Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 1
Hochgeladen von
Terry Ewe Tek Bee0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten12 SeitenCritical thinking involves evaluating arguments and making reasoned judgments to guide beliefs and actions. It is an important skill for life success. While definitions of critical thinking have evolved over time and differ between fields, it generally refers to disciplined, evaluative thinking as opposed to habitual or emotive thinking. Developing strong critical thinking requires personal strategies like carefully analyzing an argument from different perspectives to form one's own logical position.
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCritical thinking involves evaluating arguments and making reasoned judgments to guide beliefs and actions. It is an important skill for life success. While definitions of critical thinking have evolved over time and differ between fields, it generally refers to disciplined, evaluative thinking as opposed to habitual or emotive thinking. Developing strong critical thinking requires personal strategies like carefully analyzing an argument from different perspectives to form one's own logical position.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten12 SeitenLecture 1
Hochgeladen von
Terry Ewe Tek BeeCritical thinking involves evaluating arguments and making reasoned judgments to guide beliefs and actions. It is an important skill for life success. While definitions of critical thinking have evolved over time and differ between fields, it generally refers to disciplined, evaluative thinking as opposed to habitual or emotive thinking. Developing strong critical thinking requires personal strategies like carefully analyzing an argument from different perspectives to form one's own logical position.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
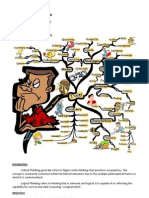
CRITICAL THINKING
DEFINITION
Broad definition: reasonable, reflecting
thinking that is focuses on deciding what to
believe or do
Criteria:
evaluative thinking
- Not necessarily negative
- Does not always lead to criticism
- Can lead to positive conclusion
WHY CT IS IMPORTANT
Good thinking is important element of life
success
Old standard in school cannot be the sole
means to judge the failure or success of
academic
Might be differentiated from creative
thinking
Need more future research and
implementation studies
CHANGES OF CT DEFINITION
It has been changing since a decade ago
Definition depend on expert from different
fields: Dominion of cognitive psychologist,
philosophers, behaviorally-oriented
psychologist and content specialist
Each group made significant contribution
in critical thinking understanding
Cognitive psychology- find the differences
between critical and creative thinking
CONT…
Philosophy- ct is a process of thinking to a
standard. The process must be guided by
belief and impact of behavior or action
Behavioral psychology- establish final
outcomes and methodologies to be used
by educator
Content specialist- demonstrate how ct can
be taught in different content areas such as
reading, literature, mathematics and
science. It help student to grip specific
knowledge
PROBLEM WITH DEFINITION
1)labeling that good thinking is critical
thinking (provided by philosophers)
Actually good thinking requires both
Found that students were more successful
in problem solving when used techniques
associated with reason and logic as well
as creativity and divergence
2) Confusing that attitudes vs actual thinking
process (ex: emotion vs cognition or
feeling vs. reasoning
CONT….
Thus; the proposed definition of ct: is the
disciplined mental activity of evaluating
arguments or proposition and making judgment
that can guide the development of beliefs and
taking actions.
Why good definition of ct is important:
- can be compared to other forms of thinking
- Ex- non critical thinking in the form of habitual
thinking, brainstorming, creative thinking,
prejudicial thinking or emotive thinking
MODEL OF CRITICAL THINKING & ITS
MODIFICATION
How the cognitive process create CT?
The critical thinking propose that the cognitive
process involved affective, conative, belief and
behavioral aspect
It’s method is evaluation of argumentation
It’s tool is affective disposition
It’s result are: confirm previous belief, new belief
establish, affective disposition to plan and take
action and activated conative component of goal
setting and self regulation
PERSONAL STRATEGIES FOR CRITICAL
THNIKING (taken from Cottrell S: 2005)
1) Make a quick reading to get the overall
view and check the initial response – and
see whether it proves true or runs
contradict to what you believe to be true
2) Compare what you read with what you
already know about the topic and with
experience
3) Make summary as you go along, hold the
overall argument in your head to make
sense of what comes next
4) Look for the author’s position or point of view
and asking ‘what are they trying to “sell me”?
5) As you read, check each section and ask
yourself if you know what it means. If not,
check again – sometimes it is more clearer
as you read for the second time. If it is still
unclear, remind yourself to come back to it
later as the rest of the passage may make it
clearer
6) Then read more carefully, seeing what
reasons the writers present and checking
whether you are persuaded by these
7) If you are persuaded, consider why? Is it
because they make use of experts in the
field? Is there research evidence that looks
thorough and convincing?
8)If you are not persuaded, then why not?
Whether you have good reasons for not being
convinced; or whether you have read other
material that contradicts it.
9) then, you create your own position, check
that your own point of view is convincing.
Could you support it if you were challenged?
