Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pantograph AND STRIGHT LINE MECHANISAMS
Hochgeladen von
Safeer M0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
806 Ansichten37 Seitenppt slide for Pantograph AND STRIGHT LINE MECHANISAMS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenppt slide for Pantograph AND STRIGHT LINE MECHANISAMS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
806 Ansichten37 SeitenPantograph AND STRIGHT LINE MECHANISAMS
Hochgeladen von
Safeer Mppt slide for Pantograph AND STRIGHT LINE MECHANISAMS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 37
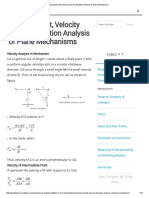
PANTOGRAPH
It is a four bar linkage used to
produce paths exactly similar to the
ones traced out by a point on the
linkage.
The paths so produced are usually on
an enlarged or reduced scale and
may be straight or curved ones.
It consists of a jointed parallelogram
ABCD as shown in the figure.
It is made up of bars connected by
turning pairs.
From similar triangles OAD and OBE,
Let O be fixed and the points D and E
move to some new positions D and E.
Then
Therefore the point E traces out the
same path as described by point D.
A pantograph is mostly used for the
reproduction of plane areas and
Straight-line Mechanisms
Generation of straight line motion
using linkage mechanisms called
straight line mechanisms
Although exact straight line cannot be
generated
simple mechanisms are designed such
that they can produce approximate
straight lines for short range of
motion.
There are two classes of straight line
mechanisms
Exact straight line linkages
Scott-Russels mechanism
Peaucellier Mechanism
Hart's Mechanism
Approximate straight line linkages
Watt's linkage
Roberts Mechanism
STRAIGHT-LINE MECHANISMS
1. Peaucellier mechanism
It consists of 8 links i.e. a fixed link
OO1 and the straight links O1A, OC,
OD, AD, DB, BC and CA are
connected by turning pairs.
The pin at A is constrained to move
along the circumference of a circle.
AC = CB = BD = DA; OC = OD; and
OO1 = O1A
From the triangles ORC and BRC,
Therefore the product OB X OA
remains constant.
Hence the point B traces a straight
path perpendicular to the diameter
OP.
2. Harts mechanism:
It consists of six links i.e. a fixed link
OO1 and straight links O1A, FC, CD,
DE and EF are connected by turning
pairs.
The pin at A is constrained to move
along the circumference of a circle.
FC = DE; and CD = EF;
The points O, A and B divide the links
FC, CD and EF in the same ratio.
Therefore the product OB X OA
remains constant. Hence the point B
traces a straight path perpendicular
to the diameter OP.
3. Scott-Russels
mechanism
It consists of a fixed member and moving
member P of a sliding pair.
The straight link PAQ is connected by
turning pairs to the link OA and the link P.
A is the middle point of PQ and OA = AP =
AQ.
If OA makes one complete revolution, then
P oscillate along the line OP through a
distance of 2 OA on each side of O, and Q
oscillate along QOQ through the same
distance 2 OA above and below O. Thus
locus of Q is a copy of the locus of P.
4. Watts mechanism
It is a crossed four bar chain mechanism and in
steam engines it guides the piston rod to have an
approximate straight-line motion.
In the mean position of the mechanism, links
OB and O1A are parallel and the coupling rod
AB is perpendicular to O1A and OB.
The tracing point P traces an approximate
straight line over certain positions of its
movement.
5. Grasshopper mechanism
It
is the modification of modified Scott-
Russels mechanism with the
difference that Point P does not slide
along straight line.
It is a four bar mechanism and all the
pairs are turning pairs.
In this, O and O1 are fixed and link OA
oscillates about O.
OA = (() / (AQ).
6. Tchebicheffs mechanism
It is a four bar mechanism in which
crossed links OA and O1B are of
equal length.
The point P, which is the mid-point of
AB, traces out an approximately
straight line parallel to OO1.
AB : OO1 : OA = 1 : 2 : 2.5
7. Roberts mechanism
It is a four bar mechanism, Where
CPD is a single integral link.
Also Dimensions AC, BD, CP and PD
and AB = 2AP
The point P trace out an
approximately straight line.
