Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Habitat Centre
Hochgeladen von
RashmiJoshiCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Habitat Centre
Hochgeladen von
RashmiJoshiCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SYNOPSIS
INTRODUCTION TO HABITAT CENTRE-
The India Habitat Centre is a multipurpose building in New Delhi, India.
It is India s most comprehensive convention centre.
It provides a combination of work, commercial and social spaces.
The India Habitat Centre was started in 1993.
The public agency for Housing and Urban Development Corporation Ltd (HUDCO)
wanted an office building for its workers and invited non-profit organzations that shared
their concern with habitat to share that work space.
The Habitat Centre is home to offices and provides wide range of facilities like
conference venue, exhibition halls, seminar rooms, restaurants and auditorium.
REGIONAL HABITAT CENTRE-
HUDCO being one of the main promoters of IHC at Delhi has decided to replicate the
concept in different states of the country.
The regional Habitat centre would provide office spaces to various organizations.
It would serve as a centre of contemporary cultural, economic, business and social
events.
Regional Habitat centre would serve as a arts and cultural hub.
SITE BRIEF-
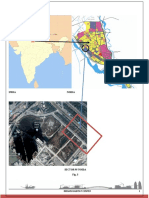
The site is located in sector 68, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar (SAS nagar ).
Named after Sahibzada Ajit Singh, the eldest son of Guru Gobind Singh, it is also
referred to as Mohali.
Being a satellite town of metropolis Chandigarh, it is extension of Chandigarhs grid
pattern.
The trio of Mohali, Panchkula and Chandigarh is called Chandigarh tricity.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SYNOPSIS
This project is part of Punjab Governments effort through Punjab Infrastructure
Development Board and Greater Mohali Area Development Authority to transform
Mohali, various projetcts fall under this scheme like
Mohali International Airport,
Knowledge city,
Aerotropolis Development,
Social recreational and sports infrastructure like Habitat Centre, Golf Course, Sports
club.
Extracts from presentation
Site is located in sector 68, Mohali.
on Mohali by GMADA
The site is a corner plot having access from two sides with one road being developed
into urban expressway within the city as part of airport connectivity.
DEVELOPMENTAL CONTROL-
Ground Coverage 40%
F.A.R 1.5
Parking 2 ECS per 100qm
VALIDITY-
Mohali is the face of developing Punjab but it lacks integrated facility which has mix of
activities providing work areas as well as rejuvenates the cultural aspect.
Mohali is emerging as a I.T destination and the presence of I.T park in Chandigarh itelf, Site for Habitat Centre, sector 68
Habitat centre would provide a platform for interaction among professionals.
Proposals like City centre, knowledge centre, Golf courses around the site makes the site
viable for the project.
Chandigarh domestic airport being converted into International airport makes the tricity
an area of tremendous growth.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SYNOPSIS
AIM-
Establish a non-profit organization to promote arts and crafts.
To provide global recognition to city.
To boost the economy of tricity by providing business centre.
To organize and promote conferences, seminars,lectures, public debates, and exhibitions relating to habitat and environment.
To make human life meaningful, healthy and responsive by providing various recreational facilities.
OBJECTIVES-
To incorporate the concept of sustainability.
To create a structure that not only caters to the functional aspects but also become an architectural landmark by incorporating the architectural style of
Le-Corbusier.
To create inter-relationship between open, semi-open and covered areas and to use landscape in such a way that each open area offers a different mood.
SCOPE-
The scope of thesis will be restricted to the detailed site plan showing the placement of various functional areas and landscaped areas.
Detailed architectural drawing and views of the identified functional areas.
Requirements
Cultural/rec- Guest
Convention
-reational Office area
areas areas house
Open air
Restaurant Health club
Art gallery theatre
Conference Business Multipurp--
Audi. Library
halls centre -ose hall
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SYNOPSIS
METHODOLOGY
SELECTION OF PROJECT
BACKGROUND STUDY
SITE SELECTION
DATA COLLECTION
LITERATURE STUDY DETAILED SITE ANALYSIS CASE STUDY
EVOLUTION OF DESIGN HILOSPHY
RELATIONSHIP OF OPEN AND BUILT SPACES
PRELIMINARY DESIGN
FINAL DESIGN
LITERATURE STUDIES-
Genzyme Centre, Cambridge to study the aspects of sustainability in office buildings.
Kimbell Arts Museum, Texas to study the lighting in art galleries and exhibition areas.
CASE STUDIES-
India Habitat Centre, New Delhi
Damcosoft Pvt.Ltd., Chandigarh
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
CHAPTER-2 LITERATURE STUDY
GENZYME CENTRE,CAMBRIDGE
KIMBELL ARTS MUSEUM, TEXAS
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
GENZYME CENTRE, BOSTON
INTRODUCTION-
Location -
Area - 10 acres
Architect - Behnsich architects,L.A
Year of - 2000-2004
construction
Genzyme centre, a LEED platinum rated building is a corporate headquarters of a
biotechnology company, the company focuses reasearch on rare genetic diseases.
It houses 920 workspaces over 12 floors, libraries, training room ,conference rooms,
cafes and public retail spaces.
The goal of design was to develop a sustainable building from individual working
environment to the overall complex.
Daylight is one of the most important features of the building.
Building uses combination of innovative features to scatter the light throughout the GENZYME CENTRE,BOSTON
building.
LOCATION -
The site is a 10 acre urban brownfield site in East Cambridge.
The site initally served as a gas manufacturing plant for 100 years, releasing toxic
chemicals in the site and converting into a brownfield.
APPROACH-
The site as access from two side, with Kendal street on south side and Athenaeum
street on west side.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
DESIGN-
The building has implementation of broad deign strategies intended to achieve the most
sustainable building, like atrium concept, natural daylight , ventilation system,
exterior facades, building management system .
The design team focused on five-part framework to frame their strategies-
Site development
Water saving
Energy and efficiency
Material selection
Indoor environment quality
ELEVATIONS- each elevation is differently engineered so that each faade can cope Inter play of projection and recessions to provide shading
with the climatic conditions.
South faade- the south faade uses double glass skin and 1.5m cavity zone
East and west faade- incorporate blinds operated on building management system that
track the sun, and the angle is adjusted so that maximum daylight is achieved without
solar gain.
North faade- clearly glazed to gain maximum daylight.
Double glazed south facade
The faade has series of projection and recessions, the projections provide shading to
spaces below
PLAN-
The plan follows the site boundaries, resulting in a building that is nearly square.
The 12 storey atrium is largely a public space having exhibition area, a grand staircase
and a large pool.