Summary?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Critical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousVon EverandCritical Thinking: The Skills and Psychology of Questioning the ObviousBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Critical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyVon EverandCritical Thinking: The Concept and Power of Thinking CriticallyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- English 4 TerjemahanDokument7 SeitenEnglish 4 TerjemahanSandra DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking SlideDokument22 SeitenCritical Thinking SlideAmilin HatiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crititcal Thinking - Robert PalDokument9 SeitenCrititcal Thinking - Robert PalPalutziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument13 SeitenCritical ThinkingRuqiyya Qayyum100% (1)
- EAPP Report InfoDokument15 SeitenEAPP Report InfoKristine Gale CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananDokument62 SeitenCCT-Module Chapter-12 AngadananRizette PaloganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking Word - Foundation5Dokument73 SeitenCritical Thinking Word - Foundation5Saraswati Learning Center SLCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Logic and Critical Thinking: Phi 1 Reference: Bachhuber SJ, AndrewDokument43 SeitenIntroduction To Logic and Critical Thinking: Phi 1 Reference: Bachhuber SJ, AndrewJohn Paul VitugNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluating Thinking Through Intellectual StandardsDokument24 SeitenEvaluating Thinking Through Intellectual StandardsHanan WaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Yourself For StudyDokument31 SeitenManaging Yourself For StudyEmellda MANoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview - Critical ThinkingDokument15 SeitenOverview - Critical ThinkingBoi NonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking BookDokument61 SeitenCritical Thinking BookArturo AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philosophy Topic 5Dokument13 SeitenPhilosophy Topic 5Sivel InamikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformDokument44 SeitenUnit 1 Reflective Writing and Critical Thinking, Educational PlatformUmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking in EducationDokument29 SeitenCritical Thinking in EducationGayathri deviNoch keine Bewertungen
- PL 212 222Dokument50 SeitenPL 212 222mbwana abdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument34 SeitenCritical ThinkingMarianne ElemosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four - Critical ThinkingDokument9 SeitenChapter Four - Critical Thinkingshumet tadeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Nursing As A Science Critical ThinkingDokument39 Seiten10 Nursing As A Science Critical ThinkingArissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ideas - Critical ThinkingDokument43 SeitenIdeas - Critical ThinkingThương NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- M3 Critical Thinking - SSY1 - 2023 - UpdatedDokument51 SeitenM3 Critical Thinking - SSY1 - 2023 - Updatedelbertpc8205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 2 Intro To Critical ThinkingDokument78 SeitenLect 2 Intro To Critical ThinkingAlven BactadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking Is The Ability To Think Clearly and Rationally About What To Do or What To BelieveDokument16 SeitenCritical Thinking Is The Ability To Think Clearly and Rationally About What To Do or What To BelieveJelaine EllanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Critical ThinkingDokument6 SeitenIntroduction To Critical ThinkingSmart catNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Critical Thinking PDFDokument24 SeitenChapter 1 Critical Thinking PDFElma YulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking ExploredDokument26 SeitenCritical Thinking ExploredJosep PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument6 SeitenCritical ThinkingMohammad Ashraful AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Jemna PitogoDokument33 SeitenPrepared By: Jemna PitogoJemna Ursal PitogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument4 SeitenCritical ThinkingjennywrenwattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Is An EntrepreneurDokument35 SeitenWho Is An EntrepreneurShailja DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Simple Definition of Critical ThinkingDokument23 SeitenWhat Is A Simple Definition of Critical ThinkingTanzeela BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument8 SeitenCritical Thinkingupma sharma100% (1)
- Critical ThinkingDokument2 SeitenCritical ThinkingMwagaVumbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Tools of Critical and Creative ThinkingDokument7 Seiten03 Tools of Critical and Creative ThinkingJuan José ObandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Critical Thinking?: ISUI-EDU-Syl-014 Effectivity: January 3, 2017 Revision: 1Dokument5 SeitenWhat Is Critical Thinking?: ISUI-EDU-Syl-014 Effectivity: January 3, 2017 Revision: 1nutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 - Thinking-Critical & Creative ThinkingDokument5 SeitenLecture 2 - Thinking-Critical & Creative ThinkingBrian MogambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Thinking: Critical Thinking Is The Ability To Think in An Organized and Rational Manner in Order To UnderstandDokument5 SeitenCritical Thinking: Critical Thinking Is The Ability To Think in An Organized and Rational Manner in Order To UnderstandRizwan MumtazNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Do We Mean by Critical ThinkingDokument4 SeitenWhat Do We Mean by Critical ThinkingBrian CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Critical ThinkingDokument14 SeitenImportance of Critical ThinkingCellanie Janson100% (1)
- Paul The State of Critical Thinking TodayDokument12 SeitenPaul The State of Critical Thinking TodaySharla Benson-Brown100% (1)
- Introduction To Critical Thinking - Updated Oct 2019Dokument27 SeitenIntroduction To Critical Thinking - Updated Oct 2019Shi Ting100% (1)
