Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DPCM
Hochgeladen von
Arun Kumar Dhupam0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
180 Ansichten10 SeitenDPCM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenDPCM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
180 Ansichten10 SeitenDPCM
Hochgeladen von
Arun Kumar DhupamDPCM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
Differential Pulse Code Modulation
Differential pulse code modulation is a technique of analog to
digital signal conversion. This technique samples the analog signal
and then quantizes the difference between the sampled value and
its predicted value, then encodes the signal to form a digital value.
Before going to discuss differential pulse code modulation, we have
to know the demerits of PCM (Pulse Code Modulation). The
samples of a signal are highly correlated with each other. The
signals value from the present sample to next sample does not
differ by a large amount. The adjacent samples of the signal carry
the same information with a small difference. When these samples
are encoded by the standard PCM system, the resulting encoded
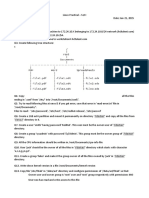
signal contains some redundant information bits. The below figure
illustrates this.
The above figure shows a continuing time signal x(t) denoted by a dotted
line. This signal is sampled by flat top sampling at intervals Ts, 2Ts,
3TsnTs. The sampling frequency is selected to be higher than the Nyquist
rate. These samples are encoded by using 3-bit (7 levels) PCM. The
samples which are quantized to nearest digital level as shown by small
circles in the above figure. The encoded binary value of each sample is
written on the top of the samples. Just observe the above figure at
samples taken at 4Ts, 5Ts, and 6Ts are encoded to the same value of (110).
This information can be carried only by one sample value. But three
samples are carrying the same information means redundant.
Now let consider the samples at 9Ts and 10Ts, the difference between
these samples only due to the last bit and first two bits are redundant
since they do not change. So in order to make the process this redundant
information and to have a better output. It is an intelligent decision to take
a predicted sampled value, assumed from its previous output and
summarise them with the quantized values. Such a process is called as
Differential PCM (DPCM) technique.
Principle of Differential Pulse Code Modulation
If the redundancy is reduced, then the overall
bitrate will decrease and the number of bits
required to transmit one sample will also reduce.
This type of digital pulse modulation technique is
called differential pulse code modulation. The
DPCM works on the principle of prediction. The
value of the present sample is predicted from the
previous samples. The prediction may not be
exact, but it is very close to the actual sample
value.
Differential Pulse Code
Modulation Transmitter
The sampled signal is denoted by x(nTs) and the predicted signal is indicated by x^(nTs). The comparator finds out
the difference between the actual sample value x(nTs) and the predicted value x^(nTs). This is called signal error
and it is denoted as e(nTs)
e(nTs)= x(nTs)- x^( nTs) .(1)
Here the predicted value x^(nTs) is produced by using a prediction filter(signal processing filter). The quantizer
output signal eq(nTs) and the previous prediction is added and given as input to the prediction filter, this signal is
denoted by xq(nTs). This makes the prediction closer to the actually sampled signal. The quantized error signal
eq(nTs) is very small and can be encoded by using a small number of bits. Thus the number of bits per sample is
reduced in DPCM.
The quantizer output would be written as,
eq(nTs)= e(nTs)+ q(nTs) (2)
Here q(nTs) is quantization error. From the above block diagram the prediction filter input xq(nTs) is obtained by
sum of x^(nTs) and the quantizer output eq(nTs).
i.e, xq(nTs) = x^(nTs)+ eq(nTs).. (3)
by substituting the value of eq(nTs) from the equation (2) in equation (3) we get,
xq(nTs) = x^(nTs)+ e(nTs)+ q(nTs). (4)
Equation (1) can written as,
e(nTs)+ x^( nTs) = x(nTs). (5)
from the above equations 4 and 5 we get,
xq(nTs) = x(nTs)+ x(nTs)
Therefore, the quantized version of signal xq(nTs) is the sum of original sample value and quantized error q(nTs).
The quantized error can be positive or negative. So the output of the prediction filter does not depend on its
characteristics.
Differential Pulse Code
Modulation Receiver
As we discussed above, the predictor undertakes
a value, based on the previous outputs. The input
given to the decoder is processed and that output
is summed up with the output of the predictor, to
obtain a better output. That means here first of
all the decoder will reconstruct the quantized
form of original signal. Therefore the signal at the
receiver differs from the actual signal by
quantization error q(nTs), which is introduced
permanently in the reconstructed signal.
Applications of DPCM
The DPCM technique mainly used Speech, image and audio
signal compression. The DPCM conducted on signals with
the correlation between successive samples leads to good
compression ratios. In images, there is a correlation
between the neighbouring pixels, in video signals, the
correlation is between the same pixels in consecutive
frames and inside frames (which is same as correlation
inside the image).
