Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Big Data: Submitted By-Rajashree Rashmita Reg - No-1825209016 Mca 4 Sem
Hochgeladen von
Rajsree Rasmita0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
119 Ansichten27 SeitenBig Data Presentation
Originaltitel
Big Data
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBig Data Presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
119 Ansichten27 SeitenBig Data: Submitted By-Rajashree Rashmita Reg - No-1825209016 Mca 4 Sem
Hochgeladen von
Rajsree RasmitaBig Data Presentation
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 27
BIG DATA
Submitted by-Rajashree Rashmita
Reg.no-1825209016
MCA 4th sem
Content
Introduction
What is BIG DATA
Examples of BIG DATA
Characteristic of BIG DATA
The structure of BIG DATA
Why BIG DATA
How it is different
BIG DATA sources
Tools used in BIG DATA
Application of BIG DATA
Risks of BIG DATA
Benefits of BIG DATA
How BIG DATA impact on IT
Future of BIG DATA
Conclusion
Introduction
BIG DATA is a term defined for data sets that are large or
complex that traditional data processing applications are
inadequate .
BIG DATA basically consists of analysis zing , capturing the
data , sharing , storage capacity , transfer, visualization and
querying and information privacy .
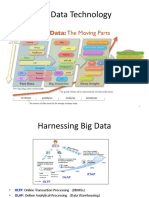
What is BIG DATA
Big Data means really a big data, it is a collection of large datasets that cannot be
processed using traditional computing techniques. Big data is not merely a data,
rather it has become a complete subject, which involves various tools, techniques
and frameworks.
Examples of BIG DATA
Ex- Face book, Flicker, YouTube, Twitter, Google,
Google news. Face book reports 2.5 billion
content items, 105 terabytes of data each half
hour, 300M photos and 4M videos posted per day .
In Twitter, Over 651 million users, generating over
6,000 tweets per second. 300 hours of video are
uploaded to YouTube every minute with more than
1 trillion video views. Google make 50 billion
pages indexed and more than 2.4 million queries
in every minute . Google news Articles from over
10,000 sources in real time . More than 4.5 million
photos uploaded in a day in Flicker. It is estimated
that all the global data generated from the
Characteristics of BIG DATA
Volume
The quantity of generated and stored data every second .
Here we are talking about Zettabyte or more .
It is the task of big data to convert such Hadoop data into
valuable information .
Data is generated by machine , networks and human
interaction on systems like social media .
The volume of data to be analyzed is massive .
Velocity
The speed of generation of data.
Perhaps action being taken upon .
The highest velocity data normally streams directly into memory
versus being written to disk .
Some Internet Of Things(IOT) requires real-time evaluation and
action .
E.g.-almost 2.5 million queries on Google are performed .
Around 20 million photos are viewed .
Every minute we upload 100 hours of video on Youtube .
300,000 tweets are sent .
Every minute over 200 million Emails are sent .
Variety
BIG DATA is not just numbers , dates ,and strings . BIG
DATA is also 3D data ,geospatial , audio and video and
unstructured text , including log files and social media .
Traditional database systems were designed to address
smaller volumes of structured data , fewer updates or a
predictable , consistent data structure .
BIG DATA includes different types of data .
Veracity
It is the extended definition for BIG DATA , which refers to
the data quality and data value .
The data quality of captured data can vary greatly , affecting
the accurate analysis .
Data quality is unreliable .
Data coming from uncontrolled environments .
The Structure of big data
Now days 8 vs
10 vs
Why BIG DATA
Growth of BIG DATA is needed .
Increase of storage capacities .
Increase of processing power .
Availability of data (different data types) .
Every day we create 2.5 quintillion bytes of data ; 90% of the
data in the world today has been created in the last 2 years
alone .
How it is different
Automatically generated by a machine (sensor embedded in
an engine)
Typically an entirely new source of data (use of the internet)
Not designed to be friendly(text streams)
May not have much values (need to focus on the important
part)
Tools used in BIG DATA
Distributed servers / cloud (Amazon EC2)-processing is
hosted .
Distributed storage (Amazon S3)-data is stored .
Distributed processing(MapReduce)-programming model .
High-performance schema –free database(MongoDB)-data is
stored and indexed .
Analytic /semantic processing-operations are performed on
data .
Continue…
Hadoop- It is a free , JAVA –based programming framework
that supports the processing large data sets in a distributed
computing environment .
