Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 10 Sampling Strategies Edited
Hochgeladen von
Ameer Al-asyraf Muhamad0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
78 Ansichten23 SeitenChapter 10 Sampling Strategies Edited
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenChapter 10 Sampling Strategies Edited
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
78 Ansichten23 SeitenChapter 10 Sampling Strategies Edited
Hochgeladen von
Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadChapter 10 Sampling Strategies Edited
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 23
CHAPTER 10
SAMPLING STRATEGIES
Business Research Methods
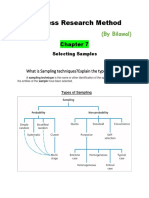
CENSUS, SAMPLING AND SURVEY
Census and Sampling are methods of
collecting data from the population.
Survey is a research strategy that collects
standardised data from a large number of
respondents.
To put the three terms together, a Sample
surveys a portion (or a subset) of a population
while a Census surveys every element in the
population.
Business Research Methods
POPULATION AND POPULATION
ELEMENTS
Population in research refers to a complete
group of people (e.g., students, employees,
teachers, managers, patients or customers) or
institutions (e.g., households, stores, schools,
hospitals or firms) that share some common
set of characteristics.
Population element refers to an individual
member in the population. Example: If
Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) students are
the population of the study, the population
element would be the individual student.
Business Research Methods
WHEN IS SAMPLING NOT USED?
Usually for a population size of fewer
than 50, it is more appropriate to
collect data from the entire
population, so no sampling is
required.
It is also more appropriate to do a
census study. Example: suppose the
target population is health tourism
hospitals in Malaysia. The sampling
frame lists the names of 41 health
tourism hospitals recognised by the
Ministry of Health. The population size
is small, suggesting that a census
study is possible, and all 41 hospitals
should be surveyed in a census study.
Business Research Methods
WHEN IS SAMPLING USED?
We hardly know who makes up the
entire population.
Cost and time constraints
There is a lot of error to control and
monitor
Lists are rarely up to date
Destruction of the Sampling Unit
The sample data are sufficient for
decision making
Business Research Methods
SAMPLING FOR QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE
STUDIES
Business Research Methods
STEPS IN SAMPLING
Business Research Methods
IDENTIFY THE TARGET POPULATION
The target population of a research
topic is defined by the researcher and
needs to be clearly identified at the
beginning of a study.
The study should be based on a clear
understanding of who or what is of
interest, as well as the type of
information required from that
population.
Business Research Methods
DETERMINE THE SAMPLING FRAME
A sampling frame is a list that records all population elements.
Once a target population is chosen, sampling frame availability
can be determined. Example: the sampling frame for a study
that assesses UPM students satisfaction level would be a list of
students provided by the registrar of UPM. If the population size
of UPM students is 25,000, the sampling frame should list
25,000 student names and contact details.
There are also times when a sampling frame is not available.
Example: international tourists are the target population, but a
sampling frame that consists of the names of all international
tourists coming to Malaysia is highly confidential (for security
reasons) and therefore not available to the researcher.
Business Research Methods
DETERMINE SAMPLING STRATEGY
The purpose of a sampling strategy is to select sampling
units (e.g., female consumers) as a sample (e.g., 500 female
consumers) from the population (e.g., 10 million).
Business Research Methods
Business Research Methods
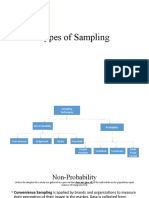
Probability Sampling Techniques
1. Simple Random Sampling
Technique
- This follows a lucky draw
procedure, where every unit in
the population has an equal
chance of being selected. First,
you assign a running number
to each unit in the sampling
frame. Then, you select a unit
randomly accordingly to the
number suggested by a
random table.
Business Research Methods
2. Systematic Random Sampling Technique
In this procedure, the first unit is
selected at random (following
random numbers). Then, the
subsequent unit is picked with kth
interval.
Say k=10 and the first random
number is 7 (from a random table).
You simply pick sampling unit
numbers 7, 17, 27, 37 and so on.
Business Research Methods
3. Stratified Random Sampling Technique
The purpose of this technique is
to provide fair representation of
subgroups. First, the population
is broken into strata
(homogeneous groups).
