Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DME Stress Concentration
Hochgeladen von
anbh30Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DME Stress Concentration
Hochgeladen von
anbh30Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MEE Design of Machine Elements
UNIT I
Stress Concentration
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Stress Concentration
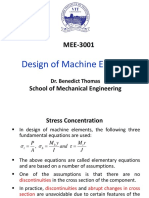
The elementary equations are based on a
number of assumptions.
One of the assumptions is that there are no
discontinuities in the cross section of the
component.
In practice, discontinuities and abrupt changes
in cross section are unavoidable due to certain
features of the component such as oil holes
and grooves, keyways and splines, screw
threads and shoulders.
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Stress Concentration
A plate with a small circular hole subjected to
tensile stress is shown in Figure.
The distribution of stresses
near the hole can be
observed by using photoelasticity technique.
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Stress Concentration
Definition:
Stress concentration is defined as the localization of high
stresses due to the irregularities present in the component and
abrupt changes of the cross section.
In order to consider the effect of stress concentration and find out
localized stresses, a factor called stress concentration factor is
used. It is denoted by Kt, and defined as
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
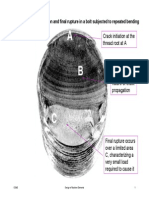
Causes of Stress Concentration
Variation in Properties of Materials
Internal cracks and flaws like blow holes
Cavities in welds
Air holes in steel components
Non-metallic or foreign inclusions
Load Application
Machine components are subjected to forces
These forces act either at point or over a small area
Since the area is small, the pressure at these points is
excessive
This results in stress concentration
Examples
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Causes of Stress Concentration
Abrupt Changes in Section
In order to mount gears, sprockets, pulleys and ball
bearings on transmission shaft, steps are cut on the shaft
and shoulders are provided from assembly considerations
Discontinuities in the Component
Certain features of machine components such as oil holes
or oil grooves, keyways and splines, and screw threads
result in discontinuities in the cross-section of the
component
Machining Scratches
Machining scratches, stamp mark or inspection mark are
surface irregularities, which cause stress concentration
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Determination of Kt
Mathematical
method
based
on
theory
of
elasticity
Experimental methods-Photo-Elasticity Technique
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Mathematical method based on theory of elasticity
It is possible for simple geometry only
Kt for a flat plate with elliptical hole subjected to tensile
force is given by
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Experimental methods
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Experimental methods
10
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Experimental methods
11
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
12
Reduction of stress concentration
Additional Notches and Holes in Tension Member
Fillet Radius, Undercutting and Notch for Member
in Bending
Drilling Additional Holes for Shaft with keyway
Reduction of Stress Concentration in Threaded
Members
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
13
Additional Notches and Holes in Tension Member
(a) Original Notch
(b) Multiple Notches
(c) Drilled Holes
(d) Removal of Undesired Materials
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
14
Fillet Radius, Undercutting and Notch for Member in
Bending
Original Component
Undercutting
Fillet Radius
Addition of Notch
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
Drilling Additional Holes for Shaft with keyway
15
7/28/16
MEE302: DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS
16
Reduction of Stress Concentration in Threaded
Members
Original Component
Reduction in Shank Diameter
Undercutting
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Common Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesVon EverandCommon Rail Fuel Injection Technology in Diesel EnginesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Strength: MEE 3001 Design of Machine ElementsDokument39 SeitenFatigue Strength: MEE 3001 Design of Machine ElementsJeevalkant DandonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Pressure DistributionDokument24 SeitenBolt Pressure DistributionbitconceptsNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUSNES Deck Machinery Installation ProcedureDokument18 SeitenPUSNES Deck Machinery Installation ProcedurexatzaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 27-Jul-2020 Module 2 Stress Concentration 5Dokument27 SeitenFALLSEM2020-21 MEE3001 TH VL2020210101665 Reference Material I 27-Jul-2020 Module 2 Stress Concentration 5AK PRODUCTIONSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Strain Gauge Rosette To Investigate Stress Concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate With Circular HoleDokument5 SeitenUse of Strain Gauge Rosette To Investigate Stress Concentration in Isotropic and Orthotropic Plate With Circular HoleHako KhechaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injector Adjustment: Table 1Dokument5 SeitenFuel Injector Adjustment: Table 1Stepan KlashevychNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em - Engine Mechanical PDFDokument24 SeitenEm - Engine Mechanical PDFMoaed Kanbar86% (21)
- 0000 Unit II 2016-17 Sent CVC PDFDokument52 Seiten0000 Unit II 2016-17 Sent CVC PDFTech N0% (1)
- E 08Dokument16 SeitenE 08João PauloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3512C HD Fuel Injector AdjustmentDokument5 Seiten3512C HD Fuel Injector Adjustmentharikrishnanpd3327100% (2)
- Fatigue FailureDokument47 SeitenFatigue FailureOmar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatique On Piston RingDokument6 SeitenFatique On Piston Ringmohanrajjercy71100% (1)
- Durability Assessments of Motorcycle Handlebars Ken-Yuan Lin, 2005 XXXXXDokument25 SeitenDurability Assessments of Motorcycle Handlebars Ken-Yuan Lin, 2005 XXXXXjaydeepnaruleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress ConcentrationDokument21 SeitenStress ConcentrationsacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Contact Stress Analysis For Fixture Design of Pressure Valve PlateDokument8 SeitenDesign and Contact Stress Analysis For Fixture Design of Pressure Valve PlatetheijesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma Ii Year Mechanical Engineering: 2011-2012 SubjectsDokument31 SeitenDiploma Ii Year Mechanical Engineering: 2011-2012 SubjectsAjay GahlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Em PDFDokument64 SeitenEm PDFGael AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pc200-8 Valve ClearanceDokument3 SeitenPc200-8 Valve ClearanceAl FurkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel SistemDokument55 SeitenFuel SistemRodolfo AlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NE04 014revbDokument23 SeitenNE04 014revbMarlene Yuriserll Ruiz MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Note 3562A XG0NDokument120 SeitenTechnical Note 3562A XG0NEeepsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3500C Engine Fuel Injector Adjustment GuideDokument5 Seiten3500C Engine Fuel Injector Adjustment GuidepaballaysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSDokument6 SeitenThermo Coupled Stress Analysis of Exhaust Manifold Assemblage Using ABAQUSInfogain publicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibrar 3500b LekDokument5 SeitenCalibrar 3500b LekAna María AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section: Engine MechanicalDokument64 SeitenSection: Engine Mechanicalvadim vadimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm E837 08 Agujero CiegoDokument5 SeitenAstm E837 08 Agujero CiegoAlfonso Bericua SierpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3,0 Worked Example 1 Production Separator ModuleDokument45 Seiten3,0 Worked Example 1 Production Separator ModuleAli HijaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsDokument27 SeitenChapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsSandeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Compression Brake Actuator Replacement MP7 CXU GU TrucksDokument6 SeitenEngine Compression Brake Actuator Replacement MP7 CXU GU TrucksChristian FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Injector s60Dokument15 SeitenInjector s60Alex Forero100% (7)
- Medición de La Presión de La Película de Aceite en El Orificio Del Bulón Del Pistón Durante El Funcionamiento Del MotorDokument13 SeitenMedición de La Presión de La Película de Aceite en El Orificio Del Bulón Del Pistón Durante El Funcionamiento Del MotorLuis HfNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 307 Machine Design I: Bolted Joint StiffnessDokument24 SeitenME 307 Machine Design I: Bolted Joint Stiffnessfog900Noch keine Bewertungen
- ME 307 Machine Design I: Bolted Joint Design and AnalysisDokument24 SeitenME 307 Machine Design I: Bolted Joint Design and Analysisfog900Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsDokument27 SeitenChapter 8: Screws, Fasteners and The Design of Nonpermanent JointsErcüment KayacıkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breakage of The Tightening Stud of Cyl - CoverDokument5 SeitenBreakage of The Tightening Stud of Cyl - Coverstergios meletisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - Motor CATDokument5 SeitenManual - Motor CATBruno GenteluciNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTMC Design AnalysisDokument5 SeitenBTMC Design AnalysisgauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verity & Ss Ansys West PNGDokument32 SeitenVerity & Ss Ansys West PNGcklconNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8-1. Disassembly and AssemblyDokument175 Seiten8-1. Disassembly and AssemblyDeyvi Cconocuyca HuallparimachiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JM Engine 20040209Dokument43 SeitenJM Engine 20040209wreckedweasel100% (2)
- Mercedes Engine TSBDokument10 SeitenMercedes Engine TSBrideanddriveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine MechanicalDokument48 SeitenEngine MechanicalKristian FonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 28: Model Airplane AnalysisDokument10 SeitenChapter 28: Model Airplane Analysisirina_andraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fatigue Analysis of I-Section and H - Section Connecting Rod Using ANSYS WorkbenchDokument14 SeitenFatigue Analysis of I-Section and H - Section Connecting Rod Using ANSYS WorkbenchInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Element Analysis of Piston in AnsysDokument9 SeitenFinite Element Analysis of Piston in Ansysstranger3333Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fracture TutorialDokument13 Seiten3 Fracture TutorialSanthosh LingappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM6D28 Manual BookDokument26 SeitenCM6D28 Manual BookNut Chen Li JunNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDokument8 SeitenInternational Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stepped Shaft Design and Stress Analysis Using Inventor ProDokument6 SeitenStepped Shaft Design and Stress Analysis Using Inventor ProMohammad AzemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fracture TutorialDokument13 Seiten3 Fracture TutorialShaikh Akhlaque100% (1)
