Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Business Plan Guide
Hochgeladen von
Syed Sufyan SubhaniOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Business Plan Guide
Hochgeladen von
Syed Sufyan SubhaniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Feasibility and
Business Planning
Back to Table of Contents
Feasibility and Business Planning
Chapter 5
Feasibility and
Business Planning
5.1
Feasibility Analysis:
Testing an Opportunity
5.2
The Business Plan
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.1
Discuss the importance of defining a prospective
business by writing a clear and concise business
concept.
Describe how a feasibility study can be used to
test a concept in the marketplace.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.1
Business concepts need to be tested in the market.
Once a concept is judged feasible, a business plan
will help the entrepreneur develop a strategy for
executing the concept.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.1
business concept
feature
feasibility analysis
industry
target customers
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
competitive grid
prototype
business model
value chain
Feasibility and Business Planning
Developing a Business
Concept
Once you have a idea for a
new business, define it by
writing a clear and concise
business concept.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
business concept
a clear and concise
description of a business
opportunity; it contains
four elements: the
product or service, the
customer, the benefit,
and the distribution
Feasibility and Business Planning
Developing a Business
Concept
In developing a business
concept, consider the
features and benefits your
product or service offers.
features distinctive
aspects, qualities, or
characteristics of a
product or service
benefits things that
promote or enhance the
value of a product or a
service to the customer
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
Feasibility and Business Planning
Testing the Concept
in the Market
An entrepreneur can use a
feasibility analysis in
order to decide if there is
enough demand for a
product or service.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
feasibility analysis the
process that tests a
business concept; it
allows the entrepreneur
to decide whether a new
business concept has
potential
Feasibility and Business Planning
Testing the Concept
in the Market
A feasibility analysis can help an entrepreneur
determine whether business conditions are
appropriate to go forward with starting a business.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
Testing the Concept in the Market
customers
product and
service
industry
value chain
Feasibility
Analysis
Questions
start-up needs
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
founding
team
competition
10
Feasibility and Business Planning
Testing the Industry
The broadest level of
feasibility analysis looks at
the industry in which the
business will operate.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
industry a group of
businesses with a
common interest
11
Feasibility and Business Planning
Talking to Customers
The most important part of
the feasibility analysis is
testing customers to
measure interest and identify
the target customers.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
target customers
people most likely to buy
a businesss products and
services
12
Feasibility and Business Planning
Testing Product or
Service Requirements
To consider all the
requirements of a product
or service, create a
prototype.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
prototype a working
model used by
entrepreneurs to
determine what it takes
to develop their products
or services
13
Feasibility and Business Planning
Studying the Competition
An easy way to evaluate
the competition is to create
a competitive grid.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
competitive grid a tool
for organizing important
information about a
business ventures
competition
14
Feasibility and Business Planning
Looking at Start-Up
Resources
A strong business model
is important to investors.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
business model a
description of how
entrepreneurs plan to
make money with their
business concepts
15
Feasibility and Business Planning
Analyzing the Value Chain
A business can create a
competitive advantage by
improving the value chain
or its products and services.
value chain the
distribution channel
through which a product
or service flows from the
producer to the customer
The value chain includes
manufacturers, distributors,
and retailers.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
16
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.1
1. Discuss the importance of defining a
prospective business by writing a clear and
concise business concept.
A clear and concise business concept is the first step
in taking an idea and building a business plan to
execute the concept. The business concept helps the
entrepreneur focus on the critical elements of the
business: the product or service, the customer, the
benefit, and the distribution.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
17
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.1
2. Describe how a feasibility study can be used
to test a concept in the marketplace.
A feasibility study determines whether a new
business concept has potentialwhether there is
enough demand for a product or service and
whether business conditions are appropriate for
proceeding with a business idea.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
18
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
Describe the importance of planning.
Identify and describe the components and
formats of a business plan.
List two of the key mistakes that entrepreneurs
make when writing a business plan.
Identify and analyze various sources of
information for a business plan.
