Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Final Year Technical Seminar: Department of Mechanical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
Nagabhushana0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
69 Ansichten10 SeitenOriginaltitel
naveenppt 11.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
69 Ansichten10 SeitenFinal Year Technical Seminar: Department of Mechanical Engineering
Hochgeladen von
NagabhushanaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
DAYANANDA SAGAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
Shavige Malleshwara Hills, Kumaraswamy Layout, Bangalore-560078
(An Autonomous Institute affiliated to VTU, Approved by AICTE &ISO 9001: 2008 Certified)
Accredited by National Assessment & Accreditation Council (NAAC) with ‘A’ Grade
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Final Year Technical Seminar
Title: “TURBOCHARGER IN IC ENGINE”
Name NAVEEN HOOGAR
USN 1DS16ME424
Guide Dr. MALLIKARJUN BIRADAR
Name
Designation
INTRODUCTION
A turbocharger is a device used to allow more power to be
produced for an engine of a given size.
A turbocharged engine can be more powerful and efficient
than a naturally aspirated engine because the turbine forces
more intake air, proportionately more fuel, into the combustion
chamber than if atmospheric pressure alone is used.
Its purpose is to increase the volumetric efficiency of the
combustion chamber.
OBJECTIVES
• To improve an engines volumetric efficiency by increasing the
intake density.
• The turbine converts the engine exhausts potential pressure
energy and kinetic velocity energy into rotational power,
which is turned used to drive the compressor.
• The power needed to spin the centrifugal compressor is
derived from the high pressure and temperature of the engines
exhausts gases.
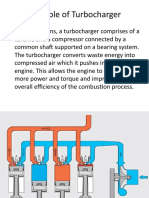
Turbocharger diagram
Turbocharger working
Working
Turbochargers are a type of forced induction system. They
compress the air flowing into the engine.
A turbocharged engine produces more power overall than the
same engine without the charging.
This can significantly improve the power to-weight ratio for
the engine. In order to achieve this boost, the turbocharger
uses the
exhaust flow from the engine to spin a turbine, which in turn
spins an air pump. The turbine
in the turbocharger spins at speeds of up to 150,000 rotations
per minute (rpm) .
Advantages
Increase the power from the engine of same size.
Reduction in size of engine with same input.
Efficiency of the engine is increased.
Less moving parts.
Disadvantages
If the turbine is damaged then the whole rotor requires
replacement.
Cost and complexity.
Space required is higher
Total system is heavier.
Applications
Diesel powered cars
Gasoline powered cars.
Trucks
Aircrafts
Marine engines
Conclusion
• From this literature review it has been concluded that from last
two decades various attempts were made to improve the power
output of an engine and to reduce its emissions by making
some changes and installing additional accessories like
intercooler in the turbocharging technology.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Turbo ChargerDokument23 SeitenTurbo Chargerselvaraj9223100% (1)
- SuperchargingDokument13 SeitenSuperchargingSaikat GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharging of Ic EnginesDokument5 SeitenTurbocharging of Ic EnginesKrishna MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger Basics - What is a TurbochargerDokument18 SeitenTurbocharger Basics - What is a TurbochargerShrwan Gyawali100% (3)
- AkooDokument14 SeitenAkooHASHIMU BWETENoch keine Bewertungen
- Supercharger VS TurbochargerDokument25 SeitenSupercharger VS TurbochargerAllen CastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument45 SeitenModule 1shubham GoundadkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Supercharging and TurbochargingDokument21 Seiten6 Supercharging and TurbochargingCh ArsalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vtec and Ivtec ComparisionDokument12 SeitenVtec and Ivtec ComparisionAjithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Himanshu Singh Turbocharger-SeminarDokument20 SeitenHimanshu Singh Turbocharger-SeminarHimanshu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boost Engine Power with Turbochargers & SuperchargersDokument21 SeitenBoost Engine Power with Turbochargers & SuperchargersB Bala Venkata GaneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etm 08 TurbochargingDokument58 SeitenEtm 08 TurbochargingjashokjackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techinical SeminerDokument23 SeitenTechinical SeminerSatish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDokument23 SeitenSupercharging and TurbochargingTrain Placement CellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super ChargingDokument24 SeitenSuper ChargingGagan KaushikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDokument16 SeitenTurbocharger and SuperchargerPrajwal ZinjadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Internal Combustion EnginesDokument19 SeitenIntroduction To Internal Combustion EnginesAkhilesh ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Forced Induction?Dokument15 SeitenWhat Is Forced Induction?Fugaru Paul - AlexandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Turbocharger in Petrol Engine With Intercooler and Discharger ChamberDokument8 SeitenDesign of Turbocharger in Petrol Engine With Intercooler and Discharger ChamberDeadman RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between: Turbocharger Vs SuperchargerDokument14 SeitenDifference Between: Turbocharger Vs SuperchargerMohammad Al QadomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 17ME655-Module 4 PDFDokument40 Seiten17ME655-Module 4 PDFVinayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo Charger - ProjectDokument36 SeitenTurbo Charger - ProjectSam Sams100% (2)
- Pre Drive Authorization With Turbo On Demand (Air From Suspensor and Tank)Dokument6 SeitenPre Drive Authorization With Turbo On Demand (Air From Suspensor and Tank)Leo BoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super ChargingDokument23 SeitenSuper Charginghirenbabaji100% (2)
- researchpaper2016Dokument7 Seitenresearchpaper2016Aditya YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences between superchargers and turbochargersDokument5 SeitenDifferences between superchargers and turbochargersANTONIO SANDATE CHAVEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDokument14 SeitenSupercharging and TurbocharginglostwithabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By: Rajesh M S (4mc04au013)Dokument18 SeitenPresented By: Rajesh M S (4mc04au013)Vinod SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Analysis and Fabrication On A Turbocharger in Two Stroke Single Cylinder Petrol EngineDokument8 SeitenPerformance Analysis and Fabrication On A Turbocharger in Two Stroke Single Cylinder Petrol Engineashan19800217Noch keine Bewertungen
- 108 PDFDokument9 Seiten108 PDFMr PolashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDokument8 SeitenSupercharging and TurbochargingMudassir Hussain100% (1)
- Seminer 6TH Sem PDFDokument22 SeitenSeminer 6TH Sem PDFChievete pfunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Project TurbochargerDokument12 SeitenMechanical Project Turbochargerinduscad100% (6)
- Seminar Report Till AbstractDokument11 SeitenSeminar Report Till Abstractsupreethgowdams86% (7)
- Performance Analysis of Ic Engine Using Supercharger and Turbocharger-A ReviewDokument6 SeitenPerformance Analysis of Ic Engine Using Supercharger and Turbocharger-A ReviewSOMESH SHARMA (B15ME036)Noch keine Bewertungen
- TURBOCHARGERDokument5 SeitenTURBOCHARGERAnand Raju100% (1)
- 8 1turbochargerDokument24 Seiten8 1turbochargerkedir67Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-12 - Turbocharger & Super MecDokument29 SeitenCh-12 - Turbocharger & Super Mecahmed jemalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shahid R Peerzade Seminar ReportDokument20 SeitenShahid R Peerzade Seminar ReportMahesh R JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kumaran 3Dokument4 SeitenKumaran 3HANUMANT MORENoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Principle of TurbochargerDokument19 Seiten03 Principle of TurbochargerSky RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineDokument10 SeitenTurbocharger: Prasented By: Yaseen M Kalawant 4MR15MR029 Final Year B.E MarineYasewn KALAWANTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of power pack on diesel locomotiveDokument25 SeitenStudy of power pack on diesel locomotiveKarim Faisal0% (1)
- Turbo ChargerDokument13 SeitenTurbo ChargerSwaraj TodankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Savings Through Electric-Assist Turbocharger For Marine Diesel EnginesDokument6 SeitenEnergy Savings Through Electric-Assist Turbocharger For Marine Diesel EnginesmasoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancement in AutomobileDokument14 SeitenAdvancement in AutomobileVardhan ChipperNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ic Engine: Assignment#02Dokument9 SeitenIc Engine: Assignment#02Jawad ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharged Single Cylinder Si Engine: AbstractDokument7 SeitenTurbocharged Single Cylinder Si Engine: AbstractKartikey GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IC Engines IIDokument57 SeitenIC Engines IISahil SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recent Trends in Automobile SeminarDokument18 SeitenRecent Trends in Automobile SeminarKkbhuvan KkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadDokument21 SeitenTurbo Charged Engine: Presenting by M. Sumanth Reddy 16701A0344 Under Guidance of M. Maruthi PrasadSumanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerDokument16 SeitenDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerNazrul Aizat ZunaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Plant Engineering Unit:Iv Gas Turbine PlantDokument30 SeitenPower Plant Engineering Unit:Iv Gas Turbine PlantshivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Power PlantDokument28 SeitenDiesel Power PlantHassan MalghaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger: Presented byDokument26 SeitenTurbocharger: Presented byYasewn KALAWANTNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Parallel and Series Turbocharging For The Diesel EngineDokument11 SeitenA Review of Parallel and Series Turbocharging For The Diesel EnginenicolasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 001 Turbo ChargerDokument26 Seiten001 Turbo ChargerfrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOTOCHARGER - MOTORCYCLE WITH TURBOCHARGERDokument14 SeitenMOTOCHARGER - MOTORCYCLE WITH TURBOCHARGERshathakhassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesVon EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Project Report Guide LinesDokument13 SeitenProject Report Guide LinesNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContinueDokument31 SeitenContinueNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TREADMILL PPT Final Year ProjectDokument13 SeitenTREADMILL PPT Final Year ProjectNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Technical Seminar: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument15 SeitenFinal Year Technical Seminar: Department of Mechanical EngineeringNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BH Usa 01 Mandy AndressDokument52 SeitenBH Usa 01 Mandy AndressJay C. KathiriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design, Modelling and Development of Electric Walking BikeDokument16 SeitenDesign, Modelling and Development of Electric Walking BikeNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAGLEV Wind Mill Power GenerationDokument16 SeitenMAGLEV Wind Mill Power GenerationNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Technical SeminarDokument12 SeitenFinal Year Technical SeminarNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNC HardwareDokument39 SeitenCNC HardwareNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Plug Weld in Low Carbon Steel by Mig Welding ProcessDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of Plug Weld in Low Carbon Steel by Mig Welding ProcessNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Application Development With ANDROIDDokument26 SeitenMobile Application Development With ANDROIDjithinaravind007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligence Template 16x9Dokument5 SeitenIntelligence Template 16x9NagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mems, Piezoelectric Sensing & ActuationDokument36 SeitenMems, Piezoelectric Sensing & ActuationNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH HovercraftDokument16 SeitenMECH HovercraftNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Application Development With ANDROIDDokument26 SeitenMobile Application Development With ANDROIDNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9080 rEVY5PCDokument15 Seiten9080 rEVY5PCNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel From Waste PlasticDokument17 SeitenFuel From Waste PlasticNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryogenic Engines ExplainedDokument23 SeitenCryogenic Engines ExplainedNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Hybrid Vehicle Test Skid ProgressDokument24 SeitenHydraulic Hybrid Vehicle Test Skid ProgressNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TREADMILL PPT Final Year ProjectDokument13 SeitenTREADMILL PPT Final Year ProjectNagabhushana50% (2)
- Lithium-Air BatteryDokument29 SeitenLithium-Air BatteryNagabhushana100% (1)
- Autonomous CarDokument28 SeitenAutonomous CarNagabhushana0% (1)
- Anti Locking Brakes: Seminar byDokument18 SeitenAnti Locking Brakes: Seminar byNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber Communication Presentation SlidesDokument20 SeitenOptical Fiber Communication Presentation SlidesNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AirbagDokument26 SeitenAirbagNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Inflating TyresDokument29 SeitenSelf Inflating TyresNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Inflating TyresDokument29 SeitenSelf Inflating TyresNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Hybrid Vehicle Test Skid ProgressDokument24 SeitenHydraulic Hybrid Vehicle Test Skid ProgressNagabhushanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Two-Way Floor SystemDokument11 SeitenTwo-Way Floor SystemJason TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Autolisp TutorialsDokument285 SeitenThe Autolisp Tutorialsmynareshk100% (7)
- ABB 4 Pole Contactor, 230V, 40ADokument1 SeiteABB 4 Pole Contactor, 230V, 40ASEERALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Diploma For CivilDokument4 SeitenAdvance Diploma For CivilAung Naing Latt AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- S5 1-Bedroom Suite FloorplanDokument1 SeiteS5 1-Bedroom Suite FloorplanAdam HudzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Postmodern Architecture Reinterprets Form & FunctionDokument5 SeitenPostmodern Architecture Reinterprets Form & FunctionNejra Uštović - PekićNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEEN 364 Lecture 4 Examples on Sampling and Aliasing PhenomenaDokument5 SeitenMEEN 364 Lecture 4 Examples on Sampling and Aliasing PhenomenaHiren MewadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CalibrationDokument7 SeitenCalibrationstolen mechieducNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Vs 3D ReviewDokument7 Seiten2D Vs 3D ReviewBhasker RamagiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Komatsu Backhoe Loaders Spec 088545 PDFDokument16 SeitenKomatsu Backhoe Loaders Spec 088545 PDFJohnny WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gearbox Efficiency and LubricationDokument6 SeitenGearbox Efficiency and Lubricationrashm006ranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC200 Inverter Manual OverviewDokument239 SeitenAC200 Inverter Manual OverviewJuliana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas SpringsDokument122 SeitenGas SpringsslavcecaciNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Data Management System ReportDokument122 SeitenSchool Data Management System ReportshekharyadawNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB MNS System GuideDokument34 SeitenABB MNS System GuideLeslie HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banner Printing Set UpDokument21 SeitenBanner Printing Set UpAsanka ChandimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Alat TSMDokument2 SeitenDaftar Alat TSMagus ImawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar Cat 320d 320dl Excavator Parts ManualDokument34 SeitenCaterpillar Cat 320d 320dl Excavator Parts ManualSara Sarmiento Echeverry100% (1)
- Cotización FM2Dokument2 SeitenCotización FM2Anonymous 3o4Mwew0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Count rows in all tablesDokument25 SeitenCount rows in all tablessatya1401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Dokument5 SeitenMobile Robots & Kinematics: Session 2: Nicol As Ilich Samus February 27, 2014Nicolás Ilich SamusNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRC800 Remote Control UserGuideDokument2 SeitenDRC800 Remote Control UserGuideLuis MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architecture Technology CurriculumDokument129 SeitenArchitecture Technology CurriculumShakib Shoumik57% (21)
- Richard GrisenthwaiteDokument25 SeitenRichard GrisenthwaitecaarthiyayiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lean & Environment ToolkitDokument96 SeitenLean & Environment Toolkittinyplankton100% (7)
- Omop Etl Template v4.0Dokument17 SeitenOmop Etl Template v4.0kartikb60100% (1)
- Variational Asymptotic BeamDokument43 SeitenVariational Asymptotic BeamAdimasu AyeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel Service Quality ChecklistDokument3 SeitenHotel Service Quality ChecklistKarthik BhandaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart is the most intelligent solution yet for urban drivingDokument8 SeitenSmart is the most intelligent solution yet for urban drivingHenrique CorreiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otis Relay Coils SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteOtis Relay Coils SpecificationsDamian Alberto EspositoNoch keine Bewertungen