Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Process of Evolution by Carla Mae
Hochgeladen von
Mads100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
103 Ansichten25 SeitenEvolution is the process by which organisms change and become more complex over generations in response to their environment. The document discusses several lines of evidence that support evolution, including fossils, comparative anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and artificial selection. It explains how Darwin's theory of natural selection and descent with modification from common ancestors can explain the diversity of life seen today through patterns of heredity and adaptation over time.
Originalbeschreibung:
The Process of Evolution
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenEvolution is the process by which organisms change and become more complex over generations in response to their environment. The document discusses several lines of evidence that support evolution, including fossils, comparative anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and artificial selection. It explains how Darwin's theory of natural selection and descent with modification from common ancestors can explain the diversity of life seen today through patterns of heredity and adaptation over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
103 Ansichten25 SeitenThe Process of Evolution by Carla Mae
Hochgeladen von
MadsEvolution is the process by which organisms change and become more complex over generations in response to their environment. The document discusses several lines of evidence that support evolution, including fossils, comparative anatomy, embryology, biochemistry, and artificial selection. It explains how Darwin's theory of natural selection and descent with modification from common ancestors can explain the diversity of life seen today through patterns of heredity and adaptation over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 25
THE PROCESS
OF EVULOTION
BY: CARLA MAE
FRANCISCO 11 PLATINUM
LEARNING COMPETENCIES
Describe evidence of EVULOTION such as
homology ,DNA ,protein sequences
tectonics , fossils record ,embryology ,and
artificial selection
Explain how population of organisms have
change over time showing patterns
Of descents with modification from common
ancestor to produce the
Organismal diversity observe today.
PROCESS OF THE EVULOTION
EVULOTION.
- As it is most famously used
Evolution is the process by which
an organism becomes more
sophisticated over time and in
response on its environment
FOSSILS
A fossils is any preserved
evidence of an organism .
Plants, Animals and even
bacteria cam form fossils in
some form
Comparative anatomy
Is the studies of similarities
and differences in the
anatomy of different
species .it is closely related
to evulotionary biology.
Comparative anatomy
Comparative embryology
Isbranch of embryology
that compares and contrast
embryos of different
species. It is used to show
how all animals are related.
Comparative embrylogy
Comparative biochemistry
IS the study of evolutionary
relationships between
organism.
Artificial selection is the intentional reproduction
of individuals in a population that have desirable
traits. In organisms that reproduce sexually, two
adults that possess a desired trait such as two
parent plants that are tall are bred together.
THE ORIGIN AND EXTINCTION
OF THE SPECIES
Darwin's theory of natural selection issued a profound challenge to orthodox
thought and belief no being or species has been specifically created all are
locked into a pitil, with extinction looming for those not fitted for the task.
On the Origins struggle for existence of Species by Means of Natural
Selection, or the Preservation of Favour
Races in the Struggle for Life), published on 24 November 1859, is a work
of scientific literature by Charles Darwin which is considered to be the
foundation of evolutionary biology. Darwin's book introduced the scientific
theory that populations evolve over the course of generations through a process
of natural selection. It presented a body of evidence that the diversity of
life arose by common descent through a branching pattern of evolution. Darwin
included evidence that he had gathered on the Beagle expedition in the 1830s
and his subsequent findings from research, correspondence, and
experimentation .
MODIFICATION OF COMMON ANCESTORS
The evolutionary term descent with modification is most
often associated with human evolution, but it is actually a
more general term than that would suggest
. means that traits are passed down from generation to generation
and sometimes undergo changes or modifications over time.
These changes may be caused by Natural Selection or even a
mutation of DNA.
The term became popular when Charles Darwin used it in his
book The Descent of Man.
Since the term was used in conjunction with his idea that humans
were related ancestrally to primates, the term descent with
modification has become synonymous with the human lineage on
the tree of life. However, this is only part of the actual meaning of
the term.
On a macroevolution level, this term would describe how a
species has changed over time and may have even become a new
species or gave rise to an additional species through speciation.
The diversity of living organisms on earth is truly astounding, almost
overwhelming. Humans have come up with ways of organizing,
or classifying, biological diversity throughout human history. Organisms
can be classified according to any number of criteria, including overall
similarities, colors, ecological functions, etc.
Although our understanding of evolutionary relationships among organisms
has greatly improved in the last century, it is by no means complete.
Relationships among organisms, and groups of organisms, continues to be
revised as new data becomes available. The rate of such revisions has
increased in recent years primarily as a result of the huge amount of new
molecular data (such as DNA sequences) that has been brought to bear on
tests of evolutionary relationships. This means that nearly
all taxonomies(systems of nomenclature) based on evolutionary
relationships among organisms are being revised, sometimes radically
classification and naming of
organisms:
Classification a system of naming objects or entities by
common characteristics. In a biological sense, classification
is the systematic grouping of organisms based on structural
or functional similarities or evolutionary history. A process of
establishing, defining, and ranking taxa within hierarchical
series of groups.
