Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Life Insurance Contractual Provisions
Hochgeladen von
radislamy-10 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten23 SeitenOriginaltitel
ch12.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten23 SeitenLife Insurance Contractual Provisions
Hochgeladen von
radislamy-1Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 23
Chapter 12
Life Insurance
Contractual
Provisions
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
Agenda
Life Insurance Contractual Provisions
Dividend Options
Nonforfeiture Options
Settlement Options
Additional Life Insurance Benefits
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-2
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
Under the ownership clause, the policyowner possesses all
contractual rights in the policy while the insured is living
Rights include naming beneficiaries and surrendering the policy for
its cash value
The policyholder can designate a new owner by filing an
appropriate form
The entire-contract clause states that the life insurance
policy and attached application constitute the entire
contract between the parties
Prevents the insurer from making amendments without the
policyholders knowledge
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-3
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
The incontestable clause states that the insurer cannot
contest the policy after it has been in force two years during
the insureds lifetime
Protects the beneficiary if the insurer tries to deny payment of the
claim years after the policy was first issued
The insurer has two years to detect fraud
The insurer can contest a claim after the incontestable period if:
The beneficiary takes out the life insurance policy with the intent of
murdering the insured
The applicant has someone else take a medical examination
An insurable interest does not exist at the inception of the policy
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-4
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
The suicide clause states that if the insured commits
suicide within two years after the policy is issued, the
face amount of insurance will not be paid; there is only
a refund of the premiums paid
Reduces adverse selection against the insurer
A life insurance policy contains a grace period during
which the policyholder has a period of 31 days to pay
an overdue premium
Prevents the policy from lapsing by giving the policyowner
additional time to pay
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-5
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
The reinstatement provision permits the owner to
reinstate a lapsed policy
To reinstate, the following requirements must be met:
Evidence of insurability is required
All overdue premiums plus interest are paid
Any policy loans are repaid or reinstated
The policy was not surrendered for its cash value
The policy must be reinstated within a certain period,
usually 3-5 years after the date of lapse
Although it may require a large outlay of cash, it may be
cheaper to reinstate a lapsed policy than to purchase a
new policy
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-6
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
The beneficiary is the party named in the policy to
receive the policy proceeds
The primary beneficiary is the first entitled to receive the
policy proceeds
A revocable beneficiary means that the policyowner
reserves the right to change the beneficiary designation
without the beneficiarys consent
An irrevocable beneficiary is one that cannot be changed
without the beneficiarys consent
A specific beneficiary is specifically identified
A class beneficiary is a member of a group, e.g., children
of the insured
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-7
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
Under the misstatement of age or sex clause, if the insureds age or
sex is misstated, the amount payable is the amount that the premiums
paid would have purchased at the correct age and sex
A change-of-plan provision allows policyowners to exchange their
present policies for different contracts
Life insurance contracts do not contain many exclusions
Suicide excluded for two years
Insurers might insert a war clause to exclude payment if the insured dies
as a direct result of war
Some policies contain aviation exclusions
Premiums can be paid annually, semiannually, quarterly, or monthly
If premiums are not paid annually, a carrying charge is applied
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-8
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
A life insurance policy is freely assignable to
another party
Under an absolute assignment, all ownership rights in
the policy are transferred to a new owner
Under a collateral assignment, the policyowner
temporarily assigns a life insurance policy to a creditor
as collateral for a loan
Only certain rights are transferred to the creditor
Purpose is to protect the insurer from paying the policy
proceeds twice
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-9
Life Insurance Contractual
Provisions
A policy loan provision allows the policyowner to borrow the
cash value
The policyowner must pay interest on the loan to offset the loss of
interest to the insurer
A policy could lapse if the policyowner does not repay a loan and the
total indebtedness exceeds the available cash value
Under the automatic premium loan provision, an overdue
premium is automatically borrowed from the cash value after
the grace period expires
Prevent the policy from lapsing
Policyowner may become lazy and exhaust all cash value
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-10
Dividend Options
If a policy pays dividends it is a participating policy
Otherwise it is a nonparticipating policy
Dividends come from three main sources:
The difference between expected and actual mortality experience
Excess interest earnings
The difference between expected and actual operating expenses
Policyowners have several ways to take dividends:
Take the cash
Reduce the next premium coming due
Let them accumulate at interest and withdraw later
Apply toward the purchase of paid-up whole life insurance under the paid-up
additions option
Apply toward the purchase of term insurance
Convert the policy to a paid-up contract, or mature a policy as an
endowment
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-11
Nonforfeiture Options
The payment to a withdrawing policyowner is known
as a nonforfeiture value or cash surrender value
A policyowner has a right to the policys accumulated
cash value; all states have standard nonforfeiture laws
Policyowners have three nonforfeiture options:
The policy can be surrendered for its cash value
Under the reduced-paid up insurance option, the cash surrender
value is applied as a net single premium to purchase a reduced
paid-up policy
Under the extended term insurance option, the net cash surrender
value is used as a net single premium to extend the full face
amount of the policy into the future as term insurance
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-12
Exhibit 12.1 Table of Guaranteed
Values*
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-13
Settlement Options
The policyowner can choose among several options for
paying the policy proceeds
Or, the beneficiary may be granted the choice
The most common options include:
Proceeds are paid in a lump sum
Under the interest option, the proceeds are retained by the insurer,
and interest is periodically paid to the beneficiary
The beneficiary can be given withdrawal rights
Under the fixed-period option, the proceeds are paid to a beneficiary
over some fixed period of time
Under the fixed-amount option, a fixed amount is periodically paid to
the beneficiary until the principal and interest are exhausted
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-14
Exhibit 12.2 Income for Elected Period
(minimum monthly payment per $1000 of
proceeds)
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-15
Settlement Options
Under the life income option, installment payments are
paid only while the beneficiary is alive and cease on the
beneficiarys death
There is no refund feature or guarantee of payments
Other life income options include:
Life income with guaranteed period: if the beneficiary dies before
receiving the guaranteed number of years of payments, the
remaining payments are paid to a contingent beneficiary
Life income with guaranteed total amount: if the beneficiary dies
before receiving installment payments equal to the total amount
of insurance placed under the option, the payments continue until
the total amount paid equals the total amount of insurance
Under the joint-and-survivor settlement option, income payments
are paid to two persons during their lifetimes, such as a husband
and wife
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-16
Exhibit 12.3 Life Income with Guaranteed
Period (minimum monthly payment per
$1000 of proceeds)
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-17
Exhibit 12.4 Life Income with Guaranteed
Total Amount (minimum monthly payment
per $1000 of proceeds)
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-18
Exhibit 12.5 Joint-and-Survivor Income Option
10-Year Guaranteed Period (minimum monthly
payment per $1000 of proceeds)
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-19
Settlement Options
Settlement options allow for periodic payments to
the family, restoring their financial security
Disadvantages include:
Interest rates offered by insurers may be lower than
rates offered elsewhere
The settlement agreement may be inflexible and
restrictive
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-20
Additional Life Insurance Benefits
Other benefits can be added to a life insurance policy for an
additional premium
Under a waiver-of-premium provision, if the insured becomes totally
disabled, all premiums coming due during the period of disability are
waived
In many cases, total disability means that the insured cannot do any of
the essential duties of his or her job for which he or she is suited based
on schooling, training, or experience
The guaranteed purchase option permits the policyowner to
purchase additional amounts of life insurance at specified times in
the future without evidence of insurability
The option guarantees the purchase of specified amounts of life
insurance in the future even though the insured may become
uninsurable
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-21
Additional Life Insurance Benefits
The accidental death benefit rider doubles the face amount
of life insurance if death occurs as a result of an accident
Also known as double indemnity
The cost-of-living rider allows the policyowner to purchase
one-year term insurance equal to the percentage change in
the consumer price index with no evidence of insurability
The accelerated death benefits rider allows insureds who
are terminally ill to collect part or all of their life insurance
benefits before they die
Forms include: a terminal illness rider, catastrophic illness rider, and
long-term care rider
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-22
Additional Life Insurance Benefits
A viatical settlement is the sale of a life insurance policy by
a terminally ill insured to another party, typically an investor
group, who hopes to profit by the insureds early death
A life settlement is the sale of a life insurance policy by a
policyowner who no longer needs or wants the insurance
These options create a moral hazard problem, and may not
be adequately regulated by the states
Copyright 2008 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 12-23
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 11 - Life Insurance in Estate PlanningDokument18 SeitenChapter 11 - Life Insurance in Estate PlanningAkshya ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Account Opening FormDokument3 SeitenAccount Opening FormJoseph VJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Pooling and Servicing Agreement PDFDokument2 SeitenExample Pooling and Servicing Agreement PDFTrentonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bank of America StatementDokument12 SeitenBank of America StatementAmin Sahil0% (1)
- Steps of The Scientific Method MYTHBUSTERS ElephantDokument19 SeitenSteps of The Scientific Method MYTHBUSTERS Elephantradislamy-10% (1)
- LLQP StudyNotesDokument8 SeitenLLQP StudyNotesikawoako100% (2)
- Statements 20210314Dokument5 SeitenStatements 20210314kevinzhuxd102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance NotesDokument38 SeitenLife Insurance Notesshahidjappa67% (3)
- Coa - M2013-004 Cash Exam Manual PDFDokument104 SeitenCoa - M2013-004 Cash Exam Manual PDFAnie Guiling-Hadji Gaffar88% (8)
- CFA Level 2 NotesDokument21 SeitenCFA Level 2 NotesFarhan Tariq100% (2)
- All About Life ProtectionDokument37 SeitenAll About Life ProtectionNilesh Shahji100% (1)
- QWR Short FormDokument5 SeitenQWR Short Formboytoy 9774Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1040 Exam Prep Module IV: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeVon Everand1040 Exam Prep Module IV: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hans Memling Life and WorkDokument38 SeitenHans Memling Life and WorkHaneen HannouchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allied Banking Corporation vs. Sps. MacamDokument2 SeitenAllied Banking Corporation vs. Sps. MacamMarvien BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECT Cleaning Procedures PowerPoint 2013Dokument24 SeitenECT Cleaning Procedures PowerPoint 2013radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Agent's unauthorized mortgage binds himself personallyDokument2 SeitenAgent's unauthorized mortgage binds himself personallyJDR JDRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variable Universal Life (VUL) Insurance ExplainedDokument8 SeitenVariable Universal Life (VUL) Insurance Explainedjack r100% (1)
- Fundamentals of insurance terminology explainedDokument16 SeitenFundamentals of insurance terminology explainedFaye Nandini SalinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retail Banking Indusind BankDokument54 SeitenRetail Banking Indusind BankNithin NitNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. Life Insurance Contractual ProvisionsDokument23 SeitenA. Life Insurance Contractual ProvisionsMadhu dollyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - Life Insurance Contractual Provisions (FULL)Dokument31 SeitenLecture 9 - Life Insurance Contractual Provisions (FULL)Ziyi YinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Life InsuranceDokument65 SeitenTypes of Life InsuranceLalit AyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Chapter 10 Analysis of Insurance ContractsDokument29 SeitenTopic 3 Chapter 10 Analysis of Insurance ContractsYu WenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Insurance Companies635905675665434363Dokument37 SeitenChapter 5 Insurance Companies635905675665434363Aastha RokkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Company OperationsDokument19 SeitenInsurance Company OperationsshazarafiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Company OperationsDokument19 SeitenInsurance Company OperationsKim Thiên ThanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MGFC20 Ch10 More InsurancesDokument5 SeitenMGFC20 Ch10 More Insurancesbingus dingusNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd UnitDokument29 Seiten2nd UnitkpericheNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRAD Simulated Exam: Mutual CompanyDokument16 SeitenTRAD Simulated Exam: Mutual CompanyErnie LadoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance and Living BenefitsDokument31 SeitenLife Insurance and Living BenefitsblairkeaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Insurance - NotesDokument4 SeitenPrinciples of Insurance - NotesTarang SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Aspects of InsuranceDokument38 SeitenLegal Aspects of Insurancebapparoy100% (1)
- Life Insurance NotesDokument6 SeitenLife Insurance Notesamol.d.kelkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument28 SeitenChapter 10Hong Hanh PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- w3 - Contract Provisions in Life InsuranceDokument31 Seitenw3 - Contract Provisions in Life InsuranceNur AliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asuransi Ch. 10Dokument23 SeitenAsuransi Ch. 10Tessa Kusuma DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDokument30 SeitenLife Insurance: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinAtiq Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Lic Surrender ValueDokument1 Seite6 Lic Surrender ValueAJIT TRADERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traditional 121Dokument5 SeitenTraditional 121alexis almasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guarantee and OptionsDokument1 SeiteGuarantee and OptionsRashi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retirement Planning and Annuities: Trieschmann, Hoyt & SommerDokument26 SeitenRetirement Planning and Annuities: Trieschmann, Hoyt & SommerRaghavendra KaranjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument3 Seiten1beaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cliff Notes - PM AnnuitiesDokument4 SeitenCliff Notes - PM AnnuitiesJohnathan JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3Dokument16 SeitenUnit 3HimangshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABATOL - Life Insurance Planning ActivityDokument2 SeitenABATOL - Life Insurance Planning ActivityEUNICE BELLE ABATOLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life insurance typesDokument6 SeitenLife insurance typesrahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 (Classification of Policies)Dokument38 SeitenChapter 6 (Classification of Policies)Khan AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 LifeDokument10 SeitenUnit 1 LifeMohammed HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prin - of Insu. Class-9Dokument6 SeitenPrin - of Insu. Class-9saroj aashmanfoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance 1 2Dokument18 SeitenInsurance 1 2Udisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance:: Principles & Practices of Insurance Unit 3Dokument6 SeitenLife Insurance:: Principles & Practices of Insurance Unit 3ashishsinghashishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 6 Life InsuranceDokument15 SeitenLecture - 6 Life Insurancegyanprakashdeb302Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Investments - HandoutDokument13 SeitenBasics of Investments - Handoutsumit.zara1993Noch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile BirlaDokument31 SeitenCompany Profile BirlaShivayu VaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traditional Insurance Mock TestDokument4 SeitenTraditional Insurance Mock TestSevy5 DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 18-19Dokument19 SeitenSession 18-19Muhammad Ubaid UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insu Class-13Dokument14 SeitenLife Insu Class-13saroj aashmanfoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Name-Vishlesh Hukmani ENROLLMENT NO.-03014901819 Course-Bba (B&I) Subject-Principles of Insurance 2 SemsterDokument4 SeitenAssignment: Name-Vishlesh Hukmani ENROLLMENT NO.-03014901819 Course-Bba (B&I) Subject-Principles of Insurance 2 SemsterVishlesh 03014901819Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cliff Notes: Preparing People To PassDokument5 SeitenCliff Notes: Preparing People To PassCole LovickNoch keine Bewertungen
- TemplateDokument36 SeitenTemplateSubhan Imran100% (1)
- IV. Life InsuranceDokument3 SeitenIV. Life InsurancelauraoldkwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finalacc LifeinsuranceDokument22 SeitenFinalacc LifeinsuranceSaras BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- IRM Chapter 6Dokument23 SeitenIRM Chapter 6Rajja RashadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life InsuranceDokument9 SeitenLife InsuranceAKHLAK UR RASHID CHOWDHURYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminologies: 1. Partial Withdrawl:-Unit Policies Provide Flexibility To ItsDokument4 SeitenTerminologies: 1. Partial Withdrawl:-Unit Policies Provide Flexibility To ItsRASHMINoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument42 SeitenChapter 5Santosh BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Life Insurance ModulesDokument67 SeitenIntroduction to Life Insurance ModulesMandy RandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 06Dokument19 SeitenCH 06Zahid HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions: 1. Why Should I Buy An Insurance PolicyDokument4 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions: 1. Why Should I Buy An Insurance PolicySatender KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LN01 Rejda99500X 12 Principles LN11Dokument29 SeitenLN01 Rejda99500X 12 Principles LN11Mahbubur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 9, Insurance Requirements for the Urgent Care CenterVon EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 9, Insurance Requirements for the Urgent Care CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- S3P2 Takashi EgawaDokument16 SeitenS3P2 Takashi Egawaradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Technology On Performance of Mobile TelephonyDokument14 SeitenEffect of Technology On Performance of Mobile Telephonyradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- S3P2 Takashi EgawaDokument16 SeitenS3P2 Takashi Egawaradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1877042814013792 MainDokument5 Seiten1 s2.0 S1877042814013792 Mainradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco IOS Mobile Wireless GGSN CommandsDokument106 SeitenCisco IOS Mobile Wireless GGSN Commandsradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Do Ran and Ryan 2013Dokument22 SeitenDo Ran and Ryan 2013radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper Understanding Mobile Terminated Call FailuresDokument15 SeitenWhite Paper Understanding Mobile Terminated Call FailuresSantosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper Understanding Mobile Terminated Call FailuresDokument50 SeitenWhite Paper Understanding Mobile Terminated Call Failuresradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- SSRN Id1082891Dokument30 SeitenSSRN Id1082891radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- SDN Introduction: Software Defined Networking and OpenFlowDokument63 SeitenSDN Introduction: Software Defined Networking and OpenFlowradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- StateFarm DangerousIntersectionsDokument4 SeitenStateFarm DangerousIntersectionsCyn SyjucoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unpan030381 3Dokument34 SeitenUnpan030381 3radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OttiptvDokument35 SeitenOttiptvradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- PWS Public Warning System: Hannu Hietalahti Kevin Holley Stephen Hayes Brian DalyDokument13 SeitenPWS Public Warning System: Hannu Hietalahti Kevin Holley Stephen Hayes Brian Dalyradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- PWS Public Warning System: Hannu Hietalahti Kevin Holley Stephen Hayes Brian DalyDokument13 SeitenPWS Public Warning System: Hannu Hietalahti Kevin Holley Stephen Hayes Brian Dalyradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Architecture of the GSM Mobile Network SystemDokument2 SeitenArchitecture of the GSM Mobile Network Systemradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- BA0442Dokument9 SeitenBA0442radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13 AppDokument14 SeitenCH 13 AppAbhimanyu VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opm101chapter15 000Dokument40 SeitenOpm101chapter15 000radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Still Visible - Cause Many DiscussionsDokument2 SeitenStill Visible - Cause Many Discussionsradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tele Services IDokument3 SeitenTele Services Iradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Background Information GGSN Behavior Cause Code 192 Error Example ScenariosDokument5 SeitenBackground Information GGSN Behavior Cause Code 192 Error Example Scenariosradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Life Insurance Contractual ProvisionsDokument23 SeitenLife Insurance Contractual Provisionsradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- OEA000210 LTE Signaling and Protocols ISSUE1.04Dokument4 SeitenOEA000210 LTE Signaling and Protocols ISSUE1.04radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- GSM: Elements and Interfaces: BSS Radio CellDokument6 SeitenGSM: Elements and Interfaces: BSS Radio Cellradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tele Services IDokument3 SeitenTele Services Iradislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Characteristics of GSM (Wrt. Analog Sys.)Dokument2 SeitenPerformance Characteristics of GSM (Wrt. Analog Sys.)radislamy-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report Ebl and SCBDokument30 SeitenFinal Report Ebl and SCBRasadul Hasan Rasel100% (1)
- 0452 w13 QP 11Dokument20 Seiten0452 w13 QP 11Naðooshii AbdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- User GuideDokument270 SeitenUser GuideJason Hall100% (1)
- 8 Day Study Tour v1 - Kasigit AGUNGDokument3 Seiten8 Day Study Tour v1 - Kasigit AGUNGnorzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remittance Form for Creditable Income Taxes WithheldDokument1 SeiteRemittance Form for Creditable Income Taxes WithheldVeronicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 6-Person Ticket from Hubli to KachegudaDokument2 SeitenBook 6-Person Ticket from Hubli to KachegudaSiva TejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 Derivatives and Risk Management No CoverDokument85 SeitenChapter 18 Derivatives and Risk Management No CoverVenn Bacus RabadonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tourist Visa ChecklistDokument3 SeitenTourist Visa ChecklistDrishty ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I - Overview of Finance and Financial Management: Notes 1 For Afm 101Dokument5 SeitenUnit I - Overview of Finance and Financial Management: Notes 1 For Afm 101MHIL RAFAEL DAUGDAUGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Commercial & Islamic BankDokument16 SeitenDifference Between Commercial & Islamic BankArafat RaufNoch keine Bewertungen
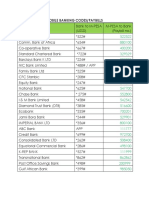
- Mobile Banking Codes PaybillDokument2 SeitenMobile Banking Codes PaybillMauriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Quote for Auto K-400 MachinesDokument3 SeitenRepair Quote for Auto K-400 MachinespamlidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uas 2012Dokument6 SeitenUas 2012ArdiSila DorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Banking of Sonali BankDokument37 SeitenE Banking of Sonali Bankmd shadab zaman RahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Hearing, 113TH Congress - Where Are We Now? Examining The Post-Recession Small Business Lending EnvironmentDokument78 SeitenHouse Hearing, 113TH Congress - Where Are We Now? Examining The Post-Recession Small Business Lending EnvironmentScribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dbms Complete Lab ManualDokument172 SeitenDbms Complete Lab ManualR Gandhimathi RajamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nadeem CV UaeDokument5 SeitenNadeem CV UaenikszoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Current Affairs Oct-2014 to Apr-2017Dokument161 SeitenBanking Current Affairs Oct-2014 to Apr-2017laksh048Noch keine Bewertungen