Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Nature of Accounting: Things A Company
Hochgeladen von
Keempee Ian Gaviran0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten10 SeitenNature of accounting
Ctto
Originaltitel
The Nature of Accounting
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenNature of accounting
Ctto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten10 SeitenThe Nature of Accounting: Things A Company
Hochgeladen von
Keempee Ian GaviranNature of accounting
Ctto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
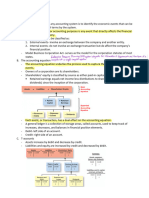
The nature of accounting
• ASSETS = things a company owns
• LIABILITIES = what the company owes to
others
• OWNER’S EQUITY = what remains after
liabilities are deducted from assets
Two main accounting concepts
1. accounting equation
2. double-entry bookkeeping
Both were developed centuries ago
but remain central to the accounting
process.
accounting equation
Assets – Liabilities = Owner’s Equity
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
two main financial statements
1. balance sheet – shows the current
financial position of a company
2. profit and loss account (income
statement AmE) – shows the results of
operations (performance) over a period
of time
Two other financial statements
3. Cash flow statement
- describes how much cash was used in corporate
operating, investment, and financing activities
over a period of time.
- The Cash Flow Statement shows how the
company is paying for its operations and future
growth, by detailing the "flow" of cash between
the company and the outside world; positive
numbers represent cash flowing in, negative
numbers represent cash flowing out.
4. Statement of changes in shareholder equity
- reconciles the difference between the equity at
the two different points in time
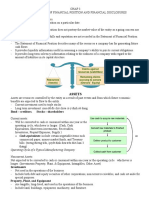
balance sheet
• Assets are divided into:
– fixed (not expected to be converted into cash
and comprise property, land and equipment)
– current (include cash and other items -
stocks, bonds, amounts due from customers,
services paid for but not yet used - that will or
can become cash within the following year
– intangible (include the costs of organizing the
business, patents on a process or invention,
copyrights on written material, trademarks,
goodwill)
balance sheet
• Liabilities are divided into:
– current (obligations that will have to be
met within a year of the date of the
balance sheet)
– long-term (obligations that fall due a
year or more after the date of the
balance sheet)
profit and loss account
• it summarizes:
– all revenues (or sales), the amounts that
have been or are to be received from
customers for goods and services delivered to
them,
– and all expenses, the costs that have arisen
in generating revenues.
– when expenses are subtracted from
revenues, we obtain the actual profit or loss of
a company – the BOTTOM LINE
Auditing
• Auditing, a related but separate discipline, has
two sub-disciplines:
– External auditing - the process whereby an
independent auditor examines an organization's
financial statements and accounting records in
order to express an opinion as to the truth and
fairness of the statements and the accountant's
adherence to Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles (GAAP).
– Internal auditing - an examination in which
management, and not the external public, is the
main beneficiary. It is carried out usually by
auditors employed by the company.
The Big 4 (sometimes written as
the Big Four)
• a group of international accountancy and
professional services firms that handles
the vast majority of audits for publicly
traded companies as well as many private
companies.
• The members of the Big 4 are:
• PricewaterhouseCoopers
• Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu
• Ernst & Young
• KPMG.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Nature of Accounting: Assets Owns Liabilities OwesDokument10 SeitenThe Nature of Accounting: Assets Owns Liabilities OwesShaina Dyanne GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ProDokument39 SeitenThe Profisho abukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCFChap002 - Financial StatementsDokument23 SeitenFCFChap002 - Financial StatementsSozia TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FINANCIAL REPORTING - ScriptDokument9 SeitenFINANCIAL REPORTING - ScriptMutesa ChrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- EBITDAC – A New Financial MetricDokument24 SeitenEBITDAC – A New Financial Metricks frNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Financial Statements and Transaction AnalysisDokument64 SeitenIntroducing Financial Statements and Transaction AnalysisHazim AbualolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTRL Vol4Dokument19 SeitenCTRL Vol4Roberto SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Financial StatementsDokument18 SeitenTypes of Financial Statementsxyz mah100% (1)