This method is suitable for real Time applications. To
understand the efficiency of this method of medical
compression and real-time application of medical imaging
such as telemedicine and online diagnosis. Therefore, it can
be efficient for lossless compression and implementation
for lossless or near-lossless medical image compression.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Differential Pulse Code Modulation Working and ApplicationDokument5 SeitenDifferential Pulse Code Modulation Working and ApplicationhicevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3-CDokument6 SeitenLab 3-CMUHAMMAD AMMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling Process: The Process of Transforming An Analog Waveform Into A Discrete Waveform IsDokument7 SeitenSampling Process: The Process of Transforming An Analog Waveform Into A Discrete Waveform IsShubham ManteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5Dokument5 SeitenLab 5viswanathrd45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM)Dokument11 SeitenDifferential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM)omarhanandehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog To Digital Conversion Digital To Analog Conversion: Tanauan City CollegeDokument44 SeitenAnalog To Digital Conversion Digital To Analog Conversion: Tanauan City CollegeRalph Laurence G VisayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8thpracticalDokument8 Seiten8thpracticalShubham RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Unit-1Dokument138 SeitenDC Unit-1swethachand7Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCM and DPCM Comparison for Signal TransmissionDokument21 SeitenPCM and DPCM Comparison for Signal TransmissionParas VekariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 1Dokument13 SeitenLec 1حسنين محمد عبدالرضا فليحNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used ToDokument53 SeitenPulse-Code Modulation (PCM) Is A Method Used Tosugu2k88983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Code Modulation and DemodulationDokument48 SeitenPulse Code Modulation and DemodulationHasib PeyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 4Dokument21 SeitenChap 4Suvo IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Code Modulation: Zakaria Sembiring, ST.,MSC Computer Engineering Politeknik Negeri MedanDokument16 SeitenPulse Code Modulation: Zakaria Sembiring, ST.,MSC Computer Engineering Politeknik Negeri MedanJordan Rionanda Simatupang Part IINoch keine Bewertungen
- COMMUNICATION 2 (Reviewer)Dokument22 SeitenCOMMUNICATION 2 (Reviewer)Jovel Jhon Opiana100% (1)
- Exp. PCMDokument9 SeitenExp. PCMsairajdreamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Code ModulationDokument5 SeitenPulse Code ModulationEr Amarsinh RNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM Telecommunication System EngineeringDokument49 SeitenPCM Telecommunication System EngineeringAliImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog to Digital Conversion Using PCMDokument17 SeitenAnalog to Digital Conversion Using PCMShakeel AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- SwitchingDokument14 SeitenSwitchingPikesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30 PCM and QuantizationDokument3 Seiten30 PCM and QuantizationJay Acera Pasadas Olaivar0% (1)
- Pulse Code PCMDokument13 SeitenPulse Code PCMumerisahfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 PCM DM DPCMDokument33 Seiten6 PCM DM DPCMWidyaninurul HidayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baseband Formatting TechniquesDokument89 SeitenBaseband Formatting TechniquesKartik SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog To DigitalDokument17 SeitenAnalog To DigitalI KaizokuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 84e58differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM)Dokument10 Seiten84e58differential Pulse Code Modulation (DPCM)Karan MaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog CommunicationDokument9 SeitenAnalog CommunicationSAMYAK SHAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog To DigitalDokument14 SeitenAnalog To DigitalHarshit PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) ExplainedDokument45 SeitenPulse Code Modulation (PCM) ExplainedKunal KatariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Dokument45 Seiten4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal KatariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM SignalsDokument16 SeitenPCM SignalsStephen AdokwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Transmission: Analog-to-Digital Conversion TechniquesDokument15 SeitenDigital Transmission: Analog-to-Digital Conversion TechniquesAkash RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer 2018-19: Nafiz Imtiaz Bin Hamid Assistant Prof., EEE DeptDokument16 SeitenSummer 2018-19: Nafiz Imtiaz Bin Hamid Assistant Prof., EEE DeptNAZIFA NAWARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment on Sampling, Quantization, Encoding and PCM/DPCM SignalsDokument13 SeitenExperiment on Sampling, Quantization, Encoding and PCM/DPCM SignalsHarshavardhan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Transmission: PCM ProcessesDokument28 SeitenDigital Transmission: PCM ProcessesLharie Mae BecinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pondicherry UniversityDokument17 SeitenPondicherry Universitygood updaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM Agenda for Electronics Engineering DepartmentDokument17 SeitenPCM Agenda for Electronics Engineering Departmentjohn billy balidioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Lecture 09 and 10Dokument14 SeitenClass Lecture 09 and 1031008Imran KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communication IntroductionDokument69 SeitenDigital Communication IntroductionlokeshwarrvrjcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog To DigitalDokument15 SeitenAnalog To DigitalMani SandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM Lab ManualDokument5 SeitenPCM Lab ManualSakshi DewadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec PU March05Dokument98 SeitenLec PU March05Muhammad Awais AshfaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITT400 - Chapter 4Dokument58 SeitenITT400 - Chapter 4NOl ShAnahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Pulse Code ModulationDokument12 SeitenDifferential Pulse Code ModulationNarasimhareddy MmkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Final MergedDokument38 SeitenUnit 2 Final MergedSwastikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohini 52093006178Dokument11 SeitenRohini 520930061782020rsee009Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPCMDokument9 SeitenDPCMhamza mohsenNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM BahaaDokument50 SeitenPCM BahaaNazar liveNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC8501 UNIT 2 Linear Predictive CodingDokument12 SeitenEC8501 UNIT 2 Linear Predictive CodingmadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Electronics & Control Engineering SECX1028 - Digital Signal Processing Unit-Iv Multi Rate Digital Signal ProcessingDokument16 SeitenDepartment of Electronics & Control Engineering SECX1028 - Digital Signal Processing Unit-Iv Multi Rate Digital Signal ProcessingS.DurgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse-code modulation (PCM) for digitizing analog signalsDokument54 SeitenPulse-code modulation (PCM) for digitizing analog signalsdiversity_86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual 19032012Dokument33 SeitenManual 19032012Hirankur KhillareNoch keine Bewertungen
- PCM: Pulse Code Modulation GuideDokument9 SeitenPCM: Pulse Code Modulation GuideMd.Robin MridhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling and PCMDokument89 SeitenSampling and PCMJincy RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersDokument33 SeitenDigital Transmission, Multiplexing and T-CarriersMukesh100% (5)
- DIGITAL CommunicationsDokument253 SeitenDIGITAL CommunicationsRachelle TungolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4 PCMDokument5 SeitenExperiment 4 PCMMs. INDU Ms. INDUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modulation Techniques PDFDokument21 SeitenModulation Techniques PDFvignesh nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Spectral Analysis MATLAB® Software User GuideVon EverandDigital Spectral Analysis MATLAB® Software User GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARM ProcessorDokument14 SeitenARM ProcessorArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument1 SeiteAbstractArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wams 2024 - V2Dokument1 SeiteWams 2024 - V2Arun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection CoefficientDokument1 SeiteReflection CoefficientArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: PercentageDokument2 SeitenObjective: PercentageArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawp 2017 2756118Dokument4 SeitenLawp 2017 2756118Arun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessors & Micro Controllers LabDokument1 SeiteMicroprocessors & Micro Controllers LabArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflex KlystronDokument1 SeiteReflex KlystronArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PATIENT CARE AND MONITORING: Elements of Intensive-Care Monitoring, PatientDokument1 SeitePATIENT CARE AND MONITORING: Elements of Intensive-Care Monitoring, PatientArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assgn 2Dokument1 SeiteAssgn 2Arun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gunn OscillatorDokument1 SeiteGunn OscillatorArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delocalization Pi Electrons Conjugation Organic Semiconductors HOMO and Lumo Valence ConductionDokument1 SeiteDelocalization Pi Electrons Conjugation Organic Semiconductors HOMO and Lumo Valence ConductionArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eca TestDokument1 SeiteEca TestArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CommunicationDokument1 SeiteCommunicationArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- OLED DetailsDokument1 SeiteOLED DetailsArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explain The Cell StructureDokument1 SeiteExplain The Cell StructureArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- LcdsDokument1 SeiteLcdsArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic TechniquesDokument1 SeiteDiagnostic TechniquesArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMEDokument1 SeiteBMEArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- State and Define The Basic Types of Electrodes Used For The Measurement of Bioelectric PotentialsDokument1 SeiteState and Define The Basic Types of Electrodes Used For The Measurement of Bioelectric PotentialsArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of transducer and biochemical transducers definedDokument1 SeitePrinciple of transducer and biochemical transducers definedArun Kumar Dhupam100% (1)
