Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1-A Classification and Types of Plumbing Materials and Pipes
Hochgeladen von
manny daleon0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten44 SeitenClassification and types of plumbing materials and pipes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenClassification and types of plumbing materials and pipes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
90 Ansichten44 Seiten1-A Classification and Types of Plumbing Materials and Pipes
Hochgeladen von
manny daleonClassification and types of plumbing materials and pipes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 44
Classification and types of
plumbing materials and pipes
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon
Trainer
CORE I-LO1
CLASSIFICATION OF STEEL PIPES
Black welded steel pipes and hot-dipped
Galvanized-welded pipes are classified as
follows:
Light-gauge(LG)
Heavy Gauge(HG)
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 2
• Required markings as per PNS 26:2003: Each pipe
should be properly marked by rolling, stamping
or stenciling, showing the following:
• Trademark of manufacturer
• Class of pipe(light gauge or heavy gauge)
• Length, m
• Nominal diameter, mm
• Product of the Philippines/PS Mark
• Country of origin/ICC Mark
• Other requirements pursuant to RA 7394 or the
Consumer Act of the Philippines
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 3
Note:
• All local and imported BI-GI steel pipes
whether with ASTM or any other international
standard markings are still required to comply
with Philippine Laws on Product Standards.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 4
APPLICATIONS:
PNS 26:2003 applies to steel pipes intended
for ordinary applications such as steam,
water, gas and air lines:
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 5
APPLICATIONS:
PNS 26:2003 applies to steel pipes intended
for ordinary applications such as steam,
water, gas and air lines:
Steam lines Centralized heating system in restaurants,
hotels, resorts, etc.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 6
APPLICATIONS:
PNS 26:2003 applies to steel pipes intended
for ordinary applications such as steam,
water, gas and air lines:
Steam lines Centralized heating system in restaurants,
hotels, resorts, etc.
Water lines Distribution lines such as water utilities,
irrigation, fire alarm sprinkler system
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 7
APPLICATIONS:
PNS 26:2003 applies to steel pipes intended
for ordinary applications such as steam,
water, gas and air lines:
Steam lines Centralized heating system in restaurants,
hotels, resorts, etc.
Water lines Distribution lines such as water utilities,
irrigation, fire alarm sprinkler system
Gas lines Centralized LPG system for hotels and malls,
petroleum and oil refineries
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 8
APPLICATIONS:
PNS 26:2003 applies to steel pipes intended
for ordinary applications such as steam,
water, gas and air lines:
Steam lines Centralized heating system in restaurants,
hotels, resorts, etc.
Water lines Distribution lines such as water utilities,
irrigation, fire alarm sprinkler system
Gas lines Centralized LPG system for hotels and malls,
petroleum and oil refineries
Air lines Compressed air supply for assembly plants and
factoriesPrepared
among others
by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 9
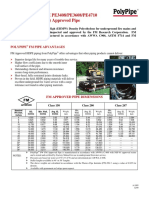
THICKNESS TOLERANCE TABLE FOR
PNS 26:2003:
LIGHT GAUGE PIPES (LG)
Nominal Size(DN) Outside Wall thickness Mass per unit length Plain
mm diameter mm end(kilogram per meter)
mm
1/2 15 21.3 2.0 1.8 0.947 0.852
¾ 20 26.7 2.3 2.07 1.38 1.242
1 25 33.4 2.6 2.34 1.98 1.782
1¼ 32 42.2 2.6 2.34 2.54 2.286
1½ 40 48.3 2.9 2.61 3.23 2.907
2 50 60.3 2.9 2.61 4.08 3.672
2½ 65 73.0 3.2 2.88 5.71 5.139
3 80 88.9 3.2 2.88 6.72 6.048
4 100 114.3 3.6 3.24 9.75 8.775
5 125 141.3 5.0 4.5 16.806 15.125
6 150 168.3 5.0 4.5 20.135 18.122
8 200 219.1 5.8 5.22 30.508 27.457
10 250 273.0 6.6 5.94 43.358 39.022
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 10
12 300 323.8 6.9 6.21 53.922 48.530
+/- 10% wall thickness tolerance
+/- 10% Mass/Weight tolerance
• For Hot-dipped Galvanized steel pipes, the
zinc coating should be 550g/m² or 78 microns
thickness.
• Note: For LG, color guide is RED.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 11
HEAVY GAUGE PIPES (HG)
Nominal Outside diameter Wall thickness Mass per unit length Plain
Size(DN) mm mm end(kilogram per meter)
mm
15 21.3 2.8 2.52 1.277 1.149
20 26.7 2.9 2.61 1.702 1.532
25 33.4 3.4 3.06 2.515 2.264
32 42.2 3.6 3.24 3.427 3.084
40 48.3 3.7 3.33 4.069 3.662
50 60.3 4.0 3.6 5.553 4.998
65 73.0 5.2 4.68 8.694 7.825
80 88.9 5.5 4.95 11.312 10.180
100 114.3 6.0 5.4 16.024 14.426
125 141.3 6.6 5.94 21.923 19.731
150 168.3 7.1 6.39 28.224 25.402
200 219.1 8.2 7.38 42.647 38.382
250 273.0 9.3 8.37 60.476 54.428
300 323.8 10.3 9.27 79.628 71.665
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 12
+/- 10% wall thickness tolerance
+/- 10% Mass/Weight tolerance
For Hot-dipped Galvanized steel pipes, the zinc
coating should be 550g/m² or 78 microns
thickness.
Note: For HG, color guide is either BLUE or
GREEN
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 13
RISKS OF USING UNCERTIFIED/SUB-
STANDARD STEEL PIPE PRODUCTS:
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 14
RISKS OF USING UNCERTIFIED/SUB-
STANDARD STEEL PIPE PRODUCTS:
Steam May cause
Lines bursting/explosion which
may lead to destruction of
properties and injuries or
even death to people
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 15
RISKS OF USING UNCERTIFIED/SUB-
STANDARD STEEL PIPE PRODUCTS:
Steam Lines May cause bursting/explosion which may lead to destruction of
properties and injuries or even death to people
Water May cause inconvenience for reworks during
Lines leakage;
May cause abnormal water consumption due
to leaks;
Fire alarm sprinkler system may function
abnormally, hence, in case of fire, may lead to
complete destruction of properties or even
death to people.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 16
RISKS OF USING UNCERTIFIED/SUB-
STANDARD STEEL PIPE PRODUCTS:
Steam Lines May cause bursting/explosion which may lead to destruction of
properties and injuries or even death to people
Water Lines May cause inconvenience for reworks during leakage;
May cause abnormal water consumption due to leaks;
Fire alarm sprinkler system may function abnormally, hence, in
case of fire, may lead to complete destruction of properties or
even death to people.
Gas May cause bursting/explosion
Lines
which may lead to destruction of
properties and injuries or even
death to people
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 17
Steam May cause bursting/explosion which may lead to destruction of
Lines properties and injuries or even death to people
Water May cause inconvenience for reworks during leakage;
Lines May cause abnormal water consumption due to leaks;
Fire alarm sprinkler system may function abnormally,
hence, in case of fire, may lead to complete destruction of
properties or even death to people.
Gas Lines May cause bursting/explosion which may lead to
destruction of properties and injuries or even death to
people
Air Lines This may entail excessive additional costs to generate
compressed air as the compressor will take a long time
running to fill up the pressure tank or worst, pipe will burst
or explode and therefore may lead to injuries or even
death to people.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 18
Reference:
• Phil. Assn. of Black Iron & Galvanized Iron
Pipes & Tubes Manufacturers, INC.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 19
KINDS OF PIPE
Ductile iron
Plastic (HDPE/PVC)
Concrete
20
Steel
Residential (copper or plastic)
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer
Types of Plastic Pipes
• The plumbing industry primarily uses six types
of plastic pipes, each of which has a different
application and installation requirement.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 21
ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene
styrene) Pipes:
Made from the thermoplastic resin, ABS is the
standard materials for many types of DWV
systems. Some of its features are as follows:
• As ABS is light, it is easy to handle and install.
• It is highly resistant to household chemicals. In
tests, it showed no effect from common products
such as detergent, bleach, and household drain
cleaners.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 22
ABS (Acrylonitrile butadiene
styrene) Pipes:
• Sewage treatment plants use ABS because it
stands up to the highly corrosive and abrasive
liquid commonly found in such systems.
• ABS is strong and long lasting.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 23
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) Pipes:
• A rigid pipe with high impact strength, PVC is
manufactured from thermoplastic materials.
This material has an indefinite lifespan under
most conditions.
Plumbers frequently use PVC in cold water
systems. PVC is interchangeable with ABS pipe
for DWV system.
It is also used to transport many chemicals
because of its chemical resistant properties.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 24
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) Pipes:
• Note:
Solid core PVC pipes can be used in high
pressure systems, but only to carry low
temperature water.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 25
CPVC (Chlorinated polyvinyl
chloride) Pipes:
• CPVC pipes and fittings are made from an
engineered vinyl polymer. Plumbers use CPVC
in hot and cold water distribution systems.
CPVC is acceptable for indoor use.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 26
CPVC (Chlorinated polyvinyl
chloride) Pipes:
• Some of the features of CPVC include the
following:
• Its molecular structure practically eliminates
condensation in the summer and heat loss in
the winter.
• It is lightweight and easy to install.
• Its strength is a clear advantage for
plumbers working in cold weather.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 27
PE (Polyethylene) Pipes:
• PE is a thermosetting plastic. Plumbers
commonly use PE for tubing because of its
strength, flexibility, and chemical resistant
properties.
PE is also corrosion-resistant which makes it
ideal for transporting chemical compounds.
Furthermore, PE does not deteriorate when
exposed to sunlight
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 28
PEX (Cross-linked polyethylene)
Pipes:
• PEX tubing is formed when high density
polyethylene is subjected to heat and high
pressure.
Plumbers commonly use PEX for manifold
plumbing distribution systems because of its
flexibility.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 29
PB (Polyebutylene) Pipes:
• PB is a thermoplastic pipe that plumbers used
extensively for water supply piping from the
late-1970s to the mid-1990s. In many cases,
the PB piping has become weak and failed
without warning.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 30
PPR
• "polypropylene random”
• PPR - Presently PP-R pipes & fittings are most
reliable in plumbing and water supply plants,
due to their chemical features and fusion
welding, which ensures the plumbing to have
a perfect seal tight system. It can be used both
as a cold water pipe or a hot water pipe.
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 31
PPR
• PPR is joined by heating both the socket and
the pipe. When melted, both parts are joined
together to become one. Here is a fusion
welder:
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 32
FUSION WELDER
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 33
PPR
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 34
PPR
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 35
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 36
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 37
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 38
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 39
PIPE STRENGTH
Different pipes have different sizes and thicknesses
Must use correct pipe to handle trench depth,
bedding type, and live loads
Must place pipe below the frost line to prevent
freezing/breakage
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 40
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 41
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 42
JOINTS
Compression
Mechanical
Flanged
Solvent
Soldered
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 43
Prepared by: Manny P. Daleon-Trainer 44
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- TUBOS PEAD PipelineDokument2 SeitenTUBOS PEAD PipelineLuís Felipe Coimbra MinelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Pipe Properties and ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenHDPE Pipe Properties and ApplicationsCarlos KraljevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Submetal (2) HdpeDokument5 SeitenSubmetal (2) HdpeEmilAbdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Pipe Dimensions and WeightsDokument16 SeitenHDPE Pipe Dimensions and WeightsAhmed HussienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hdpe Pipe ChartDokument1 SeiteHdpe Pipe ChartBENJAMIN UNALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Seamless Pipe ASTM A106Dokument3 SeitenMS Seamless Pipe ASTM A106imtz20130% (1)
- SprinklerBrochures Schedule10 40Dokument4 SeitenSprinklerBrochures Schedule10 40Keshia Murillo PinnockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheatland ASTM A 53 Schedule 40 Pipe SpecsDokument1 SeiteWheatland ASTM A 53 Schedule 40 Pipe SpecsKelvin RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE 4710 FM Pipe SpecificationDokument2 SeitenHDPE 4710 FM Pipe SpecificationJulio CongonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proteccion Conta Incendios Hdpe - KWH PipeDokument8 SeitenProteccion Conta Incendios Hdpe - KWH PipeYHASMANI SOTELO GARCIANoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Pipe Catalogue PDFDokument12 SeitenHDPE Pipe Catalogue PDFRadicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Heat Trace Self Regulating Heater Cables For Fire Sprinkler Systems en 1527968Dokument12 SeitenNelson Heat Trace Self Regulating Heater Cables For Fire Sprinkler Systems en 1527968abdulafoajjawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-Purlin Data Sheet 3-3-2014Dokument3 SeitenC-Purlin Data Sheet 3-3-2014Akhil VNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mueller PDFDokument16 SeitenMueller PDFMechanical EngineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- p7326 SPDokument2 Seitenp7326 SPchazz29hkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hdpe Spec Sheet Pe4710Dokument5 SeitenHdpe Spec Sheet Pe4710thanguctNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burnham Heating Helper Table of ContentsDokument113 SeitenBurnham Heating Helper Table of ContentsMoose McCabe100% (3)
- Fire Sprinkler Pipe BrochureDokument8 SeitenFire Sprinkler Pipe BrochureINGENIERIA8 FYSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enate50std518-Natural Standard Biozinalium PipesDokument2 SeitenEnate50std518-Natural Standard Biozinalium PipesAngelo AgostiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 5L Line Pipe ODDokument2 SeitenAPI 5L Line Pipe ODZainudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jfebear BrochureDokument12 SeitenJfebear BrochurebabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe CatalogueDokument6 SeitenPipe CatalogueirfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Steel Tension Cable & Tension RodDokument32 SeitenCarbon Steel Tension Cable & Tension RodrasheedgotzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnakabel NusantaraDokument13 SeitenMagnakabel Nusantaratees220510Noch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue Wire StrandDokument18 SeitenCatalogue Wire StrandbronsenwijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 150 Flange Dimensions & SpecsDokument3 Seiten150 Flange Dimensions & SpecsNikhil PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateDokument1 SeiteDesign Calculation Sheet: Roof Drain Vertical Leader Requirements For Horizontal Roof Areas at Various Rainfall RateAhmed Handy 911Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Mepf Design For A Mix-Use BLDGDokument91 SeitenBasic Mepf Design For A Mix-Use BLDGKristopher San JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valvula Supervisada Ranurada GD47658NFPDokument1 SeiteValvula Supervisada Ranurada GD47658NFPOscar Fernandez SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bondstrand 2400 SeriesDokument20 SeitenBondstrand 2400 SeriesTommytoo BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brosura VarifixDokument52 SeitenBrosura VarifixDan LimburgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precision Plumbing Price List 12.01.2024Dokument36 SeitenPrecision Plumbing Price List 12.01.2024Anilkumar KolpuruNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.16 MV Bahra Cables CatalogDokument2 Seiten4.16 MV Bahra Cables CatalogAssystem AxisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Spec Sheet 3608 PDFDokument5 SeitenHDPE Spec Sheet 3608 PDFfrnandoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Technical ManualDokument32 SeitenWastewater Technical ManualagonzalezcordovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Di Installation GuideDokument37 SeitenDi Installation GuidehaivikramreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Henry - 022 Safety ValvesDokument3 SeitenHenry - 022 Safety ValvesPaweł HejmowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arcelormittal Tubular Products Iasi Product Portfolio European StandardsDokument9 SeitenArcelormittal Tubular Products Iasi Product Portfolio European StandardspendulaionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sch40 80 ASTM A53 - Brochure - 042512 PDFDokument2 SeitenSch40 80 ASTM A53 - Brochure - 042512 PDFMohamed AmmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- GVK Heat ShrinkDokument4 SeitenGVK Heat ShrinkhzcbnlzwarkxojquuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSI Flange DimensnioDokument3 SeitenANSI Flange Dimensniohon choong chongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rigid PVC Pressure Piping SystemsDokument8 SeitenRigid PVC Pressure Piping Systemsarjun 11Noch keine Bewertungen
- CA Round Swirl DiffuserDokument3 SeitenCA Round Swirl DiffuserYapKJNoch keine Bewertungen
- RGU ENM 201 Wells Coursework-May2017 FinalDokument7 SeitenRGU ENM 201 Wells Coursework-May2017 FinalEmenike Donald EjiejiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acsr Tree Wire 15KV PDFDokument1 SeiteAcsr Tree Wire 15KV PDFbertovalenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Insulated PipesDokument32 SeitenPre Insulated Pipespal_stephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petrochem Catalogue 87Dokument1 SeitePetrochem Catalogue 87Oke DiliardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VALVULA CHECK DOBLE DISCO HakohavDokument1 SeiteVALVULA CHECK DOBLE DISCO HakohavDanny VenturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AEA-Pipe FitingDokument10 SeitenAEA-Pipe Fitingdechi MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0-Valvula - Unimizer 3 WaysDokument4 Seiten0-Valvula - Unimizer 3 WaysMuriloNoch keine Bewertungen
- CI2400 BS2400 Product DataDokument6 SeitenCI2400 BS2400 Product DataDaniel BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- N2XCY 1 X (1.5-800) MM 0.6/1 KVDokument5 SeitenN2XCY 1 X (1.5-800) MM 0.6/1 KVCombox BlackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation Cable BSDokument42 SeitenInstrumentation Cable BSShivaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strongwell Gridform Design GuideDokument352 SeitenStrongwell Gridform Design GuideBintee PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CI2400ENG Bondstrand 2400 Product DataDokument6 SeitenCI2400ENG Bondstrand 2400 Product DatachabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structures - Suplimentory Data - EnC CheckDokument78 SeitenStructures - Suplimentory Data - EnC Checkdinesh kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Firetuf FT30 - Standard Fire Resistant Cable: ConstructionDokument2 SeitenFiretuf FT30 - Standard Fire Resistant Cable: ConstructionAshik M RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Brochure (Lamson)Dokument6 SeitenHDPE Brochure (Lamson)arkadjyothiprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Guide to Drilling Equipment and OperationsVon EverandWorking Guide to Drilling Equipment and OperationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- OHSP HandbookDokument23 SeitenOHSP HandbookJoel Puruganan SaladinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Test ResultsDokument23 SeitenSafety Test Resultsmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business LetterDokument22 SeitenBusiness Lettermanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collection of Job Interview Questions and The AnswersDokument46 SeitenCollection of Job Interview Questions and The AnswersctansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Units Associated With Basic ElectricalDokument43 SeitenUnits Associated With Basic Electricalmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Srb-Eim-Nc IiDokument14 SeitenSrb-Eim-Nc Iimanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Interview Tips: Be On Time, Dress Properly, Establish RapportDokument1 SeiteJob Interview Tips: Be On Time, Dress Properly, Establish Rapportmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Interview Tips: Be On Time, Dress Properly, Establish RapportDokument1 SeiteJob Interview Tips: Be On Time, Dress Properly, Establish Rapportmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Record Book for Welding QualificationDokument16 SeitenStudent Record Book for Welding Qualificationmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core1-Vehicle Preventive Maintenance PDFDokument99 SeitenCore1-Vehicle Preventive Maintenance PDFmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Identify Basic Hand ToolsDokument150 SeitenIdentify Basic Hand Toolsmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Fittings by Daleon PDFDokument115 SeitenPipe Fittings by Daleon PDFmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tractor Backhoe Pre-Operation ChecklistDokument3 SeitenTractor Backhoe Pre-Operation Checklistmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Back Hoe SafetyDokument2 SeitenBack Hoe Safetymanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plumbing Systems For TarpDokument1 SeitePlumbing Systems For Tarpmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Tasks-Tvl3-4-Plumbing NC I-Ii PDFDokument2 SeitenPerformance Tasks-Tvl3-4-Plumbing NC I-Ii PDFmanny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Outs Tvl4 Jan14!18!2019Dokument22 SeitenHand Outs Tvl4 Jan14!18!2019manny daleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mensuration & Calculation For Plumbing by Daleon PDFDokument101 SeitenMensuration & Calculation For Plumbing by Daleon PDFmanny daleon100% (1)
- Plasblak® Pe2772 Black Masterbatch: Black Utility Masterbatch For Film, Molding and Extrusion ApplicationsDokument2 SeitenPlasblak® Pe2772 Black Masterbatch: Black Utility Masterbatch For Film, Molding and Extrusion ApplicationsSiddharthBhasneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- II. Polymers MCQs 1Dokument7 SeitenII. Polymers MCQs 1fuckjungali100% (1)
- Chemtura PDFDokument23 SeitenChemtura PDFchinmoyd1100% (1)
- Additive Manufacturing BTJDokument12 SeitenAdditive Manufacturing BTJHalyna HafiychukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blow MouldingDokument40 SeitenBlow MouldingDINO FANNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVS Technical Codes and BulletinsDokument10 SeitenDVS Technical Codes and BulletinsAsif SarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversion Denier To MicronDokument6 SeitenConversion Denier To Microncwqccq100% (1)
- Vista LonDokument1 SeiteVista LonVikram KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Plastic Welder Chapter 1: PlasticsDokument40 SeitenEuropean Plastic Welder Chapter 1: PlasticsJustin AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D4000 2004 PDFDokument19 SeitenAstm D4000 2004 PDFHARSHANoch keine Bewertungen
- WINDOWSTEIN As Per Po CertifiedDokument9 SeitenWINDOWSTEIN As Per Po CertifiedKarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Processes for Automobile ComponentsDokument1 SeiteManufacturing Processes for Automobile ComponentsERKATHIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yogeshwar BrochureDokument16 SeitenYogeshwar BrochureDanish KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolyesterDokument7 SeitenPolyesterRanjan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Belts For Aluminum Extrusion: The Megadyne GroupDokument8 SeitenConveyor Belts For Aluminum Extrusion: The Megadyne GroupJuan Andrés Díaz RiveroNoch keine Bewertungen
- USE OF Plastic Waste in Road ConstructionDokument19 SeitenUSE OF Plastic Waste in Road ConstructionAbhishek PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spray Layup ProcessDokument14 SeitenSpray Layup ProcessDildeep Jayadevan50% (2)
- Injection MoldingDokument42 SeitenInjection Moldinglovilove01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Significance of PolymersDokument27 SeitenUnderstanding Significance of PolymersKoduru ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- VDA Classification - Material - List - 205 - EN PDFDokument31 SeitenVDA Classification - Material - List - 205 - EN PDFgogger100% (1)
- Piping Works Daily ReportDokument19 SeitenPiping Works Daily ReportGomathyselviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Method For CompositesDokument41 SeitenManufacturing Method For CompositestpmendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aramid FibersDokument6 SeitenAramid FibersKirti NagdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Common Plastics PDFDokument1 SeiteA Guide To Common Plastics PDFmuammal abbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRE DVS Technical Codes On Plastics Joining TechnologiesDokument11 SeitenPRE DVS Technical Codes On Plastics Joining TechnologiesAmr Mohamed SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Let's Go Green! - Act 3Dokument5 SeitenLet's Go Green! - Act 3Yamelyonatan AtahuachiperezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bow Strings Pedro SerralheiroDokument9 SeitenBow Strings Pedro SerralheiroRui Manuel RomãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BR Coloration of Plastics and RubberDokument86 SeitenBR Coloration of Plastics and RubberHuynh Nam QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of ThermoplasticsDokument9 SeitenClassification of ThermoplasticsEd Willis100% (1)
- PultrsionDokument18 SeitenPultrsionHaren SinghNoch keine Bewertungen