Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor
Hochgeladen von
ronaldo0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten13 SeitenComplementary metal oxide semiconductor
Originaltitel
Cmos
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenComplementary metal oxide semiconductor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten13 SeitenComplementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor
Hochgeladen von
ronaldoComplementary metal oxide semiconductor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 13
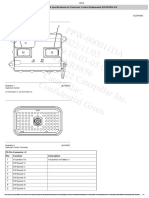
CMOS
Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor
What is CMOS?
• is an on-board, battery powered semiconductor
chip inside computers that stores the BIOS
settings. Some of these BIOS settings include
system time, date and system hardware
settings for your computer.
• is sometimes referred as Real-Time Clock
(RTC), Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM), Non-
Volatile BIOS memory
What is CMOS?
• CMOS is also a chip but a RAM chip, which
means it would normally lose the settings it
stored when the computer is shut down that
is why it used a battery to provide constant
power.
How BIOS and CMOS Work
Together
• The BIOS is a ROM chip on the motherboard -
it's purpose is to communicate between the
processor and other hardware components like
the hard drive, USB ports, sound card, video
card, and more.
• A computer without a BIOS would not understand
how these pieces of the computer work together.
How BIOS and CMOS Work
Together
• CMOS is a special type of RAM, which excels at
using very little power.
• The database is necessary for the startup
programs, as a list of the hardware which has to
be checked.
• The CMOS storage holds something like 256
bytes. Without the battery, all the information
would disappear from the CMOS.
REMEMBER
• The BIOS is a small program that controls
the computer from the time it powers on
until the time the operating system takes over.
• The BIOS is firmware, and thus CANNOT
store variable data.
• CMOS is a chip that stores variable data for
startup
REMEMBER
• The BIOS is the program that starts a
computer.
• The CMOS is the storage where the
BIOS pulls out the details it needs in
starting up the computer and saved
when you make changes to your BIOS
settings.
The Setup
• The Setup program is used to change the
settings in the CMOS storage.
• **Please note that setting up the BIOS incorrectly
could cause system malfunction.
The Setup Features
• Standard CMOS Features
- here you can change the date and time.
• Advanced BIOS Features –
- here you can set which device should be
used to boot from
• Advanced Chipset Features
- here you can setup the contents of the
chipset buffers
The Setup Features
• Integrated Peripherals
• - This menu contains settings associated
with the ATA and Super I/O controllers.
• Power Management Setup
• - The power management allows you to
setup various power saving features, when
the PC is in standby or suspend mode.
The Setup Features
• PnP/PCI Configurations
- This menu allows you to configure your PCI
slots
• PC Health Status
• - This menu displays the current CPU
temperature, the fan speeds, voltages etc.
• Set Password
• - To password protect your BIOS you can
specify a password
Resetting the CMOS storage
• Load Fail-Safe Defaults
• Load Optimized Defaults
• Move the motherboard’s jumper, start the PC,
and the data is erased. You then enter new data
and move the jumper back again.
• Remove the motherboard battery.
