Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Motors and Generators
Hochgeladen von
Mohammad Mostofa Kamal Kowshik0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
182 Ansichten29 Seitenmotors and generators
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenmotors and generators
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
182 Ansichten29 SeitenMotors and Generators
Hochgeladen von
Mohammad Mostofa Kamal Kowshikmotors and generators
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 29
1 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
2 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Electromagnetism and movement
What is the link between movement, magnetism and electric
current?
3 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
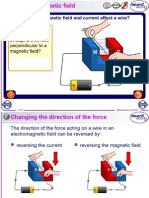
Wire in a magnetic field
4 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Changing the direction of the force
The direction of the force acting on a wire in an
electromagnetic field can be reversed by:
reversing the current reversing the magnetic field
The direction of the force is therefore relative to both the
direction of the magnetic field and the current.
5 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
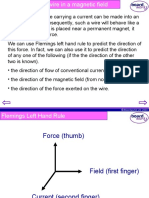
Flemings left-hand rule
It is possible to predict the direction of the force acting on
a wire its motion if the direction of the current or the
magnetic field are known. Flemings left-hand rule is
used to do this.
thuMb = Motion
First finger = magnetic Field
seCond finger = Current
6 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Increasing the size of the force
7 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Coil in a magnetic field
8 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
The motor effect: true or false?
9 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
10 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are electric motors?
How many items do you own that contain an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that
converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy to produce a
turning effect.
Most motors are powered using direct
current (DC), which is produced by
cells and batteries.
Motors powered by mains electricity
use alternating current (AC).
These motors use electromagnets
rather than permanent magnets.
11 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How does an electric motor work?
12 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
DC electric motor simulation
13 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do we increase motor strength?
Would the same strength motor be used in both of these?
How can the strength of an electric motor be increased?
increase the current flowing through the coil
increase the strength of the magnet
increase the number of turns on the coil
14 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
15 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Inducing current in a wire
16 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Flemings right-hand rule
It is possible to predict the direction of the induced current
produced by a generator if the direction of the force (or
motion) or the magnetic field are known. Flemings right-
hand rule is used to do this.
thuMb = Motion
First finger = magnetic Field
seCond finger = Current
17 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What is electromagnetic induction?
When current flows through a wire held in a magnetic field,
a force is created that moves the wire.
The opposite is also possible: if a
wire is moved across a magnetic
field, a current is produced. This is
called electromagnetic induction.
Induction also occurs if a magnet is
moved in a coil of wire, or if a coil of
wire rotates in a magnetic field.
In all these methods of inducing a current, the wire and
magnetic field move perpendicular to each other. If they
move parallel to each other, no current is induced.
18 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Inducing current in a coil
19 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
What are generators?
A generator is a device that converts mechanical energy
into electrical energy. It is the opposite of an electric motor.
Power stations use generators
to produce electricity on a large
scale. Mechanical energy is
provided by rotating turbines
that can be powered by:
high-pressure steam in
coal, oil, gas and nuclear
power stations
wind in wind turbines
falling water in hydroelectric power stations
20 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
How do AC generators work?
21 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
AC generator simulation
22 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Increasing the size of the induced current
How can the size of an induced current be increased?
increase the speed at which the coil rotates
increase the strength of the magnetic field
increase the number of turns in the coil
increase the total area of the coil.
In a power station
generator, an
electromagnet is often
used as this can provide
a stronger magnetic field
than is possible with a
permanent magnet.
23 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Factors affecting induced current
24 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Induction: true or false?
25 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
26 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Glossary
alternating current A current that constantly changes
direction. It is produced by most electrical generators.
commutator The part of a motor that enables the coil to
rotate using direct current.
direct current A current that always flows in the same
direction. It is produced by cells and batteries.
generator A device that converts mechanical energy into
electrical energy.
induction Generating a current in a wire by moving the
wire in a magnetic field, or by moving a magnet inside a coil.
motor A device that converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy.
slip rings The parts of a generator that enable the
rotating coil to produce alternating current.