- Opcode MapDokument3 SeitenOpcode MapArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio TelemetryDokument1 SeiteBio TelemetryArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Electrode and Electrode PotentialDokument1 SeiteDefine Electrode and Electrode PotentialArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical InstrumentationDokument1 SeiteBiomedical InstrumentationArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV system overviewDokument14 SeitenCV system overviewArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMEDokument1 SeiteBMEArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Wave ShapingDokument71 SeitenLinear Wave ShapingArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Communication SystemDokument1 SeiteIntroduction To Communication SystemArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Line EquationsDokument1 SeiteTransmission Line EquationsArun Kumar DhupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Get The Most Out of Your Storage With The Dell EMC Unity XT 880F All-Flash Array - InfographicDokument1 SeiteGet The Most Out of Your Storage With The Dell EMC Unity XT 880F All-Flash Array - InfographicPrincipled TechnologiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Data Transmission With The PIC MicrocontrollerDokument9 SeitenInfrared Data Transmission With The PIC MicrocontrollerVenkatesan RamamoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evidencia 2 Market ProjectionDokument5 SeitenEvidencia 2 Market ProjectionpaoesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIT ROURKELA MID-SEMESTER EXAM FOR ADVANCED SIGNAL PROCESSINGDokument2 SeitenNIT ROURKELA MID-SEMESTER EXAM FOR ADVANCED SIGNAL PROCESSINGRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your ICICI Bank Savings Statement for May 2019Dokument1 SeiteYour ICICI Bank Savings Statement for May 2019Sai Raavan Chowdary KakaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unison Light Manager v1.65 ManualDokument115 SeitenUnison Light Manager v1.65 ManualRyan5443Noch keine Bewertungen
- R20-N-Python Unit 4 - ChanduDokument56 SeitenR20-N-Python Unit 4 - ChanduMahesh SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps To Convert Autoplant Piping To Caepipe / Caesar Ii: Step 1Dokument1 SeiteSteps To Convert Autoplant Piping To Caepipe / Caesar Ii: Step 1carlawtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dijkstra's AlgorithmDokument59 SeitenDijkstra's AlgorithmTanmay BaranwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MM WM NotesDokument37 SeitenMM WM NotesRakesh Kumar BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vishu - Numerical AnalysisDokument15 SeitenVishu - Numerical Analysisayushi28Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Steel Bridge Structure Report Using Staad ProDokument45 SeitenDesign of Steel Bridge Structure Report Using Staad ProAS PALACENoch keine Bewertungen
- UMTS PagingDokument2 SeitenUMTS PagingCauTungNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevOps Guide for Cynics Highlights Benefits for Developers, Leaders and MoreDokument16 SeitenDevOps Guide for Cynics Highlights Benefits for Developers, Leaders and MoreraidenbrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CI DSA Study GuideDokument1 SeiteCI DSA Study GuidetanyamamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZXSDR BS8800 Product DescriptionDokument40 SeitenZXSDR BS8800 Product DescriptionsivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 156-215 80Dokument304 Seiten156-215 80nombreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topas 6 Whats NewDokument30 SeitenTopas 6 Whats NewEduardo ArdilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer ProblemsDokument14 SeitenInteger Problemsamangandhi03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Allplan BCM QuantitiesDokument193 SeitenManual Allplan BCM Quantitiessectiune79Noch keine Bewertungen
- Al Faisal CollegesDokument14 SeitenAl Faisal Colleges03347919292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Some New Kinds of Connected Domination in Fuzzy GraphsDokument11 SeitenSome New Kinds of Connected Domination in Fuzzy GraphsIOSRjournal100% (1)
- Hw5 SolutionDokument11 SeitenHw5 SolutionTun LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2nd - 566 - Computer ApplicationDokument36 SeitenAssignment 2nd - 566 - Computer ApplicationM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addendum Proyek Konstruksi Jalan Di Kota Palangka: Analisis Faktor Penyebab, Akibat, Dan Proses Contract RayaDokument13 SeitenAddendum Proyek Konstruksi Jalan Di Kota Palangka: Analisis Faktor Penyebab, Akibat, Dan Proses Contract RayaFahmi AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alberta HighSchool 2007 Round 1Dokument2 SeitenAlberta HighSchool 2007 Round 1Weerasak Boonwuttiwong100% (1)
- Linux-Practicals OdtDokument3 SeitenLinux-Practicals Odtsrinivas godavarthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Migrating ServerData PDFDokument2 SeitenMigrating ServerData PDFsblNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft - CMS Control StrategyDokument17 SeitenDraft - CMS Control Strategysamiao90Noch keine Bewertungen
- đáp án bài thi thực tập fptDokument16 Seitenđáp án bài thi thực tập fptVũ Hoàng LongNoch keine Bewertungen