Describe how to professionally package and
present a business plan.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
19
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
A business plan presents a strategy for turning
a feasible business concept into a successful
business.
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
20
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
business plan
vision statement
mission statement
executive summary
distribution channel
Section 5.1 Feasibility Analysis: Testing an Opportunity
direct channel
indirect channel
Small Business Administration
(SBA)
trade association
21
Feasibility and Business Planning
The Business Plan: Your Road
Map to Entrepreneurial Success
Once you have a feasible
business concept, the next
step is to develop a
business plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
business plan a
document that describes
a new business and a
strategy to launch that
business
22
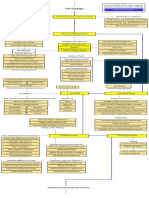
The Parts of a Business Plan
Cover Page
Market Analysis
Title Page
Competitive Analysis
Table of Contents
Marketing Plan
Executive Summary
Operations Plan
Management Plan
Organizational Plan
Company Description
Financial Plan
Product and Service Plan
Growth Plan
Mission and Vision Statements
Contingency Plan
Industry Overview
Supporting Documents
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
23
Feasibility and Business Planning
Executive Summary
The executive summary
should include the most
important information from
each section of the business
plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
executive summary a
brief recounting of the key
points contained in a
business plan
24
Feasibility and Business Planning
Executive Summary
To save time, investors and lenders rely on the
executive summary to help them decide whether
the business plan is worth pursuing.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
25
Feasibility and Business Planning
Management Team Plan
The management team presents your
qualifications and those of any partners.
You must describe how your management team
has the capabilities to execute your business plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
26
Feasibility and Business Planning
Company Description
The company description section of the business
plan outlines the companys background
information and basic business concept.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
27
Feasibility and Business Planning
Product and Service Plan
In the product and service plan section of the
business plan, you present the nature of your
business and the unique features of the product
or service.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
28
Feasibility and Business Planning
Executive Summary
The vision statement and
mission statement state
the guiding principles by
which a company functions.
vision statement a
declaration of the scope
and purpose of a
company
mission statement a
declaration of the specific
aspirations of a company,
the major goals for which
it will strive
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
29
Feasibility and Business Planning
Industry Overview
The industry overview section of the business
plan presents your research into the industry,
those companies providing similar,
complementary, or supplementary products or
services.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
30
Feasibility and Business Planning
Industry Overview
The market analysis section of the business plan
presents your research on the customer profile
gathered from primary and secondary marketing
research resources.
The results help you determine your overall
marketing and sales strategies.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
31
Feasibility and Business Planning
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis section of the business
plan should demonstrate that the proposed
business has a advantage over its competitors.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
32
Feasibility and Business Planning
Marketing Plan
A marketing plan discusses how a company
plans to make its customers aware of its
products or services.
A marketing plan also describes the market
niche, pricing, company image, marketing
tactics, a media plan, and a marketing budget.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
33
Feasibility and Business Planning
Operational Plan
The operational plan
describes all the
processes involving the
production and delivery of
the product or service.
distribution channel
the means by which a
product or service is
delivered to the customer
The operational plan
describes the
distribution channel
of the product or service.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
34
Feasibility and Business Planning
Operational Plan
The operational plan
describes the direct
channel and/or indirect
channel you will use to
deliver your product or
service.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
direct channel the
means of delivering a
service or product directly
to the customer, such as
via a Web site
indirect channel the
means of delivering a
service or product
indirectly to the customer,
such as through a
wholesaler
35
Feasibility and Business Planning
Organizational Plan
The organizational plan section of a business
plan looks at the people aspects and the legal
form of the business.
It also describes the roles and compensation of
key management personnel and important
employment policies.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
36
Feasibility and Business Planning
Financial Plan
The financial plan presents forecasts for the
future of the business.
The financial plan includes financial statements.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
37
Feasibility and Business Planning
Growth Plan
The growth plan describes how the business
will expand in the future.
Investors and lenders like to see that a
business has plans to grow in a planned and
controlled way.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
38
Feasibility and Business Planning
Contingency Plan
The contingency plan section of the business
plan looks at the risks to business, such as
changing economic conditions and lower-thanexpected sales.
It then suggests ways to minimize the risks.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
39
Feasibility and Business Planning
Cover Page, Title Page, Table of
Contents, and Supporting Documents
Every business plan should have a cover page, a
title page, a table of contents, and supporting
documents.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
40
Feasibility and Business Planning
Cover Page, Title Page, Table of
Contents, and Supporting Documents
To begin developing a business plan:
Make a research plan and gather data.
Set up a notebook to organize data.
Write a first draft.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
41
Common Mistakes in Preparing Business Plans
projecting exaggerated growth levels
trying to be have expertise in all areas
claiming performance above industry averages
underestimating the need for capital
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
42
Sources of Business Plan Information
Small Business Administration (SBA)
Service Corps of Retired Executives (SCORE)
Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs)
chambers of commerce
trade associations
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
43
Feasibility and Business Planning
Small Business
Administration (SBA)
To encourage
entrepreneurship in our free
enterprise system, the
government operates the
Small Business
Administration (SBA).
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
Small Business
Administration (SBA)
the federal agency that
provides services to small
businesses and new
entrepreneurs, including
counseling, publications,
and financial aid
44
Feasibility and Business Planning
Trade Associations
Trade associations supply
information to entrepreneurs
about start-up issues,
operating costs, and
analysis of trends.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
trade association an
organization made up of
individuals and
businesses in a specific
industry that works to
promote that industry
45
Packaging and Presenting the Business Plan
1
Bind the plan.
Use index tabs to separate sections.
Use an easily readable 12-point type.
Use bold subheadings and bullets.
Use the company logo at the top of every page.
Number each copy of the business plan and include a
statement of confidentiality.
Include a statement on the cover page prohibiting copying of
the plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
46
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
1. Describe the importance of planning.
Planning helps the entrepreneur achieve goals
and organize and analyze critical data.
Researching costs and developing strategies
about operations may reveal problems that the
entrepreneur hadnt seen previously.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
47
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
2. Identify and describe the components and
formats of a business plan.
A business plan should include these components: executive summary;
management team plan; company description; product and service plan;
vision and mission statements; industry overview; market analysis
competitive analysis; marketing plan; operational plan; organizational
plan; financial plan; growth plan; contingency plan; and cover page, title
page, table of contents, and supporting documents. There is no right or
wrong format for a business plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
48
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
3. List two of the key mistakes that
entrepreneurs make when writing a
business plan.
Common mistakes include: projecting
exaggerated growth levels, trying to be a jack-ofall-trades, claiming performance that exceeds
industry averages, and underestimating the need
for capital.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
49
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
4. Identify various sources of information
for a business plan.
Business plan information sources include: the Small
Business Administration (SBA), Service Corps of
Retired Executives (SCORE), Small Business
Development Centers (SBDCs), chambers of
commerce, and trade associations.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
50
Feasibility and Business Planning
5.2
5. Describe how to professionally package and
present a business plan.
Follow these guidelines to package a business plan: (1) Bind the plan.
(2) Use index tabs to separate sections. (3) Use an easily readable
12-point type. (4) Use bold subheadings and bullets to make information
easy to find. (5) If there is one, use the company logo at the top of every
page. (6) Number each copy of the business plan and include a
Statement of Confidentiality for the reader to sign. (7) Include a statement
on the cover page prohibiting copying of the plan.
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
51
Feasibility and Business Planning
The E-Business
Business Plan
A good business plan is as important for an
e-business as it is to any other business.
