Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)
Hochgeladen von
Eden Hazard0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten18 Seitenpower electronic - inverter
Originaltitel
Power Electronics 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenpower electronic - inverter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten18 SeitenTan Kien Hau (01Dem16F1004) ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006) Lee Zhi Shern (01Dem16F1038) Zulhilmi (01Dem16F1007)
Hochgeladen von
Eden Hazardpower electronic - inverter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 18
TAN KIEN HAU (01DEM16F1004)
ONG KANG WEI (01DEM16F1006)
LEE ZHI SHERN (01DEM16F1038)
ZULHILMI (01DEM16F1007)
SINGLE PHASE HALF BRIDGE
INVERTER AND FULL BRIDGE
INVERTER
The power in the converter is converted to DC
from AC with the use of a rectifier, and then it is
converted back to AC from DC with the use of
an inverter.
An inverter increases the DC voltage, and then
changes it to alternating current before sending it
out to power a device.
DC to AC current because the sensitive electronic
circuits need low, regulated voltage to operate.
DC1 and DC2 can be assumed to be
constants.The T1 and T2 transistors control the
entire circuit.
Having two switches and eight combinations
for the control signals ( 4 positive currents and
4 negative current) with 00,01,10, and 11.
Any combination in which T1 and T2 are turned
on will destroy the IGBT/MOSFETS
Both of them are turned off, the inverter enters
a stage called the dead-time.
During phase A), T1 is conducting – therefore there is a
positive voltage on the load and the current is slowly
getting larger, since our load is inertial.
During phase B), the polarity of the load voltage is flipped
(inverted). the current of inductor has “built up” is now
decreasing and reversing polarity. it flows through T2‘s
diode, flowing against the barrier of potential created by the
bottom voltage source.
During phase C), the load current has already changed its
polarity, so it can safely flow through T2. This phase is
symmetrical to phase A).
Phase D) is analogous to phase B) – the current cannot find
any escape path other than T1‘s diode.
Single phase full bridge inverter can be
simplifying justified with a switching scheme
of full bridge converter.
An square wave ac output voltage is
synthesized from a dc input by closing and
opening the switches in an appropriate
sequence.
The output voltage can be +Vdc, -Vdc, or zero,
depending on which switches are closed.
It consists of four choppers. Full bridge converter is
also basic circuit to convert dc to ac. An ac output is
synthesized from a dc input by closing and opening
switches in an appropriate sequence. There are also
four different states depending on which switches are
closed.
When transistors T1 and T2 are turned on
simultaneously, the input voltage appears across the
load. If transistor and are turned on at the same time,
the voltage across the is reversed and is –Vs.
Transistor T1 and T2 acts as switches S1 and S2
The output load voltage alternates between +Vs when
T1 and T2 are on and -Vs when T3 and T4 are on,
irrespective of the direction of current flow. It is
assumed that the load current does not become
discontinuous at any time. In the following analysis we
assume that the load current does not become
discontinuous at any time.
Bridge inverters are preferred over other arrangements
in higher power ratings.
With the same dc input voltage, output voltage is twice
that of the half- bridge inverter.
- Application : Used in uninterrupted power
supplies,stanby power supply, variable speed ac motor
1) Single-phase half-bridge inverter
- Low-order current harmonics get injected back to the
source voltage by the operation of the inverter.
2) The full-bridge inverter
is similar to the half bridge-inverter, but it has an
additional leg to connect the neutral point to the load.
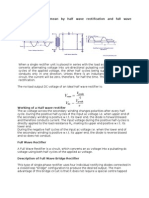
Single Phase Half Bridge Single Phase Half Bridge RL
Resistor Load
Single Phase Full Bridge Single Phase Full Bridge RL
Resistor Load
THANK YOU
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MC Murray InverterDokument92 SeitenMC Murray InverterGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (5)
- Power Electronics L2 ConvertersDokument6 SeitenPower Electronics L2 ConvertersBakri BugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDokument9 SeitenAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Buck ConverterDokument6 SeitenThe Buck ConverterjiggywiggyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverters Explained: DC to AC Conversion CircuitsDokument11 SeitenInverters Explained: DC to AC Conversion CircuitsSukhpal SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 4 - InverterDokument88 SeitenMod 4 - InverterSREEHARI V ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase InverterDokument7 SeitenSingle Phase InverterBHALAJI BIRLANoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase RectifiersDokument11 SeitenSingle Phase RectifiersMiguel MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDokument56 SeitenTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverters Half and Full BridgeDokument12 SeitenInverters Half and Full BridgeSaî CharañNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFL Lamp Circuit Detail: Q1 & Q2 D1 L R CP Co SD1351 BY399 20 H 220 Ohm 0.01 F/400V 0.1 F/400VDokument3 SeitenCFL Lamp Circuit Detail: Q1 & Q2 D1 L R CP Co SD1351 BY399 20 H 220 Ohm 0.01 F/400V 0.1 F/400VsaveyourNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: ApplicationsDokument37 SeitenUNIT 3&4 DC - AC Switched Mode Inverters: Applicationsdivya k sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Switching CircuitsDokument19 SeitenBasic Switching Circuitsash1968Noch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersDokument35 SeitenControlled Rectifiers and AC Voltage ControllersAishwaryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 05: Single Phase DC-AC Converter (Transistor Based)Dokument20 SeitenUnit 05: Single Phase DC-AC Converter (Transistor Based)vaibhav bodkheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Originalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922Dokument12 SeitenOriginalproectphysicsmsword Converted 191225064922GOKULNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Full Wave Rectifier GuideDokument9 SeitenSingle Phase Full Wave Rectifier Guideshadan alamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshDokument13 SeitenASSIGNMENT 3 - HemakeshHemkeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-AC (Inverters)Dokument30 SeitenDC-AC (Inverters)Joo AdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Supply 1Dokument6 SeitenPower Supply 1api-19786583Noch keine Bewertungen
- E1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesDokument84 SeitenE1 - Controlled Rectifiers PDF NotesSatyanarayana Gurram100% (1)
- Ac Voltage Controller of Last Years PaperDokument15 SeitenAc Voltage Controller of Last Years PaperIgombe IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inverter and ChopperDokument92 SeitenInverter and ChopperGnanaseharan ArunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC Power Supply CircuitDokument7 SeitenDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument46 SeitenChapter 3Tewodros ShegawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument46 SeitenChapter 3Tewodros ShegawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choppers 5Dokument24 SeitenChoppers 5Aditya MagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: AddedDokument39 SeitenAssignment: Addedfuh kingsleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Source InductanceDokument10 SeitenEffect of Source Inductancemeeravali_snNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zero Voltage Switching Resonant Power Devices by Bill AndrecakDokument28 SeitenZero Voltage Switching Resonant Power Devices by Bill AndrecakRekhamtrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Single Phase InverterDokument20 SeitenChapter 3 - Single Phase InverterMuhammad Izz IzzuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On InverterDokument22 SeitenProject On InverterSaikat Mitra43% (7)
- HVDC Control Principle ExplanationDokument12 SeitenHVDC Control Principle ExplanationrasashpujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersDokument21 SeitenFull Wave Rectifier: Convert AC to DC Efficiently in 40 CharactersbaradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiDokument59 Seiten2095784617.power Electronics Unit IiSaranya. M SNSNoch keine Bewertungen
- BECE Module-1 NOTESDokument28 SeitenBECE Module-1 NOTESmahendra naik100% (5)
- Single Transistor 12V To 230V InverterDokument7 SeitenSingle Transistor 12V To 230V Inverteryr48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply UnitDokument14 SeitenCircuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply Unitreddyece402Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 038 PDFDokument11 Seiten2 038 PDFAmit GauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choppers & Ac ControllersDokument28 SeitenChoppers & Ac Controllersves vegasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC TO AC INVERTERDokument93 SeitenDC TO AC INVERTERABCDNoch keine Bewertungen
- basic dc to dcDokument36 Seitenbasic dc to dcstrelectronicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACDokument7 SeitenSingle transistor circuit converts 12V DC to 230V ACyr48Noch keine Bewertungen
- Half wave and full wave rectification explainedDokument5 SeitenHalf wave and full wave rectification explainedHuidrom SharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resonant Pulse InvertersDokument19 SeitenResonant Pulse InvertersRavi ANoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument83 SeitenReportNikita SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unregulated Power Supply DesignDokument6 SeitenUnregulated Power Supply DesignGunawan RudyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDokument5 SeitenComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Wave RectifierDokument10 SeitenFull Wave Rectifierdheerajguptaandro20% (5)
- Safety-enhanced-high-step-up-DC-DC-converter-for-ac-photovoltaic-module-applications Chapter 2 DC-DC Converters 12 PageDokument16 SeitenSafety-enhanced-high-step-up-DC-DC-converter-for-ac-photovoltaic-module-applications Chapter 2 DC-DC Converters 12 PageVenkatesh ChintalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buck ConverterDokument5 SeitenBuck ConverterM Zeeshan WazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Dokument16 SeitenLecture 03 - Diode Applications (Rectification)Joseph NgowiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC-DC Switch-Mode Converters: Step-Down, Buck Converter GuideDokument35 SeitenDC-DC Switch-Mode Converters: Step-Down, Buck Converter GuideNandu JagguNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC To DC Buck and Boost ConverterDokument5 SeitenDC To DC Buck and Boost ConverterR ABHISHEKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 - Part 1Dokument17 SeitenModule 5 - Part 1SUSEELA V K RSETNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Waterproof BoxDokument129 SeitenWaterproof BoxVenkata Narayana BoddapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensional Analysis AND Similarity: Chapter-5. (Frank White)Dokument46 SeitenDimensional Analysis AND Similarity: Chapter-5. (Frank White)ShujaAmjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB ApplicationsDokument252 SeitenMATLAB Applicationsmadhuri nimseNoch keine Bewertungen
- XI-Opt. Syllabus (2023-24)Dokument29 SeitenXI-Opt. Syllabus (2023-24)INDERDEEPNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYDokument12 Seiten11 Risks and Rates of Return KEYkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Scavenge InspectionDokument36 SeitenGuide For Scavenge InspectionNeelakantan SankaranarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collet Chuck Catalog 2007 PDFDokument28 SeitenCollet Chuck Catalog 2007 PDFAlexandru Marius-catalinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On The Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDokument10 SeitenReport On The Quantitative Techniques in BusinessBaron FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hargreaves 2007Dokument15 SeitenHargreaves 2007Sam GonçalvesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence in The GPs Office A Retrospective Study On Diagnostic AccuracyDokument13 SeitenArtificial Intelligence in The GPs Office A Retrospective Study On Diagnostic Accuracymarj611582Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acid-Base Equilibrium PPT UPDATED 2022Dokument96 SeitenAcid-Base Equilibrium PPT UPDATED 2022Sara Molinaro100% (1)
- HP ALM FeaturesDokument51 SeitenHP ALM FeaturesSuresh ManthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuscript 123Dokument46 SeitenManuscript 123Datuzuharto Sultan100% (1)
- BIOLOGY Paper 1 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022Dokument4 SeitenBIOLOGY Paper 1 Marking Scheme Asumbi Girls Final Prediction 2022balozi training InstituteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Structure of C Type Hydraulic PressDokument10 SeitenAnalysis of Structure of C Type Hydraulic PressShubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accelerate your career with online coursesDokument22 SeitenAccelerate your career with online coursesAYEDITAN AYOMIDENoch keine Bewertungen
- The World of Chemistry Video Guide SetDokument10 SeitenThe World of Chemistry Video Guide SetrkvNoch keine Bewertungen
- SERO BA-2019.11 S enDokument52 SeitenSERO BA-2019.11 S enJuan AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMCP 706-185, Military Pyrotechnics - Theory and ApplicationDokument270 SeitenAMCP 706-185, Military Pyrotechnics - Theory and ApplicationASDAFF ASADNoch keine Bewertungen
- 478 - Phs 242 NotesDokument61 Seiten478 - Phs 242 NotesSovan ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Computer Engineering Academic Year 2020-21 Class: SE Computer & IT Subject: 22226 PCI (Programming in C) MCQ Unit 1: Program Logic Development MCQ Question Bank With AnswersDokument8 SeitenDepartment of Computer Engineering Academic Year 2020-21 Class: SE Computer & IT Subject: 22226 PCI (Programming in C) MCQ Unit 1: Program Logic Development MCQ Question Bank With AnswersVooovoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariDokument34 SeitenWhat Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariBayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- OMC 140 Operator Manual v1.08Dokument38 SeitenOMC 140 Operator Manual v1.08Anderson DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaDokument2 Seiten12.6 Perform An Activity - Measuring The Critical Angle For Various MediaRajeshri SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guaranteed Restore Points Oracle 11g - Flash Back to SCN or RP (39Dokument2 SeitenGuaranteed Restore Points Oracle 11g - Flash Back to SCN or RP (39PraveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP46 - Guide To Use BAPCO WPS & Welding ProceduresDokument4 SeitenIP46 - Guide To Use BAPCO WPS & Welding ProceduressajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- L - 1 - INTRO - Well LoggingDokument47 SeitenL - 1 - INTRO - Well LoggingSaaeed Ali100% (1)
- p-4500 Technical InformationDokument13 Seitenp-4500 Technical InformationElhoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT-1 Introduction To Emi: A Arunkumar GudivadaDokument47 SeitenUNIT-1 Introduction To Emi: A Arunkumar GudivadaBhagya bhagiNoch keine Bewertungen