- AFC Sensor de Presion PDFDokument10 SeitenAFC Sensor de Presion PDFCharlie BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injector AdjustmentDokument5 SeitenFuel Injector AdjustmentCeciliagorra33% (3)
- 3516B Generator Set Engine - Fuel Injector Adjustment - SIS - CATERPILLARDokument5 Seiten3516B Generator Set Engine - Fuel Injector Adjustment - SIS - CATERPILLARpevare78% (9)
- 2.engine AssemblyDokument126 Seiten2.engine AssemblyWissem RatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Final Syl BtechDokument22 SeitenMech Final Syl Btechtechy shyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- S221 Transmission System Project ME3145Dokument20 SeitenS221 Transmission System Project ME3145VIỆT LÊ BÁ QUỐCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spur Gear Cutting Using IndexingDokument7 SeitenSpur Gear Cutting Using Indexingbobcrysto100% (2)
- Sony Micro MV Mechanical Adjustment Manual 1 V Mechanism V PDFDokument48 SeitenSony Micro MV Mechanical Adjustment Manual 1 V Mechanism V PDFFrank GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Orbital Theory ExplainedDokument80 SeitenMolecular Orbital Theory ExplainedMridul Bhaskar0% (1)
- Controlling an Inverted Pendulum on a CartDokument14 SeitenControlling an Inverted Pendulum on a CartRitesh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-Delta Analysis Column ForcesDokument9 SeitenP-Delta Analysis Column ForcesMauricio CatunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02Dokument8 Seiten02Nghiem QuocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow Losses in Flexible Hose.Dokument186 SeitenFlow Losses in Flexible Hose.Anonymous K3FaYFlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankDokument17 SeitenWolfson Eup3 Ch34 Test BankifghelpdeskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radial Conduction Experiment Technical InstituteDokument5 SeitenRadial Conduction Experiment Technical InstituteWalid AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Analytical TechniquesDokument10 SeitenThermo Analytical Techniquesthamizh555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Guideline VDI 3830 Damping of Materials ADokument7 SeitenTutorial Guideline VDI 3830 Damping of Materials AcemocanaysunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids 2015 QuestionsDokument7 SeitenFluids 2015 QuestionsFaisal Al QadriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 2Dokument82 SeitenChem 2César ArenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein-Rosen Bridge Revisited and Lightlike ThinDokument15 SeitenEinstein-Rosen Bridge Revisited and Lightlike ThinSomanshu KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperDokument12 SeitenJEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- Gravity 1Dokument25 SeitenGravity 1Ana Marie ValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers Structural Erol FinalDokument6 SeitenAnswers Structural Erol FinalJACQUELINE BUHAYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling gas formative assessmentDokument3 SeitenModeling gas formative assessmentPaula AstudilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 9.1: Scalar QEDDokument15 SeitenProblem 9.1: Scalar QEDMiguel PedrazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKPART TRANSFER METHODSDokument7 SeitenWORKPART TRANSFER METHODSAnonymous MZRzaxFgVLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Properties of RocksDokument77 SeitenEngineering Properties of RocksTariq NiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.3 F.4.PhyDokument5 SeitenPusat Tuition Makrifat Chapter 3.3 F.4.PhyBazil BoliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational Motion - DPPsDokument17 SeitenRotational Motion - DPPs:-Noch keine Bewertungen
- D y N A M I C S C: Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide For The PASCO Scientific Model ME-9430Dokument383 SeitenD y N A M I C S C: Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide For The PASCO Scientific Model ME-9430Elzer Toro'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Weighting Assessment of Vulnerability Index Parameters For Reinforced Masonry StructuresDokument9 SeitenWeighting Assessment of Vulnerability Index Parameters For Reinforced Masonry StructuresTeo Peng Keat100% (1)
- Numerical and Experimental Approach For Roll Grinding ProcessDokument7 SeitenNumerical and Experimental Approach For Roll Grinding ProcessGinanjar Surya RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Footing DesignDokument21 SeitenRCC Footing Designnitin chaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction and Inclined Plane Problems ExplainedDokument116 SeitenFriction and Inclined Plane Problems ExplainedAlexander Roman Sich100% (1)
- New Mathod To Evaluate The Uplift Cap of Belled Pile in Sandy Soil PDFDokument11 SeitenNew Mathod To Evaluate The Uplift Cap of Belled Pile in Sandy Soil PDFM TaufikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Locking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationDokument3 SeitenLocking of Hene Laser Modes Induced by Synchronous Intracavity ModulationMohamad paidarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaveguidesDokument41 SeitenWaveguidesVIKALP KULSHRESTHA80% (5)
- Bridge-Design of Shallow FoundationsDokument35 SeitenBridge-Design of Shallow FoundationshassscribedNoch keine Bewertungen