An E-business plan should include the following:
timeline
functionality
style
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
metrics
hardware
international markets
52
Feasibility and Business Planning
Tech Terms
functionality
the way a product or service works, such as a Web sites features
launch
the first date on which a Web site is on the Internet
metrics
methods used to measure activity and progress, such as those on a
Web site; metrics software can measure number of visitors, time of
day the site is most active, and which products receive the most hits
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
53
Feasibility and Business Planning
Tech Terms
Web host
a business that provides server space and file maintenance services
for Web sites controlled by businesses that do not have their own Web
servers
Web server
a computer that delivers Web pages
Section 5.2 The Business Plan
54
End of
Feasibility and
Business Planning
Back to Table of Contents
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Proposals & Competitive Tendering Part 2: Managing Winning Proposals (Second Edition)Von EverandProposals & Competitive Tendering Part 2: Managing Winning Proposals (Second Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Proposals & Competitive Tendering Part 1: Strategy & Positioning to Win (Second Edition)Von EverandProposals & Competitive Tendering Part 1: Strategy & Positioning to Win (Second Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility and Business Planning: Back To Table of ContentsDokument61 SeitenFeasibility and Business Planning: Back To Table of ContentsPriscilla SamaniegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crafting A Business PlanDokument4 SeitenCrafting A Business PlanMd. Sajjad HossenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility and Business Planning GuideDokument7 SeitenFeasibility and Business Planning GuideGilbert Magdosa Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Planning Chapter 3 Business Plan GuideDokument35 SeitenFeasibility Planning Chapter 3 Business Plan GuideUsman TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business OpportunityDokument11 SeitenBusiness OpportunityElias HaileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 PresentationDokument35 SeitenChapter 5 PresentationSabeur Dammak100% (1)
- ED Final Exam Suggestions 2Dokument6 SeitenED Final Exam Suggestions 2Slantx EvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Product FeasibilityDokument16 SeitenUnderstanding Product Feasibilityolive banielNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Idea Assessment Feasibility Analysis Business ModelDokument4 Seiten02 Idea Assessment Feasibility Analysis Business ModelImaan IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study ComponentsDokument4 SeitenFeasibility Study ComponentsJerad KotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Development2023-2024Dokument22 SeitenBusiness Plan Development2023-2024muganzajesus001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Unit 9Dokument6 SeitenBusiness Plan Unit 9Disha JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4 - Writing A Business PlanDokument12 SeitenLecture 4 - Writing A Business PlanWasay HanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Seven Business PlanDokument10 SeitenChapter Seven Business PlanFarai GwataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Logo : (Project / Company Name) Business Plan (Date) (Name) (Title)Dokument12 SeitenCompany Logo : (Project / Company Name) Business Plan (Date) (Name) (Title)hr6563600Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Feasibility StudyDokument1 SeiteWhat Is A Feasibility StudyMaria Mae Pasagad JamitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEW MarketplanDokument17 SeitenNEW MarketplanAzzyHazimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBA Semester 3 - Lecture NotesDokument10 SeitenMBA Semester 3 - Lecture NotesAhmed Idi KatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK6 - Conducting A Feasibility StudyDokument31 SeitenWEEK6 - Conducting A Feasibility StudyHannah Shiela MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan BCDokument23 SeitenBusiness Plan BCAniket SheteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conducting A Feasibility StudyDokument10 SeitenConducting A Feasibility Studysignup0123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hospitality Business Plan - FinalDokument144 SeitenThe Hospitality Business Plan - Finalkdfohasfowdesh75% (4)
- Business PlanningDokument19 SeitenBusiness PlanningDavs ThorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship: Mr. Ibrahim Mohamed Ali Bba, Mba (HRM) Human Resource Director Hormuud University Mogadishu-SomaliaDokument23 SeitenEntrepreneurship: Mr. Ibrahim Mohamed Ali Bba, Mba (HRM) Human Resource Director Hormuud University Mogadishu-SomaliaAbduahi asadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hit 2201 Feasibility Study 2023 - by T.P MushayavanhuDokument22 SeitenHit 2201 Feasibility Study 2023 - by T.P MushayavanhuEnjoy Sheshe100% (1)
- Introduction To Entrepreneurship Writing A Business PlanDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Entrepreneurship Writing A Business PlandevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Develop Business PracticeDokument71 SeitenDevelop Business PracticeDesu GashawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bma1 - R2 - Tierra MoniqueDokument9 SeitenBma1 - R2 - Tierra MoniqueMonique TierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chp4 ConductingaFeasibilityAnalysisandCraftingaWinningBusinessPlan PDFDokument14 SeitenChp4 ConductingaFeasibilityAnalysisandCraftingaWinningBusinessPlan PDFAar RageediNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEP Lab Session 1Dokument14 SeitenEEP Lab Session 1AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Operation StrategyDokument10 SeitenChapter 2 - Operation Strategyrajeevseth100% (1)
- MODULE 8 EntreprenureDokument10 SeitenMODULE 8 EntreprenureQuiel Jomar GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Launching New Ventures An Entrepreneurial Approach 7th Edition Allen Solutions Manual DownloadDokument3 SeitenLaunching New Ventures An Entrepreneurial Approach 7th Edition Allen Solutions Manual DownloadWilma Willingham100% (21)
- Bahir Dar Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringDokument67 SeitenBahir Dar Mechanical and Industrial EngineeringGadisa AbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-III Product and Service DesignDokument14 SeitenChapter-III Product and Service DesignGebrekiros ArayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship DA 1Dokument13 SeitenEntrepreneurship DA 1Pushpa MahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing a Business PlanDokument20 SeitenWriting a Business PlanMuzahir Hussain JoyiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study: Presented byDokument21 SeitenFeasibility Study: Presented byTanaka dzapasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance PyramidDokument15 SeitenPerformance PyramidAsma AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan TemplateDokument5 SeitenBusiness Plan TemplateAnne RicohermosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porter's Five Forces That Shape IndustryDokument8 SeitenPorter's Five Forces That Shape IndustryLaong laanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument40 SeitenChapter 4asd123456789asdcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report No. 1 EntrepreneurshipDokument10 SeitenLab Report No. 1 EntrepreneurshipFaisal MehrbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSBMGT617 - Assessment 1 - ProjectDokument12 SeitenBSBMGT617 - Assessment 1 - Projectozdiploma assignmentsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Totalbpp 3Dokument232 SeitenTotalbpp 3TomHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palander Jere Pulkkinen Otto 2022 12 08Dokument40 SeitenPalander Jere Pulkkinen Otto 2022 12 08birhan4melkamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Strategy FormulationDokument17 SeitenMidterm Strategy FormulationEricca Joyce AndradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Business PlanDokument6 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Business PlanZatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Planning and Project Management GuideDokument20 SeitenBusiness Planning and Project Management GuideTaha MerchantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative Essay 1 - Brief, Guidelines and Marking CriteriaDokument8 SeitenSummative Essay 1 - Brief, Guidelines and Marking CriteriaRejoice MpofuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam O&PMDokument18 SeitenExam O&PMdkaluale16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formulation of Manufacturing StrategyDokument30 SeitenFormulation of Manufacturing StrategywaqasalitunioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Writing ProcessDokument45 SeitenBusiness Plan Writing ProcessCristy100% (1)
- ESBM Chapter 5Dokument36 SeitenESBM Chapter 5Ba HeinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan Handbook: Practical guide to create a business planVon EverandBusiness Plan Handbook: Practical guide to create a business planBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Assignment 02 01Dokument20 SeitenAssignment 02 01dilhaninperera47Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 11 Crafting A Business PlanDokument5 SeitenCH 11 Crafting A Business PlanNaufil BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing 2Dokument43 SeitenMarketing 2abhaydimapur007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Innovation Lecture KapeelDokument29 SeitenInnovation Lecture KapeelSyed Sufyan SubhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSK ProfileDokument3 SeitenGSK ProfileSyed Sufyan SubhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entrepreneurship Lecture 1 GuideDokument27 SeitenEntrepreneurship Lecture 1 GuideSyed Sufyan Subhani100% (1)
- Student Accountant April 2012Dokument49 SeitenStudent Accountant April 2012Syed Sufyan SubhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EY How Can You Unlock Value With Your Operating ModelDokument8 SeitenEY How Can You Unlock Value With Your Operating Modelميلاد نوروزي رهبرNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank Annual ReportDokument386 SeitenBank Annual ReportumeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 10 Most Influential Business Women Making A Difference, 2022Dokument40 SeitenThe 10 Most Influential Business Women Making A Difference, 2022The Inc MagazineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Sumit Mudgil: Course: Digital Business Innovation Project: Hamleys'SDokument7 SeitenSubmitted By: Sumit Mudgil: Course: Digital Business Innovation Project: Hamleys'SSumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023.03.01 - Entain - Annual ReportDokument240 Seiten2023.03.01 - Entain - Annual ReportLexi EisenbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sacombank EngDokument96 SeitenSacombank EngMonkey2111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Success Factors For Digitalization ProjecDokument10 SeitenCritical Success Factors For Digitalization ProjecChiraz RosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traversing The Valley of DeathDokument109 SeitenTraversing The Valley of DeathNiu WaaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Value MiningDokument53 SeitenCreating Value MiningRandy CavaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilovepdf MergedDokument657 SeitenIlovepdf MergedfarolconservadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collaborative EconomyDokument329 SeitenCollaborative EconomyMai TntNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMG Case StudyDokument5 SeitenBMG Case StudynwakahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Questions For Chapter 1 Business Information SystemsDokument2 SeitenReview Questions For Chapter 1 Business Information Systemsrobj20076404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bahria University (Karachi Campus) : Final Examination - Spring Semester - 2020 (Entrepreneurship & Leadership (HSS-421) )Dokument11 SeitenBahria University (Karachi Campus) : Final Examination - Spring Semester - 2020 (Entrepreneurship & Leadership (HSS-421) )Iyman Ahmed100% (1)
- ENTREPRENEURSHIP - FinalsDokument8 SeitenENTREPRENEURSHIP - FinalsPolNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Business Model - 24 Types of Business Models - Feedough PDFDokument9 SeitenWhat Is A Business Model - 24 Types of Business Models - Feedough PDFChristian LlerandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPO 5 Year StrategyDokument19 SeitenIPO 5 Year StrategyZulfikar FuadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINAL EXAM ENTREPRENEURIAL MINDSETDokument8 SeitenFINAL EXAM ENTREPRENEURIAL MINDSETDyna RoseteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ux DesignDokument1 SeiteUx DesignKalai ArasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Business Models and Revenue ModelsDokument8 SeitenChapter 2 Business Models and Revenue ModelsMIRELANoch keine Bewertungen
- ZARADokument15 SeitenZARAto_coolvishal67% (6)
- MIS 320 Module Four Case Study Analysis Guidelines and Rubric Organizational E-Commerce Case Study Analysis: AmazonDokument2 SeitenMIS 320 Module Four Case Study Analysis Guidelines and Rubric Organizational E-Commerce Case Study Analysis: AmazonghanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Critical Makeover For Pharmaceutical Companies PDFDokument28 SeitenA Critical Makeover For Pharmaceutical Companies PDFAylin PolatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Netflix ManagementDokument6 SeitenNetflix ManagementCarina MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gartner Reprint - IGADokument39 SeitenGartner Reprint - IGANaida KukuruzovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- JBCalunod Nov.2RevisedDokument126 SeitenJBCalunod Nov.2RevisedjmwelmerencilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- TechnopreneurshipDokument2 SeitenTechnopreneurshipAin AfiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The HR Service Delivery Model Canvas (LIVE)Dokument2 SeitenThe HR Service Delivery Model Canvas (LIVE)talentedpeopleplusNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Business Advisory Services Help SMEs SucceedDokument129 SeitenHow Business Advisory Services Help SMEs SucceedSibuleg SeduanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herrmann Et Al. - 2018 - Digital Transformation and Disruption of The HealtDokument8 SeitenHerrmann Et Al. - 2018 - Digital Transformation and Disruption of The HealtRosliana MahardhikaNoch keine Bewertungen