Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
An Tibi Otik
Hochgeladen von
Bayu Agustinus0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten5 Seitenmm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenmm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
14 Ansichten5 SeitenAn Tibi Otik
Hochgeladen von
Bayu Agustinusmm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
Antibiotik
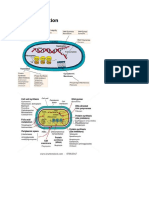
Structure of a Bacterial Cell
Cell Wall
-maintains cell structure
-composed of peptidoglycan, a
polymer of sugars and amino acids
Flagella
-tail-like structure used for locomotion
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg
Plasma Membrane
-phospholipid bilayer surrounding cell
-contains proteins that play a role in
transport of ions, nutrients, and
wastes
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of
Structure of a Bacterial Cell
Nucleoid
-region DNA is found in prokaryotes
DNA
-single double-stranded circular
chromosome
-no histone proteins
Plasmid
-small circular chromosome
-may carry an antibiotic resistance
gene
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg
Ribosomes
-site of protein synthesis (translation)
Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of
Antibiotics: Mechanisms of Action
Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
- some antibiotics bind to the large or small subunit of the
bacterial ribosome
Examples: neomycin,
streptomycin,
azithromycin,
erythromycin,
tetracycline
ciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellowshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg
of Harvard College.
Antibiotics: Mechanisms of Action
Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis
- some antibiotics bind to the large or small subunit of the
bacterial ribosome
Examples: neomycin,
streptomycin,
azithromycin,
erythromycin,
tetracycline
ciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellowshttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg
of Harvard College.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Convulsions (Seizures) : Prof. Dr. Shahenaz M. HusseinDokument26 SeitenConvulsions (Seizures) : Prof. Dr. Shahenaz M. HusseinAriefSuryoWidodo100% (1)
- Complete Blood Count in Primary CareDokument21 SeitenComplete Blood Count in Primary CareBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain LabDokument36 SeitenBrain LabBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Typhoid Fever (WHO)Dokument48 SeitenDiagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Typhoid Fever (WHO)Nina KharimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jandrol 107 004630Dokument12 SeitenJandrol 107 004630Bayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anamnesis: (Recollection, A Patient Case History)Dokument13 SeitenAnamnesis: (Recollection, A Patient Case History)AlbertoKosasihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute DiarrheaDokument32 SeitenAcute DiarrheaBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell EnvelopeDokument25 SeitenCell EnvelopeBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Berat Otak ManusiaDokument1 SeiteBerat Otak ManusiaBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic ActionDokument3 SeitenAntibiotic ActionBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal THTDokument4 SeitenJournal THTnuzzrdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Pharyngeal Packing During Nasal SurgeryDokument7 SeitenEffect of Pharyngeal Packing During Nasal SurgeryBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NICE Fever GuideDokument38 SeitenNICE Fever Guidedante_chungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jandrol 107 003731 PDFDokument9 SeitenJandrol 107 003731 PDFBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jandrol 109 009035Dokument7 SeitenJandrol 109 009035Bayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 57418347Dokument5 Seiten57418347Bayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sinusitis SmokerDokument7 SeitenSinusitis SmokerBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acupuncture For Refractory Cases of Sudden Hearing LossDokument7 SeitenAcupuncture For Refractory Cases of Sudden Hearing LossBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Reading - CoverDokument1 SeiteJournal Reading - CoverBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- OE Anak Dex Bella 8Dokument4 SeitenOE Anak Dex Bella 8Bayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Reading - CoverDokument1 SeiteJournal Reading - CoverBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal ReadingDokument19 SeitenJournal ReadingBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laparoscopy and Laparoscopic SurgeryDokument28 SeitenLaparoscopy and Laparoscopic SurgeryBayu AgustinusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rhinitis AllergiDokument9 SeitenRhinitis AllergiTri RatnawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelsDokument1 SeiteBmifa Boys Z 5 19 LabelssufigueiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)