Elements in a strata share
similar characteristics. Then,
within each strata list, a
sampling unit is picked
randomly.
Business Research Methods
4. Cluster Random Sampling
Population is broken into
heterogeneous groups or
clusters. Each cluster consists
of units with very different
characteristics.
For example, Malaysia has 13
states, representing 13
clusters where each cluster
has male and female teachers.
Within each cluster, a unit is
selected randomly (following
random numbers).
Business Research Methods
Non-probability Sampling Techniques
1. Convenient Sampling
Technique
- This technique is completely
based on the convenience of
the researcher. Thus, the
selection is of those who
happen to be at the data-
collection venue. Units are
selected conveniently.
Elements not at the data-
collection venue have no
chance of being selected.
Business Research Methods
2. Judgemental Sampling Technique
This technique imposes
judgements such as, for
example, Malaysians who have
travelled to 10 countries or
more, as they are presumed to
have rich information on issues
of interest (e.g., travel
experience). Thus, it
approaches units that meet the
criteria conveniently
Business Research Methods
3. Quota Sampling Technique
Its purpose is to have fair representation of subgroups
in the sample.
It is very similar to Stratified Sampling. The difference
is that Stratified Sampling selects units from each
strata randomly, while with this technique units within
each subgroup are selected conveniently until the
quota is achieved.
Business Research Methods
Business Research Methods
4. Snowball Sampling Technique
The initial respondents are
identified conveniently through
friends and any subsequent
respondent is referred by a first
respondent. This is most
commonly used when dealing
with rare populations (e.g., cancer
survivors).
Business Research Methods
DETERMINE SAMPLE SIZE (Quantitative)
1. Use a sample size calculator that is available
online.
2. Following a statistical rule, the desired ratio of
sample size to construct numbers should be 20:1
(Hair, Anderson, Tatham and Black 1998).
3. A minimum sample size of 30 is required for
statistical analysis of each category within the
overall sample.
4. The desired data analysis method plays a role in
determining sample size.
Business Research Methods
DETERMINE SAMPLE SIZE (Qualitative)
The sample size requirements usually follow the rule of
data saturation.
The theoretical sample size is a general guideline.
Qualitative research that aims to understand a fairly
homogeneous population requires 12 in-depth interviews
(Guest et al., 2006) while for a fairly heterogonous
population, 25-30 interviews are needed (Creswell, 2007).
Business Research Methods
SELECT THE ACTUAL SAMPLING UNIT
Select the individual unit for the sample based on the
sampling procedure of the chosen sampling technique.
Then collect data from the sampling unit (e.g., employees,
tourists or teachers) using the methods, such as
questionnaires, interviews or observations, for primary
data collection.
Business Research Methods
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Trinity 6Dokument25 SeitenTrinity 6Yonn Me Me KyawNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Target Population and Sampling StrategiesDokument36 Seiten06 Target Population and Sampling Strategiesshoaibchattha777Noch keine Bewertungen
- QT-Lecture 1Dokument64 SeitenQT-Lecture 1hlnathani.eflNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Okite MosesDokument33 SeitenBy Okite MosesBanolka NobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling TechniquesDokument96 SeitenSampling Techniquessixteen liquidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SamplingDokument66 SeitenSamplingsathish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 2Dokument21 SeitenGroup 2rimshach142Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology: Chapter 11-SamplingDokument28 SeitenResearch Methodology: Chapter 11-SamplingSerah JavaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 111a Notes - 2Dokument3 SeitenNCM 111a Notes - 2Kimberly BucoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling: ResearchDokument87 SeitenSampling: ResearchSMK MaruvsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 Sampling Techniques LectureDokument30 SeitenLecture 9 Sampling Techniques Lectureephraimsmart11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of SamplingDokument13 SeitenTypes of SamplingCAELUM ONLINENoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDokument6 SeitenSampling and Sampling DistributiontemedebereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4 - Kcmc14Dokument61 SeitenTopic 4 - Kcmc14ELDA MAUNDINoch keine Bewertungen
- Selecting Samples: Research Methods in Language Education 2 Siti Nur'Aini, PH.DDokument31 SeitenSelecting Samples: Research Methods in Language Education 2 Siti Nur'Aini, PH.DMohammad GhanaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.2.1. SAMPLING-TECHNIQUES - DR - RemoDokument56 Seiten4.2.1. SAMPLING-TECHNIQUES - DR - RemoCharlene BaclayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research MethodologyDokument36 SeitenResearch MethodologyJeca CodmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7Dokument46 SeitenTopic 7honathapyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDokument64 SeitenSampling and Sampling DistributionNIKHIL PATTNAIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4 Sampling and Sampling ProceduresDokument47 SeitenWeek 4 Sampling and Sampling ProceduresNaym HardenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Method: Unit 4Dokument17 SeitenBusiness Research Method: Unit 4Prince SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument37 SeitenPresentation 1Afia TawiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Five: Research DesignDokument33 SeitenChapter Five: Research DesignMintishu TemesgenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantitative Research Design and Sampling MethodsDokument20 SeitenQuantitative Research Design and Sampling MethodsMagnolia KhineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techniques of SamplingDokument5 SeitenTechniques of SamplingofarmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling TechniquesDokument30 SeitenSampling TechniquesMawutor AddatorviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods For Business & Management: Summer Semester - 2020/2021 Module Fourteen SamplingDokument27 SeitenResearch Methods For Business & Management: Summer Semester - 2020/2021 Module Fourteen SamplingOmar HadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four (Methods)Dokument49 SeitenChapter Four (Methods)pretoria agreement21Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIOMETRYDokument37 SeitenBIOMETRYAddisu GedamuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of SamplingDokument6 SeitenTypes of SamplingSHIVANI SHUKLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Sampling: Group MembersDokument42 SeitenPresentation On Sampling: Group MembersShahid Ali DurraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorDokument23 SeitenAmity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorMayank TayalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument5 SeitenChapter 7bilawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methods & MaterialsDokument78 SeitenResearch Methods & MaterialsSintayehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter8 Sampling IoxODokument24 SeitenChapter8 Sampling IoxOantonio montemayorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Collection UGC - NET Paper-1Dokument17 SeitenData Collection UGC - NET Paper-1Diwakar Entertainment DoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 ABRM-Sampling in ResearchDokument31 Seiten12 ABRM-Sampling in ResearchShiraz IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Techniques TULIO JO GABRIELDokument35 SeitenSampling Techniques TULIO JO GABRIELIVY FAULVENoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic6 - Sampling Design and Procedures - MSKDokument41 SeitenTopic6 - Sampling Design and Procedures - MSKSaifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Data Collection MethodsDokument23 SeitenSampling and Data Collection MethodsZairul Nisham Musa0% (1)
- 3 Is Chapter 3 Sampling Method 071917Dokument24 Seiten3 Is Chapter 3 Sampling Method 071917aidehugh8Noch keine Bewertungen
- PR2 Handout2Dokument7 SeitenPR2 Handout2Shahanna GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uma Sekaran Research Methods For Business A SkBookZa - Org1Dokument22 SeitenUma Sekaran Research Methods For Business A SkBookZa - Org1Amina FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- SamplingDokument59 SeitenSamplingpooja100% (1)
- Amity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorDokument23 SeitenAmity School of Business:, Semester IV Research Methodology and Report Preparation Dr. Deepa KapoorMayankTayal100% (1)
- BR Chapter 6 - Sample Design and Sampling ProcedureDokument18 SeitenBR Chapter 6 - Sample Design and Sampling ProcedureAsif Islam SamannoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISB 1 For Students PDFDokument54 SeitenISB 1 For Students PDFRitik AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 Research - Design AbDokument40 SeitenChapter 4 Research - Design AbGatluak Thalow KuethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology: Lecture 4Dokument43 SeitenResearch Methodology: Lecture 4TrupalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Methodology: Arturo O. Macias JR., MamtDokument32 SeitenResearch Methodology: Arturo O. Macias JR., MamtFroilan DandoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and Sampling DistributionDokument80 SeitenSampling and Sampling DistributionMohammed AbdelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Design, Sampling and Data Collection ToolsDokument40 SeitenResearch Design, Sampling and Data Collection ToolsMoud KhalfaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 - Population and SamplingDokument24 Seiten06 - Population and SamplingNdaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Method Rm-Chapter 3Dokument51 SeitenResearch Method Rm-Chapter 3GAMEX TUBENoch keine Bewertungen
- Working With Research Participants Sampling and EthicsDokument45 SeitenWorking With Research Participants Sampling and EthicsJonnel GadinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 6 IDokument33 SeitenUnit 6 Iankit mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocol Writing in ResearchDokument38 SeitenProtocol Writing in ResearchGetabalew EndazenawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systematic Sampling - Research MethodologyDokument2 SeitenSystematic Sampling - Research MethodologySouroJeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQQS1013 Elementary Statistics: Possibility A Particular Event Will OccurDokument33 SeitenSQQS1013 Elementary Statistics: Possibility A Particular Event Will OccurAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salary IncrementDokument7 SeitenSalary IncrementAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weaknesses: 1. Advertising Cost 2. Outdated TechnologyDokument1 SeiteWeaknesses: 1. Advertising Cost 2. Outdated TechnologyAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managerial Skill-Activity 1: Audit Company - Avon Cosmestic (M) SDN BHDDokument5 SeitenManagerial Skill-Activity 1: Audit Company - Avon Cosmestic (M) SDN BHDAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary 2Dokument2 SeitenSummary 2Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Different Between Islamic Marketing and ConventionalDokument10 SeitenThe Different Between Islamic Marketing and ConventionalAmeer Al-asyraf Muhamad100% (1)
- Career: Board of Director Mary Kay 1. David HollDokument4 SeitenCareer: Board of Director Mary Kay 1. David HollAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5P of Islamic MarketingDokument20 Seiten5P of Islamic MarketingEl Bachir BoussaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sqqs1013 Elementary Statistics SECOND SEMESTER SESSION 2014/2015 (A142) Group Assignment 1Dokument7 SeitenSqqs1013 Elementary Statistics SECOND SEMESTER SESSION 2014/2015 (A142) Group Assignment 1Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSMH 2013 Assignments Guideline A162Dokument2 SeitenBSMH 2013 Assignments Guideline A162Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career: Board of Director Mary Kay 1. David HollDokument4 SeitenCareer: Board of Director Mary Kay 1. David HollAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary 1Dokument2 SeitenSummary 1Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary 2Dokument2 SeitenSummary 2Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.docx Kuiz Akram AshrafDokument5 Seiten1.docx Kuiz Akram AshrafAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universiti Utara Malaysia College of Arts and Sciences School of Quantitative SciencesDokument3 SeitenUniversiti Utara Malaysia College of Arts and Sciences School of Quantitative SciencesAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQQS1013 CHP04Dokument20 SeitenSQQS1013 CHP04Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qawaid FiqhiyyahDokument56 SeitenQawaid FiqhiyyahAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary 1Dokument2 SeitenSummary 1Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal SummaryDokument10 SeitenJournal SummaryAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1-Intoduction To Usul Al-FiqhDokument32 SeitenChapter1-Intoduction To Usul Al-FiqhAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSMH 2013 Assignments Guideline A162Dokument2 SeitenBSMH 2013 Assignments Guideline A162Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Islamic Ethics in Consumerism IBSDokument16 Seiten4 Islamic Ethics in Consumerism IBSAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Calendar A161Dokument1 SeiteAcademic Calendar A161Ameer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- OligopolyDokument11 SeitenOligopolyAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Vitae (CV) English OfficialDokument7 SeitenCurriculum Vitae (CV) English OfficialAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A161 Tutorial 4 - Annual Report Fin AnalysisDokument10 SeitenA161 Tutorial 4 - Annual Report Fin AnalysisAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem of Ibe AssignmentDokument3 SeitenProblem of Ibe AssignmentAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read The Passage Below and Answers The Following QuestionsDokument1 SeiteRead The Passage Below and Answers The Following QuestionsAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Issue and ChallengeDokument5 SeitenDraft Issue and ChallengeAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joe Smith: Your UniversityDokument63 SeitenJoe Smith: Your UniversityAmeer Al-asyraf MuhamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Proposal UNICEFDokument27 SeitenTechnical Proposal UNICEFJamil HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evermotion