Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Spiritual Care
Hochgeladen von
Riski Ramadhani0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten11 Seitenkeperawatan paliatif
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenkeperawatan paliatif
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
13 Ansichten11 SeitenSpiritual Care
Hochgeladen von
Riski Ramadhanikeperawatan paliatif
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
CAM (COMPLEMENTARY AND ALTERNATIVE
MEDICINES)
IN PALLIATIVE CARE
OLEH :RETNO DYAH W
Introduction
• Complementary and alternative medicines (CAM)
comprise a diverse array of treatment modalities that
are not presently considered part of
conventional/mainstream medicine. CAM emphasize
a holistic approach towards healthcare, i.e. they are
based on the belief that mind, body an spirit are
interconnected and that health depends on
wholeness and balance between them.
Definitions
• Alternative treatments aim to replace conventional
treatments.
• Complementary treatments are used alongside the
conventional treatments
Types of therapy
• In palliative and supportive care, CAM is primarily used to
increase the client’s well-being, e.g. by alleviating pain and
other symptoms of the disease, improving sleep, reducing
stress and anxiety, or by reducing the adverse effects of
conventional treatments. They are often used as an addition
to conventional treatments. Some CAM modalities claim a
direct effect in the prevention or treatment of cancer. Widely
practised treatments are acupuncture aromatherapy,
herbalism, homeopathy, hypnotherapy, reflexology, relaxation
and spiritual healing.
• The individual therapies described in this chapter will be
considered under four headings: alternative medical
concepts; mind–body interventions, biologically based
therapies and manipulative therapies
Principles of CAM
• A central tenet of CAM is the strong belief in the
uniqueness and wholeness of the individual and the
power of the body to heal itself.
• Often, patients who consult complementary practitioners
have chronic conditions that are diffi cult to manage,
such as HIV infection, multiple sclerosis, rheumatological
conditions and cancer.
• The interest in CAM in the palliative care setting is
perhaps not surprising given the inherent need for the
terminally ill to feel supported with regard to physical,
psychosocial and emotional domains, in achieving an
acceptable quality of life.
Reasons for seeking CAM
• Possible factors contributing to CAM use
• Push factors
• Dissatisfaction with orthodox medicine:
– ineffective
– adverse effects
– poor communication with doctor
– waiting lists
• Rejection of orthodox medicine: anti-science or anti-
establishment attitude
• Desperation
Pull factors
• Philosophical congruence:
– emphasis on holism
– active role of patient
– explanation intuitively acceptable
– natural treatments
• Personal control over treatment
– Good relationship with therapist:
– on equal terms
– time for discussion
– allows for emotional factors
• Accessibility
Group 1: Alternative medical systems
• Acupuncture
• Homeopathy
Group 2: Mind–body therapies
• Relaxation therapy
• Hypnotherapy
• Guided imagery and visualization
• Meditation
• Spiritual healing
• Creative therapies :Art and Music therapies
Group 3: Biologically-based practices
• Herbal medicine
• Aromatherapy
Group 4: Manipulative and body-based
therapies
• Massage
• Refl exology
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Shop Math PDFDokument29 SeitenShop Math PDFKen LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDokument41 Seiten3 Edition February 2013: Ec2 Guide For Reinforced Concrete Design For Test and Final ExaminationDark StingyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1830PSS R36 QuickReferenceGuide 8DG60888JAAADokument66 Seiten1830PSS R36 QuickReferenceGuide 8DG60888JAAAFelippe CanatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orrick PostedbyrequestDokument4 SeitenOrrick PostedbyrequestmungagungadinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignDokument15 SeitenModeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignSalam FaithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesDokument6 SeitenQuant One Analyser – endless possibilitiesSamuel SuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011Dokument332 SeitenCERT Basic Training Participant Manual - 2011jegodfreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Dokument7 SeitenDimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Linda Garcia PNoch keine Bewertungen
- MACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSDokument1 SeiteMACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSsensoham03Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kirloskar-Oil-Engines DescriptionsDokument8 SeitenKirloskar-Oil-Engines Descriptionssinghhardeep760Noch keine Bewertungen
- Paguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFDokument88 SeitenPaguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFBoris Sitorus100% (2)
- Terminal BlockDokument12 SeitenTerminal BlockAlmaforNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Teubner Studienbücher Chemie) Brian R. Eggins (Auth.) - Biosensors - An Introduction (1996, Vieweg+Teubner Verlag) PDFDokument221 Seiten(Teubner Studienbücher Chemie) Brian R. Eggins (Auth.) - Biosensors - An Introduction (1996, Vieweg+Teubner Verlag) PDFRicardo PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raspberry PiDokument19 SeitenRaspberry PiAnonymous E4Rbo2s100% (1)
- Series: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchDokument15 SeitenSeries: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchPhúc Phan TiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneityDokument9 SeitenPurification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneitySinaí GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variants of NormalDokument9 SeitenVariants of NormalFaizah HannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Craniosacral Therapy For The Treatment of Chronic.10Dokument9 SeitenCraniosacral Therapy For The Treatment of Chronic.10Marcus Dos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- M10 - Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate Using Polystyrene in Lightweight CHB-CE-503Dokument19 SeitenM10 - Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate Using Polystyrene in Lightweight CHB-CE-503Michelle LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synchronized Natural Incubation by Free-Range Native ChickensDokument2 SeitenSynchronized Natural Incubation by Free-Range Native ChickensFilbert John MillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)Dokument7 SeitenCEFIC Guidelines Transport Equipment Packed Cargo (2010)sl1828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fodor Hungary Between East and WestDokument22 SeitenFodor Hungary Between East and WestFatih YucelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Eng Internship ReportDokument6 SeitenCivil Eng Internship ReportAromatic-O PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Guide For PpeDokument45 SeitenSolution Guide For PpeTrek Apostol57% (7)
- Limbah PabrikDokument2 SeitenLimbah Pabrikindar dewaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDokument2 SeitenSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- อัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDokument124 Seitenอัตราภาษีของไทยที่ลดให้เปรูDante FilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoDokument13 SeitenJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoNestor Gerotape DiosanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycab HT XlpeDokument33 SeitenPolycab HT Xlpezafrikhan875Noch keine Bewertungen
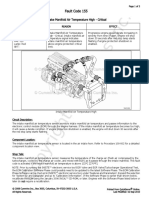
- Fault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - CriticalDokument3 SeitenFault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - Criticalhamilton miranda100% (1)