Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar Metabolisme
Hochgeladen von
Ade Yosdi Putra0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten32 Seitendfergthyjku
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldendfergthyjku
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
25 Ansichten32 Seiten1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar Metabolisme
Hochgeladen von
Ade Yosdi Putradfergthyjku
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 32
Hubungan Metabolisme
Organ Specialization
• The Brain Requires a Steady Supply of Glucose
• Muscle Utilizes Glucose, Fatty Acids, and Ketone
Bodies
• Adipose Tissue Stores and Releases Fatty Acids
and Hormones
• Liver Is the Body’s Central Metabolic Clearing
house
• Kidney Filters Wastes and Maintains Blood pH
• Blood Transports Metabolites in Interorgan
Metabolic Pathways
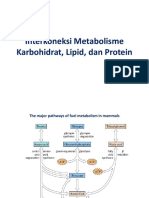
Major pathways of fuel metabolism
Acetyl-CoA - Pyruvate
• Acetyl-CoA : glucose, fatty acids, and ketogenic
amino acids.
– oxidized to CO2 and H2O via the citric acid cycle
– oxidative phosphorylation
– synthesize ketone bodies or fatty acids.
• Pyruvate : glycolysis and the breakdown of
glucogenic amino acids.
– oxidatively decarboxylated to yield acetyl-CoA
– oxidation or to the biosynthesis of fatty acids.
– pyruvate can be carboxylated via the pyruvate
carboxylase reaction to form oxaloacetate
The metabolic interrelationships
brain, adipose tissue, muscle, liver, and kidney.
Brain
• require a steady supply of glucose from the
blood
• high respiration rate : energy production,
membrane potential required for nerve
impulse transmission powers the plasma
membrane (Na–K)–ATPase
• Fast : ketone bodies
• Glucose < 5 mM : brain dysfunction, coma,
irreversible damage, and ultimately death
Muscle Utilizes Glucose, Fatty Acids,
and Ketone Bodies
• muscle carbohydrate metabolism serves only
muscle
• major fuels: glucose (from glycogen), fatty
acids, and ketone bodies.
• Muscle cannot export glucose, however,
because it lacks glucose-6-phosphatase.
• it does not participate in gluconeogenesis
Heart muscle
• Aerobic metabolism
• Metabolize: fatty acids, ketone bodies,
glucose, pyruvate, and lactate
– Fatty acids : resting heart’s fuel of choice
– Glucose: during heavy work
Adipose Tissue
• store and release fatty acids : fuel to secrete
hormones involved in regulating metabolism.
• glycerol-3-phosphate < : fatty acids are
released into the bloodstream.
• fatty acid mobilization: depends in part on the
rate of glucose uptake.
Liver
• Central Metabolic Clearinghouse
• major functions is to act as a blood glucose
“buffer.”
• Hexokinase, glukokinase,
• fructose-6-phosphate (F6P), is a competitive
inhibitor of glucokinase.
• Synthesize or Degrade Triacylglycerols
• The liver itself cannot use ketone bodies as fuel:
lack 3-ketoacyl-CoA transferase
Glucose-6-Phosphate
• G6P : converted to glucose, by the action of
glucose-6-phosphatase
• G6P : converted to glycogen
• G6P : converted to acetyl-CoA via glycolysis
• G6P : degraded via the pentose phosphate
pathway
Kidney
• Filters Wastes and Maintains Blood
pH
• Ammonia derived from glutamine or
glutamat
• Ketoglutarate :converted to glucose,
starvation (50%)
Cori Cycle
Regulasi Metabolisme
Muscle: Fasting State
1st uses own glycogen stores
2nd absorbs fatty acids and ketone bodies
Glycogen Glucose Pyruvate
Fatty Acids and Ketone Bodies Acetyl CoA
from Circulation
Allosteric
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeDokument32 Seiten1.4.5.4 - Hubungan Antar MetabolismeMulyanti YanthieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism OverviewDokument43 SeitenMetabolism OverviewWinnet MaruzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of major metabolism pathwaysDokument40 SeitenIntegration of major metabolism pathwaysseada JemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of MetabolismDokument17 SeitenIntegration of MetabolismSharif M Mizanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic InterrelationshipsDokument34 SeitenMetabolic InterrelationshipsAhmad NazharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismDokument23 SeitenLecture 11 On Regulation of MetabolismSaad KazmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestion & Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein in Non-RuminantsDokument62 SeitenDigestion & Metabolism of Carbohydrate, Fat and Protein in Non-Ruminantsrana adnan ejazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of MetabolismDokument33 SeitenSummary of Metabolismmememe123123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolisme Dan TermoregulasiDokument56 SeitenMetabolisme Dan TermoregulasiMuhammad Iqbal100% (1)
- Integration of Metabolism: Dr. Farzana Hakim Assistant Professor Biochemistry DepartmentDokument63 SeitenIntegration of Metabolism: Dr. Farzana Hakim Assistant Professor Biochemistry DepartmentGriffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochempresentationDokument12 SeitenBiochempresentationapi-310517845Noch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument72 SeitenCarbohydratesRAMA ABO SAMRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolisme Makronutrien FixDokument132 SeitenMetabolisme Makronutrien FixKadek RiskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism I GlycolysisDokument59 SeitenBIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism I GlycolysisYasin Çağrı KılıçerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interkoneksi Metabolisme Karbohidrat, Lipid, Dan ProteinDokument17 SeitenInterkoneksi Metabolisme Karbohidrat, Lipid, Dan Proteinrahmat basukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver and adipose tissue metabolismDokument35 SeitenLiver and adipose tissue metabolismLulu100% (2)
- Macronutrient Metabolism ExplainedDokument132 SeitenMacronutrient Metabolism ExplainedbelaariyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bms2 Integration of MetabolismDokument42 SeitenBms2 Integration of MetabolismhohoylandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism IntegrationDokument10 SeitenMetabolism IntegrationValine Cysteine MethionineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gluco Neo GenesisDokument19 SeitenGluco Neo GenesisessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fed State of MetabolismDokument40 SeitenFed State of MetabolismBHARANIDHARAN M.VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument19 SeitenCarbohydrate MetabolismAbhithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of MetabolismDokument40 SeitenIntegration of MetabolismIrfanArifZulfikar100% (1)
- LECTURE 3- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument40 SeitenLECTURE 3- Carbohydrate Metabolismmuhammedgmdidra95Noch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of CarbohydrateDokument11 SeitenFunctions of CarbohydrateAbdulbaasit AyoolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument38 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolismwidya nurrohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of Metabolism PathwaysDokument68 SeitenIntegration of Metabolism PathwaysCahyani Tiara Safitri100% (1)
- Glycogen MetabolismDokument34 SeitenGlycogen MetabolismJomi PorinchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit8 CarbohydrateMetabolismDokument46 SeitenUnit8 CarbohydrateMetabolismChristian Galagaran CortezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument46 SeitenCarbohydrate MetabolismLorenjoy BarridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Final - Integrated - Metabolism-16Dokument113 SeitenBiochemistry Final - Integrated - Metabolism-16keisha jonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-4 On CHO MetabolismDokument27 SeitenLecture-4 On CHO MetabolismMohammed ZeburNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Ix - Mechanism of Lipids MetabolismDokument33 SeitenChapter Ix - Mechanism of Lipids MetabolismAngelo AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration and Metabolism ProcessesDokument20 SeitenCellular Respiration and Metabolism ProcessesKewl TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- STARVE FEED CYCLE... GluconeogenesisDokument44 SeitenSTARVE FEED CYCLE... GluconeogenesisMoses MutsikwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycogen MetabolismDokument23 SeitenGlycogen Metabolismessa100% (1)
- Intergrated MetabolismDokument117 SeitenIntergrated MetabolismDerick SemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism and Regulation of GlycogenDokument24 SeitenMetabolism and Regulation of GlycogenAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of MetabolismDokument9 SeitenOverview of MetabolismbolanibongiweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organ Specialization in Fuel MetabolismDokument20 SeitenOrgan Specialization in Fuel Metabolismsaba pathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Metabolism1Dokument8 SeitenEnergy Metabolism1edimulyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismDokument8 SeitenChapter 16 - Lipid MetabolismadambridgerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glyconeogenesis - BIO 3110Dokument23 SeitenGlyconeogenesis - BIO 3110NaiomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tissue MetabolismDokument13 SeitenTissue MetabolismTonny MutisyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Dokument37 SeitenNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates Part 2 - MetabolismsDokument60 SeitenCarbohydrates Part 2 - MetabolismsNikka Mia AbadiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Oxidationand Ketogenesis 2023Dokument24 SeitenB Oxidationand Ketogenesis 2023N.h 999Noch keine Bewertungen
