Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Obstetric Instruments
Hochgeladen von
ShuvashishSunuwar100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
481 Ansichten15 SeitenThis document describes several obstetric instruments:
1) A simple rubber catheter is used to empty the bladder during pregnancy, labor, postpartum, and for other uses like as a tourniquet or to administer oxygen.
2) A Foley catheter is used for continuous bladder drainage for conditions like eclampsia, retroverted gravid uterus, and to give the bladder rest after operations or if injury is suspected. It can also be used in the management of atonic postpartum hemorrhage.
3) Sims' double bladed posterior vaginal speculum has unequal blades for easier introduction into the vagina. It is used to inspect the cervix and vagina after delivery,
Originalbeschreibung:
gyne
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document describes several obstetric instruments:
1) A simple rubber catheter is used to empty the bladder during pregnancy, labor, postpartum, and for other uses like as a tourniquet or to administer oxygen.
2) A Foley catheter is used for continuous bladder drainage for conditions like eclampsia, retroverted gravid uterus, and to give the bladder rest after operations or if injury is suspected. It can also be used in the management of atonic postpartum hemorrhage.
3) Sims' double bladed posterior vaginal speculum has unequal blades for easier introduction into the vagina. It is used to inspect the cervix and vagina after delivery,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
481 Ansichten15 SeitenObstetric Instruments
Hochgeladen von
ShuvashishSunuwarThis document describes several obstetric instruments:
1) A simple rubber catheter is used to empty the bladder during pregnancy, labor, postpartum, and for other uses like as a tourniquet or to administer oxygen.
2) A Foley catheter is used for continuous bladder drainage for conditions like eclampsia, retroverted gravid uterus, and to give the bladder rest after operations or if injury is suspected. It can also be used in the management of atonic postpartum hemorrhage.
3) Sims' double bladed posterior vaginal speculum has unequal blades for easier introduction into the vagina. It is used to inspect the cervix and vagina after delivery,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 15
OBSTETRIC INSTRUMENTS
SIMPLE RUBBER CATHETER:
It is used to empty the bladder in cases with retention
of urine during(a) Pregnancy (Retroverted Gravid
Uterus p. 311). (b) Labor(i) when the woman fails to
pass urine by herself (ii) before and after any operative
interventions (forceps delivery p. 574, destructive
operations p. 586). (c) Post-partum (i) during
management of postpartum hemorrhage (p. 414)
(ii) retained placenta (p. 418). (d) Other uses(i) as a
tourniquet (ii) to administer O2 when nasal catheter
is not available (iii) as a mucus suckerwhen it is
attached to a mechanical or electric sucker
Self assessment: (i) Length of
female urethra (p. 14).
(ii) Causes of retention of urine during
pregnancy,
labor and puerperium. (iii) Why a metal
catheter is
not used in obstetrics? Ans: To avoid
trauma to the
soft and vascular urethra
Fig. 41.3 FOLEYS
CATHETER
It is used for
continuous drainage of bladder in cases with
(i) Eclampsia (p. 234). (ii) Retroverted gravid
uterus (p. 311). (iii) To give rest to the bladder
following any destructive operation and/or in
a case with suspected bladder injury (p. 587).
It is usually kept for 710 days. (iv) In the
management of atonic PPH (p. 415). (v) To
control atonic PPH. The catheter is inserted
within the uterine cavity and the catheter
balloon is inflated with normal saline.
The balloon provides a tamponade (p. 415)
to the uterine surface. The catheter drains
the blood from the uterine cavity if there is
any.
Self assessment: (i) Indications of continuous bladder drainage (p. 234, 311,
588), (ii) Causes of atonic PPH
(p. 410).
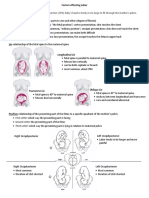
Fig. 41.4 SIMS DOUBLE BLADED POSTERIOR
VAGINAL SPECULUM:
The blades are of
unequal breadth to facilitate introduction
into the vagina depending upon the space
available (narrow blade in nulliparous and
the wider blade in parous women). It is
used in obstetrics: (1) To inspect the cervix
and vagina to detect any injury following
delivery. (2) To clean the vagina following
delivery. (3) To inspect the cervix and vagina
to exclude any local cause for bleeding
in APH (Cuscos speculum preferred).
(4) During D & E operation (p. 563).
Self assessment: (i) Common
sites of traumatic PPH (p. 411)
(ii) Diagnosis of traumatic PPH
(p. 417, 423)
(iii) Indications of D + E (p. 563) (iv)
What are the local (extra placental)
causes of APH (p. 241) (v) What is
Sims position and what is Sims triad
? See authors Text Book of
Gynecology (p. 390).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Prolonged Labor and Labor InductionDokument28 SeitenProlonged Labor and Labor InductionNovia RizqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To The Morning SessionDokument20 SeitenWelcome To The Morning SessionGENERAL sharpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birth ChecklistDokument8 SeitenBirth ChecklistLavanya MeenakshisundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNDokument352 SeitenAbnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNMercy KeruboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyhydramnios and OlygohydramniosDokument32 SeitenPolyhydramnios and Olygohydramniosafifurrahman_rizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preterm Labor and PROMDokument102 SeitenPreterm Labor and PROMDan Matthew BuriasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsDokument10 SeitenMark Fredderick R. Abejo RN, MAN: Maternal and Child Nursing BulletsMark DaenosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal Care During The First, SecondDokument85 SeitenAntenatal Care During The First, SecondhemihemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Risk Labor and DeliveryDokument5 SeitenHigh Risk Labor and DeliveryCarl John ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ArtographDokument7 SeitenP ArtographMali KanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortion II ND Yr MSC NursingDokument121 SeitenAbortion II ND Yr MSC Nursingesthereugenia100% (1)
- Antenatal PreparationDokument24 SeitenAntenatal PreparationSwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prom 1Dokument48 SeitenProm 1Tesfahun TekleNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 4 Ps of Labor: Group 1Dokument37 SeitenThe 4 Ps of Labor: Group 1ABEGAIL BALLORANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ante Partum HemorrhageDokument30 SeitenAnte Partum Hemorrhagetanmai nooluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forceps DeliveryDokument32 SeitenForceps DeliveryVijith.V.kumar50% (2)
- 1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalDokument110 Seiten1066 Complications of 3rd Stage of Labour Injuries To Birth CanalSweety YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives of Aph:: To Define About APH. To List The Causes of APHDokument42 SeitenObjectives of Aph:: To Define About APH. To List The Causes of APHReena TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antepartum HaemorrhageDokument65 SeitenAntepartum HaemorrhageAmit RamrattanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bfhi Lesson PlanDokument26 SeitenBfhi Lesson Planbaby100% (2)
- Pre-Eclampsia Lesson PlanDokument26 SeitenPre-Eclampsia Lesson PlanCoolsun SunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meningococcal MeningitisDokument22 SeitenMeningococcal MeningitisShuvashishSunuwar100% (1)
- OBG DrugsDokument85 SeitenOBG Drugsvivekkumar05468Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partograph DR OdofinDokument61 SeitenPartograph DR OdofinEkiran BabajideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine Malformations PDFDokument6 SeitenUterine Malformations PDFsaritha OrugantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Risk Pregnancy NewDokument16 SeitenHigh Risk Pregnancy NewSurya SasidharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetric Instruments: Sims' Double Bladed Posterior Vaginal SpeculumDokument15 SeitenObstetric Instruments: Sims' Double Bladed Posterior Vaginal Speculumsagi mu100% (2)
- Obgyn Anemia in Pregnancy For UG ClassDokument35 SeitenObgyn Anemia in Pregnancy For UG ClassimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- DysmenorrheaDokument28 SeitenDysmenorrheaDr Munira MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large For Gestational Age (LGA)Dokument4 SeitenLarge For Gestational Age (LGA)Aira AlaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Fetal Well BeingDokument29 SeitenAssessment of Fetal Well Beingmalaika khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology InstrumentsDokument35 SeitenObstetrics and Gynaecology InstrumentsDr-i BarreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruments in Og 2016-1Dokument65 SeitenInstruments in Og 2016-1Ragul VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterovaginal ProlapseDokument16 SeitenUterovaginal Prolapseapi-3705046100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiDokument27 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiBasudev chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bicornuate Unicolli Uterus 2Dokument46 SeitenBicornuate Unicolli Uterus 2Anjali LimbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Govt College of Nursig Mbs Hospital, Kota: A Case Study On EclampsiaDokument21 SeitenGovt College of Nursig Mbs Hospital, Kota: A Case Study On EclampsiaShalabh JoharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The UterusDokument21 SeitenAnatomy of The UterusSalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesDokument9 SeitenAntepartum Hemorrhage: Placental CausesadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Destructive Operation and Caesarian SectionDokument53 SeitenDestructive Operation and Caesarian SectionVijith.V.kumar0% (1)
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDokument36 SeitenAbnormal Uterine ActionMed PoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Describes Difficulty During Labor.: EtiologyDokument6 SeitenDescribes Difficulty During Labor.: EtiologyRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Pregnancy: Prof Uma SinghDokument53 SeitenMultiple Pregnancy: Prof Uma Singhpok yeahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unstable LieDokument7 SeitenUnstable Lieapi-370504667% (3)
- Breech Presentation 2020Dokument73 SeitenBreech Presentation 2020Max ZealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labour Chart: Intranatal Case Record - 9Dokument4 SeitenLabour Chart: Intranatal Case Record - 9Mrinmoy MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report of PPHDokument58 SeitenReport of PPHNishaThakuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- LSCS PRESENTATIONDokument13 SeitenLSCS PRESENTATIONMichael AdkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Labor PatternDokument85 SeitenAbnormal Labor PatternYibelu BazezewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal Case SheetDokument4 SeitenAntenatal Case SheetRichard SnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIV in Mothers and ChildrenDokument90 SeitenHIV in Mothers and Childrenabubaker100% (1)
- IUCDDokument24 SeitenIUCDcropsandinsects100% (1)
- Obg Drug BookDokument31 SeitenObg Drug BookANUM NOORINoch keine Bewertungen
- Assisted Vaginal DeliveryDokument26 SeitenAssisted Vaginal Deliveryapi-3705046100% (5)
- Abnormal Uterine ActionDokument33 SeitenAbnormal Uterine ActionRadwa Ebed100% (1)
- OLIGOHYDRAMNIOSDokument27 SeitenOLIGOHYDRAMNIOSSimi SaiPrasoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Antenatal ExaminationDokument7 SeitenLP Antenatal ExaminationManisha ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO Labour Care GuideDokument34 SeitenWHO Labour Care GuideAnkita Singh100% (1)
- DystociaDokument17 SeitenDystociaKarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PharingitisDokument68 SeitenPharingitisSwarantika Aulia RarasatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypoxia Classification Table - Physiological-CTGDokument1 SeiteHypoxia Classification Table - Physiological-CTGKhánh Nguyễn NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Pre Experimental Study To Assess The Effectiveness of STP On Knowledge Regarding Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Among Nursing Students at Selected Areas in JammuDokument6 SeitenA Pre Experimental Study To Assess The Effectiveness of STP On Knowledge Regarding Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Among Nursing Students at Selected Areas in JammuEditor IJTSRDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forcep DeliveryDokument11 SeitenForcep DeliveryAyushi100% (1)
- Intra Uterin Fetal DeathDokument15 SeitenIntra Uterin Fetal DeathanojanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument5 SeitenCase StudyKezya SaludesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyhydraminos and OligohydraminosDokument11 SeitenPolyhydraminos and OligohydraminosMelissa Catherine ChinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On Minor DisorderDokument23 SeitenSeminar On Minor Disorderpriti pallabi100% (1)
- Case PresentationDokument36 SeitenCase PresentationSaba TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breech PresentationDokument85 SeitenBreech Presentationwidya vannesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P PyrexiaDokument23 SeitenP PyrexiaRex BishopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breech PresentationDokument59 SeitenBreech Presentation117abdulsamadshaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystal Deposition DisordersDokument4 SeitenCrystal Deposition DisordersShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inhalational Agents: General PrinciplesDokument13 SeitenInhalational Agents: General PrinciplesShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumours: Will Aston, Timothy Briggs, Louis SolomonDokument24 SeitenTumours: Will Aston, Timothy Briggs, Louis SolomonShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ectatic ConditionsDokument11 SeitenEctatic ConditionsShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General AppearanceDokument2 SeitenGeneral AppearanceShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1Dokument9 SeitenSexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1Dokument9 SeitenSexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Cavity: Anatomy GI SystemDokument5 SeitenOral Cavity: Anatomy GI SystemShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument12 Seiten1ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1Dokument12 SeitenSexually Transmitted Infections (Stis) : 4Th October, 2015 1ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrosives 1Dokument13 SeitenCorrosives 1ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic MedicineDokument31 SeitenForensic MedicineShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HHV3Dokument6 SeitenHHV3ShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chi Kun GunyaDokument20 SeitenChi Kun GunyaShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical and Pill EsophagitisDokument3 SeitenChemical and Pill EsophagitisShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis: Synonyms - Pityrosporal Dermatitis - Dermatitis of The Sebaceous AreasDokument3 SeitenSeborrhoeic Dermatitis: Synonyms - Pityrosporal Dermatitis - Dermatitis of The Sebaceous AreasShuvashishSunuwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charity: DuaemDokument5 SeitenCharity: DuaemKalende AlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine Rupture: A Catastrophic Obstetric Emergency: OriginalDokument4 SeitenUterine Rupture: A Catastrophic Obstetric Emergency: OriginalBogdan CăpățînăNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Dokument6 SeitenPengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Geuman ChajgoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107 Intro 1Dokument34 SeitenNCM 107 Intro 1Riegne Chiara Fay AcuzarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Labor.Dokument2 SeitenFactors Affecting Labor.Salman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anwar and AzniahDokument10 SeitenAnwar and Azniahadhe yuniarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pf-Original Copy Marjh 12Dokument3 SeitenPf-Original Copy Marjh 12Artemio YadaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal Care: DR Elong Felix AdolpheDokument39 SeitenAntenatal Care: DR Elong Felix AdolpheZisuhNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17-Article Text-72-1-10-20191213Dokument8 Seiten17-Article Text-72-1-10-20191213Zahratul HayatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST. Mary Maternity HospitalDokument8 SeitenST. Mary Maternity HospitalgajendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydatidiform MoleDokument27 SeitenHydatidiform MolemanjuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infant Weight Loss GuideDokument1 SeiteInfant Weight Loss GuideCoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps To Safe - Respectful Maternity CareDokument1 SeiteSteps To Safe - Respectful Maternity CareSierra masseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Moms Our Babies The State of Maternal and Infant Health in Cincinnati and Hamilton CountyDokument7 SeitenOur Moms Our Babies The State of Maternal and Infant Health in Cincinnati and Hamilton CountyGerman Lopez100% (1)
- Cesarean Delivery - 090818183733Dokument27 SeitenCesarean Delivery - 090818183733Yared TJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Placenta PreviaDokument24 SeitenManagement Placenta PreviaMuhammad RifaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Obstetrics CasesDokument7 SeitenSummary of Obstetrics CasesMahir AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banerjee-Baranwal2020 Chapter InVitroFertilizationACaseStudyDokument12 SeitenBanerjee-Baranwal2020 Chapter InVitroFertilizationACaseStudyShaib Singh SalujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBBDokument29 SeitenMBBserul1930Noch keine Bewertungen
- Terms in Pregnancy and BirthDokument3 SeitenTerms in Pregnancy and BirthTri LestariNoch keine Bewertungen