Facebook , LinkedIn , Twitter ,eBay use Hadoop .
Hbase- A scalable , distributed database that supports
structured data storage for large tables .
Hive- A data ware house infrastucture that provides data
summerization and ad hoc querying .
Application of BIG DATA
Benefits of BIG DATA
Real-time big data is not just a process for storing petabytes
or exabytes of data in a data warehouse, it is about the ability
to make better decision and take meaningful actions at the
right time .
Fast forward to the present and technologies like Hadoop
give you the scale and flexibility to store data before you
know how you are going to process it .
Technologies such as MapReduce , Hive and impala enable
you to run queries without changing the data structures
underneath .
Continue….
Our newest research finds that organizations are using big
data to target customer-centric outcomes, tap into internal
data and build a better information ecosystem .
BIG DATA is already an important part of the $64 billion
database and data analytics market .
It offers commercial opportunities of a comparable scale to
enterprise software in the late 1980s .
And the internet boom of the 1990s , and the social media
explosion of today .
How BIG DATA impacts on IT
BIG DATA is a troublesome force presenting opportunities
with challenge to IT organization .
By 2015 4.4 million IT jobs in BIG DATA ; 1.9 million is in
US itself .
India will require a minimum of 1 lakh data scientists in the
next couple of years in addition to data analysts and data
managers to support the BIG DATA space .
Future of BIG DATA
$15 billion on software firms only specializing in data
management and analytics .
This industry on its own is worth more than $100 billion and
growing at almost 10% a year which is roughly twice as fast as the
software business as a whole .
In February , 2012 the open source analyst firm Wikibon released
the first market forecast for BIG DATA , listing $5.1 billion
revenue in 2012 with growth to $53.4 billion in 2017 .
The McKinsey Global Institute estimates that data volume is
growing 40%per year , and will grow 44x between 2009 and
2020 .
Conclusion
BIG DATA is now a reality with a huge profit potential .
Tools and Technologies are available through Open-Sourse .
Each one of us can benefit from working with BIG DATA
(Dynamic)in its pure form or in its traditional form (static) .
THANK YOU
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Big DataDokument16 SeitenBig DataPrithviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big DataDokument21 SeitenBig DatasonalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big DataDokument31 SeitenBig DataVamsikrishKokilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data AnswersDokument14 SeitenBig Data AnswersManan SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data TechnologyDokument10 SeitenBig Data Technologysharath_rakki100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence and Expert SystemsDokument36 SeitenArtificial Intelligence and Expert Systemsdivz16Noch keine Bewertungen
- AI Expert SystemsDokument38 SeitenAI Expert SystemsInvincible AmadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- HR Data Analytics and The Future of Total: August 2018Dokument18 SeitenHR Data Analytics and The Future of Total: August 2018NkvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natural Language Processing: Dr. Tulasi Prasad Sariki SCOPE, VIT ChennaiDokument29 SeitenNatural Language Processing: Dr. Tulasi Prasad Sariki SCOPE, VIT Chennainaruto sasukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intelligent Systems NotesDokument7 SeitenIntelligent Systems NotesSourav DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions On Big DataDokument2 SeitenQuestions On Big Dataabhijitp100% (3)
- Hadoop TutorialDokument3 SeitenHadoop TutorialSundaram yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data Analytics TutorialDokument25 SeitenBig Data Analytics TutorialAhmad KhadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 010 Intro Natural Language ProcessingDokument43 Seiten010 Intro Natural Language ProcessingPhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data AnalyticsDokument7 SeitenBig Data Analyticsmundal minatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visvesvaraya Technological University BelagaviDokument74 SeitenVisvesvaraya Technological University BelagavireshmaitagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To Data Mining: Dr. Dipti Chauhan Assistant Professor SCSIT, SUAS IndoreroochinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master in Business Analytics Big DataDokument40 SeitenMaster in Business Analytics Big DataGenrev GorgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data - GCP IM Point of ViewDokument38 SeitenBig Data - GCP IM Point of Viewkarthik_integerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Management For Human Resource Information SystemDokument14 SeitenData Management For Human Resource Information SystemRajeshsharmapurangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Big DataDokument117 SeitenUnderstanding Big DataHirdesh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big DataDokument48 SeitenBig DataBuat Download100% (1)
- Big DataDokument63 SeitenBig DataMemes InstagramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Artificial Intelligence in Clinical MedicineDokument13 Seiten4 Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Medicineshirish gundalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence Engineer: Master's CourseDokument21 SeitenArtificial Intelligence Engineer: Master's CourseMeghasundar MohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT04-Hadoop Infrastructure LayerDokument40 SeitenPPT04-Hadoop Infrastructure LayerTsabitAlaykRidhollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction: Data Analytic ThinkingDokument38 SeitenIntroduction: Data Analytic ThinkingGökhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expert Systems and Executive Information SystemsDokument14 SeitenExpert Systems and Executive Information SystemsDilfaraz Kalawat100% (1)
- PPT01-Introduction To Big DataDokument34 SeitenPPT01-Introduction To Big DataTsabitAlaykRidhollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Science AFADokument15 SeitenData Science AFARaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilizing Big DataDokument5 SeitenUtilizing Big DataFarheen AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expert SystemsDokument20 SeitenExpert SystemsFurqan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data: Presented by J.Jitendra KumarDokument14 SeitenBig Data: Presented by J.Jitendra KumarJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To NLP I Mid Set ADokument8 SeitenSolutions To NLP I Mid Set Ajyothibellaryv100% (1)
- World Big Data Market Opportunities 2013-2018Dokument19 SeitenWorld Big Data Market Opportunities 2013-2018VisiongainGlobalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Talent ForecastingDokument9 SeitenTalent Forecastingabhi_003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of DSSDokument25 SeitenFundamentals of DSSDoni ArthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data PPT 55b0fc01e7543Dokument31 SeitenBig Data PPT 55b0fc01e7543NISHANT SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review On Revenue RecognitionDokument7 SeitenLiterature Review On Revenue RecognitionaflshftafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pyramid Big Data TestingDokument3 SeitenPyramid Big Data Testingutagore58100% (1)
- Big Data Seminar ReportDokument19 SeitenBig Data Seminar ReportChinnu D SNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS-344 Computing Applications in Business Spring 2015 Week 3Dokument110 SeitenIS-344 Computing Applications in Business Spring 2015 Week 3Faded RianbowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Data MiningDokument21 SeitenUnderstanding Data MiningYah yah yahhhhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data Analysis Lab ManualDokument39 SeitenBig Data Analysis Lab Manualragulnagarajan896Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining With Oracle Database 11g Release 2: Competing On In-Database AnalyticsDokument26 SeitenData Mining With Oracle Database 11g Release 2: Competing On In-Database AnalyticsArul prakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eight Units DWDMDokument119 SeitenEight Units DWDMdasarioramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Data MiningDokument45 SeitenIntroduction To Data Miningshreyardx75% (4)
- MIS-15 - Data and Knowledge ManagementDokument55 SeitenMIS-15 - Data and Knowledge ManagementAbhishek PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Turnover PredictionDokument9 SeitenEmployee Turnover Predictionrohith prabhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG - Face Recognition Using Neural NetworksDokument20 SeitenUG - Face Recognition Using Neural NetworksAdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data & Business Intelligence: Presented by Binh Nguyen - Luong DinhDokument24 SeitenBig Data & Business Intelligence: Presented by Binh Nguyen - Luong Dinhgsrao_9Noch keine Bewertungen
- 391 - CS8091 Big Data Analytics - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDokument2 Seiten391 - CS8091 Big Data Analytics - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDhruviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expert SystemsDokument18 SeitenExpert SystemsNSKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT09-Big Data VisualizationDokument33 SeitenPPT09-Big Data VisualizationTsabitAlaykRidhollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Big Data: Soorya Prasanna RavichandranDokument33 SeitenIntroduction To Big Data: Soorya Prasanna RavichandranAbhishekChakladarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data AnalyticsDokument31 SeitenBig Data AnalyticsTushar SawantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big DataDokument22 SeitenBig Datavinay_krishna_1100% (3)
- Hadoop Interview QuestionsDokument27 SeitenHadoop Interview Questionsഅഭിപ്രായൻNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Data Analysis SeminarDokument15 SeitenBig Data Analysis SeminarNeha Koul100% (1)
- Big Data 8722 m8RQ3h1Dokument31 SeitenBig Data 8722 m8RQ3h1sai shivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International School of Engineering: (We Are Applied Engineering)Dokument20 SeitenInternational School of Engineering: (We Are Applied Engineering)Rajsree RasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Glass Seminar ReportDokument30 SeitenGoogle Glass Seminar ReportRajsree RasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirements Specification: Silicon Institute of TechnologyDokument15 SeitenSoftware Requirements Specification: Silicon Institute of TechnologyRajsree RasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delhi The Pollution Capital of India: by Sagar LadhwaniDokument32 SeitenDelhi The Pollution Capital of India: by Sagar LadhwaniRajsree RasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Requirement Specification: Employee Tracking SystemDokument14 SeitenSoftware Requirement Specification: Employee Tracking SystemBerker Güngör50% (4)
- Dellemc Poweredge Raid Controller h745 DatasheetDokument2 SeitenDellemc Poweredge Raid Controller h745 DatasheetAndres MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paas JDDokument1 SeitePaas JDNithesh RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Material On Computer Organization and ArchitectureDokument80 SeitenStudy Material On Computer Organization and ArchitecturetoarnabchNoch keine Bewertungen
- T-64 - WikipediaDokument22 SeitenT-64 - Wikipediadanko1du2458Noch keine Bewertungen
- Defence Expo2022Dokument111 SeitenDefence Expo2022Jyotsna Pandey50% (2)
- PTW #: Location of work:RIG FLOOR Task Description: INSTALL T Piece Supervisor: TBRA #:D-111Dokument2 SeitenPTW #: Location of work:RIG FLOOR Task Description: INSTALL T Piece Supervisor: TBRA #:D-111DrillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSC Computer Science Syllabus NepDokument17 SeitenBSC Computer Science Syllabus NepBhagya SarathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDR C366vehDokument3 SeitenPDR C366vehGI CalbuthNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Manuf Program enDokument28 SeitenE Manuf Program enPaolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC469 Nontraditional and Computer Aided Manufacturing Laboratory 14443::guravtar Singh 0.0 0.0 2.0 1.0 Practical CourseDokument3 SeitenMEC469 Nontraditional and Computer Aided Manufacturing Laboratory 14443::guravtar Singh 0.0 0.0 2.0 1.0 Practical CourseManoj MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation (Short) : FC120 Fire Control Panel (NL)Dokument8 SeitenOperation (Short) : FC120 Fire Control Panel (NL)Pedro Sanchez RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Office 2013 Activation ProcedureDokument2 SeitenOffice 2013 Activation ProcedureChandra KanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Conference NewsfgfghsfghsfghDokument3 Seiten2012 Conference NewsfgfghsfghsfghabdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Media Project GuidelinesDokument2 SeitenMulti Media Project GuidelinesAngelica AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-63833en 02 (Hardware)Dokument338 SeitenB-63833en 02 (Hardware)MANI KANDAN100% (1)
- Zelio: and To AssembleDokument20 SeitenZelio: and To AssembleaavdNoch keine Bewertungen
- GM ApqpDokument106 SeitenGM Apqpsnm60Noch keine Bewertungen
- Active Product List Aug 2015Dokument42 SeitenActive Product List Aug 2015Siva NandhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Usuario - Fluidoterapia ES y INGDokument114 SeitenManual de Usuario - Fluidoterapia ES y INGjames lopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPO1 - Module 2Dokument7 SeitenBPO1 - Module 2Jerecho InatillezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCIE LabDokument144 SeitenCCIE LabCông SơnNoch keine Bewertungen
- PUAN Internship Program 2023Dokument10 SeitenPUAN Internship Program 2023Asim SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treinamento KACE SMADokument183 SeitenTreinamento KACE SMAValériaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRDDokument26 SeitenFRDDarryl SmiLe100% (2)
- Tower Foundation BOM For SST 42m 4L 290kph - HDokument18 SeitenTower Foundation BOM For SST 42m 4L 290kph - Hhenjie mirasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOI Reports 2017-2018Dokument15 SeitenFOI Reports 2017-2018Meyan Castillo OrigenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latest - Industrial - Symphony Industrial Ai Data Sheets Watchman 360 - Brochure - 20220620Dokument3 SeitenLatest - Industrial - Symphony Industrial Ai Data Sheets Watchman 360 - Brochure - 20220620MILTON CÉSAR AGUILAR DE AZAMBUJANoch keine Bewertungen
- The History of Java Technology: James Gosling Patrick NaughtonDokument2 SeitenThe History of Java Technology: James Gosling Patrick NaughtonMiguel Angel Rivera NiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Planning Guide AIRIS IIDokument39 SeitenSite Planning Guide AIRIS IINoé GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen