Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Abby Poster
Hochgeladen von
api-378515349Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Abby Poster
Hochgeladen von
api-378515349Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Effects of Prelinguistic Milieu teaching: a naturalistic language intervention,
COLLEGE OF
EHHS on child communication in the natural environment
ABIGAIL BALL
Early Intervention/ Early Childhood Special Education
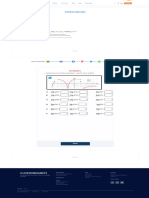
INTRODUCTION METHODS Results
► Participants: Child with expressive language delay age 22 months, Mother, Coach (Early Composite Parent Data
► This study evaluates the effects of a naturalistic language intervention on child communication within the Parent Strategy use
Intervention Master’s Student ) 35
Baseline Interventio
35
Baseline Intervention
n
context of Early intervention (EI).
► Settings: The home : in the child’s playroom, in the child’s bedroom 30 30
► Study design: AB Single Subject research design with baseline and intervention phases
► Early intervention refers to Part C of the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA). 25
25
► Study Procedures:
20
Frequency
20
Frequency
► In an early intervention context, a naturalistic environment is the current best practice. The natural
15
15
environment consists of working with a child in an everyday environment, with parents and caregivers. 1. Information shared: Strategies given through the process of coaching , the Early 10
10
Within the natural environment I was able to understand the importance of early language learning. interventionist provided resources and checked for understanding 5
5
► Milieu Teaching is a grouping of strategies for language development that is an evidence based practice 2.Intervention: The caregiver implemented the learned strategies while being video recorded 0
1 2 3 4 5
0
Sessions
1 2 3 4 5
Follow Child's lead Expansion Postive Feedback Session
3.Feedback: The Early interventionist and the mother watched the video and made comments on
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
what was done well, and what could be improved Child Communication Behaviors Composite Child Data
► What are the effects of Prelinguistic Milieu teaching: a naturalistic language intervention, on child 35
Baseline Intervention 35
Baseline Intervention
► Adult measures (Independent Variables):
communication in the natural environment? 30
30
► What are the effects of the “coaching strategy” on Prelinguistic Milieu teaching: a naturalistic language 1. Follow child's lead: The caregiver moves towards, at the same level with the child, and 25
25
intervention? participates when she is interested in an object or activity 20
Frequency
20
Frequency
2. Expansion: The parent labels and adds descriptions of objects and activities when the child 15
RESEARCH SYNTHESIS has an item, or initiates an interaction 10
15
10
Authors : Purpose : Findings : 3. Positive feedback- The parent provides specific positive feedback by clapping, smiling with 5
5
specific praise, or giving verbal praise for a correct behavior or response 0
1 2 3 4 5
0
1. Hancock, T. B., & 1.What changes in child language targets and social communication - All children showed positive increases for specific target language Sessions
1 2 3 4 5
Gesture Vocalization Words Sessions
Kaiser, A. P. (2002). skills will be observed during the clinic applications of EMT by trained - Results were maintained after 6 month follow up
► Child measures (Dependent Variables):
interventionists? - Positive changes in the complexity of diversity of language
1.Gesture: A shake of the hand, point, or shake of the head that is directed towards another
2.Will changes in child language target and social communication skills
be maintained over time?
- Parent satisfaction was high
- 3 of 4 children generalized
person or item DISCUSSION
3. Will changes indicative of child language development be observed ?
2.Vocalization: A babble, utterance, or approximation ► Previous research suggests that caregiver interactions using Milieu teaching strategies help to increase
4.Will changes in child language generalize to interactions with parents
at home ? language understanding, and communication . My study shows that through caregiver interactions using
3.Word: A word that is in the English dictionary, or a learned sign for a representation of a word
2. Roberts, M. Y., 1.What are the effects of the Teach-Model-Coach-Review instructional - The caregivers demonstrated increases in their use of each EMT language Milieu teaching, that child gestures and words have increased .
Kaiser, A. P., Wolfe, approach on caregivers’ use of four different EMT language support support strategy after instruction.
► Coaching: 10- 15 Minute Session prior to intervention . The sessions consisted of sharing
C. E., Bryant, J. D., strategies in a clinic setting?
- Generalization use to the home was limited, ► Previous research has not paired the evidence based practice of Milieu teaching with the strategy of
& Spidalieri, A. M.