Taxonomy the classification of organisms into a system
that indicates natural relationships (evolutionary
relationships); the theory and practice of describing, naming,
and classifying organisms.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Magnetic Blueprint of LifeDokument79 SeitenThe Magnetic Blueprint of Lifeadnan100% (3)
- Bio2 Initial Release 13june PDFDokument94 SeitenBio2 Initial Release 13june PDFJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 4: Evidences of Evolution and Evolutionary Relationships of OrganismsDokument8 SeitenWorksheet in General Biology 2: Quarter 1 - Week 4: Evidences of Evolution and Evolutionary Relationships of OrganismsShastine Claor100% (1)
- Animal and Plants ReproductionDokument95 SeitenAnimal and Plants ReproductionMark Repollo100% (1)
- Geologic Time ScaleDokument7 SeitenGeologic Time ScaleWilliamAporboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module I - GeneticsDokument20 SeitenModule I - GeneticsJhay Luiz Cajigal ArquinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- SystematicsDokument24 SeitenSystematicsMARCOS RODSEL CUADRASAL MATEONoch keine Bewertungen
- Unifying Themes in Life ScienceDokument55 SeitenUnifying Themes in Life ScienceCatherine MojicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Gen Bio 5Dokument3 SeitenDLL Gen Bio 5Bobby Arguilles PaboresNoch keine Bewertungen
- L7S12. The Process of Evolution MoodleDokument52 SeitenL7S12. The Process of Evolution MoodleSichayra Gamotia100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science Lesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDokument16 SeitenEarth and Life Science Lesson 2 - Unifying Themes in The Study of Lifejhondee lagramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENBIO2Dokument17 SeitenGENBIO2Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chlorophyll and Other Pigments: Week 7Dokument15 SeitenChlorophyll and Other Pigments: Week 7Rheanet UbidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Gen Chem 1Dokument6 SeitenDLL Gen Chem 1Marjorie BrondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENBIO2 Mod.18 Phylogenetic TreeDokument20 SeitenGENBIO2 Mod.18 Phylogenetic TreeBea Bayona JoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAS Week6 Q1Dokument9 SeitenLAS Week6 Q1irene belle dableolesigues100% (1)
- Rubric For Geologic Time ScaleDokument1 SeiteRubric For Geologic Time ScaleBrennan McGeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Process of EvolutionDokument23 SeitenThe Process of Evolutionwilzl sarrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- Senior Gen Biology2 Q3 - M2 - L2 For PrintingDokument19 SeitenSenior Gen Biology2 Q3 - M2 - L2 For PrintingJasmen Garnado EnojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For PcapDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan For PcapMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cladogram Lesson PlanDokument5 SeitenCladogram Lesson Planapi-665322772Noch keine Bewertungen
- Budget of Work General Biology 1 A.Y. 2020-2021 First QuarterDokument5 SeitenBudget of Work General Biology 1 A.Y. 2020-2021 First QuarterAngela Francisca Bajamundi-VelosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vol. 17. Basidiomycetes - Marasmieae. Singer, L. 1976Dokument354 SeitenVol. 17. Basidiomycetes - Marasmieae. Singer, L. 1976러카일Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATP ADP Cycle Activity PDFDokument2 SeitenATP ADP Cycle Activity PDFFaustino, Jayreign MaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosa A. Scherson, Daniel P Faith - Phylogenetic Diversity - Applications and Challenges in BiodiversityDokument223 SeitenRosa A. Scherson, Daniel P Faith - Phylogenetic Diversity - Applications and Challenges in BiodiversityAndrea Garcia CaycedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science ModuleDokument112 SeitenEarth and Life Science ModuleLeidi Mae S. TugayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 4Dokument2 SeitenGen Bio 1 Lesson 4Ric SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science-Q1-Week-5 - v.2Dokument19 SeitenEarth Science-Q1-Week-5 - v.2Edlyn PolendeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsDokument12 SeitenLearning Activity Sheet General Biology 2 (Q4 - Lessons 3 and 4) The Organ Systems of Plants and AnimalsJeffrey YumangNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Bio LatestDokument4 SeitenDLL Bio LatestGlenda AstodilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Biology Unit 2 Topic 4 Notes Study Revision Guide Summary Edexcel Practice Biodiversity Plant Cell OrganellesDokument50 SeitenAS Biology Unit 2 Topic 4 Notes Study Revision Guide Summary Edexcel Practice Biodiversity Plant Cell Organellesshamxrock90% (59)
- DLL Earth Science (6th Week)Dokument5 SeitenDLL Earth Science (6th Week)Lollette RomuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Els-Module 6 - Earth's Internal HeatDokument33 SeitenEls-Module 6 - Earth's Internal HeatMichelle Bernadette Co-Gonzales100% (1)