TASK
• Find a partner and perform BIOS
Configuration task as indicated at
the Operation Sheet.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- BIOS Basics ExplainedDokument20 SeitenBIOS Basics Explainednikhilteja2Noch keine Bewertungen
- CF-RU5102 UHF RFID Reader User's Manual V1.2Dokument35 SeitenCF-RU5102 UHF RFID Reader User's Manual V1.2Percy KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Nishant Sharma Roll No. 17 B. Tech. (Hons) - M. Tech. Integrated Program (CSE)Dokument19 SeitenBy Nishant Sharma Roll No. 17 B. Tech. (Hons) - M. Tech. Integrated Program (CSE)Nishant SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms and Elements (Chemistry Notes)Dokument4 SeitenAtoms and Elements (Chemistry Notes)wlkernanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epson L1800 PDFDokument149 SeitenEpson L1800 PDFIon Ionut50% (2)
- Image Quality Quick TestDokument74 SeitenImage Quality Quick TestFrancisco DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- How BIOS WorksDokument6 SeitenHow BIOS Worksramjee26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pinout Ecm 340-5687 ImplementDokument4 SeitenPinout Ecm 340-5687 Implementloky monsa100% (2)
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8Von EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Systems Servicing NC IIDokument74 SeitenComputer Systems Servicing NC IINoone F. moon86% (7)
- BIOS and CMOSDokument10 SeitenBIOS and CMOSbiswajit boroNoch keine Bewertungen
- A+ Chapter 3 BIOS, CMOS, Firmware - FinalDokument23 SeitenA+ Chapter 3 BIOS, CMOS, Firmware - FinalRamsesDeCastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bios & CmosDokument20 SeitenBios & CmosEllaziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2bios N CmosDokument37 Seiten2.2bios N CmosBONAM KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument100 SeitenUnit 4Somya AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gino Anna Herlyn Tle 10Dokument70 SeitenGino Anna Herlyn Tle 10Ramil AlcantaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- A+ Chapter 2 BIOS, CMOS, Firmware - Finalc-CleanDokument23 SeitenA+ Chapter 2 BIOS, CMOS, Firmware - Finalc-CleanTatenda David GondweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the Function and Configuration of BIOSDokument10 SeitenUnderstanding the Function and Configuration of BIOSArnel Cueto100% (1)
- BIOSDokument2 SeitenBIOSdkray1982_372799333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7 - BIOSDokument9 SeitenLesson 7 - BIOSAnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOSDokument5 SeitenBIOSAshifa MNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is BiosDokument13 SeitenWhat Is BiosEzequiel ElementoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOSDokument26 SeitenBIOSmarjun.delaramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure BIOS and PC Boot ProcessDokument333 SeitenConfigure BIOS and PC Boot Processjyotsna dwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Computer Hardware EssentialsDokument39 SeitenAdvanced Computer Hardware EssentialsDaniel ErgichoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assemble and Configure a Computer SystemDokument36 SeitenAssemble and Configure a Computer SystemTheoSebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- C9 Working With The BIOS Setup ProgramDokument16 SeitenC9 Working With The BIOS Setup ProgramAmir M. VillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT1204 Section 06Dokument32 SeitenIT1204 Section 06jahan2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- How BIOS Works - Bab5Dokument6 SeitenHow BIOS Works - Bab5api-19976774Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware BasicsDokument200 SeitenHardware BasicsSathish Kumar100% (1)
- 12 Bios and CmosDokument11 Seiten12 Bios and CmosJohn Patrick GuigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- How BIOS Works 4Dokument7 SeitenHow BIOS Works 4NafeesAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS10 - Q2 - Topic 1Dokument23 SeitenCSS10 - Q2 - Topic 1Alcoy NHS Tech4Ed CenterNoch keine Bewertungen
- A+ Guide To Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 6e: MotherboardsDokument36 SeitenA+ Guide To Managing and Maintaining Your PC, 6e: Motherboardsjmkcbe100% (1)