2.What are the effects of teaching caregivers to use EMT language
information, questions, and checking for understanding
(2014). - All children demonstrated gains in their use of communication targets Coaching in the natural environment. My study has done just that. I was able to coach the parent in the
support strategies on children’s expressive language skills in the clinic
- Results indicate that the Teach-Model- Coach-Review instructional approach natural environment, using the Milieu teaching strategies of “following the child’s lead , expansion, and
resulted in increased use of EMT language support strategies by caregivers.
positive feedback”.
3. Warren, S., Yoder, -Will a modified form of milieu teaching facilitate children's - The results replicated the finding that a modified version of milieu teaching
► Seeing the success of the Milieu teaching strategies paired with coaching in the natural environment these
P., Gazdag, G., Kim, prelinguistic requesting in intervention sessions with staff members? was effective in facilitating the use of intentional requesting by children with
K., & Jones, H. developmental delays in an intervention context results show the importance of quality caregiver interactions.
(1993).
4. Franco, J. H., What is the effect of PMT on the participant’s development of sustained - All of the children improved their ability to sustain social interactions, as ► Further research should look into the quality of parental praise and the effects on child language production
Davis, B. L., & social interaction within a salient play routine?” evidenced by an increase in the number of communicative interactions during
Davis, J. L. (2013). play routines. ► Limitations included : limited data points following the baseline
-Participants also increased their overall rate of initiated intentional
communication.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Treatment Project Vat - Visual Action TherapyDokument22 SeitenTreatment Project Vat - Visual Action Therapyapi-257850539100% (1)
- EHS Training MatrixDokument10 SeitenEHS Training MatrixRaquel Salamó ClaperaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Do Young People Misbehave in SchoolDokument9 SeitenWhy Do Young People Misbehave in Schoolapi-379378935Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Art and Practice of Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine. NIGEL CHINGDokument794 SeitenThe Art and Practice of Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine. NIGEL CHINGИгорь Клепнев100% (13)
- First and Second Language AcquisitionDokument1 SeiteFirst and Second Language AcquisitionGatika JessiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jessicas Final PosterDokument1 SeiteJessicas Final Posterapi-582670604Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ana Poster FinalDokument1 SeiteAna Poster Finalapi-708484558Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colleen Par PosterDokument1 SeiteColleen Par Posterapi-340263565Noch keine Bewertungen
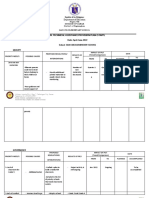
- Govph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaDokument29 SeitenGovph Home About Us Contact MOOE Report Pasay City SPED Center School SmeaCarol LaconsayNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesDokument1 SeiteWhat Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesJordan ChizickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: School Technical Assistance Provision Plan (Stapp)Dokument4 SeitenDepartment of Education: School Technical Assistance Provision Plan (Stapp)Ma.Vendetta SalurioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESIP Financial PlanDokument419 SeitenESIP Financial PlanSalome Marcellana MesiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project HealthDokument9 SeitenProject Healthjerwin remocalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Information On Each Course (Student's Version) : Prinsip Dan Amalan Dalam Pengajaran Bahasa InggerisDokument5 SeitenSummary of Information On Each Course (Student's Version) : Prinsip Dan Amalan Dalam Pengajaran Bahasa InggerisNurul IzzatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Implementation PlansampleDokument28 SeitenAnnual Implementation PlansampleNERWIN IBARRIENTOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nexus of Educational Attainment and Personal InformationDokument2 SeitenThe Nexus of Educational Attainment and Personal InformationNeil De GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mps Classroom FormDokument5 SeitenMps Classroom FormSheena C. DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MTES3052 Arts in EducationDokument10 SeitenMTES3052 Arts in EducationhyyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Implementation Plan SAMPLEDokument25 SeitenAnnual Implementation Plan SAMPLEEddie DusingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Ilp 10Dokument6 SeitenFinal Ilp 10api-557226780Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pardos TemplateDokument1 SeitePardos Templateromalyn De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sapalibutad Elementary School First Quarter Assistance Regarding The Pupils at Risk of Dropping Out (Pardos)Dokument1 SeiteSapalibutad Elementary School First Quarter Assistance Regarding The Pupils at Risk of Dropping Out (Pardos)romalyn De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSLB3052 Arts in EducationDokument10 SeitenTSLB3052 Arts in EducationTESL30621 Siti Fairus Binti Mat HanafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMK Versi Pelajar Edup3033 Learning and The Learner (BI)Dokument7 SeitenRMK Versi Pelajar Edup3033 Learning and The Learner (BI)Annette CaelyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midyear Inset 2023 2024Dokument7 SeitenMidyear Inset 2023 2024LoidaCarameNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCES3152 Digital Innovation in T - L - Student's VersionDokument5 SeitenSCES3152 Digital Innovation in T - L - Student's VersionCHIENG PEI WEN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL ClassroomDokument9 SeitenTSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL ClassroomRAVICHANTHIRANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tslb3132: Inclusive Education: Pendidikan InklusifDokument4 SeitenTslb3132: Inclusive Education: Pendidikan InklusifBlossomsky96Noch keine Bewertungen
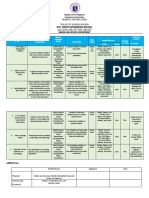
- Cebu Technological University: College of EducationDokument5 SeitenCebu Technological University: College of EducationRonnie LambotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1° Trim-Insumos Básica Media-1-1Dokument14 Seiten1° Trim-Insumos Básica Media-1-1Rina Lisbeth VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead Small TeamDokument7 SeitenLead Small TeamDark KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6.9 TleDokument1 SeiteModule 6.9 Tlejezabel romeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL Classroom PDFDokument9 SeitenTSLB3083 Teaching of Grammar in The Primary ESL Classroom PDFMuhammad SyafieNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020Dokument1 SeiteSchool Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020CHAPEL JUN PACIENTENoch keine Bewertungen
- SCES3132 Inclusive Education Jun 2021Dokument8 SeitenSCES3132 Inclusive Education Jun 2021CHIENG PEI WEN MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Zealand Aid Programme Strategic Plan 2015 19Dokument13 SeitenNew Zealand Aid Programme Strategic Plan 2015 19Djamnur AgnessiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSK 2024 School Inset Template IsukoDokument1 SeiteDSK 2024 School Inset Template IsukoRafael CasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improve Business Practice MARKDokument7 SeitenImprove Business Practice MARKDark KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Plan Lac, 2019-2020Dokument1 SeiteAction Plan Lac, 2019-2020Funny FiadcongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Action Plan I Can ReadingDokument2 SeitenAction Plan I Can ReadinghydZ ManzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic Interventionsin The Netherlands and Belgiumin Support of People With Profound Intellectual and Multiple DisabilitiesDokument1 SeiteTherapeutic Interventionsin The Netherlands and Belgiumin Support of People With Profound Intellectual and Multiple DisabilitiesNur Aeyna AliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marysol Ortiz Par PosterDokument1 SeiteMarysol Ortiz Par Posterapi-742239126Noch keine Bewertungen
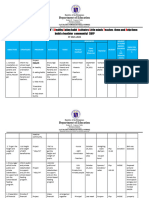
- Deped - Division of QuezonDokument5 SeitenDeped - Division of QuezonDanniese RemorozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP - 12frost - de Jesus Sinio NavarroDokument2 SeitenAP - 12frost - de Jesus Sinio NavarroLance NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosperidad National High School (School-INSET-template)Dokument3 SeitenProsperidad National High School (School-INSET-template)JEURDECEL MARTIZANONoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Leadership Project IlpDokument4 SeitenTeacher Leadership Project Ilpapi-622216865Noch keine Bewertungen
- Masterlist of Enrolled Learners With End of Program/Cy Status (Af-3)Dokument2 SeitenMasterlist of Enrolled Learners With End of Program/Cy Status (Af-3)Ian Christian Alangilan BarrugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNESCO Educational Management Information Systems An Overview 2003 en PDFDokument86 SeitenUNESCO Educational Management Information Systems An Overview 2003 en PDFArnold Pengson ManuyagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limites Laterales Interactive Worksheet - Live WorksheetsDokument1 SeiteLimites Laterales Interactive Worksheet - Live WorksheetsFranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidated DLC 1 School Opening Preparedness ReportDokument2 SeitenConsolidated DLC 1 School Opening Preparedness ReportJessa mae macasojotNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1° Trim-Insumos Básica MediaDokument13 Seiten1° Trim-Insumos Básica MediaJazmin PeñarandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Progressive Listening Comprehension Worksheet - Live WorksheetsDokument3 SeitenPresent Progressive Listening Comprehension Worksheet - Live Worksheetssteward messi ortegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result May 2022 Mpmsu MbbsDokument22 SeitenResult May 2022 Mpmsu MbbsSiya PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Area Mea DashboardDokument91 SeitenFinal Area Mea DashboardArlyn Nova AlbinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)Dokument1 SeiteInclusive Center-Based Model For Toddlers With ASD: Results of A Multi-Site Randomized Clinical Trial (Bonnie McBride)AUCDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ilp-Hayley RoyDokument6 SeitenIlp-Hayley Royapi-622216865Noch keine Bewertungen
- JEC Health Chart 11-7-09Dokument1 SeiteJEC Health Chart 11-7-09Stix1972Noch keine Bewertungen
- Increasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child DevelopmentDokument1 SeiteIncreasing Parenting Skills and Parenting E Cacy: Parent-Training Program Based Seamless Learning To Promoting Assessment Child Developmentkerja malamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0TOCDokument1 Seite0TOCdiannugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Talugtug National High School - MainDokument7 SeitenDepartment of Education: Talugtug National High School - Mainiamsireu floresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Everything Book for Child Care & Preschool, Ages 3 - 5Von EverandThe Everything Book for Child Care & Preschool, Ages 3 - 5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Ranking Universities in West Africa 2022Dokument1 SeiteTop 10 Ranking Universities in West Africa 2022Bright OtchereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aeon 4000 SDSDokument13 SeitenAeon 4000 SDSmarcos luqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1833 TX Melton, Daisy Mae DeathDokument1 Seite1833 TX Melton, Daisy Mae DeathRichard TonsingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knee Pain and The Internal Arts: Correct Alignment (Standing)Dokument7 SeitenKnee Pain and The Internal Arts: Correct Alignment (Standing)Gabriel PedrozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument2 SeitenAbstractMunifah AzisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014-1 Mag LoresDokument52 Seiten2014-1 Mag LoresLi SacNoch keine Bewertungen
- NPD Phase 1Dokument2 SeitenNPD Phase 1Abdullah ZahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokument26 SeitenSafety Roles and ResponsibilitiesAlvin Garcia Palanca100% (1)
- 16 MSDS NaHSO3Dokument6 Seiten16 MSDS NaHSO3Furqan SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Career 1Dokument2 SeitenCareer 1api-387334532Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is ISO 22000 S. 2005?: An OverviewDokument23 SeitenWhat Is ISO 22000 S. 2005?: An OverviewMario Norman B. CelerianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Know About Dengue FeverDokument11 SeitenKnow About Dengue FeverKamlesh SanghaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Form 8 sf8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition Report AutomaticDokument12 SeitenSchool Form 8 sf8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition Report AutomaticKIRSTEN DIAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterDokument37 SeitenSRM04-05 On A Silver PlatterBrandon Dempe100% (1)
- Epiglottitis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanatio N Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenEpiglottitis: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanatio N Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationfifiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinic by Alissa QuartDokument4 SeitenClinic by Alissa QuartOnPointRadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forensic MedicineDokument157 SeitenForensic MedicineKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Overload and Kidney Injury Score As A PredicDokument7 SeitenFluid Overload and Kidney Injury Score As A Predicmira srikandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLRDP 2017-2022 Midterm Update - FInalDraftDokument328 SeitenCLRDP 2017-2022 Midterm Update - FInalDraftemeyarayieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acetylsalicylic AcidDokument6 SeitenAcetylsalicylic AcidAdmin DownloadNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 2 ILP Grade 4Dokument5 SeitenWEEK 2 ILP Grade 4jean arriolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Process Patients With DiabetesDokument14 SeitenNursing Process Patients With DiabetesJelly Jia100% (2)
- Essays: 1-Title: Physical FitnessDokument7 SeitenEssays: 1-Title: Physical FitnessMy PcNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENTAL HEALTH NURSING ExamDokument5 SeitenMENTAL HEALTH NURSING ExamSurkhali BipanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumor AngiogenesisDokument35 SeitenTumor AngiogenesisDoni Mirza KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thallophytes 2Dokument32 SeitenThallophytes 2Starnley TemboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeDokument20 SeitenCommon Core Principles and Competences For Social Care and Health Workers Working With Adults at The End of LifeEng Stephen ArendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mapeh 2ND QDokument5 SeitenMapeh 2ND QMaxicris SlowerNoch keine Bewertungen