- Make Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.Dokument11 SeitenMake Notes of Special and Important Points Regarding Definition of Critical Thinking As A Subject of Study and An Action To Learn in The Skills.chanchal shahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thinking Skills FCE 3204: Semester 1 2011/2012Dokument25 SeitenThinking Skills FCE 3204: Semester 1 2011/2012Katelin MunaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 (Logic)Dokument10 SeitenWeek 3 (Logic)Michaels CulturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDokument3 SeitenSubmitted By: Leticia S. Ong: Title: Logical and Critical ThinkingDanille Ivan OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Critical ThinkingDokument17 SeitenLecture 1 - Introduction To Critical Thinkingummi syafiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- B - 1. Critical Thinking, Process & Characteristics Made Easy For University Scholars, Sussex and Peoples' Uni(s)Dokument8 SeitenB - 1. Critical Thinking, Process & Characteristics Made Easy For University Scholars, Sussex and Peoples' Uni(s)Ameem TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For StudentsDokument81 Seiten5 Important Critical Thinking Skills To Master For Students117. godlief erwin semuel migeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRWT111 FinalDokument7 SeitenCRWT111 FinalReyna Lea MandaweNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8611-1 (Spring)Dokument36 Seiten8611-1 (Spring)Danial AwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Elements of Reasoning and The Intellectual StandardsDokument2 SeitenThe Elements of Reasoning and The Intellectual StandardsnbrajkovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical ThinkingDokument12 SeitenCritical Thinkingapi-347731796Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8611, Assignment NO 1Dokument42 Seiten8611, Assignment NO 1Asad ullah100% (2)
- Creative and CriticalDokument11 SeitenCreative and Criticalaries_rupaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- COGNITIVE PSY Unit 1-2 Notes ShivaniDokument56 SeitenCOGNITIVE PSY Unit 1-2 Notes ShivaniShivani MaratheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business LogicDokument34 SeitenBusiness LogicJotaro KujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Critical ThinkingDokument2 SeitenWhat Is Critical Thinkingالزعيم العربيNoch keine Bewertungen
- InteDokument30 SeitenInteJayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Acids and Bases Lab ReportDokument4 SeitenBiochem Acids and Bases Lab ReportShaina MabborangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NDokument19 SeitenOperating Manual CSDPR-V2-200-NJohnTPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Cycle Rickshaw For School ChildrenDokument23 SeitenDesign of Cycle Rickshaw For School ChildrenAditya GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daygame by Todd Valentine NotesDokument8 SeitenDaygame by Todd Valentine NotesAdnanHassan100% (7)
- IMCI UpdatedDokument5 SeitenIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 1 1489485680Dokument52 SeitenLecture 1 1489485680Dato TevzadzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeDokument14 SeitenPractical - 2: Preparation of The FixativeIseth ISethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetable Rates - 02-01-2021Dokument454 SeitenVegetable Rates - 02-01-2021Saurabh RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.Pharm - Semester - III-10.07.2018Dokument16 SeitenB.Pharm - Semester - III-10.07.2018SAYAN BOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- The Common Reader-Virginia WoolfDokument216 SeitenThe Common Reader-Virginia WoolfRusudan VardiashviliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile Pt. KPT PDFDokument23 SeitenCompany Profile Pt. KPT PDFfery buyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleDokument5 SeitenNeuropsychological Performance in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Original ArticleRaquel DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- IDRW MagazineDokument10 SeitenIDRW MagazineVirarya100% (1)
- Load Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignDokument1 SeiteLoad Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignBunkun15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Gynecology BaruDokument79 SeitenPediatric Gynecology BaruJosephine Irena100% (2)
- 2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidDokument7 Seiten2019 - High Levels of Polypharmacy in RheumatoidGustavo ResendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Process DebottleneckingDokument46 SeitenChemical Process DebottleneckingAhmed Ansari100% (2)
- Frequency Converter English ManualDokument33 SeitenFrequency Converter English Manualproduccion multipack100% (2)
- Science: The Menstrual CycleDokument4 SeitenScience: The Menstrual CycleLena Beth Tapawan YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Stage ComplicationsDokument84 Seiten3rd Stage ComplicationsDream100% (1)
- South Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliDokument29 SeitenSouth Valley University Faculty of Science Geology Department Dr. Mohamed Youssef AliHari Dante Cry100% (1)
- Cho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Dokument503 SeitenCho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Claudemiro costaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)Dokument3 SeitenSyllabus (402050B) Finite Element Analysis (Elective IV)shekhusatavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet Chemical Pre E PresentationDokument310 SeitenWet Chemical Pre E PresentationEdwardAlexanderGarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxDokument56 SeitenLINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxFalley FasterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Famous Bombers of The Second World War - 1st SeriesDokument142 SeitenFamous Bombers of The Second World War - 1st Seriesgunfighter29100% (1)
- Original Sandeha NivariniDokument117 SeitenOriginal Sandeha NivariniHmis BlrNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiPAP ST Clinical ManualDokument37 SeitenBiPAP ST Clinical ManualEng. Edelson Martins100% (2)
- Akshaya Vanam: Indian SandalwoodDokument52 SeitenAkshaya Vanam: Indian Sandalwoodprasadgss100% (4)
- Activity - Alien DNA - CompleteDokument36 SeitenActivity - Alien DNA - CompleteJennifer ShawkiNoch keine Bewertungen