- GlycolysisDokument43 SeitenGlycolysisAshish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022Dokument52 Seiten3 Carbohydrate Metabolism 2022MarieFranz ChuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument29 SeitenUntitledKeerthivarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument27 SeitenReportJasmin BarriosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Carbohydrate MetabolismDokument45 Seiten3 Carbohydrate MetabolismDESIGNERICLELYN SORONIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid MetabolismDokument38 SeitenLipid MetabolismRøñït Roy ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism IV: Carbohydrate BiosynthesisDokument86 SeitenBIO 202 Biochemistry II by Seyhun YURDUGÜL: Carbohydrate Metabolism IV: Carbohydrate BiosynthesisYasin Çağrı KılıçerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulation of Metabolism During Feeding and FastingDokument26 SeitenRegulation of Metabolism During Feeding and FastingYINGG YIPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein MetabolismDokument3 SeitenCarbohydrate, Lipid, Protein Metabolismtritone.paradoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOM Week 3Dokument27 SeitenFOM Week 3Souravi MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism of LipidsDokument37 SeitenMetabolism of LipidsSafura IjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2Von Everand2020 The Essential Diets - All Diets in One Book - Ketogenic, Mediterranean, Mayo, Zone Diet, High Protein, Vegetarian, Vegan, Detox, Paleo, Alkaline Diet and Much More: COOKBOOK, #2Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5.1.5 - Anatomi PelvisDokument61 Seiten1.5.1.5 - Anatomi PelvisAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4.6.6 - Komposisi UrineDokument18 Seiten1.4.6.6 - Komposisi UrineAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4.4.2 - Biologi OKsidasi 2Dokument33 Seiten1.4.4.2 - Biologi OKsidasi 2IceBearNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.1.5 - Mekanisme Kerja HormonDokument28 Seiten1.2.1.5 - Mekanisme Kerja HormonAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.4.11 - Metabolisme KalsiumDokument31 Seiten1.2.4.11 - Metabolisme KalsiumAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4.4.2 - Biologi OKsidasi 2Dokument33 Seiten1.4.4.2 - Biologi OKsidasi 2IceBearNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4.4.1 - Metabolisme Dan BioenergetikaDokument27 Seiten1.4.4.1 - Metabolisme Dan BioenergetikaIceBearNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.1.5 - Mekanisme Kerja HormonDokument28 Seiten1.2.1.5 - Mekanisme Kerja HormonAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dampak Defisiensi Zat Gizi Makro: Prof - DR.DR - Delmi Sulastri, MSC, SPGKDokument33 SeitenDampak Defisiensi Zat Gizi Makro: Prof - DR.DR - Delmi Sulastri, MSC, SPGKAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2.1.4 - Klasifikasi HormonDokument65 Seiten1.2.1.4 - Klasifikasi HormonAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- KP 3.5.4.1 - Agen Penyebab Penyakit Zoonosis PDFDokument13 SeitenKP 3.5.4.1 - Agen Penyebab Penyakit Zoonosis PDFAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- KP 3.6.1.5b HipotermiDokument5 SeitenKP 3.6.1.5b HipotermiAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- KP 3.6.4.6 - Peny Guna Zat Anak RemajaDokument13 SeitenKP 3.6.4.6 - Peny Guna Zat Anak RemajaAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.5.3.3 - Postmenopausal Bone Metabolism and Structural ChangesDokument22 Seiten3.5.3.3 - Postmenopausal Bone Metabolism and Structural ChangesAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah Cedera SendiDokument45 SeitenKuliah Cedera SendiMaya Purnama SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaDokument8 SeitenOsteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaAtmayadi GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteoporosis Karena Steroid: Najirman Subbagian Reumatologi, Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK Unand/ Rsup DR M.DjamilDokument68 SeitenOsteoporosis Karena Steroid: Najirman Subbagian Reumatologi, Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK Unand/ Rsup DR M.DjamilAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- KP 3.6.3.7 - Rehab CPDokument41 SeitenKP 3.6.3.7 - Rehab CPAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaDokument8 SeitenOsteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaAtmayadi GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gannguan PubertasDokument56 SeitenGannguan PubertasAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaDokument8 SeitenOsteosarkoma Diagnosis Dan PenanganannyaAtmayadi GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1.4.1 - Disfunctional LaborDokument12 Seiten2.1.4.1 - Disfunctional LaborAde Yosdi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biocomp Exam 2011Dokument12 SeitenBiocomp Exam 2011Jaclyn ScottNoch keine Bewertungen
