Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ent Signs
Hochgeladen von
Prasun Sit Sharma0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
159 Ansichten10 SeitenThis document lists and describes various ENT signs that can indicate different medical conditions. Some examples include:
- Aquino's Sign which indicates glomus tumors and is seen when gently pressing on the carotid artery causes blanching of a tympanic mass.
- Bezold's Sign indicates mastoiditis and appears as inflammatory edema at the tip of the mastoid process.
- Browne's Sign also indicates glomus tumors and shows blanching when applying positive pressure to the tympanic membrane.
- Delta Sign seen on CT/MRI indicates lateral sinus thrombosis which appears as an empty triangle of the thrombosed sinus surrounded by contrast-enhanced dura.
- Holman Miller
Originalbeschreibung:
Ent
Originaltitel
ENT-SIGNS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document lists and describes various ENT signs that can indicate different medical conditions. Some examples include:
- Aquino's Sign which indicates glomus tumors and is seen when gently pressing on the carotid artery causes blanching of a tympanic mass.
- Bezold's Sign indicates mastoiditis and appears as inflammatory edema at the tip of the mastoid process.
- Browne's Sign also indicates glomus tumors and shows blanching when applying positive pressure to the tympanic membrane.
- Delta Sign seen on CT/MRI indicates lateral sinus thrombosis which appears as an empty triangle of the thrombosed sinus surrounded by contrast-enhanced dura.
- Holman Miller
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
159 Ansichten10 SeitenEnt Signs
Hochgeladen von
Prasun Sit SharmaThis document lists and describes various ENT signs that can indicate different medical conditions. Some examples include:
- Aquino's Sign which indicates glomus tumors and is seen when gently pressing on the carotid artery causes blanching of a tympanic mass.
- Bezold's Sign indicates mastoiditis and appears as inflammatory edema at the tip of the mastoid process.
- Browne's Sign also indicates glomus tumors and shows blanching when applying positive pressure to the tympanic membrane.
- Delta Sign seen on CT/MRI indicates lateral sinus thrombosis which appears as an empty triangle of the thrombosed sinus surrounded by contrast-enhanced dura.
- Holman Miller
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
ENT SIGNS
DR. Kamlesh Dubey
AQUINO'S SIGN: Glomus tumors
blanching of the tympanic mass with gentle pressure on
the carotid artery
BATTLE SIGN: petrous temporal bone
fracture (middle fossa #)
Bruising behind ear at mastoid region
BEZOLD'S SIGN: mastoiditis
Inflammatory edema at the tip of the mastoid process
BOCCA’S SIGN : Ca Larynx
Absence of post cricoid crackle(Muir’s crackle)
BROWNE'S SIGN : Glomus tumor
blanching noted when applying positive
pressure{with Siegel's speculum} to the tympanic
membrane
BRYCE SIGN: combined laryngocele & external
laryngocele
compression will cause a hissing sound as the air escapes
from it into the larynx (but don’t try!)
DELTA SIGN: Lateral sinus thrombosis
CT or MRI with contrast shows an empty triangle
appearance of the thrombosed sinus surrounded by
contrast enhanced dura (empty triangle sign)
DODD’S SIGN: positive in AC ployp Negative in
Angiofibroma
X-ray finding-Crescent of air between the mass and
posterior pharyngeal wall (CRESCENT SIGN)
FURSTENBERG'S SIGN: Encephaloceles
pulsation and expansion of the mass with crying, straining,
or compression of the jugular vein (Furstenberg test)
GRIESINGER'S SIGN: lateral sinus thrombosis
-Erythema and oedema posterior to the mastoid process
resulting from septic thrombosis of the mastoid emissary
vein
HALO SIGN/ HANDKERCHIEF SIGN:CSF rhinorrhea
CSF will separate from blood when the mixture is placed on filter
paper resulting in a central area of blood with an outer ring or halo
HOLMAN MILLER SIGN: JNA
anterior bowing of the posterior wall of the antrum seen on lateral
skull film
HONDOUSA SIGN (X-ray): JNA
Infratemporal fossa involvement
widening of gap between ramus of mandible and maxillary body
HENNEBERT'S SIGN : false positive fistula test
fistula of horizontal semicircular canal
meniere's disease or congenital syphilis
IRWIN MOORE’S SIGN: chronic tonsillitis
Positive squeeze test
LAUGIER'S SIGN: basilar skull fracture
Blood behind the eardrum
LEUDET'S SIGN: -Inflammation of the eustachian tube
Caused by reflex spasm of the tensor palati muscle
Clicking sound, tinnitus
LIGHT HOUSE SIGN: Acute suppurative otitis media
small pin hole perforation with a pulsatile ear discharge
LYRE’S SIGN : carotid body tumor
splaying of carotid vessels( at junction of External & internal
carotid artery)
MILIAN’S EAR SIGN: Erysipelas
can spread to pinna(cuticular affection), where as cellulitis
cannot
erysipelas involves the upper dermis and superficial
lymphatics, whereas cellulitis involves the deeper dermis and
subcutaneous fat
OMEGA SIGN: LARINGOMALACIA (epiglottis)
PHELP’S SIGN : glomus jugulare
loss of crest of bone (HRCT)) between carotid canal and
jugular canal
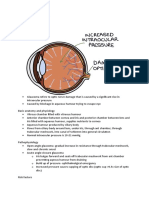
RISING SUN SIGN : red vascular hue seen behind the intact
tympanic membrane
glomus tumour
high jugular bulb
aberant carotid artery in the floor of middle ear
SCHWARTZ SIGN : active phase of otosclerosis(otospongiosis)
increased vascularity in submucous layer of promontory
flamingo flush sign
STEEPLE SIGN: Acute laryngotracheobronchitis
presence of edema in the trachea, which results in elevation of the
tracheal mucosa
loss of the normal shouldering (lateral convexities) of the air column
STANKIEWICK’S SIGN: orbital injury during FESS
fat protrude in to nasal cavity on compression of eye ball from
outside
TEAR DROP SIGN : Orbital floor fracture
tear drop shaped opacification seen hanging from the roof of the
maxillary sinus on water's view
tear-drop represents the herniated orbital contents, periorbital fat
and inferior rectus muscle
THUMB SIGN : Epiglottitis
thumb like impression (due to enlarged epiglottis) on X-STN lateral
TEA POT SIGN: CSF rhinorrhoea
Related to the relationship of the sphenoid ostium to the
sinus floor
Sphenoid ostium lies at an appreciable distance
anterosuperior from the sinus floor
Patient bends forward as an increasing amount of CSF
gains access to the ostium "teapot" sign
Uvula pointing sign: Rhinoscleroma
Rhinoscleroma involve nasopharynx ,uvula point towards
roof of nasopharynx
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ent Lecture NotesDokument2 SeitenEnt Lecture NotesThistell ThistleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent Practical Examinations Slides For StudyDokument31 SeitenEnt Practical Examinations Slides For StudyMuhdZaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical View of ENTDokument31 SeitenPractical View of ENTAbouzr Mohammed ElsaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDokument15 SeitenThe Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDrTarek Mahmoud Abo Kammer100% (2)
- Otolaryngology Mcqs & SBAs 2nd EditionDokument6 SeitenOtolaryngology Mcqs & SBAs 2nd EditionJohn M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- Maxillary Carcinoma, Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Malignancy PDFDokument18 SeitenMaxillary Carcinoma, Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Malignancy PDFSuprit Sn100% (2)
- Orthodontic Appliances or 411Dokument31 SeitenOrthodontic Appliances or 411Prasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapeh Grade 8 Third QuarterDokument4 SeitenMapeh Grade 8 Third QuarterPhilip Jansen Guarin100% (2)
- MCQsDokument13 SeitenMCQsVinay BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signs in EntDokument10 SeitenSigns in EntAbhishek BhardwajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Its Variations For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10013-1122Dokument8 SeitenAnatomy and Its Variations For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10013-1122opi akbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Auditory Canal Osteoma A Case ReportDokument4 SeitenExternal Auditory Canal Osteoma A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent AnaDokument79 SeitenEnt AnaGyanendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent LQ1Dokument41 SeitenEnt LQ1Raven CocjinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Praveen PresentationDokument63 SeitenDr. Praveen PresentationPraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Sinus AnatomyDokument71 SeitenBasic Sinus AnatomyTalal AlanzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal PolypDokument3 SeitenNasal PolypPuteri Atiqah SyaqilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ent NotesDokument3 SeitenEnt Notesapi-26186766Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy PharynxDokument15 SeitenAnatomy PharynxNina ZabrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sailedinitis PDFDokument8 SeitenSailedinitis PDFNavatha MorthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keratosis ObturansDokument12 SeitenKeratosis ObturansRahma LuthfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bailey CH 7 1 - 20Dokument42 SeitenBailey CH 7 1 - 20rama mandelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Department Cornwall Regional Hospital (W.R.H.A)Dokument1 SeiteOtorhinolaryngology, Head & Neck Surgery Department Cornwall Regional Hospital (W.R.H.A)Giovanni HenryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neet ENTDokument391 SeitenNeet ENTwilliamsjoseff0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Airway ObstructionDokument17 SeitenUpper Airway ObstructionRai Hana100% (1)