- National University of Modern Languages: Booting A Computer BiosDokument3 SeitenNational University of Modern Languages: Booting A Computer BiosMuhammad BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HjshbjdhfkajDokument37 SeitenHjshbjdhfkajBhargavi GordeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seminar Report ON: Rom-BiosDokument12 SeitenA Seminar Report ON: Rom-Bioshart18987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bios 2 PDFDokument4 SeitenBios 2 PDFpeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bios Cmos MemoryDokument23 SeitenBios Cmos MemoryEmman BalicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On Computer Architecture: Bios and Os LoadingDokument57 SeitenPresentation On Computer Architecture: Bios and Os LoadinghamanvikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic-Input-Output-System (BIOS) Configuration: Information Sheet 1.1-4Dokument2 SeitenBasic-Input-Output-System (BIOS) Configuration: Information Sheet 1.1-4Donn SabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOSDokument11 SeitenBIOSnitinhandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard, BIOS and POST ExplainedDokument13 SeitenMotherboard, BIOS and POST ExplainedAleciafyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard, BIOS and POSTDokument13 SeitenMotherboard, BIOS and POSTBhavikk KotadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard, BIOS and POSTDokument13 SeitenMotherboard, BIOS and POSTPrateek KhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard, BIOS and POST: Understanding the Key ComponentsDokument13 SeitenMotherboard, BIOS and POST: Understanding the Key ComponentsM SaefulahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motherboard, BIOS and POST ExplainedDokument13 SeitenMotherboard, BIOS and POST ExplainedPeni PerdiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure BIOS SettingsDokument37 SeitenConfigure BIOS Settingsmarisol PayraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxDokument33 SeitenComputer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxSaima Binte IkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology Project ON: Parts of Comuter-CPUDokument26 SeitenInformation Technology Project ON: Parts of Comuter-CPUshreyashk1010Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIOS TroubleshootingDokument16 SeitenBIOS TroubleshootingHusnil Wafa HerliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 07Dokument7 SeitenLesson 07Rohit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOS Startup ScreenDokument9 SeitenBIOS Startup ScreenSNTCC107CHAITANYA6826Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5 Post and Bios Beep CodesDokument17 SeitenLesson 5 Post and Bios Beep CodesagwonadavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- MotherboardDokument41 SeitenMotherboardjoseph rey ybiosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOS Setup GuideDokument4 SeitenBIOS Setup GuideVishv PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3: Advanced Computer Hardware: Instructor MaterialsDokument62 SeitenChapter 3: Advanced Computer Hardware: Instructor MaterialsRadot chandra adiputra100% (1)
- What Is BIOS ?Dokument24 SeitenWhat Is BIOS ?Leonides AgravanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Inside: Central Processing Unit (CPU)Dokument50 SeitenOn The Inside: Central Processing Unit (CPU)vinay136384Noch keine Bewertungen
- GeForce6100PM - M2 (2 - 0A) 33 PDFDokument1 SeiteGeForce6100PM - M2 (2 - 0A) 33 PDFhamfrostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schools Division of Parañaque City Tle 10 Computer System Servicing First Quarter Week 4Dokument11 SeitenSchools Division of Parañaque City Tle 10 Computer System Servicing First Quarter Week 4Jezrhil R. VivarNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is BIOS and its functionsDokument14 SeitenWhat is BIOS and its functionsAshu KalraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC Repair Fundamentals CITA-120 Computer Concepts and Operating SystemsDokument22 SeitenPC Repair Fundamentals CITA-120 Computer Concepts and Operating SystemseosmancevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMOS Devices Used in Logic Circuits, Memory, and ProcessorsDokument18 SeitenCMOS Devices Used in Logic Circuits, Memory, and ProcessorsJohn YohansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bios (Basic Input Output Service)Dokument21 SeitenBios (Basic Input Output Service)mahmoudaladawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inside the Computer: A Guide to Basic Hardware ComponentsDokument31 SeitenInside the Computer: A Guide to Basic Hardware ComponentsEswaran arunachalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polarized-That Is, Each Has Two Sides or Ends Called North-Seeking and South-Seeking Poles. Like Poles Repel One AnotherDokument2 SeitenPolarized-That Is, Each Has Two Sides or Ends Called North-Seeking and South-Seeking Poles. Like Poles Repel One AnotherronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chess Record Sheet: Division Sports and Athletics Challenge 2016Dokument1 SeiteChess Record Sheet: Division Sports and Athletics Challenge 2016ronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Melon HeadDokument1 SeiteMr. Melon HeadronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Right Hand RuleDokument1 SeiteRight Hand RuleronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Directory ExplainedDokument5 SeitenActive Directory ExplainedronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divisibility Rules 1-12Dokument1 SeiteDivisibility Rules 1-12ronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Directory ExplainedDokument5 SeitenActive Directory ExplainedronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screening Committee Register: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga PeninsulaDokument15 SeitenScreening Committee Register: Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Ix, Zamboanga PeninsularonaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConduitBenderGuide PDFDokument12 SeitenConduitBenderGuide PDFCarlos Daniel Ayala GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate of RecognitionDokument1 SeiteCertificate of RecognitionSchool of Law TSUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Research ProblemDokument68 SeitenChapter 1 - Research ProblemronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form TESDADokument2 SeitenForm TESDANhor MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form TESDADokument2 SeitenForm TESDANhor MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form TESDADokument2 SeitenForm TESDANhor MannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure Wireless Router - WAPDokument28 SeitenConfigure Wireless Router - WAPronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Network ConceptsDokument24 SeitenBasic Network ConceptsronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Presentation Rubric: ORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC: Tabon M. Estrella National High SchoolDokument2 SeitenOral Presentation Rubric: ORAL PRESENTATION RUBRIC: Tabon M. Estrella National High SchoolronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of A ComputerDokument56 SeitenComponents of A ComputerronaldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital energy meter with serial interfaceDokument34 SeitenDigital energy meter with serial interfaceMary Ann Cadena CabañasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Comfortstar Ductless Catalog PDFDokument68 Seiten2019 Comfortstar Ductless Catalog PDFoscar100% (2)
- Brochure 4nov2017Dokument2 SeitenBrochure 4nov2017SGI AUTOMOTIVE PVT LTDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 1-1 PDFDokument4 SeitenAssignment No. 1-1 PDFPrasad AhireNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE500Dokument4 SeitenAE500Pyrosales Pty LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report On Standard DiodeDokument13 SeitenLab Report On Standard DiodeDANSTAN KULENoch keine Bewertungen
- Order Vamp IED 321Dokument2 SeitenOrder Vamp IED 321Thiago Henrique SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- PM-SMS HVDCDokument20 SeitenPM-SMS HVDCMuhittin KNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Electrical CharacteristicsDokument16 Seiten05 Electrical CharacteristicsSandesh Kumar B VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Title - Basic Electrical Engineering: First Semester BE Degree ExaminationDokument3 SeitenSubject Title - Basic Electrical Engineering: First Semester BE Degree ExaminationSathishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICROCONTROLLERDokument26 SeitenMICROCONTROLLEREnrique “khosrau” AlgunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Manual - Rotel RMB 1095Dokument8 SeitenService Manual - Rotel RMB 1095leorassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sci5q3 - Summative Test No. 3 - 2022-2023Dokument3 SeitenSci5q3 - Summative Test No. 3 - 2022-2023Caila GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Gas Analyser: Specialist of UV SpectrosDokument8 SeitenOnline Gas Analyser: Specialist of UV Spectroslaoying qdNoch keine Bewertungen
- p335 10Dokument1 Seitep335 10ابزار دقیقNoch keine Bewertungen
- DGFT Notification No.115 (RE-2013) /2009-2014 Dated 13th March, 2015Dokument5 SeitenDGFT Notification No.115 (RE-2013) /2009-2014 Dated 13th March, 2015stephin k jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small, Low Power, 3-Axis 3 G Accelerometer ADXL335: Features General DescriptionDokument16 SeitenSmall, Low Power, 3-Axis 3 G Accelerometer ADXL335: Features General DescriptionGirish Kumar .R. GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX DiagDokument10 SeitenDX Diagاشرف البخيتيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuits 1 Problems SolvedDokument86 SeitenCircuits 1 Problems SolvedMarvin SinuesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPLAB User GuideDokument120 SeitenMPLAB User Guidesrs818Noch keine Bewertungen
- 32av833g Sb-Kl-Si 1351167578Dokument51 Seiten32av833g Sb-Kl-Si 1351167578Jacob EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco 640-721: Practice Exam: Question No: 1Dokument66 SeitenCisco 640-721: Practice Exam: Question No: 1mario1349Noch keine Bewertungen
- UL13 Instrumentation Cable Technical DataDokument1 SeiteUL13 Instrumentation Cable Technical DataMario MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Vista Installation GuideDokument8 SeitenWindows Vista Installation GuideThi HaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Note: PIC Enabled LidarDokument2 SeitenApplication Note: PIC Enabled Lidarm_heckNoch keine Bewertungen