8. Kempes Mechanism
Here, AB = AD, BC = CD = CE, BF = FE
and (AB/BC) = (BC/BF).
It is obvious that angle ABC = angle
ADC = angle CEF.
Now we can show that as this linkage
(with any of the links in the chain
fixed) moves, the line DE always
remains perpendicular to AB
Ackerman Steering
Mechanism
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Math Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)Dokument542 SeitenMath Quest Math Methods VCE 12 (2016 Edition)NhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD-CAM Power Point PresentationDokument102 SeitenCAD-CAM Power Point PresentationArgAshishGargNoch keine Bewertungen
- ComparatorsDokument54 SeitenComparatorsbasanna_rvce60% (5)
- 44-Slider Crank Mechanism Using HacksawDokument15 Seiten44-Slider Crank Mechanism Using HacksawsathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduation Program FinalDokument13 SeitenGraduation Program FinalJoy Pasion100% (1)
- Velocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationDokument63 SeitenVelocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationMPee Finance SumerpurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line Motion Mechanisms OldDokument28 SeitenStraight Line Motion Mechanisms OldVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (4)
- Conjugate Tooth-1-2 PDFDokument8 SeitenConjugate Tooth-1-2 PDFHarshavardhan Kutal100% (1)
- KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY: UNIT 2: VELOCITY & ACCELARATION: Objective Questions From Gate With SolutionsDokument7 SeitenKINEMATICS OF MACHINERY: UNIT 2: VELOCITY & ACCELARATION: Objective Questions From Gate With SolutionsVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Suspension System With Preview ControlDokument5 SeitenActive Suspension System With Preview Controlrudey18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsDokument13 SeitenMachine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsHimanshuSisodiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1Dokument41 SeitenLecture 1norhaslina_aa33% (3)
- Cotter Joint - Design Procedure, Problems & Question AnswerDokument15 SeitenCotter Joint - Design Procedure, Problems & Question AnswernkchandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Modeling and Assembly of Screw JackDokument8 Seiten2 Modeling and Assembly of Screw Jackselva_raj215414Noch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Drawing-Short Answer QuestionsDokument3 SeitenMachine Drawing-Short Answer QuestionsfatehjitsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering CurvesDokument80 SeitenEngineering CurvesUtkarsh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Riveted JointsDokument72 Seiten7 Riveted JointsanirudhNoch keine Bewertungen
- EG All Problems Tutorials TW 06-07Dokument19 SeitenEG All Problems Tutorials TW 06-07Chirag Patel100% (2)
- Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Plane MechanismsDokument10 SeitenDisplacement, Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Plane MechanismsHimmatSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD VIVADokument6 SeitenAutoCAD VIVADeva RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With AnswersDokument6 SeitenME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With Answerspremgmech762Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 PPT DOM 3.9.21Dokument27 SeitenUnit 2 PPT DOM 3.9.21MURALI KRISHNAN RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of MachineDokument21 SeitenTheory of MachineVaibhav Vithoba NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Unit II Imp QuestionsDokument2 SeitenDom Unit II Imp QuestionsSree MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and Torque MeasurementsDokument30 SeitenForce and Torque MeasurementsArunabha Datta100% (3)
- Unit2&3 HRDokument60 SeitenUnit2&3 HRtarasasankaNoch keine Bewertungen
- V2 ECU For AMT TurbinesDokument26 SeitenV2 ECU For AMT TurbinesAmin Anjom100% (1)
- AIP Lab Manual - 012110050524 - 1Dokument11 SeitenAIP Lab Manual - 012110050524 - 1Martin De Boras PragashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Aided Machine DrawingDokument16 SeitenComputer Aided Machine DrawingAmit Bhagure0% (1)
- Lesson 9 Development of Surfaces - IDokument12 SeitenLesson 9 Development of Surfaces - IAKSHANSH MATHURNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering DrawingDokument17 SeitenEngineering DrawingprashmceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 and 3 Mechanics of MachinesDokument21 SeitenUnit 2 and 3 Mechanics of MachinesYogaraja JeyarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-4 Design of RivetDokument15 SeitenCh-4 Design of RivetTadesse AyalewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineeeing DRAWING PDFDokument8 SeitenEngineeeing DRAWING PDFMUHAMMAD KAMRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 40905-Engineering Graphics PDFDokument2 Seiten40905-Engineering Graphics PDFKrishna MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Drawing Sample QuestionDokument10 SeitenEngineering Drawing Sample QuestionDeepakDhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Design-II Question BankDokument9 SeitenMachine Design-II Question BankProf. Avinash MahaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ED Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument7 SeitenED Multiple Choice QuestionsLaxmireddy Peram43% (7)
- Kom Basics of MechanismsDokument64 SeitenKom Basics of MechanismsRadhaboy Karthi0% (1)
- Lathe Feeding and Apron MechanismDokument22 SeitenLathe Feeding and Apron Mechanismadhees100% (2)
- Brakes & Dynamometers - Machine Dynamics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDokument7 SeitenBrakes & Dynamometers - Machine Dynamics Questions and Answers - SanfoundryINFO TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyDokument54 SeitenUnit - V: Manufacturing TechnologyIjanSahrudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering-Curves 1Dokument17 SeitenEngineering-Curves 1api-327264533Noch keine Bewertungen
- Projection of SolidsDokument27 SeitenProjection of SolidsAYUSH ACHARYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinematics of Machines PDFDokument133 SeitenKinematics of Machines PDFarjunNoch keine Bewertungen
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 MarksDokument20 Seiten081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - 2 Markssara vanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad Cam Mtexam 2Dokument3 SeitenCad Cam Mtexam 2khalil alhatabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Transmission SystemDokument23 SeitenDesign of Transmission Systemspsurya2013100% (2)
- Machine Drawing Question BankDokument11 SeitenMachine Drawing Question BankSheshikanth DonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-4-Computer Aided DesignDokument15 SeitenUnit-4-Computer Aided DesignMuthuvel M100% (2)
- Mechanisms With Lower PairsDokument43 SeitenMechanisms With Lower PairsVincentius NikimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bcme NotesDokument112 SeitenBcme NotesSms RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument1 SeiteAssignment 1Frank JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Machine and MechanismsDokument21 SeitenTheory of Machine and MechanismssrujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.acceleration of Gear SystemDokument9 Seiten6.acceleration of Gear SystemMuhammed Shameem N Edavannappara50% (2)
- Me 8594 Dynamics of Machinery Unit 1 Online Video LectureDokument42 SeitenMe 8594 Dynamics of Machinery Unit 1 Online Video LecturesankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turner Question and Answer Bank 2014 PDFDokument88 SeitenTurner Question and Answer Bank 2014 PDFBhanupratap MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism Synthesis, Graphical - Lect1Dokument22 SeitenMechanism Synthesis, Graphical - Lect1Naveen KanchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line Motion MechanismsDokument5 SeitenStraight Line Motion MechanismsSyed RoshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Straight Line Motion Mechanisms: Rajesh KumarDokument59 SeitenStraight Line Motion Mechanisms: Rajesh KumarSaiharsha VardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KOM DrawingsDokument36 SeitenKOM Drawingsdineshkarthikofficial280903Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Steering MechanismDokument19 SeitenTypes of Steering MechanismAnkit TaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Questions DomDokument5 SeitenPrevious Questions DomSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kerala Water Authority Assistant Engineer PDFDokument7 SeitenKerala Water Authority Assistant Engineer PDFSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 6: Department of Mechanical Engineering MKSSS's Cummins College of Engineering For WomenDokument7 SeitenExperiment No. 6: Department of Mechanical Engineering MKSSS's Cummins College of Engineering For WomenSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me306 ADokument2 SeitenMe306 ASafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V PDFDokument27 SeitenUnit V PDFSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.bpt 1213 PDFDokument110 Seiten3.bpt 1213 PDFSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collage Making CompetitionDokument1 SeiteCollage Making CompetitionSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example 1 - Automatic Coffee Maker Answer A. Product RequirementsDokument2 SeitenExample 1 - Automatic Coffee Maker Answer A. Product RequirementsSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDM KTU AMT Notes Module 4Dokument37 SeitenEDM KTU AMT Notes Module 4Safeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijenm-2011-Ptr, PRR, TGDokument13 SeitenIjenm-2011-Ptr, PRR, TGSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Third Semester B.Tech Degree Model Examination, Dec 2015 Me 14 307 Computer Assisted Machine DrawingDokument4 SeitenThird Semester B.Tech Degree Model Examination, Dec 2015 Me 14 307 Computer Assisted Machine DrawingSafeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- En09 108 Engg Graphics - May11Dokument2 SeitenEn09 108 Engg Graphics - May11Safeer MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Managers of Their Homes Schedule Tues - FriDokument2 SeitenOur Managers of Their Homes Schedule Tues - Frifourshopping100% (2)
- Smaga Resume 2014Dokument2 SeitenSmaga Resume 2014api-253376205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Folding CirclesDokument3 SeitenFolding CirclesAnonymous Y2qwEuA100% (1)
- Modul 10 Set K2Dokument8 SeitenModul 10 Set K2Ting ShiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karmen Jones Resume WordDokument3 SeitenKarmen Jones Resume Wordapi-356487836Noch keine Bewertungen
- CD - CBSE X - Mathematics-Standard - Paper - 1Dokument8 SeitenCD - CBSE X - Mathematics-Standard - Paper - 1Pushpakar ChandrakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ivo Andrić THE RED FLOWERDokument10 SeitenIvo Andrić THE RED FLOWERivandelachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacc Program Emcee Guide 2012Dokument7 SeitenBacc Program Emcee Guide 2012Antonette HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Key & Sol'sDokument19 Seiten01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Key & Sol'sGowri ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 11Dokument9 SeitenApril 11Catherine LapeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabassum BhuiyanDokument1 SeiteTabassum Bhuiyanapi-570828846Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rampem Pradeep 12 ADokument27 SeitenRampem Pradeep 12 Aprabhaharendra24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Herbert J. Bernstein and Anthony V. Phillips - Fiber Bundles and Quantum TheoryDokument25 SeitenHerbert J. Bernstein and Anthony V. Phillips - Fiber Bundles and Quantum TheoryJummoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW 1 SolutionsDokument11 SeitenHW 1 Solutionsellie<3100% (1)
- RECOGNITION AWARD CERTIFICATE FormatDokument6 SeitenRECOGNITION AWARD CERTIFICATE FormatJeremy VicerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Lets PlayDokument59 SeitenUnit 2 Lets PlayNURALIAH IZATI BINTI MAT JANI KPM-GuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Stephanie Joy D. Frane Date: June 4, 2021 Grade & Section: 8-Leeuwenhoek Performance Task 2Dokument3 SeitenName: Stephanie Joy D. Frane Date: June 4, 2021 Grade & Section: 8-Leeuwenhoek Performance Task 2mark_anthony_vidalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics QuizDokument2 SeitenMathematics QuizCyril DaguilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure in The Ranking of Honor PupilsDokument15 SeitenProcedure in The Ranking of Honor PupilsNormandy MiraflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA211 Assignment 1 Cover PageDokument11 SeitenMA211 Assignment 1 Cover PageNikasha DeviNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Grade Geometry and Fractions-1Dokument72 Seiten2nd Grade Geometry and Fractions-1Ирина ДумитрашкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- Missouri Learning Standards For Math 2017Dokument3 SeitenMissouri Learning Standards For Math 2017Cheryl Townsend DickNoch keine Bewertungen
- RD Sharma Solutions (Ex - 1. 5, 1.6, 1.7 & 1.8) - Rational Numbers - RD Sharma SolDokument15 SeitenRD Sharma Solutions (Ex - 1. 5, 1.6, 1.7 & 1.8) - Rational Numbers - RD Sharma SolSunil AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea 2Dokument10 SeitenTarea 2Felipe López GarduzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics Question Bank For Summative AssesmentDokument29 SeitenMathematics Question Bank For Summative AssesmentApex InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ersw Narrative EssayDokument4 SeitenErsw Narrative Essayapi-275340609Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contoh Judul Skripsi Tentang English SpeakingDokument2 SeitenContoh Judul Skripsi Tentang English Speakingtuti purnama0% (1)