Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
An Engine or Motor Is A Designed To Convert One Form of Into
Hochgeladen von
madhesu0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten15 Seitenhhghgjgjgj
Originaltitel
AE IC Engine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenhhghgjgjgj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
54 Ansichten15 SeitenAn Engine or Motor Is A Designed To Convert One Form of Into
Hochgeladen von
madhesuhhghgjgjgj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 15
1.
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert
one form of energy into mechanical energy.
2. A machine with moving parts that converts power
into motion.
3. Heat engines burn a fuel to create heat, which then
creates a force.
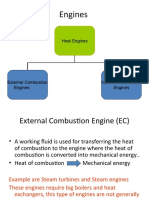
Types of Engines
1. External combustion (E.C.) Engine
It is an engine in which combustion of fuel take place
outside of the engine.
2. Internal Combustion (I.C.) Engine
It is an engine in which combustion of fuel take place
inside the engine.
Types of I.C. Engine
According to number of stroke:
1. Two stroke engine
2. Four stroke engine
According to design of engine:
1. Reciprocating engine (piston engine)
2. Rotary engine (Wankel engine)
According to fuel used:
1. Diesel engine
2. Petrol engine
3. Gas engine
4. Electric engine
Cond…
According to air intake process:
1. Naturally aspirated
2. Supercharged engine
3. Turbocharged engine
Cond…
According to method of ignition:
1. Compression ignition engine
2. Spark ignition engine
According to number of cylinder:
1. Single cylinder engine
2. Multi-cylinder engine
According to arrangement of cylinder:
1. In-line engine
2. V-type engine
3. Opposed cylinder engine
4. W-type engine
5. Opposite piston engine
6. Radial engine
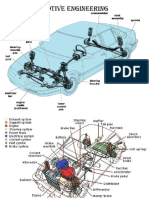
IC ENGINE PARTS:
WORKING:
Cond…
PARTS:
Internal combustion Engine Components:
Block : Body of the engine containing cylinders,
made of cast iron or aluminium.
Cylinder : The circular cylinders in the engine block
in which the pistons reciprocate back and forth.
Head : The piece which closes the end of the
cylinders, usually containing part of the clearance
volume of the combustion chamber.
Combustion chamber: The end of the cylinder
between the head and the piston face where
combustion occurs.
The size of combustion chamber continuously changes
from minimum volume when the piston is at TDC to a
maximum volume when the piston at BDC.
• Crankshaft : Rotating shaft through which engine work
output is supplied to external systems.
– The crankshaft is connected to the engine block with
the main bearings.
– It is rotated by the reciprocating pistons through the
connecting rods connected to the crankshaft, offset
from the axis of rotation. This offset is sometimes
called crank throw or crank radius.
• Connecting rod : Rod connecting the piston with the
rotating crankshaft, usually made of steel or alloy forging in
most engines but may be aluminum in some small engines.
• Piston rings: Metal rings that fit into circumferential
grooves around the piston and form a sliding surface against
the cylinder walls.
• Camshaft : Rotating shaft used to push open valves
at the proper time in the engine cycle, either
directly or through mechanical or hydraulic linkage
(push rods, rocker arms, tappets) .
• Push rods : The mechanical linkage between the
camshaft and valves on overhead valve engines with
the camshaft in the crankcase.
• Crankcase : Part of the engine block surrounding
the crankshaft.
– In many engines the oil pan makes up part of
the crankcase housing.
• Exhaust manifold : Piping system which carries
exhaust gases away from the engine cylinders,
usually made of cast iron .
• Fuel injector : A pressurized nozzle that sprays fuel
into the incoming air (SI engines )or into the cylinder
(CI engines).
• Fuel pump : Electrically or mechanically driven pump
to supply fuel from the fuel tank (reservoir) to the
engine.
• Glow plug : Small electrical resistance heater mounted
inside the combustion chamber of many CI engines,
used to preheat the chamber enough so that
combustion will occur when first starting a cold
engine.
– The glow plug is turn off after the engine is started.
• Starter : Several methods are used to start IC engines.
Most are started by use of an electric motor (starter)
geared to the engine flywheel. Energy is supplied from
an electric battery.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 3200 MCQ Ce PDFDokument12 Seiten3200 MCQ Ce PDFmadhesu64% (11)
- Eddy Current TestingDokument48 SeitenEddy Current TestingBhuvanesh Ponnan86% (7)
- Design A Sequential Circuit With Four Flip-Flops ABCDDokument4 SeitenDesign A Sequential Circuit With Four Flip-Flops ABCDSiva Guru100% (1)
- Annotated Bibliography Assignment 2Dokument5 SeitenAnnotated Bibliography Assignment 2Kam MoshierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engine Components GuideDokument7 SeitenInternal Combustion Engine Components GuideengineeringdesignNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines GuideDokument41 SeitenIC Engines GuideSatya NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME4001: Internal Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines GuideDokument66 SeitenME4001: Internal Combustion Engines and Gas Turbines GuideSubodh DanaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyDokument67 SeitenSME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyAshwin KudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument42 SeitenChapter 1Naol EmanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration of Compression and Expansion Process in Engine! Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines!Dokument49 SeitenDemonstration of Compression and Expansion Process in Engine! Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines!SHANTHARAMAN P PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Engine NotesDokument60 SeitenIc Engine Notessamarth motka100% (1)
- IC Engine NotesDokument21 SeitenIC Engine NotesVishal MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines GeneralDokument46 SeitenIC Engines Generalirfan khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Ic Engine Unit 1 1515773629 20707Dokument39 SeitenPresentation Ic Engine Unit 1 1515773629 20707Ram MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compression EngineDokument15 SeitenCompression EngineAlina RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types, Components & Working Principles of Internal Combustion EnginesDokument41 SeitenTypes, Components & Working Principles of Internal Combustion EnginesNauman QureshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Internal Combustion EnginesDokument46 SeitenIntroduction to Internal Combustion Enginesranjith kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To IC EngineDokument48 SeitenIntroduction To IC EngineNur JemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines Unit 4 - TDDokument43 SeitenIC Engines Unit 4 - TDchincha chuNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines PPT Lecture No 1Dokument33 SeitenIC Engines PPT Lecture No 1VishweshRaviShrimali100% (1)
- Heat engine types and componentsDokument38 SeitenHeat engine types and componentshodNoch keine Bewertungen
- I C Engine TerminologyDokument47 SeitenI C Engine TerminologyShubham SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICE Components & SystemsDokument50 SeitenICE Components & Systemssukku18121991Noch keine Bewertungen
- EnergyDokument14 SeitenEnergyNirmal DharavathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic CarDokument3 SeitenAutomatic CarBasnet VlogsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engine - Lecture 1Dokument55 SeitenIC Engine - Lecture 1darshan008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion EngineDokument542 SeitenInternal Combustion EngineArihant ShijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyDokument29 SeitenSME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine Terminologykishan24812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IV Internal Combustion EnginesDokument116 SeitenUnit IV Internal Combustion Enginesjaycee68Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cams Day 2Dokument86 SeitenCams Day 2u2003067Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 BmeDokument114 SeitenUnit 3 BmeSallin CdryNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines GuideDokument116 SeitenIC Engines GuidevelavansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Engine ReportDokument11 SeitenAutomotive Engine ReportAly MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Internal Combustion Engine by Sarvam ChaurasiyaDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To Internal Combustion Engine by Sarvam ChaurasiyasarvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentDokument8 SeitenIC Engines Power Transmission: Module ContentVinayaka GpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines OverviewDokument21 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines OverviewRex SabersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Project PresentationDokument24 SeitenMini Project PresentationHarshit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument32 SeitenUnit 1Rakeshkumarceg100% (1)
- Construction Details PDFDokument58 SeitenConstruction Details PDFP.Prem Kumar AP - I - MechanicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - 1 Internal Combustion Engine ARM - 070003Dokument37 Seiten03 - 1 Internal Combustion Engine ARM - 070003Johnmer amanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument41 SeitenChapter 2Ibrahim KhaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC EnginesDokument44 SeitenIC EnginesIbrahim KhaleelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications: and TheirDokument88 SeitenApplications: and TheiralexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion Engines Classification and ComponentsDokument22 SeitenInternal Combustion Engines Classification and ComponentsSarthak LalchandaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1Dokument35 SeitenLab 1Mamoon KhiljiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering Guide to Prime Movers & Heat EnginesDokument13 SeitenMechanical Engineering Guide to Prime Movers & Heat EnginesSinchana GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-2 (IC Engine)Dokument69 SeitenModule-2 (IC Engine)WasteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine and TransmissionDokument26 SeitenEngine and TransmissionWFilmy STARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2Dokument82 SeitenUnit 2dineshvaricomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Engineering