The reception is on the first floor and is reached by grand timber staircase.
The circulation spaces are larger than functionally necessary in the belief that informal
discussions on stair, lifts, coffee machines can encourage knowledge transfer.
Instead of providing large management and research offices, various terraces,
walkways, corners are furnished to encourage spontaneous discussions.
Plan- integrating green areas into the
built environment
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
SUSTAINABLE FEATURES-
ATRIUM-
The atrium is major source of cross and stack effect ventilation.
Most offices overlook the atrium.
The Genzyme Centre by design through its central 12 storey atrium maximizes natural
light .
Stack effect- the warmer indoor air rises up through the building and escapes at the top
through openings in the ceiling, the rising warm air reduces the pressure in the base of
the building, drawing cold air in through openings.
DAYLIGHTING-
As a result of the design, 75% of the employees have outside views and 90% employees Stack effect- hot air expelled out, cool air forced in
have sufficient natural light.
Technologies used are- double glazed windows, heliostats, reflective ceiling tiles,
prismatic chandeliers.
Double glazed windows- They works by trapping air between two panes of glass.
The building is enveloped in a double faade of glass, called the loggia, which covers
over 32 percent of the building exterior.
The double glazed windows have vents to draw in fresh air while minimizing solar heat
gain.
Heliostats- the amount of daylight is further increased by seven moveable heliostats.
Heliostats on the roof track the sun and direct it to the mirrors installed on the roof. Double glazed facades Prism chandelier to distribute light
The mirrors then directs it to the building atrium.
Prism chandelier- the distribution of light is further enhanced by 768 prismatic plates
that reflect light into the building and also act as a piece of art.
During the day they reflect the sunlight and at night they diffuse light and eliminate
glare from the halogen lights that are turned on at night.
Sun rays Heliostat Mirrors Prism chandelier
Heliostats on roof track the sun and
redirect solar radiations on the mirrors
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
LIGHT WALL-
The atrium has a light wall.
Light walls is cladedd with polished aluminium panels, which redirect solar radiation
incident on them.
PERFORATED BLINDS-
Along the glass exterior, computer-controlled blinds automatically track the suns
position and open to desired angles to let light in.
All of the blinds close automatically at night to prevent light pollution in the
surrounding neighborhood. Light wall reflects the light and increases its penetration
Daylight from the exterior is then directed to reflective ceiling panels which carry the
light into the core of the building.
GREEN ROOFS-
The green roof of Genzyme centre spread across 50% of the roof .
Plantings on the roof reduce storm water runoff and absorb heat ,these arid plants
require little water.
INTERIORS-
A large twelve storey brings daylight deep into the building using heliostats, mirrors,
and prim chandelier.
Large stairways, multiple open lounge areas are dispersed throughout the building, such
open spaces allow for air and light circulation. Perforated blinds to let-in light
18 interior gardens, 4 accessible terrace gardens, prism chandelier, reflective pool on
first floor increase workers connection with nature and contribute to quality indoor
environment.
Interiors-Genzyme centre
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
WATER CONSUMPTION AND CONSERVATION-
The building uses 34% less water than conventional buildings.
Water conservation measures include installation of low flow fixture, waterless urinals,
Open plan
water fountains with motion sensors. to allow
Moisture sensors in landscaping to reduce uneccessary watering. daylight
Stormwater collected from roof is used for irrigation. Waterless
fixtures Use of
Unused stormwater is treated before releasing it to drain system. atrium
Rainwater
collection
LANDSCAPING- Energy Use of
Water skylights
The property is landscaped with native and adaptive plants to reduce water, fertilizer Native
plantations use of
and pesticide use.
photovoltai
Irrigation c panels
SUSTAINABLE MATERIALS- systems
occupancy
The property is landscaped with native and adaptive plants to reduce water, fertilizer sensors
and pesticide use.
23% of the materials used in the construction had recycled content, including steel,
aluminium, tiles, ceilings, carpets.
The steel rebar is 100% post consumer waste recycled content, steel railings have 70%
recycled content.
In addition to using recycled content materials,70% of the materials used were from Allow
Certified outdoor
local sources, choosing locally made products reduces the amount of fuel consumed in wood views
delivery .
Recycled Indoor
Wood used inside is certified, meaning that the wood was harvested from a forest that Material content environme
bring in
nature
was being sustainably managed. s material nt
93% of the construction waste was recycled. Locally Ample
available daylight
PARKING- materials
Parking is provided below the building, in the basement to reduce hard paved surfaces
and reduce heat island effect.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
KIMBELL ARTS MUSEUM, TEXAS
INTRODUCTION-
Location - Texas
Area - 10 acres
Architect - Louis Kahn
Year of - 1967-1972
construction
INTRODUCTION-
Kimbell Museum is one of the finest lighted buildings in the world.
Kahn designed a building in which light is the theme.
The museum is famous for its vaults and lighting system.
As expansion of the museum, a modern pavillion was built in 2013. Kimbell Art Museum, Texas
Kahn took three years to produce four designs proposals for the museum , the common
element in all of its proposals was the use of cycloid roofs.
Each space should be defined by its structure and the nature of its natural light.
Even a dark space designed to remain in dark should be light enough, from any
mysterious openings, which shows us how dark it is in reality.- Louis-i-kahn
CONCEPT- Roman arches and vaults as source of inspiration
Kahn designed a building in which light is the theme.
The structure is inspired from Roman architecture particularly the use of vaults,
storage warehouses to Egyptian warehouses.
The structure is designed as a room with a vaulted ceiling that would allow natural light
to enter the space from above.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
SITE-
The museum is located in Fort Worth with total site area of 3.8 hectares.
The site houses Kahns designed museum on the eastern side and Renzos museum on
the western side.
The two structures face each other and are located at a distance of 61mts from each
other.
Piano pavilion consists of 2 blocks separated by glazed passage.
Piano Pavilion
Kahn building
Renzo Piano Kahn Building
Piano Pavilion consists of two structures, with one at ground lvl.
and other one below the ground lvl.
2 1. Entrance lobby
PLAN, KAHN BUILDING- 3 6 2. Auditorium
3. Book store
6 1 5 4. North gallery
The plan is C shaped with three wings, each 100 long .
6 5. South gallery
North and south wing each have six vaults, five vaults act as roofing for interior spaces 4 6. Courtyard
and sixth vault act a porticos.
The western side forms a recessed entry porch, facing a courtyard partially enclosed by
two outside wings.
Exhibition galleries are located on both sides of the entrance under the vaults.
The museum ha three glass walled courtyards that bring in natural light to gallery space. 1
The plan is open in nature with supports at only at corners to minimize obstruction in 2
gallery spaces. 3
The galleries are as flexible as possible within the spaces roofed by vaults, moveable
4
walls can be attached to the soffits (underside of the vaults).
The galleries are provided at upper floors to have maximum natural light. 5
Six vaults,5 act as roofing system and
6th act a portico
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
DAYLIGHT-
The element of natural light is the theme of the design.
The museum is constructed of a series of vaults, each 100 long and 23 wide with a
clear skylight at ridge.
The skylight admits light through the use of curved aluminum reflectors which reflect
most of the light onto the underside of the vault and downward to the floor.
Additional natural light enters the space at each end wall through a narrow glass light
band that follows the curvature of the vault.
Two rails of spotlights are provided beneath the reflector panel. Vaulted ceiling with central slit for light
RENZO PIANO PAVILION- KIMBELL ARTS MUSEUM
New structure called the Piano Pavilion was constructed to accommodate the Kimbell
Museums growing art collection.
New building sets across the garden and faces the Kahns building.
Pianos design draws inspiration not only from its architectural organization, materials
and textures but also its use of natural light.
The building is finished with glass and light grey concrete. Glass band b/w vaults to admit light
Pianos pavilion houses gallery spaces, 298 seat auditorium, clasrooms, offices, library,
art preparation area, cafe and book store.
The buildings 300 long entrance faade is divided into three bays , a recessed glass
entrance and a wing to each side .
Buildings are located at right distance to have a dialogue- Ar. Renzo Piano,
On being asked about the distance between Kahns bldg. and Piano Pavilion
Recessed main entrance- Piano Pavilion
2nd block tucked
below ground
Entrance faade divided intro three bays level
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
LITERATURE STUDY
PLAN-
The new building consists of two connected structures.
The front section- the flying pavilion has museum entrance and two galleries spaces.
A glazed passageway leads to the second structure.
The second structures is tucked under green roof and houses auditorium, gallery of light
sensitive exhibits and offices.
The second structure is below the ground level.
THE ROOF-
29 pairs of 100 long wooden beams allow the galleries to be completely open and
system of moveable partitions can be arranged below the beam.
LED spotlights are suspended from the tracks positioned in between the wooden beams.
The roof performs array of functions, above the glass roof is photovoltaic louver
system, which regulate the amount of light entering the space and it can be fully of
partially opened between 0-45 deg. Plan- Renzo Pavilion , two blocks connected by glazed passage
The photovoltaic cells generate enough power to meet about 70% of energy.
DAYLIGHT-
The glass roof admits light into the galleries, the amount of light is regulated by
louvers.
Full glazed facades on eastern and western sides light up the interiors.
Natural light enters the auditorium via light well.
The light well sits behind the rear glass curtain wall.
SUSTAINABILITY- Photovoltaic louvers on glass roof regulating the amt of light
The new building uses half the amount of energy as compared to Kahn building.
Much of the structure is below the ground level and only 1/3 is above the ground level.
The structure above the ground level accommodating the galleries is shaded by over
hanging glass roof.
The roof supports system PV panels that shade the direct sun and generate 50% of the
power required.
Glass roof of galleries
Light well of auditorium
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
CHAPTER-3 CASE STUDY
INDIAN HABITAT CENTRE,NEW DELHI
DAMCOSOFT PVT. LTD, CHANDIGARH
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
INDIA HABITAT CENTRE, NEW DELHI
INTRODUCTION-
Location - Lodhi road ,Delhi
Area - 9 acres
Architect - Joseph Allen Stein
Year of - 1988-93
construction
Indian Habitat centre was constructed to develop an integrated environment in which
various professions and institutions dealing with habitat and habitat related
environmental issues would function.
It is a place that handles an enormous variety of public and private activities, from
housing to banking to entertainment to food.
Indian Habitat Centre is home to 37 institutions, like TERI , HUDCO, COA, NID etc.
Though of an imposing nature, the building complex manages to blend in with its
surroundings through its natural embellishments.
In keeping with its habitat theme, the whole complex has been generously provided
with natural greenery to provide an undiluted experience of open nature. INDIA HABITAT CENTRE,NEW DELHI
The principle resolve of the centre- to restore at every level- environment and
ecological- a balanced and improved way of life to be reflected in concept and design.
FACILITIES-
1The I.H.C. provides the following facilities for
the use of member:
2 40,000 square meters of office accommodation
3 Conference rooms with a total capacity of 1000 in 10 locations.
4 60 Guest room, five suites.
5 A 700 sqm exhibition area.
6 A 250 seat amphitheatre.
7 An auditorium with 500 capacity.
Inter play of open areas and built-up
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
SITE ANALYSIS
LOCATION-
The India Habitat Centre (IHC) is located along the Lodhi Road on the fringes
of Lutyens Delhi.
Lodhi road Is home to various renowned organizations like India International
Centre, The Ford Foundation , Indian Meteorological Dept, Research And Analysis
Wing (RAW), to name a few.
ACCESSIBILTY- SITE SURROUNDINGS-
From Distance Time Lodhi Road , New Delhi is named after
the Lodhi Gardens located on it.
International 15 Kms. 30
Airport mins. A number of cultural ,educational
international institutions line the road India Habitat centre Location of Habitat centre
Domestic 12 Kms. 20
Airport mins.
Site surroundings include organizations
New Delhi 07 Kms. 15
like India International centre, The Ford
Railway mins.
Foundation , Indian Meteorological Dept,
Station
Research and analysis wing (RAW)
Old Delhi 16 Kms. 30
Railway mins. The area was referred to as
Station STEINABAD due to presence of
Ford Foundation India International Centre
Connaught 05 Kms. 07 various architectural creations of Stein on
Place mins. this stretch.
OBSERVATION-_
India Gate 03 Kms. 05
Building has typical character, somins.
it impresses the passerby.
On both sides are roads having fast moving traffic leading to noise disturbance,
so maximum landscaped are provided near periphery to overcome this.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
APPROACH- Entry for convention centre
Service entry
(Gate-3)
The site has access from three sides, having the Lodhi Road on the north,
Max Muller Marg towards the west and Vardhaman Marg on the southern side.
SITE CHARACTER-
Total Site Area 9 acres
Fire Tender
entry
Topography Plot is L-shaped with primarily flat terrain. ( Gate-2A)
CIRCULATION-SITE LEVEL
The L-shaped complex has an access from three sides, with the Lodhi Road
(Gate-1) on the north, Max Muller Marg (Gate-2 ,2A) towards the west and
Vardhaman Marg (Gate 3,3A) on the southern side.
Entrance
For office
All the gates lead to the double basement parking. blocks
Gate-1 on Lodhi Road has surface parking for chauffer driven cars. ( Gate-2)
Lodhi road has dedicated pedestrian entry.
Gate 2A serves as entrance for fire tender.
Entrance for
Gate 3A is used as service entry for restaurants and Office blocks Pedestrian entry
guest house. ( Gate-1)
Vehicular movement is restricted to the periphery
Circulation pattern at site level
of the site.
Block-4A Block-5
CIRCULATION-BUILDING LEVEL
India Habitat Centre is designed as a vehicle-free environment. Amphi- Open
Exhibi-
All the cars and two wheelers are directed to two levels of basement after Block- theatre Middle
court tion Gate-2
drop-off. 4B court court
On site circulation becomes part of the activity.
Courtyards act as a important link in the circulation pattern.
Block-6 Pedestrian Block7
entry
Courtyards as important link in circulation
pattern at bldg lvl.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
ZONING-
The complex is divided into two blocks -
17% 16%
North block -The block adjoining the Lodhi Road is further divided into four zones 67% office zone
4, 5, 6 and 7.
This block comprises of public facilities like art gallery, restaurant on ground floor, top
floor have office areas.
South block, North block,
South block- This block is further divided into two zones 1 & 2,.
Houses most of the ancillary facilities of the North block like auditorium ,guest
rooms, conference, library, health club, swimming pool and restaurant etc.
PLANNING-
Habitat Centre is organized as a series of 5-6 storey blocks.
The complex has a thoughtful zoning of spaces-
The areas which expect large inflow of public are placed near the entrance. Vertical zoning-restaurant, gallery on GF and office on upper floors
The two blocks on the Lodhi road have public facilittis on ground floor and office areas
on the upper floors.
The blocks housing the offices are articulated to form courtyards, the courts also being
public spaces for exhibition
Offices have entrances from inner side of the courtyard.
The blocks facing the housing areas on Vardhman marg have been kept low height.
The courtyards become active areas after office hours. Articulation of bldg to create Courtyards as activity areas
Upper floors are cantilevered to provide shading to the floors below. open spaces
Reflectors above courtyards
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
COURTYARDS-
Apart from the iconic architecture, India Habitat Centre is known for its public spaces, 1. Southern court
the courtyards. 2. Stepped plaza and
1 amphitheatre court
Courtyards are provided with sitting areas and act as active gathering spaces with 3. Open exhibition court
multifunctional use from display of artifacts to informal conferences. 2 4. Middle court
Each courtyard serves a different purpose.
2 4
3
Southern Court Stepped Plaza, Amphitheatre court
Open to sky, bordered by built-up. Nature marked by play of levels.
Accomodates outdoor sitting for Space for small informal events.
restaurant.
Mystery of space is accentuated
Spill up area for convention centre. with change in levels.
Open Exhibition Court-
Middle court-
Vegetation is aligned to indicate the Middle court acts as a common
direction of building. gathering point.
Outdoor buffet- Amphitheatre Maze of levels-
Used as outdoor exhibition area. Southern court Amphitheatre court
Spill over space for office areas.
SHADING DEVICE OVER COURTYARDS-
Reflectors are installed above courtyards to provide shade and prevent sun from
entering into the building.
Reflectors are aligned at an angle which reflects back 70% of the sunlight and change
their angle in winters to let in sun. Landscaped areas in direction
Reflectors above courtyard
of building- Transition corridor
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
ARCHITECTURAL EXPRESION-
The exterior is cladded with red bricks, whereas the interior facades have combination of
bricks and stone.
The monotony of horizontal stretch is broken by vertical ribbon windows on external
faade.
Interior surfaces have horizontal ribbon windows.
The ribbon windows have slots for plantation which add to the beauty of the entire
complex.
The bridge connecting the various blocks have exposed concrete finish. Exterior faade in bricks, Stone cladded interior faade
Windows have planters painted in primary colors. with vertical ribbon with horizontal ribbon
Convention centre is defined by huge pergolas. windows windows
Separation between walls are lined with tile and help in disposal of rain water.
The top two floors are projected twice which provide shading to the floors below.
BRIDGES-
The buildings are built around courts and linked at 5/6 th floor by bridges to form huge
gateways.
These multi level bridges provide office spaces , restaurants as well as links between
various zone. Concrete finished bridge Bridges create strong sense of
The bridges help in shading of public area. . entry
The bridges form framed views and vistas and complete the character of the enclosed
courts.
BUILT-UP -OFFICE AREAS
Offices areas which expect large inflow of public are planned near the
entrances.
Office blocks have entrances form inner side of the courtyards.
Office spaces are large areas without permanent internal partitions. Office blocks and the location
Internal finishes and layout are done as per individual concern. of vertical cores.
Floor to floor height is 3.75m with clear height of 3m.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
Service entry Entry for convention centre
CONVENTION CENTRE- (Gate-3)
Collectively called HABITAT WORLD.
Convention centre block is divided into two structures auditorium and convention block. Habitat world has
Segregation helps in better handling of crowd. separate entrance form
Convention block has separate entry from Vardhman marg. Vardhman marg and has
drop-off and baement
parking facilties.
STEIN AUDITORIUM-
ARCHITECTURAL EXPRESSION-
Exterior faade is cladded with red bricks on ground floor, upper floor has jaali
pattern.
Entrance from within the Habitat centre is adourned with double storey height
pergolas.
Porch has exposed concrete finish.
PLANNING-
Total capacity 537
Area- 6206 sqft Audi- as viewed from Entranace with double
Sitting in two levels. Vardhman marg storey pergolas
Stairs only way of vertical circulation.
THE FOYER- the foyer area is inadequate and becomes overcrowded.
The foyer houses reception area and security checking area.
Foyer directly leads to top most entries on ground floor.
AUDIENCE TRAFFIC- the foyer accomodates two staircases.
The staircases lead to upper level of auditorium and to theatres below the auditorium.
Ground floor has 5 entries/exit for public and 2 entries for performers.
SEATING- total eating capacity of 530, 350 in main hall and 180 as balcony seating.
The seats are staggered to provide best view.
Height of riser is kept 4.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
Hall has straight radial aisles and no cross aisle.
STAGE- stage area is
Stage has no separate orchestra pit.
Teakwood paraquet flooring is provided.
Back stage area has 2 green rooms and one V.I.P lounge.
Walla are cladded with wooden panels.
Carpet flooring is provided for better acoustics.
THE THEATRE- Audi seating in two levels V.I.P lounge area
The space below the audi seating accommodates the theatre- Amaltas (1760 sqft)
Kadamba (620 sqft Rudraksha ( 620 sqft).
The staircase in the foyer of Stein Auditorium leads to the theatre area.
The trinity of rooms is extremely flexible, with individual as well as combined usage A R
posibilities.
The theatres have buffet area in front. K
THE HALLS-
SILVER OAK- the largest hall of habitat world has area 13200 sqft. Amaltas theatre Buffet area of theatres
It has outdoor attachment in form of a patio as well as garden space.
It allows versatile use of space from exhibitions, conferences, seminars to banquet *
parties.
The hall can further be divided into spaces.
It can accommodate upto 600 people .
The capacitiy can further be increased by combining the foyer.
GULMOHAR-large fixed seating hall of area 2870 sqft used for lectures, seminars
and press conferences.
MAGNOLIA AND MAPPLE- small sized halls for parties and press conferences.
Magnolia- 1540 sqft, can accommodate a maximum of 120 persons in theatre style.
Mapple 1270 sqft, can accommodate a maximum of 50 persons.
* Habitatcentre world.com
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
JACARANDA- the largest hall after silver oak with an area of 3700 sqft.
It can accommodate upto 300 perons in theatre style seating.
CHINAR AND WILLOW halls with area 320sqft and 570 sqft.
Best suited for small meetings, conferences and parties.
Can accommodate 25 and 44 persons in theatre style seating.
VISUAL ART GALLERY-
The art gallery houses permanent as well as temporary exhibits.
The gallery has a open exhibition area called The Palm Court.
Gallery lacks natural lighting facilities and is totally dependent on artificial
means.
GUEST HOUSE- The plan has series of projections
and recessions to create interest.
Guest rooms from 1st to 5th floor, with All American Dinner restaurant and
guest house lobby at ground floor.
Each floor consists of 12 rooms, service core and house keeping.
46 standard room, 8 superior rooms and 8 suites.
Services like laundry, linen room, storage areas are located in the baement.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
PARKING ANALYSIS-
All the entrances lead to basement parking.
Surface parking is provided only for chauffer driven cars from gate no.1
There are two basements each of area 8000 sqm.
The lower basement houses parking and service areas like electric room, generator
room,pump room whereas the upper basement houses parking only.
Both the basement can accommodate around 1000 car.
STRUCTURE- Upper basement
Rcc framed structure is employed.
Houses parking of
about 600 cars
Buildings are grouped around semi- covered courts and linked at the 5th
th and 6th
th floor level
and above by bridges. these bridge are strengthed by iron girders.
SERVICES-
D.G SET- four D.G sets, two with capacity of 100kv and other two with capacity of 500kv.
D.G sets provided in lower basement.
A.C PLANT ROOM- installed in lower basement and the chillers are placed on ground.
There are 5 A.H.U for north block (office area) and 8 A.H.U for south block (convention
Lower basement
area) Houses parking of
about 400 cars and
WATER SUPPLY- no over head water tank. service area
Water filtration plant in the lower basement.
Daily requirement of water is around 14 lac.
INFERENCES-
Locally available materials are effectively used and the building has a appealing character.
Open areas are crucial part of the layout and give a distinct identity to each zone.
Relationship of exterior and interior is maintained by limiting the height of the buildings.
Chiller camouflaged by brick jali wall
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
DAMCOSOFT PRIVATE LTD., CHANDIGARH
INTRODUCTION-
Location - I.T Park, Chandigarh
Area - 9 acres
Architect - Sangeet Sharma
Year of - 2014
completion
Damcosoft is a leading software developement company.
The company has demonstrated expertise on multiple technologies such a oracle,IBM.
The company has presence across U.K, U.S.A, Canada, Australia and India.
Damcosoft ,Chandigarh houses more than 500 workspaces over 5 floors.
The site being small, there was no space for green areas, so green spaces were created
on all floor which makes the structure a better place for work.
Various techniques are used to minimize heat gain
DAMCOSOFT PVT. LTD., CHANDIGARH
LOCATION-
The site is located on the outskirts of From Distance Time
Chandigarh in Rajiv Gandhi Technology International Airport 9 Kms. 20 mins.
Park (I.T Park).
Railway stattion 04 Kms. 07 mins.
The site provides good view of shivalik
ISBT sector 17 09 Kms. 25 mins.
range.
I.T Park houses renowned I.T buildings like CBD sector17
Infosys, Tech Mahindra, Airtel Bharti. View of shivalik range
Capital complex
ACCESSIBILITY-
The site has approach from Chandigarh
.
Panchkula highway and interector road of
Mansa Devi Complex form Panchkula side.
Being on traffic free highway, the site is
easily approachable.
Site lies in phase-2 of RGT
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
SITE SURROUNDINGS-
The site is located in Rajiv Gandhi Technology Park.
The site is surrounded by various renowned I.T companies like Infosys, Airtel Bharti and
Tech mahindra.
Infosys Airtel Bharti
SITE CHARACTER-
Total site area- 3639.90 sqm/0.89 acres
The site is rectangular with flat terrain.
ORIENTATION-
The site is N-S oriented so the longer facades of the site experience maximum
exposure.
The ancillary areas like toilets, A.H.U rooms, reception area and circulation spine is on EDC Tech Mahindra
the west side so that the working areas do not encounter heat gain.
CONCEPT-
The site being small does not have provision of green areas.
Vertical garden is provided in terms of planters, trough for planters is provided outside
the working areas.
The faade has stepped balconies with trough for planters.
This green feature creates a buffer around the building and helps in temperature
regulation.
The plan follows the site boundaries, resulting in a building that is purely rectangular.
AREA ANALYSIS-
Total site area - 3639.90 sqm
Permissible ground coverage - 40% ( 1455.96 sqm)
Achieved ground coverage - 30% ( 1109.11 sqm)
Permissible F.A.R - 1.5
Achieved F.A.R - 1.428
Vertical garden in form of planters
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
SITE CIRCULATION-
The site has access from northern faade.
The site has one entrance and one exit, these are used for vehicular, pedestrian as well
as service entry.
Loop pattern of circulation is used.
The circulation is planned in such a way that the management and employees have
separate entrance into the building.
A drop-off landing is provided for management staff in the ramp leading to basement.
Entrance and exit from basement is from rear side of the building.
ZONING- To/from basement Entrance for M.D Drop-off
This is the landscaped area. An uninterrupted space is created
Since there is little space on the as work space making it easier to
ground floor for landscaping so monitor and control for supervisor.
planters are provided on all floors.
Planters are provided in stepped Drop-off landing in ramp to
form. basement.
This acts as entrance for
management staff.
These are the off-sets on each side.
Side off-sets are 6m and 8m. Vertical circulation core is
The front off-set is 15m. provided in the centre to prevent
The rear off-set is 10m. long corridors.. Site circulation for staff and management
Ancillary areas like toilets, A.H.U, M.D has independent space, office,
on west side so that working areas meeting area and landcaped terrace
do not experience heat gain.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
BUILDING ANALYSIS- GROUND FLOOR PLAN
Total covered area of ground floor is 1109.11 sqmt.
Entrance to ground floor is at level 1.50m.
Ground floor has three entry/exists, the northern entrance is dedicated to general public and
staff, the western one for staff and the eastern for management .
A 1.5m wide ramp is provided for disabled persons.
Entrance is through a depressed faade which is fully glazed in zig-zag pattern and provides
dynamic landscaped area.
The lobby area has a full height cut-out which gives an illusion of openess in otherwise
insufficient area of 5.5x6.8m.
Ground floor consists of reception, M.D office area, workstations, board rooms,
conference room.
Complete segregation of working area and public area.
The M.D has a dedicated boardroom, dining room and the office overlooks the landscaped
terrace.
A complete segregation of staff working area and M.D office.
Centrally located service shafts and vertical circulation core to avoid long corridors.
The rear terrace area has skylights which provide natural light to the basement.
Two cut-outs at northern and southern end provide natural light to the doubly loaded
corridor.
Fire Side Work- Board
Esca worktation
worktation stairs
17% 14% ent station room
-pe Land-
16% scaped
10% Circulation spine
38% area
5% Main entrance
Rec. worktation Toi. Side Toi. office M.D
(f) Ent. (m) office
reception workstation
services coffee area
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
BUILDING ANALYSIS- FIRST, SECOND FLOOR PLAN
Total covered area on first floor is 1006.36 sqm.
First floor mainly consists of software development area, caf and conference rooms.
Two major cuts-outs at both ends provide natural light to doubly loaded corridor, these
decrease at every floor by 1m to provide balcony which serves as a space for interaction.
The southern end has a staff dining room.
Vertical core at the centre to provide easy access and prevent long corridors.
The two major cuts-outs at southern and northern decrease at each floor to provide a
stepping form as architectural feature.
The zig-zag cut on the northern faade provides a dynamic green element.
The southern end has a 1.5m wide fire escape staircase, the main circulation staircase acts
as fire escape for the northern end.
The planning is done in such a manner that it results in uninterrupted working spaces,with
each working area having it own ancillary spaces like conference room.
cabin stairs
worktation
worktation
5% 5%
18% Cut-
61% Circulation spine
11% out
Toi. Side Toi. I.T
cabin worktation cafe
(f) Ent. (m) room
working area caf circulation
services conference
Conference room lacks
Reception area seating for sub-ordinates
Terrace at rear side as a place for interaction
and serving area.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
BUILDING ANALYSIS- THIRD,FOURTH FLOOR PLAN
Total covered area on this floor is 1004.61
First floor mainly consists of software development area, caf and conference rooms.
Two major cut-outs decrease by 4m at fourth floor.
The planters outside the working areas supplement the lack of planned open areas.
The planning creates uninterrupted working areas.
The cut-outs are covered with pergolas.
conf. stairs
worktation
worktation
Rm.
5% 5%
18% Confer-
61% Circulation spine
11% -ence
Toi. Side Toi. A.H.U
conf. worktation Work-
(f) Ent. (m) room
Rm. station
working area caf circulation
services conference
The cut-out decreases by 1m on each floor The zig-zag cut-out covered with pergolas
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
BUILDING ANALYSIS-UPPER BASEMENT
Lower basement accomodates car parking and services whereas upper basement
accomodates parking.
number of cars required- 104 cars (as per ecs)
Total no. of car parking in low basement with double stack parking- 57
Total no. of car parking in upper basement with double stack parking- 47
Surface parking provided - 11
Total cars parking - 115 cars
Space per car -2.4x4.8m
Lower basement houses fire tanks, pump room.
Skylights in rear terrace and ventilators along the ramp provide natural light to basements.
Basement walls have cut-outs with louvers for natural ventilation.
Skylights in rear terrace of ground floor
provide natural light to the basements
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
CASE STUDY
ARCHITECTURAL EXPRESSION-
The structure fails to create an architectural landmark.
The front faade is divided into three wings, the central depressed faade forming the
entrance is cladded with A.C.P, the side wing are purely glazed.
slanting y-columns at the front and rear faade act as a structural and aesthetic feature.
The exposed beams give an illusion of a loop holding all the elements together.
Inclined glazed admits natural light and prevents heat gain.
SERVICES-
The building has its own STP at the southern end, the treated water is re-used in W.C, Inclined glazed faade supported on y-
urinals and for landscaping purpose. columns
WATER SUPPLY- three underground water tanks are provided, out of which two are
domestic water tanks and one fire fighting tank.
Three overhead tanks, from which two are domestic and one is fire fighting.
Wash basins
FIRE FIGHTING- Tanks Treatment plant
Hydrant ring mains runs all around the site, with yard hydrants at suitable intervals.
Drinking water
Two fire fighting tanks are provided, out of which one is underground and one is
overhead.
Treated landscaping
HVAC- D.G sets are located at the southern end of the site. W.C/urinals water tank
Separate air handling units for each floor.
The pipes take water to the A.H.Us, the A.H.U sucks in air, the air come in contact with
water and cools down, the cool air is expelled through vents in the ductwork.
INFERENCES-
The building fails to be a architectural landmark. Undergroud Overhead
Vertical gardens in exposed beams compensate the lack of landscaped areas. mains
water tank tank
The building floors provide hindrance free working space.
Water supply
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SITE ANALYSIS
CHAPTER-4 SITE ANALYSIS
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SITE ANALYSIS
SITE ANALYSIS
LINKAGES TO SITE- sector 68, Mohali
Inter-sectoral road
The site has access from two sides, the shorter face has access from inter-sectoral
road, whereas intra-sectoral road runs parallel to the longer face of site. Intra-sectoral road
Proposal to develop the inter-sector road as urban expressway within Mohali as
part of airport connectivity.
Section-Inter-sectoral road, 6- lane road with service lane
SITE CONNECTIVITY-
Airport - 15 Km
Bus stand - 6 km Section-Intra-sectoral road
Railway station - 12 Km
P.C.A stadium - 3 Km
SITE SURROUNDINGS-
The rear side of the site is residential area.
Municipal corporation building on the right side of the site.
Land opposite the south west side of the site is left vacant for I.T institutions.
Adjoining areas have number of I.T and government buildings like KMG tower and Sebiz
building and Forest Complex Office.
Residential area at back M.C building
Site as viewed from
service lane
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
SITE ANALYSIS
SITE CHARACTER-
The site is corner plot with area- 4.92 acres.
Site is rectangular in form.
Site is adjoined by two roads one on north west and other on other on south east.
TOPOGRAPHY-
The site has flat topography with no undulations.
M.C building KMG Tower Forest complex
LANDSCAPING-
The site has row of trees on three sides which will act sound barrier between fast moving
traffic of roads and the site.
CLIMATE-
Mohali has a sub-tropical continental climate characterized by hot summers, slightly cold
winters, and great variation in temperature (1 to 44 C ).
Summer: The temperature in summer may rise to a maximum of 47 C . Temperatures
generally remain between 30 and 40 C .
Autumn: In autumn, the temperature may rise to a maximum of 36 C . Temperatures
usually remain between 16 and 27 C .
Winter: Average temperatures in winter (November to February) remain at (maximum) 7 to
15 C and minimum at 5 C .
Spring temperatures vary between 16 and 25 C .
RAINFALL-
Average rainfall received each year is 114 cm.
BUILT CHARACTER OF SURROUNDING-
Absence of a architectural landmark in surrounding areas.
The area witnesses use of A.C.P cladding with full glazed facades.
HABITAT CENTRE, MOHALI
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CASE STUDIES Convention Centre - Indian Habitat Centre and Indian International CentreDokument43 SeitenCASE STUDIES Convention Centre - Indian Habitat Centre and Indian International Centrerachnasant62% (50)
- India International CentreDokument20 SeitenIndia International CentreAnoop Sharma62% (13)
- Synopsis, Indraprastha Sanskriti Kala Kendra, Dwarka, DelhiDokument14 SeitenSynopsis, Indraprastha Sanskriti Kala Kendra, Dwarka, DelhiCelcius KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aranya Housing Final To Be Submitted PDFDokument37 SeitenAranya Housing Final To Be Submitted PDFsucheta100% (4)
- Cultural Centre at RohtakDokument17 SeitenCultural Centre at RohtakTabish Raza100% (1)
- Dilli Haat PitampuraDokument11 SeitenDilli Haat Pitampuraprofessional_architect3094% (18)
- Din V 18599-8Dokument81 SeitenDin V 18599-8Milos PetrovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Habitat CenterDokument2 SeitenIndian Habitat Centernupoor8991% (11)
- India Habitat CentreDokument10 SeitenIndia Habitat Centreramluramana50% (2)
- India Habitat CentreDokument4 SeitenIndia Habitat CentreSimran Bohra100% (2)
- IhcDokument9 SeitenIhcSomesh Siddharth100% (1)
- Ihc Case Study PDFDokument2 SeitenIhc Case Study PDFSuraj Chaturvedi71% (7)
- Iic DelhiDokument12 SeitenIic DelhiGeetanjali Khanna100% (4)
- Triveni Kala SangamDokument6 SeitenTriveni Kala SangamAh AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE STUDY-pragati MaidanDokument3 SeitenCASE STUDY-pragati MaidanCamilla Fernandez67% (21)
- Site Analysis-Noida Sec 32Dokument1 SeiteSite Analysis-Noida Sec 32arunavails100% (2)
- Synopsis City CentreDokument6 SeitenSynopsis City CentreUbaid Khan50% (2)
- Mylapore SettlementDokument6 SeitenMylapore SettlementHues of SundropNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEW Cultural Centre SynopsisDokument32 SeitenNEW Cultural Centre SynopsisAbdul Sakur76% (29)
- Site AnalysisDokument9 SeitenSite Analysisarunavails100% (5)
- Centre of TranquilityDokument3 SeitenCentre of TranquilityMonika Maharana100% (3)
- Kala AcademyDokument21 SeitenKala AcademyNeha Rathna Ashok80% (5)
- Jalmahal ProjectDokument5 SeitenJalmahal ProjectAdnanKhan100% (1)
- Literature Study of Habitat CentreDokument101 SeitenLiterature Study of Habitat Centrenc100% (6)
- Hardik WorkDokument11 SeitenHardik WorkTanuj GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Habitat Centre ReportDokument87 SeitenHabitat Centre Reportnc85% (13)
- Habitat Centre SynopsisDokument4 SeitenHabitat Centre Synopsismadhavi100% (1)
- SYNOPSIS Hedrabad Habitat CentreDokument23 SeitenSYNOPSIS Hedrabad Habitat CentreMOHAMMAD SIDDIQ SALIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Location:: Various Components (Functional Areas) and Their InterrelationshipDokument6 SeitenLocation:: Various Components (Functional Areas) and Their InterrelationshipHarinder KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- IhcDokument25 SeitenIhcramluramana92% (13)
- Abitat Enter: Handra Prabha B.Arch. IV Year BCA 2012-13Dokument59 SeitenAbitat Enter: Handra Prabha B.Arch. IV Year BCA 2012-13Aravind Bachu83% (23)
- Litrature Case Study Kala AcademyDokument3 SeitenLitrature Case Study Kala AcademyAbdul Sakur100% (1)
- Indian Habitat CentreDokument20 SeitenIndian Habitat CentrePrakriti GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- India International CentreDokument14 SeitenIndia International CentreShubham Srivastava0% (1)
- DCR ThanjavurDokument3 SeitenDCR ThanjavurShubhani Chandra100% (5)
- Ihc Case StudyDokument11 SeitenIhc Case StudyDipaliMaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Habitat CenterDokument8 SeitenIndia Habitat CenterZyla Mirza100% (4)
- Case Studies Bharat Bhavan Triveni Kala Sangam IIC PDFDokument2 SeitenCase Studies Bharat Bhavan Triveni Kala Sangam IIC PDFAishwarya Misaki Animae100% (6)
- Dilli Hatt, Pitampura Case StudyDokument19 SeitenDilli Hatt, Pitampura Case StudySaransh YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- IndianhabitatcenterDokument29 SeitenIndianhabitatcentercoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies: Bharat Bhavan, Triveni Kala Sangam, IIC.Dokument2 SeitenCase Studies: Bharat Bhavan, Triveni Kala Sangam, IIC.Muddassir Iqbal89% (19)
- Jaipur Habitat CentreDokument3 SeitenJaipur Habitat CentreAyushi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On Slums in India: Kachipura, Nagpur, Maharashtra, IndiaDokument20 SeitenCase Study On Slums in India: Kachipura, Nagpur, Maharashtra, IndiaSophia ChinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyderabad Habitat CentreDokument3 SeitenHyderabad Habitat Centrebhagyasri100% (1)
- NEW Cultural Centre SynopsisDokument32 SeitenNEW Cultural Centre Synopsistannu singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project:-Hi-Tech Habitat Centre, Noida: EntertainmentDokument2 SeitenProject:-Hi-Tech Habitat Centre, Noida: Entertainmentar jain100% (2)
- Case Study On Kalagram ChandigarhDokument1 SeiteCase Study On Kalagram Chandigarhniki niks50% (2)
- Case Study-1Dokument7 SeitenCase Study-1Shajil VP92% (13)
- Asiad Village - GRP 6Dokument28 SeitenAsiad Village - GRP 6nadiajmi90% (10)
- Socio-Culture CenterDokument4 SeitenSocio-Culture CenterAesha Upadhyay67% (6)
- India Habitat Centre Case StudyDokument4 SeitenIndia Habitat Centre Case StudyAqdas UsmaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chokhi DhaniDokument14 SeitenChokhi DhaniSuvarna Jadhav100% (5)
- SynopsisDokument4 SeitenSynopsisrutujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilli Haat Janakpur Casestudy 21 SeptDokument9 SeitenDilli Haat Janakpur Casestudy 21 SeptpranotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- India Habitat Centre: A Case "Building in TheDokument20 SeitenIndia Habitat Centre: A Case "Building in TheKapil SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Synopsis & Site Analysis - A1Dokument1 Seite1.1 Synopsis & Site Analysis - A1Sonu ChahalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Square StudyDokument29 SeitenUrban Square Studyraziyya100% (1)
- About The Project:: HABITAT CENTRE Is Now Home Not Only ToDokument34 SeitenAbout The Project:: HABITAT CENTRE Is Now Home Not Only ToAr Aditya SagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proposed Site:: India NoidaDokument48 SeitenProposed Site:: India NoidaBhavya Kumar SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center in HillDokument4 SeitenCenter in Hilljebin boseNoch keine Bewertungen
- District Hall BostonDokument5 SeitenDistrict Hall BostonClara AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architecture DesignDakshinachitraAug2007 PDFDokument4 SeitenArchitecture DesignDakshinachitraAug2007 PDFRashmiJoshi0% (1)
- Cihc Master PlanDokument164 SeitenCihc Master PlanRashmiJoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Thesis IITKgpDokument36 SeitenList of Thesis IITKgpRashmiJoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Projects LISTDokument4 SeitenThesis Projects LISTRashmiJoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Odwadniacz Termostatyczny th13Dokument1 SeiteOdwadniacz Termostatyczny th13Fernando Moreno pereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Static and Dynamic Testing of Welded and Woven Mesh For Rock SupportDokument11 SeitenStatic and Dynamic Testing of Welded and Woven Mesh For Rock SupportAyleen LealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme B16.21 (2005) PDFDokument22 SeitenAsme B16.21 (2005) PDFLevi Porter100% (1)
- Floating Roof Seals PDFDokument4 SeitenFloating Roof Seals PDFAnonymous dSFbLxc9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tegomer Dispersing at Its BestDokument32 SeitenTegomer Dispersing at Its BestHiếu Mai ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural DrawingsDokument1 SeiteStructural DrawingserniE抖音 AI Mobile Phone Based MovieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al CoatingDokument17 SeitenAl Coatingjijith njNoch keine Bewertungen
- Painting Procedure - PolyurethaneDokument2 SeitenPainting Procedure - PolyurethanesanjeetkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BOQ-Part D M&EDokument430 SeitenBOQ-Part D M&ECharitha Ranwala100% (1)
- Pocket PenetrometerDokument4 SeitenPocket Penetrometertag_jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Strength For Concrete With GGBS and Cement Using Accelerated Curing MethodDokument5 SeitenComparison of Strength For Concrete With GGBS and Cement Using Accelerated Curing MethodvardhangargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Torsion by ACI 318-11-3SlidesPerPage.272121622Dokument17 SeitenTorsion by ACI 318-11-3SlidesPerPage.272121622oqusousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Vs 3D ReviewDokument7 Seiten2D Vs 3D ReviewBhasker RamagiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manejadora Adp Lennox PDFDokument15 SeitenManejadora Adp Lennox PDF45saulNoch keine Bewertungen
- M y Units of Gasket Seating StressDokument11 SeitenM y Units of Gasket Seating StressLcm TnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alloy and Temper DesignationDokument14 SeitenAlloy and Temper DesignationKrishna KishoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Waste Plastic BottlesDokument14 SeitenUse of Waste Plastic BottlesnehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- En7936 4 09 17 - Ofu PDFDokument4 SeitenEn7936 4 09 17 - Ofu PDFJhonny Velasquez PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Structure Interaction in COMSOLDokument33 SeitenFluid Structure Interaction in COMSOLVoona RanganadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMSM Module 4Dokument27 SeitenAMSM Module 4Shaji EtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 - Sprinkler Hydraulic Calculation For Ordinary Hazard-1 For VideoDokument6 Seiten0 - Sprinkler Hydraulic Calculation For Ordinary Hazard-1 For Videoariseelectricals18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sardar Vallabhai Patel Indoor StadiumDokument3 SeitenSardar Vallabhai Patel Indoor StadiumRájDèép TrìpâţhíNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN15 1718 PDFDokument46 SeitenLN15 1718 PDFelty TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument5 SeitenAssignmentAbdul HannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Valve Cast A494 CW12MW Body UNS N10276 TrimDokument1 SeiteGate Valve Cast A494 CW12MW Body UNS N10276 TrimGiovanni PetrizzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nonlinear AnalysisDokument118 SeitenNonlinear Analysisabhinavka123Noch keine Bewertungen
- SX022a-En-EU-Example - Calculation of Effective Section Properties For A Cold-Formed Lipped Channel Section in BendingDokument10 SeitenSX022a-En-EU-Example - Calculation of Effective Section Properties For A Cold-Formed Lipped Channel Section in BendingWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epoxy Coated TMTDokument14 SeitenEpoxy Coated TMTVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Intake SystemDokument27 SeitenAir Intake SystemrahulNranaNoch keine Bewertungen