Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mass Spectros
Hochgeladen von
Bea Uy0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten5 SeitenBrief Overview of Mass Spectroscopy
Originaltitel
Mass Spectroscopy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBrief Overview of Mass Spectroscopy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
19 Ansichten5 SeitenMass Spectros
Hochgeladen von
Bea UyBrief Overview of Mass Spectroscopy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
MASS SPECTROSCOPY
ILLUSTRATION:
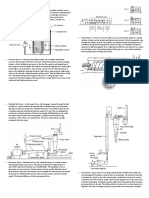
Molecular ion peak
[CO ]+
2 = 44
Figure 1.1: Components of a Mass Spectrometer
Fragment Peaks
[C]+ = 12 [O]+ = 16 [CO]+ = 28
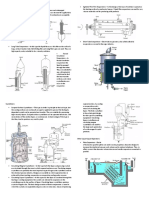
PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION:
Production of gas phase ions of the compound, basically by electron
ionization
The ions are then separated in the mass spectrometer according to
their mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), and are detected in proportion to
their abundance
A mass spectrum of the molecule is thus produced
APPLICATIONS:
Mass spectroscopy can be used in:
Determination of molecular weight
Determination of molecular formula
Determination of isotope abundance
Determination of ion-molecule reactions
Detection of impurity
Identification of unknown compounds
Measurement of ionization potential
ADVANTAGES: DISADVANTAGES:
Reduces background Difficult for non-volatile
interference compounds
Accurate identification of It doesn't directly give
unknowns or confirmation structural information
the presence of suspected about the unknown
compounds compound
Without a molecular ion
peak as a reference, the
difficulty of interpreting a
mass spectrum increases
markedly.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Ring Roll Mill: Presented By: Key Marie I. BarbasDokument5 SeitenRing Roll Mill: Presented By: Key Marie I. BarbasBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- DAO AccronymsDokument2 SeitenDAO AccronymsBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edge Runner MillDokument6 SeitenEdge Runner MillBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Particle Tech ReportDokument5 SeitenParticle Tech ReportBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Edge Runner Mill & Ring Roll MillDokument7 SeitenEdge Runner Mill & Ring Roll MillBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Production of Filter Paper Using Green Algae & Recycled PaperDokument5 SeitenProduction of Filter Paper Using Green Algae & Recycled PaperBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Miss Tashie 2.1.19Dokument14 SeitenMiss Tashie 2.1.19Bea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Particle Tech ReportDokument5 SeitenParticle Tech ReportBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Edge Runner MillDokument2 SeitenEdge Runner MillBea Uy100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- DryersDokument3 SeitenDryersBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Evaporator SDokument5 SeitenEvaporator SBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- NMR SpectrometryDokument5 SeitenNMR SpectrometryBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ring Roll PerrysDokument1 SeiteRing Roll PerrysBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Cosmetic IndustriesDokument8 SeitenCosmetic IndustriesBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Infrared SpectrosDokument5 SeitenInfrared SpectrosBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Chapter1.1 Algal Filter PaperDokument12 SeitenChapter1.1 Algal Filter PaperBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Algal Filter PaperDokument15 SeitenAlgal Filter PaperBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDokument5 SeitenAtomic Absorption SpectrosBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared SpectrosDokument5 SeitenInfrared SpectrosBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmetic IndustriesDokument8 SeitenCosmetic IndustriesBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper ChromatographyDokument5 SeitenPaper ChromatographyBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Thin Layer ChromatographyDokument5 SeitenThin Layer ChromatographyBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultraviolet SpectrosDokument5 SeitenUltraviolet SpectrosBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- METHODOLOGY BeaDokument6 SeitenMETHODOLOGY BeaBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDokument15 SeitenNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas - Liquid ChromatographyDokument7 SeitenGas - Liquid ChromatographyBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDokument5 SeitenHigh Performance Liquid ChromatographyBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column ChromatographyDokument5 SeitenColumn ChromatographyBea UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Atomic Emission SpectrosDokument5 SeitenAtomic Emission SpectrosBea Uy0% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)