Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Steering Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Hochgeladen von
J Naveen Kumar0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
45 Ansichten25 Seitensteer
Originaltitel
fundamentalofsteeringsysteminautomotivecar-160906085614
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldensteer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
45 Ansichten25 SeitenSteering Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Hochgeladen von
J Naveen Kumarsteer
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 25
Steering Fundamentals
Chapter 65
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Objectives
List the parts of steering systems
Describe the principles of operation of steering
systems
Compare linkage systems to rack and pinion
Describe how power steering systems operate
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Steering Systems
Steering system works with the suspension
system
Components
Steering gear
Steering linkage
Steering wheel
Steering column
Styles of steering
Gear box and parallelogram linkage
Long rack with linkage extending from ends
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Steering Gears
Common types
Recirculating ball and nut steering gear
Rack and pinion steering gear
Steering ratio
Amount of steering wheel rotation
Steering wheel turned all the way in one direction:
stops against a lock
Turning radius
Amount of space required for a vehicle to turn
around
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Recirculating Ball and Nut
Steering Gear
Sector gear meshes with ball nut
Ball nut rides on bearings on the worm shaft
Provides smooth steering feel
Ball nut has curved channels
Steering shaft has bearing channels
Balls rotate and recirculate through tubes
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Rack-and-Pinion Steering
Characteristics
End of steering shaft has a pinion gear
Meshes with the rack gear
Lighter and easier to install than standard
steering gears
Often has a faster ratio
More easily damaged when front wheels hit a
curb or rock
Transmit more road shock
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Steering Linkage
Steering gear is connected to wheels by
steering linkage
Parts vary depending on design
Tie-rods
Steering arms
Steering-knuckle
Parallelogram steering design
Most popular
Used with long and short arm suspension
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Parallelogram Steering Linkage
Recirculating ball gear uses parallelogram
steering
Name comes from parallelogram shape made by
steering linkage during a turn
Characteristics
Tie-rods on each side connected by center link
Pitman arm connects steering box to center link
Idler arm supports center link on passenger side
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Ball Sockets
Ball sockets connect steering linkage parts
Allow parts to rotate during a turn
Pivot as the steering deflects during a bump
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Tie Rods
Tie-rod ends attached to pivot points at front
wheels
Transmit motion from steering wheel to front
wheels
Maintain correct front wheel toe
Threaded adjusting sleeve connects inner and
outer tie-rods
Right-hand thread on one end
Left-hand on other
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Steering Arm
Tie-rods attach to front wheels at steering arms
Steering arm is attached to steering knuckle
Includes spindle
During a turn
Inside wheel must turn sharper than outside
wheel
Steering arms angled inward
Ackerman angle
Toe-out-on-turns
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Rack-and-Pinion Steering
Linkage
Rack and pinion: less complicated
Two tie-rods come out of steering rack
Conventional tie-rod end ball sockets on outer
ends
Inner tie-rod ends are ball sockets enclosed in
rubber bellows or boots
Steering damper
Minimizes effect of road shocks to steering wheel
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Steering Column
Steering wheel splined to steering shaft located
in center of steering column
Locknut retains steering wheel to shaft
Shaft supported by bearings at top and bottom of
column
Tilt columns allow driver to adjust steering wheel
angle
Air bags are installed on steering wheel
There is flexible coupling between steering shaft
and splined input shaft of steering gear
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Power Steering
Steering systems on most cars today are power
assisted
Some manual units are still made
Most power steering is hydraulic
Pressure supplied from crankshaft by belt-driven
pump
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Power Steering Pump
Steering pump driven by crankshaft belt
supplies hydraulic pressure to assist steering
Power steering pump types: roller, vane, and
slipper
Operation
Pump develops more flow at higher speeds
Flow control valve is almost always working
Requires considerable horsepower to operate
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Types of Power Steering
Power steering is either rack-and-pinion or
conventional recirculating ball and nut units
Most power steering systems are integral
Recirculating ball power steering
Gear boxes use pivot lever or torsion bar acting
on spool valve
Rack-and-pinion systems
Fluid is directed to a chamber on either side of
the rack
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Electronically Controlled
Variable Effort Power Steering
Reasonable speed: fixed power assist not
necessary
Late-model vehicles: vehicle speed determines
amount of power assist
Pump-controlled units: actuator solenoid
changes fluid flow
Steering gearcontrolled steering assist: boost is
sensed by module
Four-wheel steering systems: improve handling
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Electronically Controlled
Steering Systems
Can be steering-by-wire or mechanically
connected using electro-hydraulic steering gear
AFS system changes between low and high
speed steering assist
Electric motorpowered steering systems use a
rack-and-pinion steering gear
Electric power steering improves fuel economy
Controls amount of assist by regulating current
Planetary gear active steering
Input is sun gear and output is planetary carrier
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2012 Delmar, Cengage Learning
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Steering System Service: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument33 SeitenSteering System Service: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningRonald TaganasNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Rebuild & Modify Ford C4 & C6 Automatic TransmissionsVon EverandHow to Rebuild & Modify Ford C4 & C6 Automatic TransmissionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
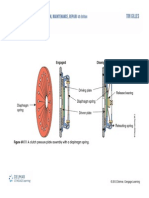
- Clutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument24 SeitenClutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learningshreyas jadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Front-Wheel-Drive (Transaxle and CV Joint) Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument25 SeitenFront-Wheel-Drive (Transaxle and CV Joint) Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningMatthew SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument24 SeitenClutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningNarendren KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clutch FundamentalsDokument24 SeitenClutch FundamentalsYerbol KabyshevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument24 SeitenClutch Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningRahul BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Trans ConceptsDokument32 SeitenAuto Trans ConceptsnavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- S Announcement 4431Dokument25 SeitenS Announcement 4431DragonviewerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheel Alignment Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument23 SeitenWheel Alignment Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learningmichael majadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 276992Dokument23 Seiten276992Pratik SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheel Alignment Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument23 SeitenWheel Alignment Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningVivek ChhabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Clutch Operation-1Dokument4 SeitenHydraulic Clutch Operation-1Gthulasi78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engine ClasificationDokument13 SeitenEngine Clasificationvasanth9046Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steering FundamentalDokument25 SeitenSteering FundamentalLUCIFERBREONoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To The Automobile: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To The Automobile: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningpallabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting System Service: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument24 SeitenStarting System Service: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningJM Llaban RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tire and Wheel Theory: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument25 SeitenTire and Wheel Theory: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningRonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosing Engine Mechanical Problems: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument25 SeitenDiagnosing Engine Mechanical Problems: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningSinggih DonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SteeringDokument191 SeitenSteeringANKIT NAPHADENoch keine Bewertungen
- Antilock Brakes, Traction, and Stability Control: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument25 SeitenAntilock Brakes, Traction, and Stability Control: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage Learningsengottaiyan100% (1)
- P - 4-Automotive Steering SystemsDokument37 SeitenP - 4-Automotive Steering Systemsbudi waluyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering Systems BasicsDokument36 SeitenSteering Systems Basicsali awadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Сцепление автомобиляDokument14 SeitenСцепление автомобиляберен галымNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Size and Measurements: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument29 SeitenEngine Size and Measurements: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningKeno DomingoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering SystemDokument57 SeitenSteering Systemsharad100% (2)
- Engine Dimension SelectionDokument29 SeitenEngine Dimension SelectionNeeraj YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 08 - Four-Wheel-Drive SystemsDokument36 SeitenCH 08 - Four-Wheel-Drive SystemsRevanth BhattaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- BVA2124 Steering Systems (Lecture 1)Dokument31 SeitenBVA2124 Steering Systems (Lecture 1)AdnannnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Types of Steering System, Steering GeometryDokument32 SeitenVarious Types of Steering System, Steering GeometrySumit Choudhary100% (1)
- Week 10Dokument41 SeitenWeek 10Jeyson Minaya PantojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering For Dummies: Tanmay Shankar 2 Year, MechDokument14 SeitenSteering For Dummies: Tanmay Shankar 2 Year, MechHarshal PaunikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automobile Engineering: TME-802 B. Tech Viii SemDokument33 SeitenAutomobile Engineering: TME-802 B. Tech Viii SemAmit TewariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartDokument55 SeitenAutomotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartgvnagamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 ShemalisDokument90 SeitenChapter 4 ShemalisLeta SK100% (1)
- Unit Iv SmeDokument118 SeitenUnit Iv SmeSuprithNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuspensionDokument47 SeitenSuspensiongsaratkumar50% (2)
- Bma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Dokument36 SeitenBma4723 Vehicle Dynamics Chap 8Fu HongNoch keine Bewertungen
- BrakesDokument27 SeitenBrakesNiño Jhim AndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering System PresentationDokument19 SeitenSteering System PresentationSagar GhusalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brakes and Logistics Meeting ReportDokument8 SeitenBrakes and Logistics Meeting ReportDhanush PrabhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Transmission: Presented byDokument48 SeitenAutomotive Transmission: Presented bySumit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC EngineDokument20 SeitenIC Enginemebratu AssefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drum BrakesDokument14 SeitenDrum Brakesmoskesama214Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chassis InformationDokument11 SeitenChassis InformationManny AnacletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 TTWDokument67 SeitenUnit 4 TTWMohsin EngrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering System PDFDokument27 SeitenSteering System PDFwanawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5 - Transmission SystemDokument41 SeitenLecture 5 - Transmission SystemengineeringdesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perform Mensuration and Calculation: LO1. Select Measuring InstrumentsDokument21 SeitenPerform Mensuration and Calculation: LO1. Select Measuring InstrumentsGb NYlztEnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Auto SystemsDokument32 Seiten2-Auto Systemsallan747Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lighting and Wiring Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningDokument30 SeitenLighting and Wiring Fundamentals: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningAjinkya JagtapNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTC ServicingDokument66 SeitenPTC Servicingfrankhil ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 27 BennetDokument56 SeitenChapter 27 BennetpapipapiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission SystemDokument92 SeitenTransmission SystemmubarakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CDokument29 SeitenGood Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CSrikar ChinmayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransmissionDokument97 SeitenTransmissionArjun ReghuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Fabrication of Mechanical Power SteeringDokument20 SeitenDesign and Fabrication of Mechanical Power SteeringAkhil NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gears & Drives: MEC1010 Design and Manufacturing 1 Dr. Simon SmithDokument50 SeitenGears & Drives: MEC1010 Design and Manufacturing 1 Dr. Simon SmithDavid MbikayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Philosophy of A Protective Relaying System 1Dokument6 SeitenIntroduction and Philosophy of A Protective Relaying System 1J Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Fuel InjectionDokument13 SeitenElectronic Fuel InjectionTerrence JimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Gate MeritDokument241 SeitenNon Gate MeritJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics-272 Lecture 20: - AC Power - Resonant Circuits - Phasors (2-Dim Vectors, Amplitude and Phase)Dokument37 SeitenPhysics-272 Lecture 20: - AC Power - Resonant Circuits - Phasors (2-Dim Vectors, Amplitude and Phase)J Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression of Interest - AnnexureDokument11 SeitenExpression of Interest - AnnexureJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer BrochureDokument20 SeitenTransformer BrochureJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of CPRIDokument21 SeitenOverview of CPRIJ Naveen Kumar100% (1)
- Petrol Bill SDokument1 SeitePetrol Bill SJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does A Car Steering WorkDokument8 SeitenHow Does A Car Steering WorkJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TO Automotive Steering SystemDokument22 SeitenTO Automotive Steering SystemJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Steering System: A Seminar Report OnDokument25 SeitenPower Steering System: A Seminar Report OnJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAS-10 Steering System and Wheel Alignment PDFDokument25 SeitenMAS-10 Steering System and Wheel Alignment PDFJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date:December Work Done Statement: 01.12.2 016 DDA Office Vivst Discuss Sujalla Expose Visit Bike 100Dokument2 SeitenDate:December Work Done Statement: 01.12.2 016 DDA Office Vivst Discuss Sujalla Expose Visit Bike 100J Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Fuel Injection System: Karthick S Iii-Mct 12BMT017Dokument17 SeitenElectronic Fuel Injection System: Karthick S Iii-Mct 12BMT017J Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Fuel Injection by Dr.S.John AlexisDokument32 SeitenElectronic Fuel Injection by Dr.S.John AlexisJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureDokument19 SeitenAutomotive: Describe EFI Engine Working ProcedureJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DascoDokument2 SeitenDascoJ Naveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUNY Maritime 8520 Teu Dual Fuel ContainershipDokument137 SeitenSUNY Maritime 8520 Teu Dual Fuel Containershipntontarski100% (1)
- d6d CatalogoDokument380 Seitend6d CatalogoHelio100% (7)
- Guide To Astm Test Methods For The Analysis of Coal and CokeDokument7 SeitenGuide To Astm Test Methods For The Analysis of Coal and Cokeecsuperal50% (2)
- NSNSNSN SNJSJDokument53 SeitenNSNSNSN SNJSJMayank VisalparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROSPER CompleteDokument1.471 SeitenPROSPER Completehamidahaku100% (1)
- B2202aso PDFDokument79 SeitenB2202aso PDFNinou NinouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perkins APD1100P (New)Dokument4 SeitenPerkins APD1100P (New)elnath wallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- View Brochure Fxzor 3029 TF 158 (1500 RPM)Dokument2 SeitenView Brochure Fxzor 3029 TF 158 (1500 RPM)Shahzad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aggreko Generator ManualDokument5 SeitenAggreko Generator Manualmuzica cu versuri0% (1)
- Oxygen Sensor 2Dokument2 SeitenOxygen Sensor 2Kevin Strong100% (1)
- Fire Investigation HandoutDokument38 SeitenFire Investigation HandoutAnonymous FRGDkENoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Power Plant and Steam Generators (Boilers)Dokument319 SeitenSteam Power Plant and Steam Generators (Boilers)Kama RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplement For 6 Cylinder Engine Section PDFDokument910 SeitenSupplement For 6 Cylinder Engine Section PDFMayobanex Moya MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shanmuk Kharavela AnnepuDokument2 SeitenShanmuk Kharavela AnnepuJyotsna NamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolymerDokument89 SeitenPolymerFatema Khatun100% (1)
- Indian Oil CorporationDokument16 SeitenIndian Oil CorporationMintu ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co2 RecoveryDokument10 SeitenCo2 RecoveryvijayxmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parameters Affecting The Removal of Naphthalene Over A Fixed Biomass Char BedDokument8 SeitenParameters Affecting The Removal of Naphthalene Over A Fixed Biomass Char BedMarco BarbaneraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Control: - Improving Efficiency of Boiler SystemsDokument4 SeitenBoiler Control: - Improving Efficiency of Boiler SystemsAtef LasheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedures For Pigging OperationsDokument5 SeitenProcedures For Pigging Operationsテレブリコ ジェファーソン78% (9)
- Output Ratings Ratings and Performance Data: 16.5 kVA 13.2 KW 18.0 kVA 14.4 KW 20.0 kVA 16.0 KW 22.0 kVA 17.6 KWDokument4 SeitenOutput Ratings Ratings and Performance Data: 16.5 kVA 13.2 KW 18.0 kVA 14.4 KW 20.0 kVA 16.0 KW 22.0 kVA 17.6 KWCiprian SorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- D12D380, Em-Ec96 - Esa - 02 - 586088Dokument2 SeitenD12D380, Em-Ec96 - Esa - 02 - 586088asif basha100% (2)
- 6 Arb ObdDokument43 Seiten6 Arb ObdGIUSEPPENoch keine Bewertungen
- NCND 3 PartiesDokument10 SeitenNCND 3 PartiesYOSOYKRITO CAMBIANDO TU ESTILO DE VIDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Arctic Cat 2011 150 Service ManualDokument8 SeitenArctic Cat 2011 150 Service Manualalvin100% (49)
- Product Guide o e w34dfDokument248 SeitenProduct Guide o e w34dfalkhayat1Noch keine Bewertungen
- E-Style Tubing Rotator BrochureDokument4 SeitenE-Style Tubing Rotator BrochureEvolution Oil ToolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 304D TYK00743 TA1 - Excavator Inpection ReportDokument11 Seiten304D TYK00743 TA1 - Excavator Inpection ReportCesar Eduardo Contreras CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- BURNY10 (Eng) ManualDokument57 SeitenBURNY10 (Eng) ManualHo NgocNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRM Saudi Arabia: Net Power RequirementDokument7 SeitenSRM Saudi Arabia: Net Power RequirementAlanNoch keine Bewertungen