Devices & Power PlantsDokument83 SeitenThermal Engineering Devices & Power Plantsommech2020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction IC EnginesDokument8 SeitenIntroduction IC EnginesSarmad Altaf Hafiz Altaf HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelDokument11 SeitenStudy of Components, Systems & Working of Diesel Engine ModelFaisal NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes ON Internal Combustion Engine: Course Code: Me 4101Dokument10 SeitenLecture Notes ON Internal Combustion Engine: Course Code: Me 4101MahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic EnginesDokument85 SeitenIc Enginessupertpm127Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction IC Engine and Reciprocating Machine CH - 1Dokument57 SeitenIntroduction IC Engine and Reciprocating Machine CH - 1heonetubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FC01 UpdatedDokument13 SeitenFC01 UpdatedSOLAIMANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic EngineDokument23 SeitenIc EngineGanesh kumar100% (1)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVDokument116 SeitenBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit IVA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (4)
- 1-Ic EngineDokument66 Seiten1-Ic EngineTOBIN THOMAS ME100% (1)
- 1.1 Construction&OperationDokument27 Seiten1.1 Construction&OperationAniket 19SB18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Engines & Its ComponentsDokument33 SeitenClassification of Engines & Its ComponentsSunil DhankharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engines MaterialsDokument20 SeitenEngines MaterialsMarkos100% (1)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiVon EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Engine or Motor Is A Designed To Convert One Form of IntoDokument15 SeitenAn Engine or Motor Is A Designed To Convert One Form of IntomadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyDokument54 SeitenSME015 - 4PD0240I C Engine TerminologyzetseatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical ElectronicsDokument6 SeitenMedical ElectronicsmadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A - B - C - D - A - B - C - D - A - B - C - DDokument1 SeiteA - B - C - D - A - B - C - D - A - B - C - DmadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Lab ManualDokument1 SeiteDom Lab ManualmadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermalDokument1 SeiteThermalmadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Lab ManualDokument1 SeiteDom Lab ManualmadhesuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Road Design for Tabo-an Public Market in Cebu CityDokument12 SeitenAccess Road Design for Tabo-an Public Market in Cebu CityMariel Ann B. SantoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business DevelopmentDokument46 SeitenProject Report: Social Media Marketing As A Tool For Business Developmentayushi gargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine: 1760kVA - 2500kVA 50 HZ 1825kW - 2250kW 60 HZDokument4 SeitenDiesel Generator Set QSK60 Series Engine: 1760kVA - 2500kVA 50 HZ 1825kW - 2250kW 60 HZ3efooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rollback HUAWEI ALE-L21 from Android 6.0 to 5.0Dokument5 SeitenRollback HUAWEI ALE-L21 from Android 6.0 to 5.0Anca Ioana StanciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Control of Ac Motor Using TriacDokument40 SeitenSpeed Control of Ac Motor Using Triacchanchal2100% (2)
- 1 Essay Tu Viet LaidocxDokument2 Seiten1 Essay Tu Viet LaidocxLy Ngoc Thanh B1906074Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volvo XC90 AccessoryDokument4 SeitenVolvo XC90 AccessoryTeravut SuwansawaipholNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aethra BG1220Dokument2 SeitenAethra BG1220Priscila Vanegas100% (1)
- Automatic Dustbin Using Arduino: By-Yash Nawghare (PG18) Manav Walunj (PG21) Kaustubh Jagtap (PG24) Kundan Walunj (PG29)Dokument14 SeitenAutomatic Dustbin Using Arduino: By-Yash Nawghare (PG18) Manav Walunj (PG21) Kaustubh Jagtap (PG24) Kundan Walunj (PG29)Manav WalunjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Media Tune UpDokument31 SeitenSocial Media Tune UpTran Minh TriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProxyDokument7 SeitenProxybeatnikthedoerNoch keine Bewertungen
- XML File UploadDokument5 SeitenXML File Uploadkanhaiya_priyadarshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Performance RubricsDokument3 SeitenExperimental Performance RubricsAhmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM20150930 35537 44540Dokument2 SeitenCM20150930 35537 44540fangrui maiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NetHSM Quick Start GuideDokument4 SeitenNetHSM Quick Start GuidegoldminerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jet Propulsion ExplainedDokument20 SeitenJet Propulsion Explainedruthvik mocharlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bist Tutorial 2 PDFDokument9 SeitenBist Tutorial 2 PDFjcfermosellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Organization PDFDokument2 SeitenComputer Organization PDFCREATIVE QUOTESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two Marks - Unit-4Dokument7 SeitenTwo Marks - Unit-4Aravinth SankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 64 QAM FeatureDokument9 Seiten64 QAM Featurenassr_ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- EasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130Dokument4 SeitenEasyLogic PM2000 Series - METSEPM2130ٍJordan SportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edit and query features offlineDokument4 SeitenEdit and query features offlinenagendra reddy panyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- FANUC CNC Maintenance Manual SectionsDokument2 SeitenFANUC CNC Maintenance Manual Sectionsmcantraks17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Kubota Serie Ed1105 - 30Dokument2 SeitenManual Kubota Serie Ed1105 - 30Alvaro Escalona GtzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instalação Unificontroler Debian 10Dokument4 SeitenInstalação Unificontroler Debian 10PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDR COLLECTION DOCUMENTATION FOR EWSD SWITCHDokument11 SeitenCDR COLLECTION DOCUMENTATION FOR EWSD SWITCH830139Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiplex Ticket Booking SystemDokument23 SeitenMultiplex Ticket Booking SystemMohit Kumar Lal100% (1)