Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Private & Public Ipv4 Addressing
Hochgeladen von
Ashar Fraz0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten12 SeitenIt is about the IP subnetting, i have made the complete course for udemy.
Originaltitel
10. IP Addressing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenIt is about the IP subnetting, i have made the complete course for udemy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten12 SeitenPrivate & Public Ipv4 Addressing
Hochgeladen von
Ashar FrazIt is about the IP subnetting, i have made the complete course for udemy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 12
Lecture 10
Private & Public IPv4 Addressing
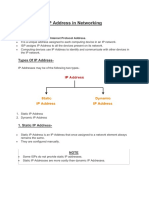
What is IP Address
A unique identifier assigned to a machine on an IP network.
It is a software address, not associated with Hardware.
It allows the communication between hosts on different networks.
According to IP Terminology Bit = 1 or 0
Byte = 8 bits
Octet = Byte = 8 Bits
Network Address = It is used in the routing process to deliver the packet
to a remote network, - for example 192.168.0.0, 172.16.0.0, 10.0.0.0
Broadcast Address = An address used by application to send
information to all network nodes is called Broadcast address. For
example 255.255.255.255 means any network and all nodes.
Hierarchical 32-bit IP Addressing
An IP Address is composed of 32 bits information.
32 Bits are divided into four sections.
Each section is referred to as octet or byte.
IP Address can be represented in Dotted Decimal, Binary or
Hexadecimal format.
It can handle 4.3 billion address (4,294,967,296).
Network Address
A Network Address is also called a Network Number.
A network number is a unique network identifier.
Every host on a network shares the same network address as a
part of their IP address.
Network Classes i.e. Class A, Class B, Class C
Class Selection Depends upon network size.
Network Addressing
Class A Addresses
Network . Node . Node . Node
The First byte Must be between 1 and 126 with prefix /8.
First bit in the First byte of class A address is always 0 or off.
Example: 10 . 12 . 11 . 1 /8
Class A address has 3 bytes (24 bits) for node address.
Total Number of nodes 16,777,216 minus 2 with Unique addresses.
Two node address with all 0 bits and all 1 bits in node octet are reserved.
All node bits off is network address i.e. 10.0.0.0
All node bits on is broadcast address i.e. 10.255.255.255
Class B Addresses
Network . Network . Node . Node
The First byte Must be between 128 and 191 with prefix /16.
First bit in the First byte of class B address is always 1 or on while the
second bit is always off.
Example: 172 . 16 . 3. 1 4 / 16
Class B address has 2 bytes (16 bits) for network address and 2 bytes (16
bits) for node address.
Total Number of network addresses 16,384 and 65,534 possible usable
addresses for each network.
Two node address with all 0 bits and all 1 bits in node octet are reserved.
All Host bits turned off is network address = 172.16.0.0
All Host bits on is broadcast address = 172.16.255.255
Class C Addresses
Network . Network . Network . Node
The First byte Must be between 192 and 223 with prefix /24.
First two bits in the First byte of class C address are always 1 or on while
the third bit is always 0 or off.
Example: 19 2. 168 . 1 . 1 / 24
Class C address has 3 bytes (24 bits) for network address and 1 bytes (8
bits) for node address space.
Total Number of network addresses 2,097,152 and 254 possible usable
addresses for each network.
Two node address with all 0 bits and all 1 bits in node octet are reserved.
All Host bits turned off is network address = 192.168.1.0
All Host bits on is broadcast address = 192.168.1.255
Private / Reserved IP Address Space
Class A : 10.0.0.0 through 10.255.255.255
Class B: 172.16.0.0 through 172.31.255.255
Class C: 192.168.0.0 through 192.168.255.255
Unicast Address
Used to Direct Traffic to a specific host.
Broadcast Address
Used to Direct Traffic to all hosts.
Multicast Address
Used to send traffic to all hosts on a network.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IP Addressing SchemeDokument30 SeitenIP Addressing SchemedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handling Qualites of CanardDokument49 SeitenHandling Qualites of CanardUsman GhummanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addresses and SubnettingDokument22 SeitenIP Addresses and SubnettingKumar R Ranjan100% (2)
- SubnettingDokument16 SeitenSubnettingVishal Jain100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Waiting Line ModelsDokument46 SeitenChapter 11 Waiting Line ModelsLara FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ip Address ClassificationDokument3 SeitenIp Address ClassificationAshish100% (10)
- Reading #2: Participatory Action ResearchDokument45 SeitenReading #2: Participatory Action Researchapi-3723169100% (2)
- IPAddressDokument33 SeitenIPAddressBrij ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internetworking or Network LayerDokument94 SeitenInternetworking or Network LayerWaleed MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing: Format of An IP AddressDokument8 SeitenIP Addressing: Format of An IP AddressLovemore ManyerukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponty Maurice (1942,1968) Structure of BehaviorDokument131 SeitenPonty Maurice (1942,1968) Structure of BehaviorSnorkel7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Laurel VS GarciaDokument2 SeitenLaurel VS GarciaRon AceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture24 25 SubnettingDokument46 SeitenLecture24 25 SubnettingFiroz kumar100% (2)
- The Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaDokument5 SeitenThe Flowers of May by Francisco ArcellanaMarkNicoleAnicas75% (4)
- 03 - Internet Protocol (IP)Dokument29 Seiten03 - Internet Protocol (IP)hizbullahjamily2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ip Addresssing and Classes of Ip AddressingDokument18 SeitenIp Addresssing and Classes of Ip AddressingShahzeb KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Data Comm Ethio-ItalyDokument41 SeitenChapter 3 Data Comm Ethio-ItalyrtyiookNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10Dokument15 SeitenChapter 10Ethio DotNetDeveloperNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch4 Ip AddressingDokument73 Seitench4 Ip AddressinggargiwawreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ambo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceDokument48 SeitenAmbo University Woliso Campus, Technology and Informatics School Department of Computer ScienceNoel GirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net Lec7Dokument25 SeitenNet Lec7api-3701823Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC and CN Chapter-7Dokument31 SeitenDC and CN Chapter-7habtamud655Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6.0 IP Addressing: 6.1 IP Address Class 6.2 IP V4, IPV6Dokument19 Seiten6.0 IP Addressing: 6.1 IP Address Class 6.2 IP V4, IPV6Samuel ZodinglianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Five: IP Address and Sub-NettingDokument50 SeitenChapter Five: IP Address and Sub-NettingBehru. SherefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Five: IP Address and Sub-NettingDokument46 SeitenChapter Five: IP Address and Sub-Nettingalebachew destawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Today We Will Discuss:: - IP Addressing - SubnettingDokument46 SeitenToday We Will Discuss:: - IP Addressing - SubnettingfraserNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Address & SubnetingDokument50 SeitenIP Address & SubnetingLê DuẩnNoch keine Bewertungen
- File 034Dokument25 SeitenFile 034Zulkernain Omer TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument78 SeitenChapter 5Omkar DhumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- YyyyyyyyyyDokument36 SeitenYyyyyyyyyyMarven JuadiongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 IPv4 Part2Dokument38 Seiten3 IPv4 Part2Easha AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- The First. Ipv4 Address StructureDokument3 SeitenThe First. Ipv4 Address StructureĐức trọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing ModesDokument30 SeitenAddressing ModesAyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 IP AddressingDokument95 Seiten1 IP AddressingJeet KarmakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is IPv4Dokument15 SeitenWhat Is IPv4throw151awayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 NetworkingDokument42 SeitenUnit 4 NetworkingDaniel AshagrieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ip Address ClassDokument3 SeitenIp Address Classluizam213180Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 IP AddressingDokument45 SeitenChapter 4 IP Addressingmisix23317Noch keine Bewertungen
- IP AddressingDokument28 SeitenIP AddressingOdoch JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Ip AddressDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Ip AddressMetsi KinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classful AddressingDokument81 SeitenClassful AddressingYash AllampalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing: Classful and Classless Addressing: DR - Shiny Duela J Associate ProfessorDokument16 SeitenIP Addressing: Classful and Classless Addressing: DR - Shiny Duela J Associate ProfessorshinyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CN U4 Network LayerDokument47 SeitenCN U4 Network LayerAravind SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Module 4 18 Mar 2021material I 18 Mar 2021 IP AddressDokument65 Seiten6 Module 4 18 Mar 2021material I 18 Mar 2021 IP AddressPIYUSH RAJ GUPTA 19BCE2087Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Semester 1: Routing & AddressingDokument88 SeitenCCNA Semester 1: Routing & AddressingTung HoangNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing and SubnettingDokument11 SeitenIP Addressing and SubnettingAriel RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ip Addressing 1Dokument37 SeitenIp Addressing 1otienoonyangotonnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WINSEM2020-21 ITE3001 ETH VL2020210503484 Reference Material I 03-Apr-2021 IP Addresses Classes and Subnets 13Dokument73 SeitenWINSEM2020-21 ITE3001 ETH VL2020210503484 Reference Material I 03-Apr-2021 IP Addresses Classes and Subnets 13KUTHURU SREE SHANTHAN REDDY 19BIT0086Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Computer Networks: Spring 2020-21 Lect. #06Dokument15 SeitenAdvance Computer Networks: Spring 2020-21 Lect. #06Ishwar MhtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unix Network ProgrammingDokument21 SeitenUnix Network ProgrammingMonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCN 03Dokument132 SeitenDCN 03Riya SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument44 SeitenChapter 4Nahom E.Noch keine Bewertungen
- IP Address in NetworkingDokument11 SeitenIP Address in NetworkingSumit PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesDokument33 SeitenTcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesjayshreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPV4 and Subnetting StrategyDokument39 SeitenIPV4 and Subnetting StrategyrolandsabitNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing LectureDokument10 SeitenIP Addressing Lecturechibi00wolframNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Protocol (Ip) and SubnettingDokument106 SeitenInternet Protocol (Ip) and SubnettingJermyn G EvangelistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 IP AddressingDokument46 SeitenChapter 4 IP AddressingAklilu AyeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Mod051 01Dokument11 Seiten1 Mod051 01tanboonkiatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument37 SeitenChapter 2Vi RusNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing: Classful and Classless Addressing: DR - Shiny Duela J Associate ProfessorDokument22 SeitenIP Addressing: Classful and Classless Addressing: DR - Shiny Duela J Associate ProfessorshinyNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Addressing & SubnettingDokument72 SeitenIP Addressing & SubnettingFrancis PulaiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 3Dokument12 SeitenUnit - 3Syed AijazNoch keine Bewertungen
- SubnettingDokument29 SeitenSubnettingDiom ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworksDokument24 SeitenComputer NetworksTushar BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing Table PopluationDokument3 SeitenRouting Table PopluationAshar FrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN Switching ConceptsDokument4 SeitenLAN Switching ConceptsAshar FrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA3 Lab 3.5.1Dokument13 SeitenCCNA3 Lab 3.5.1Mike OntiverosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Ccie Rs Advanced Lab Workbook Ver 4 Vol1Dokument15 SeitenSample Ccie Rs Advanced Lab Workbook Ver 4 Vol1Gabo Sab100% (1)
- Chi Nog 03 Ine Ccie Rsv5 ChangesDokument42 SeitenChi Nog 03 Ine Ccie Rsv5 ChangesdibpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anais Nin - Under A Glass Bell-Pages-29-32 WordDokument6 SeitenAnais Nin - Under A Glass Bell-Pages-29-32 WordArmina MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Relative Maxima, Relative Minima and Saddle PointsDokument3 Seiten1 Relative Maxima, Relative Minima and Saddle PointsRoy VeseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP.-Habitat-of-Animals Lesson PlanDokument4 SeitenLP.-Habitat-of-Animals Lesson PlanL LawlietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Reported SpeechDokument3 SeitenExercise Reported Speechapi-241242931Noch keine Bewertungen
- AIW Unit Plan - Ind. Tech ExampleDokument4 SeitenAIW Unit Plan - Ind. Tech ExampleMary McDonnellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootDokument19 SeitenCatalyst 3750 Series Switches TroubleshootSugumar DuraisamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Review QuestionsDokument2 SeitenChapter 8 Review QuestionsSouthernGurl99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Causing v. ComelecDokument13 SeitenCausing v. ComelecChristian Edward CoronadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnglishFile4e Intermediate TG PCM Vocab RevDokument1 SeiteEnglishFile4e Intermediate TG PCM Vocab RevB Mc0% (1)
- Creating The HardboiledDokument20 SeitenCreating The HardboiledBen NallNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11v.jigisha Chaptear2Dokument53 Seiten11v.jigisha Chaptear2Anirban PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MKF Tool HelpDokument6 SeitenMKF Tool HelpRob GoetzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hussain Kapadawala 1Dokument56 SeitenHussain Kapadawala 1hussainkapda7276Noch keine Bewertungen
- P.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsDokument19 SeitenP.E and Health: First Quarter - Week 1 Health-Related Fitness ComponentsNeil John ArmstrongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final DemoDokument14 SeitenFinal DemoangieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akhbar Al Fuqaha Narration - Non Raful Yadayn From Ibn Umar - Reply To Zubair Ali ZaiDokument15 SeitenAkhbar Al Fuqaha Narration - Non Raful Yadayn From Ibn Umar - Reply To Zubair Ali ZaiAbdullah YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cns Spectrums: The Clinical Challenges of Akathisia CME Review ArticleDokument16 SeitenCns Spectrums: The Clinical Challenges of Akathisia CME Review Articledzakiyah nurul israNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schemes and Tropes HandoutDokument6 SeitenSchemes and Tropes HandoutJohn LukezicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaDokument26 SeitenWorking With Regular Expressions: Prof. Mary Grace G. VenturaAngela BeatriceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stability Result 15275 MT - Initial StowageDokument1 SeiteStability Result 15275 MT - Initial StowageLife with Our planetNoch keine Bewertungen
- AL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)Dokument7 SeitenAL Applied Mathematics 1989 Paper1+2 (E)eltytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureDokument2 SeitenTask 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureJaepiNoch keine Bewertungen
- JKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiDokument3 SeitenJKSSB Panchayat Secretary Adfar NabiSHEIKHXUNINoch keine Bewertungen
- What If The Class Is Very BigDokument2 SeitenWhat If The Class Is Very BigCamilo CarantónNoch keine Bewertungen