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDokument87 SeitenAcute Suppurative Otitis MediaHermawan Surya Dharma100% (1)
- Otitis Media With EffusionDokument3 SeitenOtitis Media With EffusionAnish RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal GranulomasDokument127 SeitenNasal GranulomasKamal SaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital Complications of SinusitisDokument32 SeitenOrbital Complications of SinusitisDr. Janarthanan VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chhabhadiya Laxman (Ent)Dokument7 SeitenChhabhadiya Laxman (Ent)Venkatesh GarikapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillectomy Slides 050427Dokument62 SeitenTonsillectomy Slides 050427Aidiel FikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of Sinus Surgery SariDokument38 SeitenComplications of Sinus Surgery SariFebryantiPBundaayabariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal Rhinosinusitis: Todays PresenterDokument33 SeitenFungal Rhinosinusitis: Todays Presenterimran qaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- PGMEEnotes ENTnotes ENT Occasionally Asked TopicsDokument11 SeitenPGMEEnotes ENTnotes ENT Occasionally Asked TopicskishorechandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAR MCQs Points Rida NaqviDokument6 SeitenEAR MCQs Points Rida NaqviÅli Raza ChaudaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Teams A4 PDFDokument288 SeitenENT Teams A4 PDFEbrahim JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bailey CH 9 144-155. CH 7 1-18 2Dokument62 SeitenBailey CH 9 144-155. CH 7 1-18 2laringfaring updateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemoprevention Head Neck MalignanciesDokument3 SeitenChemoprevention Head Neck MalignanciesSuprit Sn100% (2)
- Branchial Cleft CystsDokument8 SeitenBranchial Cleft CystsHere LeafsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT MneumonicDokument4 SeitenENT MneumonicVolksWongsathornNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Imp QuestionsDokument3 SeitenENT Imp QuestionsS Balagopal SivaprakasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ENT Exam 2011 Class of 07Dokument8 SeitenFinal ENT Exam 2011 Class of 07John M. HemsworthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes EntDokument43 SeitenNotes Entadriana azmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTDokument48 SeitenBenign and Malignant Neoplasia of URTsahirbuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ KhaldounDokument9 SeitenMCQ Khaldounadham bani younesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Hou-Yong KangDokument12 SeitenSudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Hou-Yong KangsuciNoch keine Bewertungen
- External Ear Pathology - PresentationDokument25 SeitenExternal Ear Pathology - PresentationNipun MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Medicine-ENT Self-Assessment: D. Laryngitis Often Lasts A Month or MoreDokument7 SeitenClinical Medicine-ENT Self-Assessment: D. Laryngitis Often Lasts A Month or MoretaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Review - Fossa of RosenmullerDokument4 SeitenQuick Review - Fossa of RosenmullerDavis KallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ورق مذاكره PDFDokument100 Seitenورق مذاكره PDFsalamred100% (1)
- 300 Fcps Mcq's SolvedDokument16 Seiten300 Fcps Mcq's SolvedFarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: FaringDokument49 SeitenRecurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: FaringIchsanJuliansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fellowships in OtolaryngologyDokument17 SeitenFellowships in OtolaryngologyasiyazaidiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Head Neck EMRCS MCQDokument23 SeitenAnatomy Head Neck EMRCS MCQTowhid HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep Neck InfectionsDokument54 SeitenDeep Neck InfectionsAmr ElsaadenyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinicals ENTDokument70 SeitenClinicals ENTMarrow Pg42Noch keine Bewertungen
- Head and Neck Surgery QDokument6 SeitenHead and Neck Surgery Qمحمد حميدانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nasal Septal Hematoma DrainageDokument21 SeitenNasal Septal Hematoma DrainageRaja AlfatihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head and Neck Cancer Care in a Pandemic: Prioritizing Safe CareVon EverandHead and Neck Cancer Care in a Pandemic: Prioritizing Safe CareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandConsultant in Audiology: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thalidomide in Patients With Multiple Myeloma and Renal FailureDokument2 SeitenThalidomide in Patients With Multiple Myeloma and Renal FailurePrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Root Coverage Procedures SantDokument22 SeitenRoot Coverage Procedures SantPrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Up KarmaDokument11 SeitenUp KarmaPrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrthodDokument10 SeitenOrthodPrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevalence of Dental Health Problems Among School Going Children in Rural KeralaDokument5 SeitenPrevalence of Dental Health Problems Among School Going Children in Rural KeralaPrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH06Dokument56 SeitenCH06Prasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Drug Dosage and Body Surface Area of ChildrenDokument5 SeitenCalculation of Drug Dosage and Body Surface Area of ChildrenPrasun Sit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 2018: Frcpath Questions Hemato-OncologyDokument24 SeitenSeptember 2018: Frcpath Questions Hemato-OncologySyed Danish Ali100% (1)
- Yoga and MeditationDokument28 SeitenYoga and MeditationVivek VashisthNoch keine Bewertungen
- RANZCPdepression 2Dokument120 SeitenRANZCPdepression 2Random_EggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis A Systematic Review of Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument18 SeitenConjunctivitis A Systematic Review of Diagnosis and TreatmentdasityarachmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrated Comprehensive Test IiiDokument14 SeitenIntegrated Comprehensive Test IiiGhee Lardizabal0% (1)
- Miss Purkiss 135 QuestionsDokument2 SeitenMiss Purkiss 135 QuestionsJemima Hui-Tung ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hiatal HerniaDokument6 SeitenHiatal HerniaMaria Donabella OngueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q&A FractureDokument13 SeitenQ&A FractureRed JimenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sea RemediesDokument2 SeitenSea Remedieskaravi schiniasNoch keine Bewertungen
- OphthalmologyDokument24 SeitenOphthalmologyJessica McCroryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio PDFDokument94 SeitenCardio PDFSalwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteomyelitis Akut Dan KronikDokument63 SeitenOsteomyelitis Akut Dan KronikAri SetiawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE PRESENTATION NEPHROTIC Syndrome-1Dokument20 SeitenCASE PRESENTATION NEPHROTIC Syndrome-1rohankananiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Dynamic Profile: Wellness ReportDokument17 SeitenYour Dynamic Profile: Wellness Reportvica sibueaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acu PressureDokument26 SeitenAcu PressureMuthuvel M100% (4)
- Health FceDokument5 SeitenHealth FceDoru AndreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DebateDokument1 SeiteDebateDont CareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis: Repertorium Homoeopathicum SyntheticumDokument29 SeitenSynthesis: Repertorium Homoeopathicum SyntheticumSk Saklin Mustak67% (3)
- Flu Vaccine: Information For People at RiskDokument8 SeitenFlu Vaccine: Information For People at Riskkovi mNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21st Century DiseasesDokument8 Seiten21st Century DiseasesPapanaga ArinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goddess Isis - 7D InitiationDokument6 SeitenGoddess Isis - 7D InitiationEmeraldRayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sarah Ballantyne ABCs of PALEO PDFDokument31 SeitenSarah Ballantyne ABCs of PALEO PDFalbinutaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExcerptDokument2 SeitenExcerptcoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paragraph DevelopmentDokument7 SeitenParagraph DevelopmentJacqueline Gregorio RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Kerbala College of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Clerkship Log-Book (Years 4) 2020-2021Dokument57 SeitenUniversity of Kerbala College of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Clerkship Log-Book (Years 4) 2020-2021صفا أحمد هاشم جبار 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Larsen, J.K. (2017)Dokument8 SeitenLarsen, J.K. (2017)Ale ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Malnutrition On Immunity and InfectionDokument17 SeitenImpact of Malnutrition On Immunity and InfectionYusuf NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word FormationDokument20 SeitenWord FormationSilviu EnglishNoch keine Bewertungen