- Cervantes, Charry Vida R. DLLDokument3 SeitenCervantes, Charry Vida R. DLLCharry CervantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Paper StardustDokument3 SeitenReaction Paper StardustMads100% (2)
- Senior High School First Quarterly Examination Scheddule S.Y. 2018 - 2019Dokument10 SeitenSenior High School First Quarterly Examination Scheddule S.Y. 2018 - 2019Julius Vendero SinenengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endogenic ProcessesDokument36 SeitenEndogenic Processesantonio AlmiranesNoch keine Bewertungen
- PERFORMANCE TASK FOR SCIENCE 9 PoDokument4 SeitenPERFORMANCE TASK FOR SCIENCE 9 PoMarianne SerranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 WHLP Week 1 2Dokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 WHLP Week 1 2maryNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 2 Learning Activity Sheet 5Dokument4 SeitenGeneral Biology 2 Learning Activity Sheet 5Arjay CarolinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- V5 Earth and Life Science WHLP, Summative Assessments, Performance TasksDokument8 SeitenV5 Earth and Life Science WHLP, Summative Assessments, Performance TasksMoiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 MELC 1Dokument11 SeitenWeek 1 MELC 1Ronald ArtilleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth & Life ScienceDokument23 SeitenEarth & Life ScienceBella ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Origin and Structure of The EarthDokument19 SeitenOrigin and Structure of The EarthEunice DualloNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBM Dod Assessment 2 1Dokument21 SeitenSBM Dod Assessment 2 1E MORTOLA100% (1)
- DLL Earth and Life Science October 24, 2022Dokument6 SeitenDLL Earth and Life Science October 24, 2022Mailene Magsico100% (1)
- Senior High School: Department of Education - Division of PalawanDokument27 SeitenSenior High School: Department of Education - Division of PalawanDorothy Yen EscalañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unifying Themes of LifeDokument32 SeitenUnifying Themes of LifeZay SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Tasks 2 3Dokument2 SeitenPerformance Tasks 2 3chewie bleNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectDokument35 SeitenGeneral Chemistry 2 - Introduction of The SubjectNina Grace FamosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Task in Earth Science-2nd QuarterDokument2 SeitenPerformance Task in Earth Science-2nd QuarterKarylle DeniseNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1aDokument14 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Quarter 2 WEEK 1 Module 1aJohn Brylle UrsuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Budget-of-Work-Earth and Life ScienceDokument5 SeitenBudget-of-Work-Earth and Life Sciencejoei Arquero100% (1)
- Perpetuation of LifeDokument22 SeitenPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Parallel Assessment 3&4Dokument2 SeitenGENERAL BIOLOGY 2 Parallel Assessment 3&4rhaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADM Grade 11 Quarter 1S1112ES IB 10 3 EditedDokument23 SeitenADM Grade 11 Quarter 1S1112ES IB 10 3 EditedLebz RicaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science: Get Ready To RockDokument9 SeitenEarth and Life Science: Get Ready To RockBAYANI VICENCIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Q2 W4 W5 W6 General Biology 1Dokument4 SeitenQ2 W4 W5 W6 General Biology 1Samantha ManibogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Science - Grade 11 Ola and OlcDokument6 SeitenEarth Science - Grade 11 Ola and OlcDalope CstrNoch keine Bewertungen
- My COTDokument3 SeitenMy COTShellane Blanco SarduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genbio2 12 Q3 SLM1Dokument14 SeitenGenbio2 12 Q3 SLM1Jhude JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Life Science DLL Week 2Dokument8 SeitenEarth Life Science DLL Week 2Janice Danieles Siano-TahuyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Learning Program (DLP) General Biology 2Dokument4 SeitenDynamic Learning Program (DLP) General Biology 2Paolene GolondrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL General Biology 1 Quarter 1 WeekDokument3 SeitenDLL General Biology 1 Quarter 1 WeekRubin RubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1M03 Complete ReviewDokument38 SeitenBiology 1M03 Complete ReviewAJDanglesNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionnairesDokument2 SeitenQuestionnairesMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Women During The Pre-Colonial PeriodDokument29 SeitenWomen During The Pre-Colonial PeriodMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug StudyDokument5 SeitenDrug StudyMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology: Vagal StimulationDokument1 SeitePathophysiology: Vagal StimulationMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Soccer SkillsDokument19 SeitenBasic Soccer SkillsMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epiglottitis ReportDokument4 SeitenEpiglottitis ReportMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Sector Reform Agenda - CHNDokument3 SeitenHealth Sector Reform Agenda - CHNMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harvest Moon PSP GuideDokument106 SeitenHarvest Moon PSP GuideMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vitamins (Lecture For Biochemistry)Dokument12 SeitenVitamins (Lecture For Biochemistry)MadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of PCAPDokument8 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of PCAPMads0% (1)
- Human ExperimentsDokument44 SeitenHuman ExperimentsMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samples of Medication FormatsDokument2 SeitenSamples of Medication FormatsMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
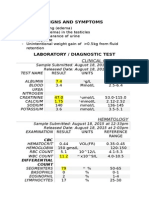
- Nephrotic Syndrome Lab Results PresentationDokument3 SeitenNephrotic Syndrome Lab Results PresentationMadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGNOU FEG-02 (2011) AssignmentDokument4 SeitenIGNOU FEG-02 (2011) AssignmentSyed AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Scale Dependent Framework For Trade Offs, Syndromes, and Specialization in Organismal BiologyDokument25 SeitenA Scale Dependent Framework For Trade Offs, Syndromes, and Specialization in Organismal BiologyDavid CultureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 Lecture 3 Value of Biodiversity: Consumptive Use, Productive Use, Social, Ethical, Aesthetic and Option Values Consumptive UseDokument2 SeitenUnit 4 Lecture 3 Value of Biodiversity: Consumptive Use, Productive Use, Social, Ethical, Aesthetic and Option Values Consumptive UseAthira SubinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hobbs and Harris 2001Dokument8 SeitenHobbs and Harris 2001BaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Lab 3: Comparing DNA Sequences To Understand Evolutionary Relationships With BLASTDokument11 SeitenAP Lab 3: Comparing DNA Sequences To Understand Evolutionary Relationships With BLASTZurab BasilashviliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ForlornDokument383 SeitenForlornHoward HillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monograph of Andira (Legimnosae-Papilionoideae)Dokument144 SeitenMonograph of Andira (Legimnosae-Papilionoideae)MauriciofigueiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growth and Reproduction of Bradybaena SimilarisDokument8 SeitenGrowth and Reproduction of Bradybaena SimilarisNgoc HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutDokument13 SeitenKomposisi Jenis Dan Struktur Vegetasi Hutan GambutI2O42OO54 IRFAN FAUZINoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity HotspotsDokument23 SeitenBiodiversity HotspotsJithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plowman 1982Dokument25 SeitenPlowman 1982Peter PoufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution and Origins of TobamovirusesDokument10 SeitenEvolution and Origins of TobamovirusesTony WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology A Systems Approach Cowan 3rd Edition Test BankDokument25 SeitenMicrobiology A Systems Approach Cowan 3rd Edition Test BankHeather Dixon100% (36)
- Environmental Science 14th Edition Enger Test BankDokument36 SeitenEnvironmental Science 14th Edition Enger Test Bankfloroncozwkk100% (26)
- Donoghue, 1985. A Critique of The Biological Species Concept and Recommendations For A Phylogenetic AlternativeDokument11 SeitenDonoghue, 1985. A Critique of The Biological Species Concept and Recommendations For A Phylogenetic AlternativeRaissa SiqueiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Wild Animals PDFDokument25 SeitenMarking Wild Animals PDFSantosh BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBO06Dokument504 SeitenMBO06sportzz clipsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ielts Mock Test 2020 February Reading Practice Test 2 v9 2481644Dokument37 SeitenIelts Mock Test 2020 February Reading Practice Test 2 v9 2481644ducdu2371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 18.3 Guided NotesDokument5 SeitenBiology 18.3 Guided Notesericaoh0709Noch keine Bewertungen
- Larrea-Alcazar Et Al 2011Dokument16 SeitenLarrea-Alcazar Et Al 2011Carlos Murillo SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRE - 2010 2019 - GRE 2018 Sample Question Paper 9Dokument28 SeitenGRE - 2010 2019 - GRE 2018 Sample Question Paper 9Juhi Deora100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Biodiversity ScriptDokument7 SeitenChapter 4 Biodiversity ScriptApodedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolutionarty Biology-Reproductive IsolationDokument2 SeitenEvolutionarty Biology-Reproductive IsolationNika MatammuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers For 3.4 THE CHARTS NEED WORKDokument33 SeitenAnswers For 3.4 THE CHARTS NEED WORKProsper NimleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio IiDokument12 SeitenGen Bio Iireganitjonalee431Noch keine Bewertungen