27 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Anagrams
28 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Multiple-choice quiz
29 of 29 Boardworks Ltd 2007
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Properties of WavesDokument9 SeitenProperties of WavesKatiana KamdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- TorqueDokument26 SeitenTorquewalyat100% (2)
- Wave Properties v2.0Dokument28 SeitenWave Properties v2.0h a100% (1)
- A Level PhysicsDokument28 SeitenA Level PhysicsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of WavesDokument56 SeitenProperties of WavesDessy Norma JuitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages and Disadvantages of FrictionDokument2 SeitenAdvantages and Disadvantages of Frictionselvadz00Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 ElectronDokument53 Seiten5.1 ElectronFarish MikhaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Wave Properties v2 0Dokument28 Seiten9 Wave Properties v2 0salmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Series and Parallel CircuitsDokument44 SeitenSimple Series and Parallel CircuitsOyasor Ikhapo Anthony100% (1)
- Igcse AtomsDokument29 SeitenIgcse AtomsRahul VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KS4 Electricity - Static ElectricityDokument45 SeitenKS4 Electricity - Static Electricityganesh80% (5)
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDokument3 SeitenSummary Notes - Topic 6 Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Edexcel Physics IGCSESoo Kim KuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force & MotionDokument47 SeitenForce & MotionDitaS IdnayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lenses 1Dokument13 SeitenLenses 1Yuni MuliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Work FormulaDokument4 SeitenMechanical Work FormulavikassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits 7 QPDokument16 SeitenElectric Circuits 7 QPChong Xue ErNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.3 Magnetism %Dokument62 Seiten4.3 Magnetism %Anisha BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faraday's LawDokument35 SeitenFaraday's LawMasterArvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 - Module 5 - Simple Electric Motor and Generator-Fajardo-MaryroseDokument46 SeitenScience 10 - Module 5 - Simple Electric Motor and Generator-Fajardo-Maryrosemary rose fajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCMTDokument37 SeitenDCMTGloria HolcombNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Less Electro-Magnetic GeneratorDokument21 SeitenMotion Less Electro-Magnetic Generatormdayyub100% (1)
- 13.0 ELECTROMAGNETISM My NC Notes PDFDokument29 Seiten13.0 ELECTROMAGNETISM My NC Notes PDFRanga MudzieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDokument12 SeitenMotionless Electromagnetic GeneratorRajesh Chary100% (2)
- WTS 12 ElectrodynamicsDokument28 SeitenWTS 12 ElectrodynamicsTondani100% (1)
- Ac DC Solution 1Dokument4 SeitenAc DC Solution 1John Miko JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC GeneratorDokument7 SeitenAC Generatoraswardi8756Noch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrodynamicsDokument40 SeitenElectrodynamicssaskiahnyoni18Noch keine Bewertungen
- DCMTDokument37 SeitenDCMTarattupuzhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Motors and GeneratorsDokument19 SeitenElectric Motors and GeneratorsfahrimmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCS3304 3Dokument35 SeitenMCS3304 3Muhammad Ibrahim IsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eddy Current Braking System: T. K. M. College of Engineering, Kollam, IndiaDokument21 SeitenEddy Current Braking System: T. K. M. College of Engineering, Kollam, IndiaNaveen VkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI6402 - Electrical Machines Department of EIE&ICE 2016-2017Dokument91 SeitenEI6402 - Electrical Machines Department of EIE&ICE 2016-2017Dhivya SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Engineering - Chap08 - LectureDokument37 SeitenWind Engineering - Chap08 - LectureKağan YalçınNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Aparatus Group ActivityDokument8 SeitenElectrical Aparatus Group ActivityJohnLoyd DYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armature (Electrical Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument3 SeitenArmature (Electrical Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChytra DivakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Form 5 - 8.2 Force Acting On A Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldsDokument20 SeitenPhysics Form 5 - 8.2 Force Acting On A Current Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldsNoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromanetic InductionDokument53 SeitenElectromanetic InductionNor RazmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProjectDokument25 SeitenProjectAsif MuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Generator InvestigatoryDokument22 SeitenAC Generator InvestigatoryTarun NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palermo AcDc 2Dokument9 SeitenPalermo AcDc 2Palermo MelvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotorDokument93 SeitenElectrical Machines-Ch2-DcmotoradamwaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Energy Magnetic Motor: A Project OnDokument4 SeitenFree Energy Magnetic Motor: A Project OnEr Prem PrincepsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motionless Electromagnetic GeneratorDokument8 SeitenMotionless Electromagnetic Generatorraja100% (1)
- Experiment No: 9 (A) : AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: Demonstration of Faraday's Law ObjectivesDokument8 SeitenExperiment No: 9 (A) : AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT: Demonstration of Faraday's Law ObjectivesAbhishek RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines 2 A-C Machines PDFDokument654 SeitenElectrical Machines 2 A-C Machines PDFdhanz_99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fleming Left and RightDokument4 SeitenFleming Left and RightHarpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilations of Assignment EE330-ACDCDokument173 SeitenCompilations of Assignment EE330-ACDCDECIPOLO, KENNETH JOHN E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Motion Less Electromagnetic GeneratorDokument9 SeitenMotion Less Electromagnetic GeneratormycatalystsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.5 Electromagnetic EffectsDokument24 Seiten4.5 Electromagnetic EffectsSolutions ManualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Mark QuestionDokument20 SeitenTwo Mark QuestioncoolrajeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformersDokument40 SeitenTransformersAhmed TahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phre411 Lecture 1 NotesDokument8 SeitenPhre411 Lecture 1 Notesasphaltnoob8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Text Books: Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiDokument19 SeitenText Books: Department of Ece, Adhiparasakthi College of Engineering, KalavaiAubie MaopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BoardworksDokument11 SeitenBoardworksAjay PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2 - DC Machines PDFDokument123 SeitenUnit-2 - DC Machines PDFsujithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Science Extra Questions With AnswersDokument9 SeitenMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Class 10 Science Extra Questions With AnswersGurinder SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generation of ElectricityDokument5 SeitenGeneration of Electricityanimationindia3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Montfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClassDokument12 SeitenMontfort Secondary School Chapter 21: Electromagnetism: Name: Date: ClasssonghannNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Machines PresentationDokument66 SeitenDC Machines PresentationMarcos AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Motors and Generators PDFDokument20 SeitenPhysics Motors and Generators PDFlen2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Esr Test2 11112017 - MANASH SIRDokument2 SeitenEsr Test2 11112017 - MANASH SIRAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test: Ac+Induction Class Xii FM:33 TIME: 90 Min DATE:10/11/2019 1 Marks (1 X 6 06)Dokument2 SeitenTest: Ac+Induction Class Xii FM:33 TIME: 90 Min DATE:10/11/2019 1 Marks (1 X 6 06)Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Subject-Physics Class-9Dokument1 SeiteWorksheet Subject-Physics Class-9Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hots From Gravitation Answer All The Questions 1Dokument1 SeiteHots From Gravitation Answer All The Questions 1Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Velocity Questions Physics Form 4Dokument3 SeitenVelocity Questions Physics Form 4Angie Kong Su MeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Rayoptics Xii02102017Dokument1 SeiteTest Rayoptics Xii02102017Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ntse 1Dokument2 SeitenNtse 1Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Formula Booklet Physics X1Dokument38 SeitenFormula Booklet Physics X1Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Waveoptics 21102017Dokument1 SeiteWaveoptics 21102017Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Projmotion XIDokument23 SeitenVector Projmotion XIAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newton XIDokument3 SeitenNewton XIAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetDokument1 SeiteTreasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon - Comp Class X DSDokument19 SeitenCarbon - Comp Class X DSAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tithi Trtha 2Dokument6 SeitenTithi Trtha 2Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetDokument1 SeiteTreasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dora Model 1Dokument7 SeitenDora Model 1Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Krishi Agro TechDokument1 SeiteKrishi Agro TechAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Office of The Headmaster Mohanpur H.S School Mohanpur, West TripuraDokument14 SeitenOffice of The Headmaster Mohanpur H.S School Mohanpur, West TripuraAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Absent Without LeaveDokument2 SeitenAbsent Without LeaveAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pollution and Its TypeDokument32 SeitenPollution and Its Typeursaravana100% (1)
- Treasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetDokument1 SeiteTreasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetDokument1 SeiteTreasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- BirthdateDokument9 SeitenBirthdatesvmanivannan100% (1)
- Atomic Structure: Kotz CH 7 & CH 22 (Sect 4,5)Dokument37 SeitenAtomic Structure: Kotz CH 7 & CH 22 (Sect 4,5)Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetDokument1 SeiteTreasury Operation System, Tripura: Payment Data Input SheetAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 8 Science - LightDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 8 Science - LightAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 8 Science - LightDokument3 SeitenCBSE Class 8 Science - LightAnonymous JamqEgqqh1100% (2)
- Test: Modern Physics F.M: Time:: 1 Mark QuestionsDokument2 SeitenTest: Modern Physics F.M: Time:: 1 Mark QuestionsAnonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Induction 2015Dokument2 SeitenAc Induction 2015Anonymous JamqEgqqh1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrographic Survey: Ecg 305: Chapter 7Dokument24 SeitenHydrographic Survey: Ecg 305: Chapter 7Ahmad ZahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hot Pumps & Thermal ExpansionDokument3 SeitenHot Pumps & Thermal ExpansionMahmoud Al Homran100% (1)
- EC160B/180B/210B/240B/290B/360B/460B: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuDokument31 SeitenEC160B/180B/210B/240B/290B/360B/460B: Click The Volvo-Logo in The Lower Right Corner To Return To This Menu Main MenuMACHINERY101GEAR97% (71)
- ChemicalEq DroppersDokument13 SeitenChemicalEq DroppersUtkarsh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red MarsDokument16 SeitenRed Marsfz.fathima50% (2)
- Protection For HV Line BayDokument3 SeitenProtection For HV Line BayhasaladNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP 15-Dy1038ca Emglish ManualDokument78 SeitenHP 15-Dy1038ca Emglish ManualRoxana PetrescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Vetotouch Europa - Group 170821Dokument2 Seiten03 Vetotouch Europa - Group 170821HalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPP ReportDokument5 SeitenCPP ReportSujay Hazra100% (1)
- Security For VPNs With IPsec Configuration Guide - 15.2MTDokument166 SeitenSecurity For VPNs With IPsec Configuration Guide - 15.2MTAnonymous fIXhrYSmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Users Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsDokument40 SeitenUsers Manual For Oslo, Bremen and Turboaire.: Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructionsbuttler25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Voltage DetectorsDokument4 SeitenVoltage DetectorsKarthik SriramakavachamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Vital BleachingDokument19 SeitenNon Vital BleachingPriyabrat Pattanaik100% (1)
- Lennox - G40UH - Service ManualDokument46 SeitenLennox - G40UH - Service ManualKen Christoffersen0% (1)
- A Time To Build: People's Housing in Asia: Photograph By: Yann Arthus-BertrandDokument14 SeitenA Time To Build: People's Housing in Asia: Photograph By: Yann Arthus-BertrandarchitectsforumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Vehicle Components - BackDokument20 SeitenUnit 1 Vehicle Components - BackCarlos CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevOps For VMware Administrators (VMware Press Technology) - 1-321Dokument321 SeitenDevOps For VMware Administrators (VMware Press Technology) - 1-321mailboxrohitsharma100% (1)
- Thermozorb Heatless Regenerative Air Dryer: TZ22 - TZ142Dokument2 SeitenThermozorb Heatless Regenerative Air Dryer: TZ22 - TZ142Емил ГавриловNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avx 10k Data Sheet Data Sheets enDokument6 SeitenAvx 10k Data Sheet Data Sheets enAerotia InternationalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MQ-4C TritonDokument2 SeitenMQ-4C TritonLeakSourceInfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Reference Guide OptiPoint 500 FamilyDokument92 SeitenQuick Reference Guide OptiPoint 500 FamilyAlvaro ManjarresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 002 Danfoss PICV Energy Valve Ver 090821 r0Dokument2 Seiten002 Danfoss PICV Energy Valve Ver 090821 r0Pattana MekkhumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durability of Clay BricksDokument18 SeitenDurability of Clay BricksEmmanuel okelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Armor Piercing Bullets With Sintered Carbide Cores PDFDokument137 SeitenArmor Piercing Bullets With Sintered Carbide Cores PDFfogdartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artikel 7Dokument8 SeitenArtikel 7Andri PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free Body DiagramDokument8 SeitenFree Body Diagramabdullah hamba allahNoch keine Bewertungen
- VSL Technical Report - PT ExternalDokument36 SeitenVSL Technical Report - PT ExternalTran Nguyen KhiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atulya Beharwal: Class - 7 ADokument15 SeitenAtulya Beharwal: Class - 7 AAtul Beharwal100% (1)
- 5 Gaikindo Production Data Jandec2018 Rev HondaDokument3 Seiten5 Gaikindo Production Data Jandec2018 Rev HondaWira WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen