biological
specificity
Separate molecules
based on size
Separates
molecules based
on charge
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
MCQ Advice
Get your lab books up to date (e.g. Tables,
graphs)
If you have problems with the questions ask a
demonstrator (or me)
When it comes to the exam, revise all of the lab
book (including the introductory notes)
Read over lab slides available on the teaching
website
BY1101 Introduction to Molecular and Cellular Biology
Next week
- Developmental biology: Embryology
- Lectures 3, 4 and 5
- Campbell: Chapter 47 (section 47.1)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- DLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyDokument15 SeitenDLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyNiña Angeline PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- 20 Organic Chemistry Synthesis Iedxcel PDFDokument10 Seiten20 Organic Chemistry Synthesis Iedxcel PDFMohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Chemcoat 101 PCDokument3 SeitenChemcoat 101 PCghazanfarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- General Chemistry 1 - Q3 - Module 3 - Week 5 - April 26-April 30 With InstructionDokument22 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 1 - Q3 - Module 3 - Week 5 - April 26-April 30 With InstructionRona Mae BetitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Distributed byDokument2 SeitenMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Distributed byRC VilledaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Organic Chemistry 9th Edition Wade Test BankDokument46 SeitenOrganic Chemistry 9th Edition Wade Test Bankjavierwarrenqswgiefjyn100% (26)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Surface Modification Methods For Improving The Dyeability of Textile FabricsDokument20 SeitenSurface Modification Methods For Improving The Dyeability of Textile Fabricshamidrahmany3657Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Investigation - in - Plasma - Nitriding - Process (1) IMPDokument41 SeitenInvestigation - in - Plasma - Nitriding - Process (1) IMPSama UmateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Silver Nanoparticles Synthesis Propertie PDFDokument33 SeitenSilver Nanoparticles Synthesis Propertie PDFCiprian FodorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Selective Sulfide Precipitation of Copper, Cobalt and Iron From Leach SolutionDokument51 SeitenSelective Sulfide Precipitation of Copper, Cobalt and Iron From Leach Solutionjoseph kafumbilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lindgren 1935Dokument16 SeitenLindgren 1935Harold G. Velasquez SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- EUDIOMETRYDokument4 SeitenEUDIOMETRYSushila SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Enhanced Oil Recovery: Aliya Yernazarova Gulzhan KaiyrmanovaDokument24 SeitenMicrobial Enhanced Oil Recovery: Aliya Yernazarova Gulzhan KaiyrmanovaSayed Afg HashimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Acids and Alkali - ChemistryDokument9 SeitenAcids and Alkali - ChemistrySamaira SavlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Face ScrubDokument11 SeitenFormulation and Evaluation of Herbal Face ScrubIJRASETPublicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Characterization and Applications of Keratinase Enzyme by Bacillus Thuringiensis Ts2Dokument8 SeitenCharacterization and Applications of Keratinase Enzyme by Bacillus Thuringiensis Ts2Tun Huong100% (1)
- Volumetric Analysis - Class Xi: Experiment-1 AimDokument4 SeitenVolumetric Analysis - Class Xi: Experiment-1 AimKirtan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical (VFT-5) Fortnightly Test-5 (04!09!2023) - NEET-2025 - Questions PaperDokument26 SeitenMedical (VFT-5) Fortnightly Test-5 (04!09!2023) - NEET-2025 - Questions Paperharsh sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- CHAPTER 2 Extra CycloalkanesDokument13 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Extra Cycloalkanesellina safian100% (1)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Act.7 Ieng70Dokument2 SeitenAct.7 Ieng70Denz DavenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosurfactants As Useful Tools in BioremediationDokument19 SeitenBiosurfactants As Useful Tools in BioremediationDenny H. PiliangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air and Water Worksheet ADokument2 SeitenAir and Water Worksheet AGBENGA100% (1)
- InorganicDokument137 SeitenInorganicShaswata Roy50% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Enthalpy WKST KEYDokument4 SeitenEnthalpy WKST KEYمحمد گراوندNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miller Periodic TableDokument2 SeitenMiller Periodic TableMehmet SoysalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Dokument36 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Chapter 2Kavitha VijeandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- TL 502 ScopeDokument21 SeitenTL 502 Scopeca_rl_4Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Mole Concept - DPP 03 (Of Lec 05)Dokument2 SeitenMole Concept - DPP 03 (Of Lec 05)shubhamshekhar2003Noch keine Bewertungen
- RGPV BE Syllabus BE-101 Engineering ChemistryDokument2 SeitenRGPV BE Syllabus BE-101 Engineering ChemistryDeepak prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap - 9 SolutionsDokument9 SeitenChap - 9 SolutionsKamal KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)