- CigFil RhodiaDokument65 SeitenCigFil RhodiaAditya ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tin (IV) Compounds of Tridentate Thiosemicarbazone Schiff Bases Synthesis, Characterization, In-Silico Analysis and in Vitro CytotoxicityDokument12 SeitenTin (IV) Compounds of Tridentate Thiosemicarbazone Schiff Bases Synthesis, Characterization, In-Silico Analysis and in Vitro CytotoxicityGustavo MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garima Kaushik (Eds.) - Applied Environmental Biotechnology - Present Scenario and Future Trends-Springer India (2015)Dokument178 SeitenGarima Kaushik (Eds.) - Applied Environmental Biotechnology - Present Scenario and Future Trends-Springer India (2015)Carlos Andres Lopez Ramirez100% (1)
- Basic Characteristics of PolymersDokument32 SeitenBasic Characteristics of PolymersFeni Utari BasyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Powdered Detergent: Adamson University College of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDokument6 SeitenPowdered Detergent: Adamson University College of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringHoneylet Recaña TayactacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Métodos en Farmacognosia European Pharmacopoeia 8 0 2 - AceitesDokument12 SeitenMétodos en Farmacognosia European Pharmacopoeia 8 0 2 - AceitesMarco AronesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytosomes: A Novel Dosage Form For Enhancement of Bioavailability of Botanicals and NeutraceuticalsDokument5 SeitenPhytosomes: A Novel Dosage Form For Enhancement of Bioavailability of Botanicals and NeutraceuticalsSiva PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm F645Dokument8 SeitenAstm F645Hernando Andrés Ramírez Gil0% (1)
- Analytical Biochemistry: T.Z. Rzezniczak, L.A. Douglas, J.H. Watterson, T.J.S. MerrittDokument3 SeitenAnalytical Biochemistry: T.Z. Rzezniczak, L.A. Douglas, J.H. Watterson, T.J.S. MerrittGustavo FelpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heterocyclic Chemistry and Spectroscopy C 22022/CHE 22022: Course Lecturer: Dr. Dinusha UdukalaDokument26 SeitenHeterocyclic Chemistry and Spectroscopy C 22022/CHE 22022: Course Lecturer: Dr. Dinusha UdukalaDidula ThrimannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE317 - Process Modelling and Simulation (3 Units: LH 45)Dokument51 SeitenCHE317 - Process Modelling and Simulation (3 Units: LH 45)Iteoluwakiishi AberuagbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crystals 08 00101Dokument38 SeitenCrystals 08 00101Madhu Kiran DhondalayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ AduaDokument4 SeitenMCQ AduaSummer Mamun100% (1)
- Polymer: Types of PolymersDokument6 SeitenPolymer: Types of PolymersSarah SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Scale Methaforming Unit Maximizes ProfitsDokument16 SeitenSmall Scale Methaforming Unit Maximizes ProfitsramatajamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CRISPR Launch Flyer (Global) - FLRDokument2 SeitenCRISPR Launch Flyer (Global) - FLRAdrian Corredor LondoñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimal Synthetic GenomeDokument13 SeitenMinimal Synthetic Genomedilan guerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dna StructureDokument28 SeitenThe Dna Structuremark gonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production and Characterization of Biodigradable Platic From BananaDokument63 SeitenProduction and Characterization of Biodigradable Platic From BananaSeyid YassinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules: Loumelyn Rose B. BayatoDokument7 SeitenBiomolecules: Loumelyn Rose B. BayatoLR B Bayato100% (1)
- 3.chemical Reactions and Reaction StoichiometryDokument5 Seiten3.chemical Reactions and Reaction StoichiometryJey Vee SalcedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Black Fillers in EPDM Extrusion Formulation (Peroxide Cured) PDFDokument28 SeitenNon Black Fillers in EPDM Extrusion Formulation (Peroxide Cured) PDFdargil66Noch keine Bewertungen
- Balanccing 2Dokument3 SeitenBalanccing 2Anant MadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2022 (v1) QPDokument16 SeitenJune 2022 (v1) QPHarpreet KaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improvised Okra Floor Wax ResearchDokument29 SeitenImprovised Okra Floor Wax Researchj sgyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Bhopal Region Preboard Examination 2020-21 Class Xii - Question Paper - Set ADokument7 SeitenKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Bhopal Region Preboard Examination 2020-21 Class Xii - Question Paper - Set AMeghesh SamadhiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Named Reactions GuideDokument8 SeitenNamed Reactions GuideYo100% (2)
- Ms. Rima DessaiDokument46 SeitenMs. Rima DessaiSanghaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations TutorialDokument9 SeitenCalculations Tutorialricara alexia moodley0% (1)