Archmodels Vol 57 PDFDokument2 SeitenEvermotion Archmodels Vol 57 PDFPriscillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Equipment MaintenanceDokument6 SeitenMedical Equipment Maintenancever_at_workNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assesment Task 4 Learning and Development Project Evaluation ReportDokument6 SeitenAssesment Task 4 Learning and Development Project Evaluation ReportAgus BudionoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behavior Change ProjectDokument5 SeitenBehavior Change Projectapi-313808473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Informal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateDokument7 SeitenInformal Financial Institutions and Small and Medium Scale Enterprises Performance in Akoko South West Local Government, Ondo StateAkingbesote VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making Pain Visible - An Audit and Review of Documentation To Improve The Use of Pain Assessment by Implementing Pain As The Fifth Vital SignDokument6 SeitenMaking Pain Visible - An Audit and Review of Documentation To Improve The Use of Pain Assessment by Implementing Pain As The Fifth Vital SignWahyu WidiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delay in Construction Projects - A Study of Scenario of Pondicherry RegionDokument4 SeitenDelay in Construction Projects - A Study of Scenario of Pondicherry RegionAnonymous izrFWiQ100% (1)
- NuclearDokument7 SeitenNuclearJoydev GangulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Framework Adapted From Allyn & Bacon Guide To Writing, 8: EditionDokument2 SeitenFramework Adapted From Allyn & Bacon Guide To Writing, 8: EditionKim LaceyNoch keine Bewertungen
- GlobalMapper LiDAR PDFDokument2 SeitenGlobalMapper LiDAR PDFscridbcasadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eureka Math Grade 6 Module 6 Parent Tip SheetDokument2 SeitenEureka Math Grade 6 Module 6 Parent Tip Sheetapi-324380772Noch keine Bewertungen
- 360db English Daksha Mains Mentoring ProgramDokument4 Seiten360db English Daksha Mains Mentoring ProgramABHISHEK KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defined Contribution / 401 (K) Fee StudyDokument33 SeitenDefined Contribution / 401 (K) Fee StudyHai V. PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading ResearchDokument8 SeitenReading ResearchJean Dela Cruz OmayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vic 1-3Dokument25 SeitenVic 1-3Ibrahim AlabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA231 Mathematics III Nov Dec 2007Dokument3 SeitenMA231 Mathematics III Nov Dec 2007aniruthgsabapathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines Mindanao State University Maigo School of Arts and Trades Maigo, Lanao Del Norte College Department S.Y. 2020-2021Dokument3 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines Mindanao State University Maigo School of Arts and Trades Maigo, Lanao Del Norte College Department S.Y. 2020-2021Jean Aireen Bonalos EspraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Scheduling - Probabilistic PERTDokument23 SeitenProject Scheduling - Probabilistic PERTSanjana GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics For Business and EconomicsDokument13 SeitenStatistics For Business and Economicsakhil kvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Behavioral Skills Training To Teach Behavioral Interventions and Milieu Teaching: A Systematic Review of The Literature and Empirical InvestigationDokument165 SeitenUsing Behavioral Skills Training To Teach Behavioral Interventions and Milieu Teaching: A Systematic Review of The Literature and Empirical InvestigationBruno KudekenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pca IcaDokument34 SeitenPca Icasachin121083Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Solve A Case StudyDokument3 SeitenHow To Solve A Case Studyshazeb zafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ankit New SynopsisDokument5 SeitenAnkit New SynopsisAnkit GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research-Informed Curriculum Design For A Master's-Level Program in Project ManagementDokument32 SeitenResearch-Informed Curriculum Design For A Master's-Level Program in Project ManagementMariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing Household Survey Samples (Practical Guidelines)Dokument240 SeitenDesigning Household Survey Samples (Practical Guidelines)Maritess Delfin VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRP Guidelines 2020-21Dokument13 SeitenFRP Guidelines 2020-21Shreshth SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Hard and Fast Rule For Identifying MeasuresDokument2 SeitenNo Hard and Fast Rule For Identifying MeasuresLiana CanizaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix B Load TestDokument17 SeitenAppendix B Load Testanjas_tsNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Dokument29 SeitenI. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Mae DinDinNoch keine Bewertungen