Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Salts
Hochgeladen von
ONG TEIK MING -Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Salts
Hochgeladen von
ONG TEIK MING -Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Topic 8 Salts
8.1 Salts
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Examples Of Salts Used In Daily Life
Salt exist naturally around us. We use salt in our food, things that we
used and others.
Baking Calcium
Calcium
Baking sulphate,
powder
powder or
or sulphate,
Table
Table salt,
salt, Marble,
Marble, CaSO
CaSO4 4 isis used
used
sodium
sodium
NaCl CaCO as
NaCl CaCO3 3 bicarbonate,
bicarbonate, as plaster
plaster toto
NaHCO support
support broken
broken
NaHCO3 3 bones
bones
Ammonium
Ammonium Silver
Silver bromide,
bromide,
phosphate, AgBr
phosphate, AgBr is used
is used toto
(NH
(NH4)43)PO
PO4 4isisused make
3
used make filmfilm and
and
as
as fertilisers
fertilisers inin photography
photography
agriculture
agriculture paper
paper
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Contoh Garam Yang Digunakan Dalam Kehidupan Seharian
Garam wujud secara semula jadi di sekeliling kita. Kita menggunakan garam di
dalam makanan, barangan yang digunakan dan sebagainya .
Kalsium
Kalsium sulfat,
sulfat,
Serbuk
Serbuk penaik
penaik CaSO
CaSO4 4
Marmar,
Marmar, atau natrium
atau natrium
Garam digunakan
digunakan
Garam biasa,
biasa, CaCO
CaCO3 bikarbonat,
bikarbonat, sebagai
NaCl
3
NaHCO sebagai plaster
plaster
NaCl NaHCO3 untuk
3
untuk
menyokong
menyokong
tulang
tulangpatah
patah
Ammonium
Ammonium fosfat, Argentum
(NH ) PO
fosfat, Argentum bromida,
bromida,
(NH4 43)3PO4 4 AgBr
AgBr digunakan
digunakan
digunakan
digunakan sebagai
sebagai untuk membuat
untuk membuat
baja dalam filem
baja
pertanian
dalam filem dan kertas
dan kertas
pertanian fotografi
fotografi
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
The Meaning Of Salt
Salt is formed in neutralisation process. Salt consist of cation from base
that combines with anion from acid.
Cation from the base
HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O
Anion from the acid
Thus, salt is defined as a compound produced when hydrogen ion, H+
from an acid is replaced by a metal ion or ammonium ion, NH4+.
Zn2+ ( NO )2 K+ NO 3
3
H+ NO 3
Cu2+ (NO 3 )2 NH4+ NO 3
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Garam
Garam terbentuk dalam proses peneutralan. Garam mengandungi kation
daripada bes yang bergabung dengan anion daripada asid.
Kation daripada bes
HCl (ak) + NaOH (ak) → NaCl (ak) + H2O
Anion daripada asid
Oleh itu, garam ditakrifkan sebagai sebatian yang terhasil apabila ion
hidrogen H+ daripada asid digantikan oleh ion logam atau ion
ammonium, NH4+.
Zn2+ ( NO )2 K+ NO 3
3
H+ NO 3
Cu2+ (NO 3 )2 NH4+ NO 3
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
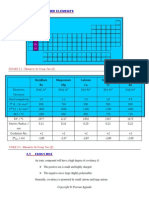
Soluble And Insoluble Salt
Salts can be classified according to its solubility in water. Some are soluble in
water and some are insoluble in water.
Soluble Salts Insoluble
All nitrate salts Nitrate salts No nitrate salts are insoluble
Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3
Potassium carbonate, K2CO3 Carbonate salts All other carbonate salts
Ammonium carbonate, (NH4)2CO3
All chloride salts except some • Silver chloride, AgCl
Chloride salts • Lead (II) chloride, PbCl2
chloride salt
• Lead (II) sulphate, PbSO4
All sulphate salts except some Sulphate salts • Calcium sulphate, CaSO4
sulphate salts
• Barium sulphate, BaSO4
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Garam Larut Dan Garam Tak Larut
Garam boleh dikelaskan mengikut keterlarutannya dalam air. Sesetengah garam
larut dalam air dan sesetengah tidak larut.
