Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Flowers Lecture 2016 2017
Hochgeladen von
Kristiane Reyes De Villa0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten22 Seitena power point presentation about the formation of flowers in Angiosperm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldena power point presentation about the formation of flowers in Angiosperm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten22 SeitenFlowers Lecture 2016 2017
Hochgeladen von
Kristiane Reyes De Villaa power point presentation about the formation of flowers in Angiosperm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
Flowers
Flowers
A modified reproductive shoots
(A stem with an apical meristem that give rise leaf
primordia)
Has determinate growth
Modified leaf bearing sporophylls
Flower Anatomy and Physiology
Perianth
Androecium
Gynoecium
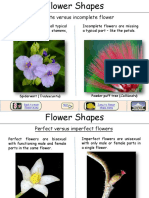
Flower Sex- refers to the
presence/absence of
male and female parts
Perfect/Bisexuals- both
stamen and carpels
are present
Imperfect/Unisexualspresence of either
stamen or carpels
Two types of imperfect flower:
1. pistillate
female flower
2. staminate
male flower
Plant Sex- refers to the
presence and distribution
of perfect and imperfect
flowers on individuals of a
species.
Hermaphroditic- with only
bisexuals flowers
Monoecious- with only
unisexual flowers (both
staminate and pistillate in
one individual)
Dioecious- plant with one
unisexual flowers but with
staminate and pistillate on
separate individual
Plant Sex Examples
3. Number of flower parts
a. Dicotyledonous
- flower parts in 4s
and 5s or divisible by
4 or 5
ex. magnolia
b. Monocotyledonous
- flower parts are in 3s
or divisible by 3s
Patersonia
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
-
Explains the genetics behind the
formation of the different whorls
in a flower
it was proposed by George
Haughn and Chris Somerville
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
KEY CONCEPTS
-A, B and C Genes
-A and C are equally dominant
-B is always expressed in
association with A and C
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
A= Sepals
A + B = Petals
B + C = Stamen
C = Carpel
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
WILD TYPE (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
A alone
A+B
B+C
C alone
C
B
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene A (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
A alone
A+B
B+C
C alone
C
B
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene A (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl
Whorl1:1:CARPEL
SEPAL
Whorl
Whorl2:2:STAMEN
PETAL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
C alone
alone
A
B+C
A+B
B+C
C alone
C
B
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene B (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
A alone
A+B
B+C
C alone
C
B
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene B (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
SEPAL
CARPEL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
A alone
AA+B
alone
C B+C
alone
C alone
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene C (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
Whorl 3: STAMEN
Whorl 4: CARPEL
A alone
A+B
B+C
C alone
C
B
ABC MODEL OF FLORAL DEVELOPMENT
Mutation in Gene C (Arabidopsis thaliana)
Whorl 1: SEPAL
Whorl 2: PETAL
Whorl
Whorl3:3:STAMEN
PETAL
Whorl
Whorl4:4:CARPEL
SEPAL
A alone
A+B
B+C
A+B
C
A alone
A
B
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Caraway. The Genus Carum (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants - Industrial Profiles)Dokument198 SeitenCaraway. The Genus Carum (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants - Industrial Profiles)Stefan CarareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methods of Hybrid Seed ProductionDokument16 SeitenMethods of Hybrid Seed ProductionSantosh Badiger UHS19UG4508Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flora of British in 02 Hook RichDokument808 SeitenFlora of British in 02 Hook Richsksingl350100% (1)
- PD Budget of Work-PerdevDokument1 SeitePD Budget of Work-PerdevKristiane Reyes De Villa67% (3)
- Chem Micropipette Calibration 2014Dokument15 SeitenChem Micropipette Calibration 2014Elisa PattonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusDokument17 SeitenStructure and Function of The Flower: CXC Biology SyllabusAmit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristic Features of FamilyDokument37 SeitenCharacteristic Features of FamilyRamling PatrakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parol Making ContestDokument1 SeiteParol Making ContestKristiane Reyes De Villa0% (1)
- NMAT 2019 Practice SetDokument72 SeitenNMAT 2019 Practice SetKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regional Business Plan-Manuscript-Of-EibagDokument12 SeitenRegional Business Plan-Manuscript-Of-EibagKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Equipment HandoutDokument4 SeitenLaboratory Equipment HandoutKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Woking PlanDokument1 SeiteWoking PlanKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenses and Mirrors PDFDokument13 SeitenLenses and Mirrors PDFKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProposalDokument1 SeiteProposalKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer SheetDokument1 SeiteAnswer SheetKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Wiz 2017Dokument1 SeiteScience Wiz 2017Kristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FBZ Plant TissueDokument6 SeitenFBZ Plant TissueKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH NR 01 en PDFDokument111 SeitenPH NR 01 en PDFKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 6 WorksheetDokument2 SeitenCHAPTER 6 WorksheetKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationDokument7 SeitenExp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationNurul Hana OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorbtion of WHP - Final of The FINALDokument6 SeitenAbsorbtion of WHP - Final of The FINALKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossword Puzzle AnswersDokument1 SeiteCrossword Puzzle AnswersKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Trees1Dokument6 SeitenCommon Trees1Kristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Thing I Ask PDFDokument2 SeitenOne Thing I Ask PDFNancy AlgosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6Dokument4 SeitenChapter 6Kristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationDokument7 SeitenExp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationNurul Hana OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding TyphoonsDokument10 SeitenUnderstanding TyphoonsKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationDokument7 SeitenExp 3 Flame Tests ConfigurationNurul Hana OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absorbtion of WHP - Final of The FINALDokument6 SeitenAbsorbtion of WHP - Final of The FINALKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Oxygen CycleDokument2 SeitenCarbon Oxygen CycleKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake 101Dokument3 SeitenEarthquake 101Kristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modified RootsDokument5 SeitenModified RootsKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Foood MacronutrientsDokument2 SeitenTesting Foood MacronutrientsKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roots and Its PartsDokument3 SeitenRoots and Its PartsKristiane Reyes De VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roots Developing From Plant Parts Other Than Radicle Are (1) Fibrous (2) Epicaulous (3) Adventitious (4) EpiphyllousDokument92 SeitenRoots Developing From Plant Parts Other Than Radicle Are (1) Fibrous (2) Epicaulous (3) Adventitious (4) EpiphyllousMonish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10.1023@A@1006063010677 Trema MicranthaDokument8 Seiten10.1023@A@1006063010677 Trema MicranthaClaudio SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBO10Dokument528 SeitenMBO10asmeraamde21Noch keine Bewertungen
- NON Flowering PlantsDokument3 SeitenNON Flowering PlantsPranay BendreNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDokument8 SeitenGRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Log Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Fridaymarjorie maraveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany (Flower)Dokument15 SeitenBotany (Flower)Louis Fetilo FabunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flower ShapesDokument27 SeitenFlower ShapesAnonymous 3GtngK6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class X Diwali Holiday AssignmentDokument47 SeitenClass X Diwali Holiday AssignmentAyush LanjiwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproduction in PlantsDokument10 SeitenReproduction in PlantsTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biology of Agricultural CropsDokument29 SeitenThe Biology of Agricultural Cropskaye nicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Reproduction SystemDokument30 SeitenPlant Reproduction SystemIzzati Zulaikha AmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangladesh Seed Production PDFDokument125 SeitenBangladesh Seed Production PDFYanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEB 2019-20 (24 Nov 2019) - Biology - Que & Ans - Revised PDFDokument12 SeitenNSEB 2019-20 (24 Nov 2019) - Biology - Que & Ans - Revised PDFMohammad Ashhar ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ProjectDokument26 SeitenBiology ProjectSaptarsi BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLASS - 7th SCIENCE, CHAPTER 8 (REPRODUCTION IN PLANTSDokument1 SeiteCLASS - 7th SCIENCE, CHAPTER 8 (REPRODUCTION IN PLANTSexperimentoboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flower Class 9Dokument10 SeitenFlower Class 9Shikha SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional BIOLOGY 12th NM Pa 1Dokument8 SeitenAdditional BIOLOGY 12th NM Pa 1JAGMOHAN SHARDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1 Bio PPT With HopeeeeDokument45 SeitenGroup 1 Bio PPT With HopeeeeLJ Princess Mary MontenegroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Botanical Terms - WikipediaDokument412 SeitenGlossary of Botanical Terms - WikipediaJanani SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany PPT 1Dokument60 SeitenBotany PPT 1SidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genbio 2 Las Q4 W1Dokument32 SeitenGenbio 2 Las Q4 W1Carmelia Jhan Fate AbrajanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-Flowering PlantsDokument45 Seiten03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET Biology Reproduction NotesDokument8 SeitenNEET Biology Reproduction NotesShubham Aggarwal0% (1)
- Minor Products of Philippine Fo - Brown, William HenryDokument450 SeitenMinor Products of Philippine Fo - Brown, William Henrydcollot8026Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDokument46 SeitenHow Do Organisms Reproduceharshita0% (1)