Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
BGP Route Reflectors and Confederation: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Hochgeladen von
Kashif HussainOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BGP Route Reflectors and Confederation: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Hochgeladen von
Kashif HussainCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
BGP Route Reflectors and
Confederation
www.huawei.com
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved
Foreword
BGP typically requires all BGP speakers in an AS to form connectivity
through a full mesh implementation. IBGP peering limitations, used to
prevent iBGP loops, hinders the scalability of BGP. BGP route reflectors
and BGP confederations are BGP extension techniques used to provide
a solution to this problem, and shall be introduced in this section.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 2
Objectives
Upon completion of this section, you will be able to:
Understand BGP route reflection principles
Understand BGP confederation principles
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 3
Contents
Introduction
BGP route reflection
BGP confederation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 4
The Extensibility Problem in IBGP
How does BGP prevent the routing loops?
EBGP
− EBGP prevents the routing loop through AS-PATH
attribute. Router that receives an update containing its
local AS number in the AS_PATH attribute from EBGP
peer knows that a routing loop has occurred. To prevent
routing loops, the router will ignore the update.
IBGP
− BGP router will not announce the update information
received from its IBGP peer to other IBGP peers.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 5
The Extensibility Problem in IBGP
The loop prevention mechanism in IBGP introduces the
problem below
To ensure all the IBGP peers can receive the update
information
− IBGP Speaker must be fully meshed
▪ requires to maintain n*(n-1)/2 unique IBGP sessions
Solution
Route Reflection (RFC2796)
Confederation (RFC3065)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 6
Solution of IBGP Extensibility Problem
Route Reflection (RFC 2796)
It works by relaxing the rule that a BGP speaker cannot
advertise the routes learned from IBGP peer to other IBGP
peers. It allows a BGP speaker(“known as "Route Reflector")
to advertise IBGP learned routes to certain IBGP peers.
Confederation (RFC3065)
A confederation is an AS that has been subdivided
into a group of sub-autonomous systems, known as
member AS. EBGP peer relationship is formed
between the sub-autonomous systems. IBGP peer
relationship is formed between the BGP speaker in the
same member AS.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 7
BGP Route Reflector
AS 200 AS 200
RTA RTB RTA RTB
IBGP
IBGP IBGP IBGP IBGP
RTC RTC
IBGP Full Mesh Specify RTC as Route Reflector
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 8
BGP Confederation
AS 65001
AS 100
AS 65003
AS 101 AS 65002
EBGP
IBGP
EBGP_Confed
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 9
Contents
Introduction
BGP route reflection
BGP confederation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 10
Different Roles of the peers
The IBGP peers inside an AS can be Cluster
divided into:
Client
Client Client
− The clients peer with the route
reflector and exchange routing
information with it.
Non-Client
RR
− All peers of the route reflector
that are not part of the cluster.
Route Reflector
Non- Non-
− a router that performs the route Client Client
reflection function. IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 11
The Relationship between Peers
Client needs to maintain only the IBGP session between the
client and RR
IBGP full mesh is required between the RRs
IBGP full mesh is required between the Non-clients
IBGP full mesh is required between the RR and Non-Client
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 12
The Advertisement Principle of Route Reflection
Cluster
Select the best route based on the
BGP route selection process Client Client
For the route received from Non-client
IBGP
RR
Reflect only to all the Client Peers
Non- Non-
Client Client
IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 13
The Advertisement Principle of Route Reflection (Cont.)
Cluster
For the route learnt from Client IBGP Client Client
Reflect to all Clients and Non-
Clients
RR
Non- Non-
Client Client
IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 14
Route Reflection Cluster
Inside an AS, multiple RRs might exist to provide redundancy for the
Clients. As a result, the routing update between the RRs might
generate a routing loop. We use the concept of cluster to prevent this
from happen.
RR RR
Cluster
Client
Cluster Client
Client
RR RR
IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 15
What is a Cluster?
A cluster is identified by the 4 bytes Cluster_ID. A loopback
address is usually used as the Cluster_ID.
It is possible to have multiple RRs in the same cluster; one
client can belong to multiple clusters at the same time
If the route reflector receives a routing update that contains the
local CLUSTER_ID value, the update message will be
discarded.
RR RR
Cluster
Client 10.1.1.2
Cluster Client
10.1.1.1
Client
RR RR
IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 16
Loop Prevention Mechanism used in Route
Reflection - Originator_ID
ORIGINATOR_ID is an optional, non-transitive BGP attribute of Type code 9.
An originator_ID is created by the first route reflector and will not be changed by
the subsequent route reflectors
The originator_ID attribute is 32 bits long, it should be received only from an
IBGP peer
It is the Router ID of:
− routes that are originated by the local AS:Router ID of the BGP speaker
that advertise the route
− routes that are not originated by the local AS:Router ID of the border
router in the local AS
A router which recognizes the ORIGINATOR_ID attribute should ignore a route
received with its ROUTER_ID as the ORIGINATOR_ID.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 17
Loop Prevention Mechanism used in Route
Reflection - Cluster_List
Cluster-list is an optional, non-transitive BGP attribute of Type code 10.
It is a sequence of CLUSTER_ID values representing the reflection path
that the route has traversed. The new CLUSTER_ID is prepended to
the CLUSTER_LIST.
If the local CLUSTER_ID is found in the cluster-list, the advertisement
received should be ignored.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 18
Several clusters in an AS
Client
Cluster1
AS100
Client
RR Client
Cluster2 Cluster3
Client
Client
Client
RR RR
IBGP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 19
Hierarchical Route Reflection
Level 2 RR
Level 1 RR/Client
Client
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 20
Contents
Introduction
BGP route reflection
BGP confederation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 21
Confederation Terminology
Member AS
AS Confederation AS 1001
AS 100
AS 1003
AS 1002
EBGP
AS 101
IBGP
EBGP_Confed
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 22
AS-Path Review
Four types of AS-Path:
Value Segment Type
=======||=================
1 AS_SET
2 AS_SEQUENCE
3 AS_CONFED_SEQUENCE
4 AS_CONFED_SET
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 23
AS_Path Modification Process
AS 1001
AS 100
AS 1003
AS 1002
AS 101
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 24
AS_Path Modification Process
AS 1001
AS 100
AS 1003
AS 1002
AS 101
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 25
Confederation vs. Route Reflection
Reference Comparison
Factor
Both of the methods can further increase their extensibility by supporting
Multi-level multiple-level function. Route reflector supports multiple level reflection
Support structures. Confederation support the used of route reflection in a sub-
autonomous system.
Both of the methods support route selection by using policy control. However,
Policy Control
the use of policy control in confederation is much more flexible.
Migrating from a non-route reflector to a route reflector design is easy.
Complexity of
Conventional This is because the changes that happen to the whole network as a result of
IBGP the migration is less. However, the migration from non-confederation to
Migration confederation design requires major reconfiguration of the routers and a
major change in the logical topology.
All routers in a confederation must understand and support
confederations. This is because all the routers must understand the
Capability AS_PATH attribute used for confederation. In contrast, only the route
Support reflectors themselves must understand route reflection. However, the
client is also required to understand the reflector attribute in new
design of cluster division.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 26
Confederation vs. Route Reflection
Reference Comparison
Factor
Inside an AS, route reflection requires only a single IGP. On the other hand,
confederation could be used to run an IGP in one sub-AS independently of
Control of IGP IGPs in other sub-AS, and provides a possible advantage of using
Expansion confederation over route refection. When an IGP grows exponentially,
management can become difficult, the confederation can be used to
reduce the size of the IGP routing table.
Most of the service providers have deployed route reflection rather than
Implementation
confederation. Therefore, a lot of experience in route reflection has been
Experience
obtained.
In fact, AS combination is irrelevant with the IBGP expandability. It is mentioned
here because it is one of the advantages of confederation. An AS can be
AS Combination
combined with an existing confederation. This can be realized by taking the
new AS as the sub-AS of the confederation.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 27
Summary
Explain which problem is resolved
through using route reflectors or BGP
confederation.
Describe the advertisement rules
surrounding route reflectors in BGP.
Describe the variations of AS_PATH
used with BGP confederation.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 28
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. All rights reserved Page 29
Thank You
www.huawei.com
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Sublime QR CodeDokument6 SeitenSublime QR Codejeff_sauserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- McKinsey & Co - Nonprofit Board Self-Assessment Tool Short FormDokument6 SeitenMcKinsey & Co - Nonprofit Board Self-Assessment Tool Short Formmoctapka088100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Final Exam: Functional Performance Testing: Technical vs. Process CommissioningDokument9 SeitenFinal Exam: Functional Performance Testing: Technical vs. Process CommissioningBen MusimaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- RealPOS 70Dokument182 SeitenRealPOS 70TextbookNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Personality Trait-Based Interactionist Model of Job PerformanceDokument18 SeitenA Personality Trait-Based Interactionist Model of Job PerformanceAlvina AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Factors That Affect Information and Communication Technology Usage: A Case Study in Management EducationDokument20 SeitenFactors That Affect Information and Communication Technology Usage: A Case Study in Management EducationTrần Huy Anh ĐứcNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingDokument30 SeitenThe Basics of Hacking and Pen TestingAnonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grammar Booster: Lesson 1Dokument1 SeiteGrammar Booster: Lesson 1Diana Carolina Figueroa MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- TheMindReader TeaserA WhatDokument7 SeitenTheMindReader TeaserA WhatnakulshenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Failure Reporting, Analysis, and Corrective Action SystemDokument46 SeitenFailure Reporting, Analysis, and Corrective Action Systemjwpaprk1Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- A Comparative Marketing Study of LG ElectronicsDokument131 SeitenA Comparative Marketing Study of LG ElectronicsAshish JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Receiving Welcoming and Greeting of GuestDokument18 SeitenReceiving Welcoming and Greeting of GuestMarwa KorkabNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Vocabulary Prefixes ExercisesDokument2 SeitenVocabulary Prefixes ExercisesMarina García CarrascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Malla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous)Dokument17 SeitenMalla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous)Ranjith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Assignment 1 - Tiered LessonDokument15 SeitenAssignment 1 - Tiered Lessonapi-320736246Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
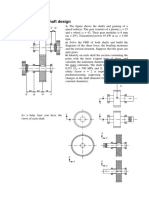
- Shaft design exercisesDokument8 SeitenShaft design exercisesIvanRosellAgustíNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Windows Server 2016 Editions ComparisonDokument4 SeitenWindows Server 2016 Editions ComparisonmasterredhardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- Roland Barthes and Struggle With AngelDokument8 SeitenRoland Barthes and Struggle With AngelAbdullah Bektas0% (1)
- MVC ImpDokument4 SeitenMVC ImpsrinathmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodDokument5 SeitenA Method For Identifying Human Factors Concerns During The HAZOP Process - Dennis AttwoodAlvaro Andres Blanco GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mathematics I - Class Test December 2015Dokument6 SeitenEngineering Mathematics I - Class Test December 2015Kunal RamnatsingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH13 QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCH13 QuestionsAngel Itachi MinjarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity Emcee Mid-Year INSET 2021Dokument3 SeitenActivity Emcee Mid-Year INSET 2021Abegail A. Alangue-Calimag67% (6)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Humanities Unit Plan Plus Lesson PlansDokument12 SeitenHumanities Unit Plan Plus Lesson Plansapi-298200210Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0418 w08 QP 1Dokument17 Seiten0418 w08 QP 1pmvarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedural Text Unit Plan OverviewDokument3 SeitenProcedural Text Unit Plan Overviewapi-361274406Noch keine Bewertungen
- NX569J User ManualDokument61 SeitenNX569J User ManualHenry Orozco EscobarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circle Midpoint Algorithm - Modified As Cartesian CoordinatesDokument10 SeitenCircle Midpoint Algorithm - Modified As Cartesian Coordinateskamar100% (1)
- Lenovo IdeaPad U350 UserGuide V1.0Dokument138 SeitenLenovo IdeaPad U350 UserGuide V1.0Marc BengtssonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of Vaiseshika's PragabhavaDokument5 SeitenSignificance of Vaiseshika's Pragabhavavskanchi0% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)