Larut Garam Tak Larut
Tiada garam nitrat yang tidak
Semua garam nitrat Garam nitrat
larut
Natrium karbonat, Na2CO3
Semua garam karbonat yang
Kalium karbonat, K2CO3 Garam karbonat
lain
Ammonium karbonat, (NH4)2CO3
• Argentum klorida, AgCl
Semua garam klorida kecuali • Plumbum (II) klorida,
Garam klorida
beberapa garam klorida PbCl2
• Plumbum (II) sulfat,
Semua garam sulfat kecuali PbSO4
Garam sulfat
sesetengah garam sulfat • Kalsium sulfat, CaSO4
• Barium sulfat, BaSO4
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
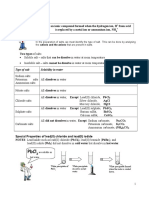
Preparation Of Soluble Salts
Method • Sodium salts Method
Other salt • Potassium salts
• Ammonium salts
Acid+ Metal Oxide →Salt + Water
Neutralisation
Acid+ Metal → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Acid+ Alkali → Salt + Water
Acid+ Metal carbonate → Salt + Water + Carbon
dioxide
Soluble salts are not pure and contain impurities. They are purified through
recrystallisation process.
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Penyediaan Garam Larut
Kaedah • Garam natrium Kaedah
Garam lain • Garam kalium
• Garam ammonium
Asid+ Oksida logam →Garam + Air
Peneutralan
Asid+ Logam → Garam + Gas hidrogen
Asid+ Alkali → Garam + Air
Asid+ Karbonat logam → Garam + Air + Karbon
dioksida
Garam larut tidak tulen dan mengandungi bendasing. Ia akan ditulenkan
melalui proses penghabluran.
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Physical Characteristics Of Crystal
Crystal of sodium Crystal of potassium Crystal of copper (II)
chloride dichromate sulphate
• Crystals have flat surfaces, sharp corners and straight sides.
• Crystals have different geometrical shapes such as cuboids, rhombic or
prism.
• Crystals have fixed angles between two neighbouring surfaces.
• Crystals of the same substance have same shape but different in sizes.
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Sifat Fizik Hablur
Hablur natrium klorida Hablur kalium dikromat Hablur kuprum (II)
sulfat
• Hablur mempunyai permukaan yang rata, bucu tajam dan sisi lurus.
• Hablur mempunyai bentuk geometri yang berbeza seperti kuboid, jarum
atau kepingan.
• Hablur mempunyai sudut tetap diantara dua permukaan bersebelahan.
• Hablur bahan yang sama mempunyai bentuk yang sama tetapi saiz yang
berbeza.
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Preparation Of Insoluble Salts
• Insoluble salts are ionic compounds consist of cations and anions. Example:
Lead (II) iodide consists of Pb2+ ions (cation) and I- ions (anion).
• Insoluble salts are prepared through precipitation reaction where two different
aqueous solution containing ions of insoluble salt are mixed together.
Aqueous solution Aqueous solution Insoluble salt obtained
+ containing anions through filtration
containing cations
• Examples: Lead (II) sulphate
Pb (NO3) (aq) + Na2 SO4 (aq) → PbSO4 (s) + 2NaNO3 (aq)
• Calcium carbonate
Ca Cl2 (aq) + Na CO3 (aq) → CaCO3 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Penyediaan Garam Tak Larut
• Garam tak larut merupakan sebatian ionik yang mengandungi kation dan anion.
Contoh: Plumbum (II) iodida mengandungi ion Pb2+ (kation) dan ion I- (anion).
• Garam tak larut disediakan melalui tindak balas pemendakan di mana dua
larutan akueus berbeza yang mengandungi ion garam tak larut dicampur
bersama.
Larutan akues Garam tak larut
Larutan akues
+ mengandungi anion diperolehi melalui
mengandungi kation
penapisan
• Contoh: Plumbum (II) sulfat
Pb (NO3) (ak) + Na2 SO4 (ak) → PbSO4 (p) + 2NaNO3 (ak)
• Kalsium karbonat
Ca Cl2 (ak) + Na CO3 (ak) → CaCO3 (p) + 2NaCl (ak)
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Chemical And Ionic Equations
• Steps in writing an ionic equation from a chemical equation.
Example: The formation of precipitate of barium sulphate, BaSO4
• Step 1 : Write down the chemical equation
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (aq) + 2 NaCl (aq)
• Step 2 : Write down all the ions of reactants and products in aqueous state
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq) → BaSO4 (aq) + 2 NaCl (aq)
Ba2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + 2Na+(aq) +SO42 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2Na+(aq) + 2Cl- (aq)
-
• Step 3: Cancel the ions that do not take part in the reaction. The ionic
equation for the formation of barium sulphate, BaSO44:
Ba2+ (aq) + SO42 (aq) → BaSO4 (s)
-
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Persamaan Kimia Dan Ion
• Langkah-langkah dalam menulis persamaan ion daripada persamaan kimia.
Contoh: Pembentukan mendakan barium sulfat, BaSO4
• Langkah 1 : Tulis persamaan kimia
BaCl2 (ak) + Na2SO4 (ak) → BaSO4 (ak) + 2 NaCl (ak)
• Langkah 2 : Tulis semua ion bahan tindak balas dan hasil dalam keadaan akues.
BaCl2 (ak) + Na2SO4 (ak) → BaSO4 (ak) + 2 NaCl (ak)
Ba2+(ak) + 2Cl-(ak) + 2Na+(ak) + SO42 (ak) → BaSO4 (p) + 2Na+(ak) + 2Cl- (ak)
-
• Langkah 3: Potong ion yang tidak mengambil bahagian dalam tindak balas.
Persamaan ion bagi pembentukan barium sulfat, BaSO44:
Ba2+ (ak) + SO42 (ak) → BaSO4 (p)
-
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Constructing Ionic Equations Using The
Continuous Variation Method
The ionic equation for the formation of insoluble salt can be constructed through the
continuous variation method.
The methods in the continuous variation method:
• Determine mole ratio of cations A that reacts completely with anions B.
Example: x mol of cations A react completely with y mol of anions B.
• Determine empirical formula of the insoluble salt.
Example: x mol of cations A react completely with y mol of anions B to
form Ax By insoluble salt.
• Thus, the ionic equation is :
x (ion A) + y (ion B) Ax By
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Membina Persamaan Ion Menggunakan Kaedah
Perubahan Berterusan
Persamaan ion dalam pembentukan garam tak larut boleh dibina melalui kaedah
perubahan berterusan.
Kaedah dalam kaedah perubahan berterusan adalah:
• Tentukan nisbah mol kation A yang bertindak balas selengkapnya dengan
anion B.
Contoh: x mol kation A bertindak balas sepenuhnya dengan y mol anion B.
• Tentukan formula empirik bagi garam tak larut.
Contoh: x mol kation A bertindak balas sepenuhnya dengan y mol
anion B untuk membentuk garam tak larut Ax By.
• Oleh itu, persamaan ion adalah:
x (ion A) + y (ion B) Ax By
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Salts
Numerical Problems Involving Stoichiometric
Reactions In The Preparation Of Salts
In preparation of insoluble salt, 4.25 g of silver nitrate, AgNO 3 react with zinc chloride,
ZnCl2 to produce silver chloride. Calculate the mass of zinc chloride, ZnCl 2 used in
this reaction.
[Relative atomic mass: N, 14; O, 16; Cl, 3.5; Zn, 65; Ag, 108]
Solution
1. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
ZnCl2 (aq) + 2 AgNO3 (aq) 2 AgCl (s) + Zn(NO3)2 (aq)
2. Calculate the number of moles of AgNO3.
Number of moles of AgNO3 = 4.25 0.025mol
170
3. Compare the mole ratio of ZnCl2 and AgNO3.
1 mol ZnCl2 react with 2 mol AgNO3
Therefore, number of moles of ZnCl2 = 0.025 mol 0.0125mol
2
4. Calculate the mass of ZnCl2
Mass of ZnCl2 = Number of moles x Relative atomic mass
= 0.0125 mol × 136
= 1.7 g
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Garam
Masalah Kuantitatif Melibatkan Tindak Balas
Stoikiometri Dalam Penyediaan Garam
Dalam penyediaan garam tak larut, 4.25 g argentum nitrat, AgNO 3 bertindak balas
dengan zink klorida ZnCl2, untuk menghasilkan argentum klorida. Hitung jisim zink
klorida, ZnCl2 menggunakan tindak balas ini.
[Jisim Atom Relatif : N, 14; O, 16; Cl, 3.5; Zn, 65; Ag, 108]
Penyelesaian
1. Tulis persamaan kimia yang seimbang untuk tindak balas tersebut.
ZnCl2 (ak) + 2 AgNO3 (ak) 2 AgCl (p) + Zn(NO3)2 (ak)
2. Hitung bilangan mol AgNO3.
Bilangan mol AgNO3 = 4.25 0.025mol
170
3. Bandingkan nisbah mol ZnCl2 dan AgNO3.
1 mol ZnCl2 bertindak balas dengan 2 mol AgNO3
Oleh itu, bilangan mol ZnCl2 = 0.025 mol 0.0125mol
2
4. Hitung jisim ZnCl2.
Jisim ZnCl2 = Bilangan mol x Jisim atom relatif
= 0.0125 mol × 136
= 1.7 g
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
8.2 Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Qualitative
QualitativeAnalysis
AnalysisOf
Of
Salts
Salts
Is used to determine the Steps to be taken in
substances present in a identifying anions and
compound. cations present in salts
are:
Observation
Confirmatory
on the Test for
Action of heat test for
physical cations and
on salts cations and
properties of anions
anions
salts
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Analisis
AnalisisKualitatif
Kualitatif
Garam
Garam
Langkah yang perlu
Digunakan untuk
diambil dalam mengenal
menentukan identiti
pasti anion dan kation
sesuatu bahan dalam
dalam suatu garam
sebatian.
adalah:
Ujian
Pemerhatian Tindakan Ujian bagi
pengesahan
ke atas sifat haba ke atas kation dan
bagi anion
fizik garam garam anion
dan kation
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Observations On The Physical Properties Of Salts
The physical properties of salts that need to be observed are:
• Physical state • Colour • Solubility in water
Colour of solid and solution of salts:
Colour
Cations / anions / salt
Solid Aqueous solution
Salts of Ca2+, Mg2+, Al3+,Pb2+ White Colourless
Yellow when hot
ZnO Insoluble
White when cooled
Copper (II) salts,
• CuCO3, •Green • Insoluble
•Blue • Blue
• CuSO4, Cu (NO3)2 •Black • Insoluble
• CuO
Ferum (II) salts,
FeSO4, Fe (NO3)2, FeCl2 Green Green
Ferum (III) salts, Yellow/ brownish-yellow/
Fe2 (SO4)3, Fe (NO3)3, FeCl3
Brown
Brown
Brown when hot
PbO Insoluble
Yellow when cooled
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Pemerhatian Ke Atas Sifat Fizik Garam
Sifat fizikal garam yang perlu diperhatikan adalah:
• Keadaan fizik • Warna • Keterlarutan dalam air
Warna Pepejal Dan Larutan Garam:
Warna
Kation / anion / garam
Pepejal Larutan akues
Garam bagi Ca2+, Mg2+,
Putih Tidak berwarna
Al3+,Pb2+
Kuning apabila panas
ZnO Tak larut
Putih apabila sejuk
Garam kuprum (II),
• CuCO3, •Hijau • Tak larut
•Biru • Biru
• CuSO4, Cu (NO3)2 •Hitam • Tak larut
• CuO
Garam ferum (II),
FeSO4, Fe (NO3)2, FeCl2
Hijau Hijau
Garam ferum (III), Kuning/ Kuning
Fe2 (SO4)3, Fe (NO3)3, FeCl3
Perang
keperangan/ Perang
Perang apabila panas,
PbO Tak larut
kuning apabila sejuk
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Test For Gases
• Salts may produce certain gases in reactions carried out during laboratory
test on salts.
• The gas evolved may be identified by:
• Observation of the colour
• Test with moist blue and red litmus paper
• Test with lime water
• Test with a glowing wooden splinter
• Test with KMnO4 solution
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Ujian Gas
• Garam mungkin menghasilkan gas tertentu dalam tindak balas yang
dijalankan ke atas garam sewaktu ujikaji di dalam makmal.
• Gas yang dibebaskan mungkin boleh dikenali dengan:
• Memerhatikan warnanya
• Diuji menggunakan kertas litmus biru lembap dan kertas litmus
merah lembap
• Diuji dengan air kapur
• Diuji menggunakan kayu uji berbara
• Diuji dengan larutan KMnO4
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Inference On The Type Of Salt Based On The Gas
Gas released Salt
O2 KNO3 and NaNO3
All carbonate salts except K2CO3 and
CO2
Na2CO3
All nitrate salts except KNO3 and
NO2 and O2
NaNO3
NH3 Ammonium salt
SO2 Several SO42- salts
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Inferens Ke Atas Jenis Garam Berdasarkan Gas Yang Dibebaskan
Gas yang terbebas Garam
O2 KNO3 dan NaNO3
Semua garam karbonat kecuali
CO2
K2CO3 dan Na2CO3
Semua garam nitrat kecuali KNO3
NO2 dan O2
dan NaNO3
NH3 Garam ammonium
SO2 Beberapa garam SO42-
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Action Of Heat On Salts
Salts will decompose when heated. It may result in a colour change or
evolution of gas or water vapour.
Effect
Effectof
ofheat
heaton
onsalts
salts
Carbonate salts Nitrate salts
Decompose when heated
Decompose when heated to and release O2 gas.
release CO2 gas. Except However, group 1 nitrate,
Na2CO3 and K2CO3 NO3- salts only form NO2- salt
and O2.
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Tindakan Haba Ke Atas Garam
Garam akan terurai apabila dipanaskan. Ini menyebabkan garam
mengalami perubahan warna, perwapan air dan perubahan gas.
Tindakan
TindakanHaba
HabaKe
KeAtas
AtasGaram
Garam
Garam karbonat Garam nitrat
Terurai apabila dipanaskan
dan membebaskan gas O2.
Terurai apabila dipanaskan
untuk membebaskan gas
Walaubagaimanapun, untuk
CO2. Kecuali Na2CO3 dan
kumpulan 1 nitrat, garam
K2CO3. NO3- hanya membentuk
garam NO2- dan O2.
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Test For Anions
Carbonate ions, CO32, chloride ions, Cl-, sulphate ions, SO 42 and nitrate ions, NO 3
- -
are tested in qualitative analysis through various chemical test.
Anion Carbonate ion, Chloride ion, Sulphate ion, Nitrate ion,
Test CO 2-
Cl- SO 2- NO 3
3 4
Effervescence.
Dilute hydrochloric Gas released
No change No change No change
acid turns lime water
cloudy
Dilute hydrochloric
acid + Barium No precipitate No precipitate White precipitate No precipitate
chloride solution
Dilute nitric acid +
No precipitate White precipitate No precipitate No precipitate
silver nitrate solution
Dilute sulphuric acid +
Iron (II) sulphate
solution + No change No change No change Brown ring
concentrated
sulphuric acid
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Ujian Bagi Anion
Ion karbonat, CO32 , ion klorida, Cl-, ion sulfat, SO42 , dan ion nitrat, NO 3 ,diuji dalam
- -
analisis kualitatif melalui pelbagai ujian kimia.
Anion Ion karbonat, Ion klorida, Ion sulfat, Ion nitrat,
Ujian CO 2-
Cl- SO 2-
NO 3
3 4
Pembuakan. Gas
yang terbebas
Asid hidroklorik cair Tiada perubahan Tiada perubahan Tiada perubahan
menjadikan air
kapur keruh
Asid hidroklorik cair
+ larutan barium Tiada mendakan Tiada mendakan Mendakan putih Tiada mendakan
klorida
Asid nitrik cair +
larutan argentum Tiada mendakan Mendakan putih Tiada mendakan Tiada mendakan
nitrat
Asid sulfurik cair +
larutan ferum (II) Gelang perang
Tiada perubahan Tiada perubahan Tiada perubahan
sulfat + asid sulfurik terbentuk
pekat
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Test
TestFor
ForCations-
Cations-Sodium
SodiumHydroxide
HydroxideSolution
Solution
Aqueous cation solution
+
Sodium hydroxide solution in excess
NH4+ Zn2+ / Al3+ /
Mg2+ / Ca2+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+
Pb2+
White White Blue Green Brown
precipitate precipitate precipitate precipitate precipitate
No
insoluble in soluble in insoluble in insoluble in insoluble in
precipitate
NaOH NaOH NaOH NaOH NaOH
solution solution solution solution solution
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Ujian
UjianBagi
BagiKation-
Kation-Larutan
LarutanNatrium
NatriumHidroksida
Hidroksida
Larutan akues kation +
Lebihan larutan natrium hidroksida
NH4+ Zn2+ / Al3+ /
Mg2+ / Ca2+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+
Pb2+
Mendakan Mendakan Mendakan Mendakan Mendakan
putih tidak putih larut biru tidak hijau tidak perang tidak
Tiada
larut dalam dalam larut dalam larut dalam larut dalam
mendakan
larutan larutan larutan larutan larutan
NaOH NaOH NaOH NaOH NaOH
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Test
TestFor
ForCations-
Cations-Ammonia
AmmoniaSolution
Solution
Aqueous cation solution
+
Ammonia solution
NH4+ / Ca2+ Mg2+ /Al3+ /
Zn2+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+
Pb2+
Blue
precipitate
White White Green Brown
soluble in
precipitate precipitate precipitate precipitate
ammonia
No reaction insoluble in soluble in insoluble in insoluble in
solution to
ammonia ammonia ammonia ammonia
form a dark-
solution solution solution solution
blue
solution
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Ujian
UjianBagi
BagiKation-
Kation-Larutan
LarutanAmmonia
Ammonia
Larutan Akueus Kation
+
Larutan Ammonia
NH4+ / Ca2+ Mg2+ /Al3+ /
Zn2+ Cu2+ Fe2+ Fe3+
Pb2+
Mendakan
biru larut
Mendakan Mendakan Mendakan Mendakan
dalam
putih tidak putih larut hijau tidak perang tidak
Tiada tindak larutan
larut dalam dalam larut dalam larut dalam
balas ammonia
larutan larutan larutan larutan
membentuk
ammonia ammonia ammonia ammonia
larutan biru
gelap
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
Topic 8 Salts
Qualitative Analysis Of Salts
Confirmatory
ConfirmatoryTest
Test For
ForFe
Fe
2+
,Fe
2+
,Fe
3+
,Pb
3+
,Pb 2+and
2+
and
NH 4 ions
ions
Pb2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ NH 4
Add Add
acidified Add
Confirmatory test potassium
potassium potassium
iodide Add Nessler
manganate, thiocyanate,
solution and reagent
KMn04 KSCN
heat the
solution
solution solution
Yellow
Observation precipitate
formed. The Purple
Blood red Brown
precipitate colour
solution is precipitate
dissolves in solution is
formed is formed
the solution bleached
when
heated
ITeach – Chemistry Form 4
Topik 8 Garam
Analisis Kualitatif Garam
Ujian
UjianPengesahan
PengesahanBagi
BagiIon
IonFeFe2+,Fe
2+
,Fe3+,Pb
3+ 2+
,Pb2+
dan
danIon
Ion NH 4
Pb2+ Fe2+ Fe2+ NH 4
Tambah Tambah
larutan Tambah
Ujian pengesahan larutan
kalium larutan Tambah
kalium
manganat, kalium reagen
iodida dan
KMn04 tiosianat, Nessler
panaskan
KSCN
larutan berasid
Mendakan
Pemerhatian kuning
terbentuk.
Larutan
Mendakan Warna ungu Mendakan
merah
terlarut larutan perang
darah
dalam dilunturkan terbentuk
terbentuk
larutan
apabila
dipanaskan
ITeach – Kimia Tingkatan 4
The End
i - Teach
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Preparation Of Soluble And Insoluble SaltsDokument34 SeitenPreparation Of Soluble And Insoluble Saltscar_yii100% (1)
- Types of Carbon CompoundsDokument306 SeitenTypes of Carbon CompoundsJerry Sumok WalterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clays and Clay Minerals: Proceedings of the Fourteenth National Conference, Berkeley, CaliforniaVon EverandClays and Clay Minerals: Proceedings of the Fourteenth National Conference, Berkeley, CaliforniaS. W. BaileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufactured Substances in Industry2Dokument20 SeitenManufactured Substances in Industry2Sam ZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Chemistry of Zirconium and Hafnium: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryVon EverandAnalytical Chemistry of Zirconium and Hafnium: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021Dokument41 SeitenTopic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021HotTornado XDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparative Methods in Solid State ChemistryVon EverandPreparative Methods in Solid State ChemistryPaul HagenmullerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrolysisDokument31 SeitenElectrolysisteddaboyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufactured Substances in IndustryDokument16 SeitenManufactured Substances in IndustryAhda Sabila Yusuf100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Dokument23 SeitenChemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Ng Wan LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacture D Substances in IndustryDokument53 SeitenManufacture D Substances in IndustrySuriana ShamsuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsDokument9 SeitenTetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsXue Yi LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionDokument16 SeitenChapter 6b Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionKavitha ThayagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18Dokument126 SeitenChemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18nalla casuga100% (1)
- Patterns in Period 3 ElementsDokument18 SeitenPatterns in Period 3 ElementsDania Dobbs100% (2)
- Natural Rubber Properties and UsesDokument15 SeitenNatural Rubber Properties and UsesHazilah AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-Reactivity of Metals and Displacement ReactionsDokument3 Seiten10-Reactivity of Metals and Displacement ReactionsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valency TableDokument2 SeitenValency TableashokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Chapter 8Dokument60 SeitenForm 4 Chapter 8Rabbi 08Noch keine Bewertungen
- P BlockDokument52 SeitenP BlockYogendra GangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedDokument21 SeitenOxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedKaroline UhlemannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisDokument30 SeitenAcid Base and Salts - Part 6-Qualitative AnalysisKronix GamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1.3 Exercise 1 - Water of CrystallisationDokument1 Seite1.1.3 Exercise 1 - Water of CrystallisationFakhar LateefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project 2016Dokument20 SeitenChemistry Project 2016Divya KumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Air & Atmosphere Syllabus NotesDokument4 SeitenChemistry Air & Atmosphere Syllabus NotesDavid Sutanto100% (6)