- Financial Acct Midterm Study GuideDokument11 SeitenFinancial Acct Midterm Study GuideRobin TNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRA-NewDokument31 SeitenFRA-NewAbhishek DograNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branches of Accounting ExplainedDokument54 SeitenBranches of Accounting ExplainedAbby Rosales - Perez100% (1)
- Lecture 3 DoubleentrysystemDokument47 SeitenLecture 3 Doubleentrysystem叶祖儿Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHAP 1 FinaccDokument19 SeitenCHAP 1 FinaccQuyên NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repaso Capítulo 2 ContabilidadDokument9 SeitenRepaso Capítulo 2 ContabilidadpaulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial StatementDokument16 SeitenFinancial StatementCuracho100% (1)
- Financial Statements, Cash Flow, and TaxesDokument52 SeitenFinancial Statements, Cash Flow, and TaxesOwais MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 17Dokument4 SeitenCH 17lamarbawazeerrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anglais s1Dokument9 SeitenAnglais s1JassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teorico Comercial PDFDokument27 SeitenTeorico Comercial PDFluisinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial StatementsDokument31 SeitenFinancial StatementsJeahMaureenDominguez100% (2)
- Chap 4 - 7 KTTCDokument14 SeitenChap 4 - 7 KTTCQuyên NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting ProcessDokument17 SeitenAccounting ProcessDurga Prasad100% (1)
- Basic Accounting Reviewer: (Fundamentals)Dokument7 SeitenBasic Accounting Reviewer: (Fundamentals)Jonica Lou EugenioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow of Costs: Module 2 Introducing The Fin Statements, and Transaction Analysis. Start by Looking atDokument36 SeitenFlow of Costs: Module 2 Introducing The Fin Statements, and Transaction Analysis. Start by Looking atLong NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Terms Definitions GuideDokument8 SeitenAccounting Terms Definitions GuideNoby Ann Vargas LobeteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of AccountingDokument16 SeitenBasics of Accountingmule mulugetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Accounting PrinciplesDokument27 SeitenUnderstanding Accounting PrinciplesRaahim NajmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FABM 2 Key Elements and Financial StatementsDokument5 SeitenFABM 2 Key Elements and Financial StatementsLenard TaberdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PC-14 - Day 1 - Session-1 - 22.03.2023Dokument14 SeitenPC-14 - Day 1 - Session-1 - 22.03.2023Ajaya SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: A Framework For Financial Accounting: (Owner's ClaimsDokument26 SeitenChapter 1: A Framework For Financial Accounting: (Owner's ClaimsGenevieve SaldanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tally Chapter 3Dokument54 SeitenTally Chapter 3bhavya gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Financial StatementsDokument9 SeitenUnderstanding Financial StatementsAbsa TraderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary Unit19Dokument44 SeitenVocabulary Unit19Anna EgriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3.1Dokument23 SeitenChapter 3.1NaveenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting - An IntroductionDokument30 SeitenFinancial Accounting - An IntroductionShavik BaralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit I - Accounting EquationDokument6 SeitenUnit I - Accounting EquationAnime LoverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial StatementsDokument11 SeitenFinancial StatementsMab ShiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16 - Understanding Accounting and Financial InformationDokument6 SeitenChapter 16 - Understanding Accounting and Financial InformationsyyleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. Accounting in ActionDokument3 SeitenChapter 1. Accounting in ActionÁlvaro Vacas González de EchávarriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finance Ch4Dokument41 SeitenFinance Ch4Tofig HuseynliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial AccountingDokument13 SeitenFinancial AccountingBogdan MorosanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2Dokument38 SeitenLec 2Mohamed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Major AccountsDokument43 SeitenTypes of Major AccountsMaeshien Posiquit AboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument40 SeitenChapter 1Galata NugusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIMTECH PGDM (RM) 2020-22 Financial and Management AccountingDokument44 SeitenBIMTECH PGDM (RM) 2020-22 Financial and Management AccountingShubham DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 2: Financial Reporting and AccountingDokument41 SeitenLecture - 2: Financial Reporting and AccountingMuhammad Waheed SattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 2 Accounting TransactionsDokument52 SeitenCH 2 Accounting TransactionsGizachew100% (1)
- Finanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountDokument26 SeitenFinanacial Statements: Balance Sheet & Profit and Loss AccountAshok SeerviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument36 SeitenChapter 7Natanael Pakpahan100% (1)
- Introduction To AccountingDokument15 SeitenIntroduction To Accountingluna dupontNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1 FM2Dokument30 SeitenLesson 1 FM2Julie Opimo100% (1)
- Accounting Chap 4Dokument4 SeitenAccounting Chap 4kate santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- D196 Study Guide Answers & NotesDokument21 SeitenD196 Study Guide Answers & NotesAsril DoankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 002Dokument39 SeitenChap 002عادل الزرقيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abm01 - Module 4.2Dokument25 SeitenAbm01 - Module 4.2Love JcwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting and Financial Management in LogisticsDokument23 SeitenAccounting and Financial Management in LogisticsWah KhaingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apuntes AccountingDokument35 SeitenApuntes AccountingPatricia Barquin DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ihe 304Dokument283 SeitenIhe 304hoboda9159Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting - TestDokument9 SeitenFinancial Accounting - TestAdriana MassaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"Von Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"Noch keine Bewertungen
- MARGARINE INDUSTRIES 2011 Annual ReportDokument60 SeitenMARGARINE INDUSTRIES 2011 Annual Reportrachna357100% (1)
- Kunci Jawaban Semua BabDokument46 SeitenKunci Jawaban Semua BabMuhammad RifqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Cost AccountingDokument41 SeitenChapter 2 - Cost AccountingCarina Carollo Malinao100% (2)
- VNXX Fico BBPDokument36 SeitenVNXX Fico BBPvinay bangrawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOAL LATIHAN OSN tHE AKUNTANSIDokument2 SeitenSOAL LATIHAN OSN tHE AKUNTANSIBiEbbah MiszDhieysieysiey GitäLoversNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 ProblemsDokument8 Seiten3 ProblemsHassan SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 AISDokument3 SeitenChapter 2 AISgailmissionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partner profit division scenariosDokument7 SeitenPartner profit division scenariosTherese Janine HetutuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FAC1502 Study Unit 6 2021Dokument22 SeitenFAC1502 Study Unit 6 2021edsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test BankDokument26 SeitenTest BankMonica BuscatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 8 AssignemnetDokument8 SeitenCHP 8 AssignemnetBeenish JafriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Financial Accounting and Reporting 2nd Sem AY 2020 2021 Institutional Mock Board ExamDokument10 SeitenBasic Financial Accounting and Reporting 2nd Sem AY 2020 2021 Institutional Mock Board ExamBai Dianne BagundangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 1.0 - Break Even & Marginal AnalysisDokument6 SeitenMODULE 1.0 - Break Even & Marginal AnalysisTyron TayloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting 504 - Chapter 02 AnswersDokument19 SeitenAccounting 504 - Chapter 02 AnswerspicassaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACC 140 1 Period - Quiz 2Dokument7 SeitenACC 140 1 Period - Quiz 2Rica Mille MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument54 SeitenChapter 2Léo AudibertNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Book Answers 1Dokument50 SeitenAll Book Answers 1Josh Gabriel BorrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of Content Title Page NoDokument26 SeitenTable of Content Title Page Nopradeep110Noch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Evaluation & Ratio Analysis: Meghna Cement Mills LTDDokument10 SeitenPerformance Evaluation & Ratio Analysis: Meghna Cement Mills LTDSayed Abu SufyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 3a - Intrinsic ValuationDokument13 SeitenSession 3a - Intrinsic ValuationQuynh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11Dokument33 SeitenChapter 11pranav sarawagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teresita Buenaflor Shoes Canlas Paolo Luis Ca1aDokument60 SeitenTeresita Buenaflor Shoes Canlas Paolo Luis Ca1aracc wooyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DepreciationDokument19 SeitenDepreciationamit palNoch keine Bewertungen
- FY22 SingleAudit WBDokument79 SeitenFY22 SingleAudit WBDUSHIME Jean claudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reynaldo Gulane Cleaners Trial Balance and Financial StatementsDokument4 SeitenReynaldo Gulane Cleaners Trial Balance and Financial StatementsNicole Sarmiento83% (6)
- Journals in ScopusDokument119 SeitenJournals in ScopusAmir Asraf0% (1)
- CIE ANNUAL REPORT HIGHLIGHTSDokument8 SeitenCIE ANNUAL REPORT HIGHLIGHTSSana ZargarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Paper by Paper Guide (1) CimaDokument24 Seiten2010 Paper by Paper Guide (1) CimaUpeksha SrilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indofood CBP: Navigating WellDokument11 SeitenIndofood CBP: Navigating WellAbimanyu LearingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdc Journal ListDokument192 SeitenAbdc Journal ListRuwan Dileepa0% (1)