Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Eukaryotic Cells
Hochgeladen von
taengoo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten10 Seiteneukaryotic cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldeneukaryotic cell
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten10 SeitenEukaryotic Cells
Hochgeladen von
taengooeukaryotic cell
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
2.
3: EUKARYOTIC CELLS
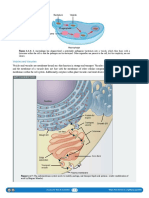
2.3.1, 2.3.2: Liver cell
2.3.3: Electron micrograph of liver
cell (rat)
Glycogen
2.3.4: Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic cell
FEATURE
Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cell
DNA
Naked DNA
DNA associated
with proteins
Ribosomes
70s
80s
DNA
DNA inside the
cytoplasm
DNA enclosed
by a membrane
Mitochondria
no
yes
Internal
membranes
no
yes
2.3.5: State three differences between plant and animal cells
1.
2.
3.
4.
Plant cells have large vacuoles and animal cells do not
have large vacuoles.
Plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not have a
cell wall.
Plant cells (may) have chloroplasts and animals do not
have chloroplasts.
Plant cells store excess glucose as starch and animal cells
store excess glucose as glycogen.
2.3.6: Outline two roles of extra cellular components
The plant cell wall
maintains cell shape,
prevents excessive
water uptake, and hold
the whole plant up
against the force of
gravity.
Glycoproteins
Animal cells secrete
glycoproteins that
form the extracellular
matrix. This functions
Animal cells secrete glycoproteins, which are composed of a protein and a
in support, adhesion
carbohydrate.
and movement.
Glycoproteins
are used in proteins that are located in the extracellular
matrix (the space outside the cell).
One example of glycoproteins found in the body are mucins, which are
secreted in the digestive tracts. The sugars attached to mucins make them
resistant to proteolysis by digestive enzymes.
Glycoproteins on the surface of lymphocytes allow them to stick to other
IB Question: Eukaryotic cells have intracellular and extracellular
components. State the functions of one named extracellular component. [4]
IB Question: Eukaryotic cells have intracellular and extracellular
components. State the functions of one named extracellular component. [4]
name of component [1 max] e.g. plant cell wall/cellulose/interstitial
matrix/basement membrane/glycoprotein/bone matrix;
functions [3 max]
EITHER
e.g. (plant cell wall) strengthens/supports the cell/plant (against gravity);
prevents the entry of pathogens;
maintains the shape of plant cells;
allows turgor pressure/high pressure to develop inside the cell;
prevents excessive entry of water to the cell;
OR
helps cells to stick together/adhere;
needed to hold cells/tissues together / example of cells/tissues holding
together;
forms interstitial matrix / forms basement membrane to support single layers
of cells;
e.g. around a blood capillary;
forms (part of the) filtration membrane in the glomerulus; [4 max]
IB Question: Compare the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. [5]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TEXTBOOK BIOSEL and BIOMOLDokument89 SeitenTEXTBOOK BIOSEL and BIOMOLTsamarah NafisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology NotesDokument18 SeitenCell Biology NotesZara100% (2)
- Miller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 SummaryDokument6 SeitenMiller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 Summarybob0% (1)
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksVon EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDokument13 SeitenThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Biology Topic 1 CellsDokument10 SeitenIb Biology Topic 1 Cellswee100% (1)
- Functions Practice ProblemsDokument4 SeitenFunctions Practice ProblemstaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Biology Syllabus NotesDokument52 SeitenSL Biology Syllabus NotesRyel MuchunkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Dokument6 SeitenGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISA Samples Writing G7 - 10Dokument42 SeitenISA Samples Writing G7 - 10taengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsDokument3 SeitenIB Biology Notes - 23 Eukaryotic CellsJohn Philip D. NapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Cell StructureDokument40 SeitenEukaryotic Cell StructureJevaughn SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDokument11 Seiten2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Buffers 2021Dokument13 SeitenIntroduction and Buffers 2021Kipchirchir AbednegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook Cell BiologyDokument50 SeitenTextbook Cell Biologyaeisyah hananiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 001 Real Slide First SemesterDokument44 SeitenBIO 001 Real Slide First Semestermarkwelly367Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PlantDokument7 SeitenCell PlantEbiz MarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument61 SeitenCellAbdul Rehman100% (1)
- Plant Cell OrganellesDokument13 SeitenPlant Cell OrganellesKritika MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1Dokument5 SeitenBiology 1Zeynep AkıNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question No 1:: 15Bt101-Biology For EngineersDokument7 SeitenQuestion No 1:: 15Bt101-Biology For EngineersPrachi ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDokument4 SeitenChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellmzunl254760% (1)
- Bio SciDokument6 SeitenBio ScilovemeluffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Dokument7 SeitenSLM Biotech Wekk 1 2Petronila LumaguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Wall StructureDokument2 SeitenCell Wall StructureDl Al-azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal CellsDokument4 SeitenPlant and Animal Cellsapi-238421605Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology F4 Teaching ModuleDokument13 SeitenBiology F4 Teaching ModuleNurfatin Jamaludin100% (1)
- 2 BioenergeticsDokument27 Seiten2 BioenergeticshanniemaelimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems SolutionDokument3 SeitenProblems SolutionJanelle Jabby ReidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestDokument8 SeitenCHAPTER III-3. The Cellular Basis of Life: Self TestLyka Abdullah TayuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Size and Shape - : Cells Ii: Cellular OrganizationDokument27 SeitenCell Size and Shape - : Cells Ii: Cellular OrganizationcadimogirlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance and Importance of Biochemistry in Nursing: UNIT-1Dokument7 SeitenSignificance and Importance of Biochemistry in Nursing: UNIT-1Sunil PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 9Dokument10 SeitenBio 9Rose Marie AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellDokument9 SeitenBiology Worksheet Activity 2 The CellAaron Lance LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDokument10 SeitenCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL CellsDokument8 Seiten2.1 Cell Theory: Heba Abd El Fattah May 2011 Biology SL Cellsansarish94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Euk. vs. ProkDokument46 SeitenEuk. vs. ProkDORY CAROLINA VICY OMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Date: - Biology F4 Rev. - Chapter 2 - Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokument2 SeitenName: - Date: - Biology F4 Rev. - Chapter 2 - Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationCasuarina NiraimathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineDokument2 SeitenL041 - Laboratory Exercise No. 1B - Dautil JastineJastine Managbanag DautilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The Cell WallDokument28 SeitenParts of The Cell WallJOSHUA DICHOSONoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology PROJECT REPORTDokument21 SeitenBiology PROJECT REPORTsahana nNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyDokument15 SeitenDLS 213 Selected Topics in BiologyNiña Angeline PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cell SummaryDokument3 SeitenAnimal Cell SummaryYasine Ayman TawfeekNoch keine Bewertungen
- AY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Dokument7 SeitenAY 2020 Sem 1 A104 P01 WS Team 2Lim Liang XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Chemistry 11Dokument250 SeitenBio Chemistry 11kalaikalai360100% (2)
- Biology Notes Chpter 2Dokument10 SeitenBiology Notes Chpter 2Wan HasliraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells Cell Membrane Over-Expansion Cell Plants Fungi Prokaryotic MycoplasmasDokument5 SeitenCells Cell Membrane Over-Expansion Cell Plants Fungi Prokaryotic MycoplasmasbbhoeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Biology Full NotesDokument12 SeitenUnit 1 Biology Full Notesbasima jawaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell BiologyDokument9 SeitenCell Biologyrubab azizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Prokaryotic CellsDokument33 Seiten3 Prokaryotic CellsYousef Wardat100% (1)
- Biology Unit 3. ContentsDokument7 SeitenBiology Unit 3. ContentsThanusri Vasanth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationDokument24 SeitenEukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationVARIGALA SAI CHARAN GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayDokument64 SeitenCell Structure: Abejay, Vanessa D. Balsomo, Princess Bangalan, JhayVanessaDulayAbejayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Life Science Module 5Dokument15 SeitenEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Theory: Functions of LifeDokument12 SeitenCell Theory: Functions of LifeSeila MoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Lesson NotesDokument8 SeitenCell Lesson NotesNikshita KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejercicios Del Tema 5Dokument44 SeitenEjercicios Del Tema 5Natalia Ricoy CallejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDokument2 SeitenCell Parts and FunctionsMian Nakahara0% (1)
- Reviewer in Science BDokument5 SeitenReviewer in Science BAshliah Aira MarohomNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS 2 The Cell TypesDokument11 SeitenLAS 2 The Cell TypesJeremie CataggatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C1 Algebra (Quadratics) PDFDokument5 SeitenC1 Algebra (Quadratics) PDFtaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community-Based Tourism (CBT) : Local Community Perceptions Toward Social & Cultural ImpactsDokument9 SeitenCommunity-Based Tourism (CBT) : Local Community Perceptions Toward Social & Cultural ImpactstaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium Review SL: Answers in Back!Dokument8 SeitenEquilibrium Review SL: Answers in Back!taengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRINTED ChemT4HLQDokument18 SeitenPRINTED ChemT4HLQtaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.2 Notes BioDokument2 Seiten8.2 Notes BiotaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS: Use of Maths Algebra & Graphs Practice Sheet Rearranging FormulaeDokument5 SeitenAS: Use of Maths Algebra & Graphs Practice Sheet Rearranging FormulaetaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debt Relief For Poor Countries: Rationale and ExpectationsDokument9 SeitenDebt Relief For Poor Countries: Rationale and ExpectationstaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exponential and Log Functions Quiz Non-Calculator MarkschemeDokument9 SeitenExponential and Log Functions Quiz Non-Calculator MarkschemetaengooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 NotesDokument30 SeitenChapter 5 NotestaengooNoch keine Bewertungen