- Elements in Period 3Dokument13 SeitenElements in Period 3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongDokument73 SeitenManufactured Subtances in Industry: By: Nurfarahain Binti Ahmad 4ST SMK SG AbongSanthiya MadhavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal DisplacementDokument27 SeitenMetal DisplacementAnas MariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Half Equations Worksheet ClassDokument1 SeiteWriting Half Equations Worksheet ClassJasmine YenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peculiar Behaviour of CarbonDokument7 SeitenPeculiar Behaviour of Carbonhussail sarmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- HalogenDokument37 SeitenHalogenPutri Dierla Dela100% (1)
- Exercise With AnsDokument22 SeitenExercise With Ansd anjilappa100% (1)
- Tetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsDokument9 SeitenTetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsXue Yi LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CeramicsDokument39 SeitenCeramicsraja keshavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of ReactionDokument20 SeitenRate of ReactionQueen BlehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qualitative Analysis Notes: Cedar College Salt Analysis Theory 1Dokument19 SeitenQualitative Analysis Notes: Cedar College Salt Analysis Theory 1Daniyal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ProcessDokument60 SeitenChemical ProcessThung LingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives NewDokument18 SeitenCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Newxinying94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Polymerisation MethodDokument56 SeitenChapter Polymerisation MethodwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals: Sci 401 Lecture 8Dokument54 SeitenMetals: Sci 401 Lecture 8Niña Viaña BinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids, Bases & Salts 1 QP PDFDokument9 SeitenAcids, Bases & Salts 1 QP PDFSatria HalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of MetalsDokument17 SeitenProperties of MetalsDavies MasumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Metall RgyDokument136 SeitenChemistry: Metall Rgymukesh kannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Group II Lecture Notes (Student) .UnlockedDokument20 Seiten2013 Group II Lecture Notes (Student) .UnlockedKwok Yee TherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metals and Their Properties - Physical and ChemicalDokument5 SeitenMetals and Their Properties - Physical and Chemicalcourtz911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Family TKCHDokument21 SeitenCarbon Family TKCHPrasanna NadkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About SaltsDokument32 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About SaltsSabriza Hassan Assa'ariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Fajan's RuleDokument13 Seiten3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework Reacting Masses (42 MarksDokument4 SeitenHomework Reacting Masses (42 MarksloloNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Solubility RulesDokument1 SeiteThe Solubility RuleslvicencioaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Chemical CompoundsDokument7 SeitenEbook Chemical CompoundsRahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Block2012 457Dokument143 SeitenP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- Nitrogen and Its CompoundsDokument13 SeitenNitrogen and Its Compoundsapi-3734333100% (2)
- Group IV Trends - Carbon To LeadDokument76 SeitenGroup IV Trends - Carbon To LeadRhondene WintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Dokument67 SeitenChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDokument24 SeitenChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundTiviya Tarini ManiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Chapter 8 SaltsDokument32 SeitenChemistry Chapter 8 SaltsnorlieyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic Carbonyls and NitrilesDokument40 SeitenMetallic Carbonyls and NitrilesSandipan Saha100% (1)
- 02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4Dokument20 Seiten02 - Modul A + Kimia Tg4ONG TEIK MING -100% (1)
- Double and Triple Bond (Covalent Bond) No.27Dokument3 SeitenDouble and Triple Bond (Covalent Bond) No.27ONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Science - An OverviewDokument20 SeitenIntroducing Science - An OverviewwshopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 The Structure of The Atom: 2.1 MatterDokument59 SeitenTopic 2 The Structure of The Atom: 2.1 MatterONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Book of Natural DisastersDokument10 SeitenBook of Natural DisastersONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 SetsDokument30 SeitenChapter 3 SetsONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1-Memahami Pembentukan Sebatian (English)Dokument4 Seiten5.1-Memahami Pembentukan Sebatian (English)ONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- GROW Ver4.3Dokument225 SeitenGROW Ver4.3ONG TEIK MING -Noch keine Bewertungen
- A-Bromination Using HBR H2O2 APKDokument7 SeitenA-Bromination Using HBR H2O2 APKAshutosh BhaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- KetonesDokument3 SeitenKetonespixiedustNoch keine Bewertungen
- XUEWU, Et Al., 1996 - Rheological Models For Xanthan GumDokument7 SeitenXUEWU, Et Al., 1996 - Rheological Models For Xanthan GumJorge Alberto CardosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- All-in-One: PrakashanDokument22 SeitenAll-in-One: PrakashanGamerNeverDiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM1031 Course OutlineDokument16 SeitenCHEM1031 Course OutlineTravolta TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Concentration Units: Chemistry (2 Semester) - SY 2019 - 2020Dokument9 SeitenI. Concentration Units: Chemistry (2 Semester) - SY 2019 - 2020Jay Vee Manuel PatengaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Chemical Analysis of Shea Butter Tree Butyrospermum Parkii Latex PDFDokument9 SeitenPreliminary Chemical Analysis of Shea Butter Tree Butyrospermum Parkii Latex PDFAdufe RufaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1021@acsreagents 4191Dokument2 Seiten10 1021@acsreagents 4191Hans TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF HEXANE, ACETONE, ETHANOL AND WATER EXTRACT FROM BAY LEAVES (Syzygium Polyanthum (WIGHT) WALP.)Dokument12 SeitenQUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF HEXANE, ACETONE, ETHANOL AND WATER EXTRACT FROM BAY LEAVES (Syzygium Polyanthum (WIGHT) WALP.)Harrizul RivaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solubility Equil2014 PDFDokument5 SeitenSolubility Equil2014 PDFKhaled AbeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EVA Copolymer SDSDokument8 SeitenEVA Copolymer SDSlobocernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extrusion-Spheronization ManufactureDokument6 SeitenExtrusion-Spheronization ManufactureJosé RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDokument6 Seiten2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO Drug Information Vol 35, No. 1, 2021 Highlights WHO Certification Scheme UpdateDokument273 SeitenWHO Drug Information Vol 35, No. 1, 2021 Highlights WHO Certification Scheme UpdateKulfi BarfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checal ReviewerDokument8 SeitenChecal ReviewerChristian Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pure Substances and MixturesDokument19 SeitenPure Substances and MixturesBrennan ColdwellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report ExtractionDokument7 SeitenLab Report Extractionhellothere50% (4)
- Exp 5 - Isolation of Casein and Lactose From MilkDokument7 SeitenExp 5 - Isolation of Casein and Lactose From MilkDenise R. Samonte100% (2)
- Leather Industry's Environmental ImpactDokument21 SeitenLeather Industry's Environmental ImpactAnup Agarwal100% (5)
- Direct Hydration of Propylene in Liquid Phase and Under Supercritical Conditions in The Presence of Solid Acid CatalystsDokument6 SeitenDirect Hydration of Propylene in Liquid Phase and Under Supercritical Conditions in The Presence of Solid Acid Catalystsssargo100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Solubility CurvesDokument10 SeitenLesson 3 - Solubility CurvesDannBjornNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darkening Hydraulic FluidDokument6 SeitenDarkening Hydraulic FluidKelly RobertsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vogel, Arthur - Qualitative INORGANIC Analysis - (5th Ed - 1979) PDFDokument617 SeitenVogel, Arthur - Qualitative INORGANIC Analysis - (5th Ed - 1979) PDFmanix_23100% (4)
- UnfinishedDokument8 SeitenUnfinishedDaniel TorralbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SolubilityworksheetDokument4 SeitenSolubilityworksheetScorpio AvengerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity On MolarityDokument3 SeitenActivity On MolarityMIRIAM TAMBANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatographic Separation and Spectro-Analytical Characterization of A Natural African Mineral DyeDokument12 SeitenChromatographic Separation and Spectro-Analytical Characterization of A Natural African Mineral DyeyaredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tank CleaningDokument19 SeitenTank CleaningWiwatthana Kumpim100% (4)
- Phytochemical Testing On Red GingerDokument48 SeitenPhytochemical Testing On Red GingerIrvandar NurviandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reineveld CentrifugeDokument12 SeitenReineveld CentrifugeI. Murali KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen