Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Foundations of Nursing Research and Evidence-Based Practice
Hochgeladen von
Florence Dian Nafesti Wahyudi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten17 SeitenYyyyy
Originaltitel
Lllll
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenYyyyy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten17 SeitenFoundations of Nursing Research and Evidence-Based Practice
Hochgeladen von
Florence Dian Nafesti WahyudiYyyyy
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 17
Foundations of Nursing Research
and Evidence-Based Practice:
Introduction
Universitas Advent Indonesia
Program Studi Ilmu Keperawatan
School Year of 2018-2019
Samuel M. Simanjuntak, Ph.D
RESEARCH METHOD FOR UNDERGRADUATE
STUDENTS IN NURSING
Faculty: Nursing Science
Semester/Academic Year: Regular Semester
2018-2019
Lecturers: Samuel M. Simanjuntak, PhD
Credit Hours: 2 Credits
Day/Time: Monday (08:00 – 10:00)
A. Course Objectives
The primary objectives of this
Research Method course are:
• To guide student to
understand the research
process and able to read
nursing research
publications with critical
perspective,
• To carry out circumscribed
research project, and
integrate the reasoning and
observations that make
nursing research scientific.
B. Teaching Strategies
• Class meeting will be executed
for 12 class periods and
laboratory meetings.
• Several teaching strategies are
employed to promote the
successful achievement of
theoretical and skills’
objectives, such as
lectures/dicussion, peer group
activity, reading assignments,
audiovisual, test writing and
review, demonstration, and
module practices.
• Students are required to
attend 80% class meetings at
minimum.
C. EVALUATION METHODS
A. Module practice and evaluation will be multiple choice and
essay that will reflect the classroom learning activities.
B. Research proposal by group is to be submitted on time,
demonstrate college level thinking and behavior. All
required work must be turned in before the final
examination schedule.
C. Percentage weighing for grade:
• Seminar participation (attendance, preparation,
participation): -------------------------------------------- 25%
• Practice module: ----------------------------------------- 50%
• Research proposal by group report & presentation: 25%
Total: 100%
C. EVALUATION METHODS
Grade is calculated on the following classification:
• 96 – 100% = A 66 – 71 % =C+
• 90 – 95 % = A- 60 – 65 % =C
• 84 – 89 % = B+ 56 – 59 % = C-
• 78 – 83 % = B 50 – 55 % =D
• 72 – 77 % = B- Below 50 % =F
D. REFERENCES:
Polit F. Denise & Beck T. Cheryl (2004). Nursing research: generating and
assessing evidence for nursing practice. 8th edition, Wolter Kluwer,
Philadelphia.
Macnee L. Carol & McCabe Susan (2008). Understanding nursing research:
reading and using research in evidence-based practice. 2nd edition,
Wolter Kluwer, Philadelphia.
Miller A. Scott (2007). Developmental research methods. 3rd edition, Sage,
U.K.
Seaman C.H. Catherine (1982). Research methods for undergraduate Students
in Nursing. 2nd edition, Appleton-Century-Croft, new York.
Who is Nurse?
The NURSE is a person who has completed a
program of basic, generalized nursing education
and is authorized by the appropriate regulatory
authority to practice nursing in his/her country.
Basic nursing education is a formally recognized program of
study providing a broad and sound foundation in the
behavioral, life, and nursing sciences for the general practice
of nursing, for a leadership role, and for post-basic education
for specialty or advanced nursing practice.
What the nurse does?
The nurse is prepared and authorized (ICN, 1987):
1) to engage in the general scope of nursing practice,
including the promotion of health, prevention of
illness, and care of physically ill, mentally ill, and
disabled people of all ages and in all health care and
other community settings;
2) to carry out health care teaching;
3) to participate fully as a member of the health care
team;
4) to supervise and train nursing and health care
auxiliaries; and
5) to be involved in research.
What is Nursing?
• Nursing encompasses autonomous and
collaborative care of individuals of all ages,
families, groups and communities, sick or well
and in all settings.
• Nursing includes the promotion of health,
prevention of illness, and the care of ill, disabled
and dying people. Advocacy, promotion of a safe
environment, research, participation in shaping
health policy and in patient and health systems
management, and education are also key
nursing roles (ICN, 2002).
Introduction
Goals of nursing research:
1. To teach you to
practice nursing
2. To find answers to
clinical questions
3. To live Evidence-based
Practice (EBP) in
practicing nursing
Introduction
Nursing research develops
knowledge to:
• Build the scientific
foundation for clinical
practice
• Prevent disease and
disability
• Manage and eliminate
symptoms caused by
illness
• Enhance end-of-life and
palliative care
Introduction
• Nurses use research to
provide evidence-
based care that
promotes quality
health outcomes for
individuals, families,
communities and
health care systems.
Introduction
• Nurses also use
research to shape
health policy in direct
care, within an
organization, and at the
local, state and federal
levels.
• Nurses conduct
research, use research
in practice, and teach
about research.
Position Statement
“Nursing research worldwide is committed to
rigorous scientific inquiry that provides a
significant body of knowledge to advance nursing
practice, shape health policy, and impact the
health of people in all countries. The vision for
nursing research is driven by the profession's
mandate to society to optimize the health and
well-being of populations.”
(American Nurses Association, 2003; International
Council of Nurses, 1999)
Position Statement
• Nurse researchers bring a holistic perspective
to studying individuals, families, and
communities involving a bio-behavioral,
interdisciplinary, and translational approach to
science.
Position Statement
• The priorities for nursing research reflect
nursing's commitment to the promotion of
health and healthy lifestyles, the advancement
of quality and excellence in health care, and
the critical importance of basing professional
nursing practice on research.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PD 1067 Water Code of The Philippines and Clean Water ActDokument44 SeitenPD 1067 Water Code of The Philippines and Clean Water ActNovy Jamboy Ragmac100% (2)
- Risk Management Plan TemplateDokument10 SeitenRisk Management Plan Templateamit singh0% (1)
- Evidence-Based Practice and Nursing ResearchDokument24 SeitenEvidence-Based Practice and Nursing ResearchMelody B. Miguel75% (4)
- Automated Sf8 ApitongDokument32 SeitenAutomated Sf8 Apitongjocelyn berlin100% (2)
- Evidence Based PracticeDokument28 SeitenEvidence Based PracticeSathish Rajamani100% (7)
- The Care Process: Assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation in healthcareVon EverandThe Care Process: Assessment, planning, implementation and evaluation in healthcareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scope of Nursing ResearchDokument16 SeitenScope of Nursing Researchvincy100% (6)
- Health Educ1Dokument43 SeitenHealth Educ1Querubin DandoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilferage Control in HospitalsDokument4 SeitenPilferage Control in HospitalsDr. Rakshit Solanki100% (3)
- Theoretical Foundation NursingDokument9 SeitenTheoretical Foundation NursingRyan Michael Oducado93% (14)
- Evidence-Based Practice: An Independent Study Short Course For Medical-Surgical NursesDokument32 SeitenEvidence-Based Practice: An Independent Study Short Course For Medical-Surgical Nursesamir hamzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code of EthicsDokument5 SeitenCode of EthicspvlreyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liver Anatomy and ResectionDokument62 SeitenLiver Anatomy and ResectionNurfa Mustamir100% (1)
- Philosophy of Nursing CollegeDokument4 SeitenPhilosophy of Nursing CollegeDelphy Varghese67% (3)
- Priorities of Nursing ResearchDokument37 SeitenPriorities of Nursing ResearchJisna AlbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research Power PointDokument125 SeitenNursing Research Power Pointrubycorazon_ediza100% (1)
- Health Education ReviewerDokument16 SeitenHealth Education ReviewerKiara Ash Beethoven100% (1)
- HEALTH EDUCATION PrelimsChapter1Lesson123Dokument12 SeitenHEALTH EDUCATION PrelimsChapter1Lesson123Ethel May GranilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchDokument22 Seiten1-Significance and Purposes of Nursing ResearchPrincess Ivan Gayagoy100% (1)
- Course Syllabus For Health EducationDokument7 SeitenCourse Syllabus For Health Educationseham_guirguis4808100% (5)
- EQ11151903A ThyssenKrupp Full and Public ContractDokument130 SeitenEQ11151903A ThyssenKrupp Full and Public Contractmozhi selvamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Health Lab Syllabus 2013 A (5a)Dokument8 SeitenAdult Health Lab Syllabus 2013 A (5a)mergreimelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Ed - Chapter 1Dokument29 SeitenHealth Ed - Chapter 1Kevin Camiloza100% (5)
- What Is RCM and RBIDokument2 SeitenWhat Is RCM and RBIChihiya Fitria Nurhayati0% (1)
- Syllabus Nursing Leadership and ManagementDokument13 SeitenSyllabus Nursing Leadership and ManagementMevelle Laranjo Asuncion100% (1)
- Research and Statistics IDokument9 SeitenResearch and Statistics IjonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum DevelopmentDokument38 SeitenCurriculum DevelopmentSharon Denham100% (1)
- Lesson 1 - Intro To Nursing Research 1Dokument24 SeitenLesson 1 - Intro To Nursing Research 1Jaylen CayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 00 - Course OutlineDokument6 Seiten00 - Course OutlineNicole ShereniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Research MethodsDokument40 SeitenOverview of Research MethodsOpuruiche ChukwudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- He Copy For The ClassDokument42 SeitenHe Copy For The Classjolibel gao-ayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Research Challenges and OpportunitiesDokument27 SeitenNursing Research Challenges and Opportunitiessara mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicalsurgicalnursing PDFDokument47 SeitenMedicalsurgicalnursing PDFJalak PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nurse As EducatorDokument28 SeitenNurse As Educatornaelnael chaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master Rotation PlanDokument13 SeitenMaster Rotation Plannathsujitkr1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- NSG 120 Funda LecDokument43 SeitenNSG 120 Funda LecNashebah A. BatuganNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.SC INTRODUCTIONDokument11 SeitenB.SC INTRODUCTIONmeiyappan.rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week1 Intro To NresDokument38 SeitenWeek1 Intro To Nresbailey ButcherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus Keperawatan Lintas Budaya 1st Sem 2019Dokument3 SeitenSyllabus Keperawatan Lintas Budaya 1st Sem 2019Yunus ElonNoch keine Bewertungen
- NURS 3305 Syllabus Spring 2022Dokument13 SeitenNURS 3305 Syllabus Spring 2022Chris GongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nur 302 Health AssessmentDokument4 SeitenNur 302 Health AssessmentCandy YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST John'S University of Tanzania School of Nursing: Ester Mbusa Mscanp BSCN RNM Evolution of NursingDokument93 SeitenST John'S University of Tanzania School of Nursing: Ester Mbusa Mscanp BSCN RNM Evolution of NursingIwenimacho kachiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 18 20 Teri Tench Power Point PresentationDokument27 Seiten3 18 20 Teri Tench Power Point Presentationapi-371944008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Community Health Nursing: Rica Marie B Valdez, RN, MAN University of Northern Philippines College of NursingDokument35 SeitenUnit 1 Community Health Nursing: Rica Marie B Valdez, RN, MAN University of Northern Philippines College of NursingMarjorie UmipigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Concepts of Nursing Processes 2Dokument12 SeitenBasic Concepts of Nursing Processes 2joya anggraNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE - SIGNIFICANCE - OF - THEORY - TO - NURSING - AS - A - PROFESSION - (TFN - Updated) (2) (Autosaved)Dokument36 SeitenTHE - SIGNIFICANCE - OF - THEORY - TO - NURSING - AS - A - PROFESSION - (TFN - Updated) (2) (Autosaved)Galenn BarrionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Education LM Week 1 and 2Dokument8 SeitenHealth Education LM Week 1 and 2Joice LenteriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Education SCRBDDokument44 SeitenHealth Education SCRBDgrindave09302010Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evidence-Based Practice: An Independent Study Short Course For Medical-Surgical NursesDokument33 SeitenEvidence-Based Practice: An Independent Study Short Course For Medical-Surgical NurseschrisyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SGT University: M. Sc. NursingDokument9 SeitenSGT University: M. Sc. NursingRajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabarrubias Jovelyn - Enrichment Activity For Module 1Dokument3 SeitenCabarrubias Jovelyn - Enrichment Activity For Module 1cabarrubiasjovy40Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 .2 Nursing Research 9-9Dokument22 SeitenTopic 1 .2 Nursing Research 9-9Xy-nique De Leon100% (1)
- 1706169175090-Evidence - Based - Practice 2Dokument31 Seiten1706169175090-Evidence - Based - Practice 2balshhry598Noch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Alignment and EvaluationDokument11 SeitenCurriculum Alignment and Evaluationapi-695177304Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHN IDokument17 SeitenCHN IMuqaddas TasneemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Nursing ResearchDokument44 SeitenIntroduction To Nursing ResearchpremaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Overview of ResearchDokument22 Seiten1 - Overview of ResearchYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Theory I Obstetric and Pediatric Nursing CURRICULUM (PDFDrive)Dokument201 SeitenNursing Theory I Obstetric and Pediatric Nursing CURRICULUM (PDFDrive)HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance and Purposes of Research: Instruction: Answer Comprehensively and ExtensivelyDokument3 SeitenImportance and Purposes of Research: Instruction: Answer Comprehensively and ExtensivelyKarl Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 111 OverviewDokument3 SeitenNCM 111 OverviewDan HizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Health Nursing Approach: Mrs - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingDokument21 SeitenCommunity Health Nursing Approach: Mrs - Neethu Vincent Asst Professor KVM College of NursingNeethu VincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovativejournal,+Journal+Manager,+OVERVIEW of NURSING RESEARCHDokument9 SeitenInnovativejournal,+Journal+Manager,+OVERVIEW of NURSING RESEARCHEmmanuela AzubugwuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical SupervisionDokument19 SeitenClinical Supervisionsrinivasana100% (1)
- Future Directions of Research in Nursing+Importance of Research in Nursing 2 +overview of Research ProcessDokument8 SeitenFuture Directions of Research in Nursing+Importance of Research in Nursing 2 +overview of Research Processمهند جمال اسدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module guideNURS209 ClinicalDokument40 SeitenModule guideNURS209 ClinicalScelo CalvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Template For Evaluation of Curriculum Week 4Dokument12 SeitenTemplate For Evaluation of Curriculum Week 4api-598498344Noch keine Bewertungen
- B260: Fundamentals of Nursing Practice: Spring, 2015 SyllabusDokument6 SeitenB260: Fundamentals of Nursing Practice: Spring, 2015 Syllabuslouie john abilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIVDokument1 SeiteHIVFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
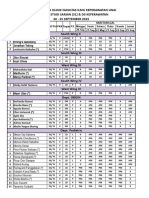
- Jadwal Praktek Klinik Fakultas Ilmu Keperawatan Unai Program Studi Sarjan (S1) & D3 Keperawatan 20 - 25 SEPTEMBER 2015Dokument24 SeitenJadwal Praktek Klinik Fakultas Ilmu Keperawatan Unai Program Studi Sarjan (S1) & D3 Keperawatan 20 - 25 SEPTEMBER 2015Florence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HIVDokument1 SeiteHIVFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
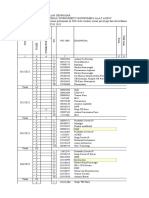
- NO Nama Mahasiswa Nilai Lab Nilai Mid KuisDokument2 SeitenNO Nama Mahasiswa Nilai Lab Nilai Mid KuisFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadwal JIKOM S-1 Section ADokument3 SeitenJadwal JIKOM S-1 Section AFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
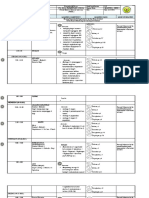
- Absen Praktek Profesi Ners Section F Gerbong: Keperawatan GerontikDokument13 SeitenAbsen Praktek Profesi Ners Section F Gerbong: Keperawatan GerontikFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadwal Jikom PKK Sec. ADokument3 SeitenJadwal Jikom PKK Sec. AFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LinkDokument1 SeiteLinkFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd. CADDokument60 Seiten3rd. CADstevenhtktNoch keine Bewertungen
- LinkDokument1 SeiteLinkFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Learninginnursingeducation ChallengesandopportunitiesDokument4 SeitenE Learninginnursingeducation ChallengesandopportunitiesFlorence Dian Nafesti WahyudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Situation Analysis: Children in Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoDokument335 SeitenSituation Analysis: Children in Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim MindanaoTerence YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coonrad Morrey ElbowDokument2 SeitenCoonrad Morrey Elbowgcif88Noch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Soares+et+al V3Dokument7 Seiten05 Soares+et+al V3Elsa Marta SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Addiction - ResearchDokument13 SeitenInternet Addiction - ResearchpipedsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDokument8 SeitenNursing Skills Checklistapi-353656227Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medihuanna Brand GuidelinesDokument71 SeitenMedihuanna Brand GuidelinespuskickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pandakaking-Puti: KampupotDokument10 SeitenPandakaking-Puti: KampupotgosmileyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Scoping DocumentDokument10 SeitenDraft Scoping DocumentJohn N. AllegroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPRDokument45 SeitenCPRJames Elwood DoyolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baba Farid University of Health Sciences, Faridkot Provisional Merit List of Candidates Applied For Admission To MBBS/BDS Courses Under NEET UG-2021Dokument130 SeitenBaba Farid University of Health Sciences, Faridkot Provisional Merit List of Candidates Applied For Admission To MBBS/BDS Courses Under NEET UG-2021Nitish GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Instrumentatio N: Hanif Andhika WDokument35 SeitenSpinal Instrumentatio N: Hanif Andhika WHanifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba-40l Buffering Agent - 1Dokument9 SeitenBa-40l Buffering Agent - 1Sherlock HolmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irradiated Foods 2003 PDFDokument52 SeitenIrradiated Foods 2003 PDFDiana BratuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Jurnal Varicella - Dewi Manik Aulia Fadli - 16700096Dokument26 SeitenReview Jurnal Varicella - Dewi Manik Aulia Fadli - 16700096Lia FadliNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Nisi Dominus Frustra" College of Nursing & Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern LeyteDokument2 Seiten"Nisi Dominus Frustra" College of Nursing & Allied Health Sciences Maasin City, Southern Leytecoosa liquorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genesis Platinum Manual 8090Dokument23 SeitenGenesis Platinum Manual 8090Huni BuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diverifikasi DPJP AgustusDokument6 SeitenDiverifikasi DPJP AgustusKadek candraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing Elements of Therapeutic ConversationDokument16 SeitenHealing Elements of Therapeutic ConversationFERNANDO CABRERA SANTOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental Monitoring Incubation Conditions - JustificationDokument4 SeitenEnvironmental Monitoring Incubation Conditions - Justificationveerreddy_157808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Closure MineDokument14 SeitenClosure MineAmilton filhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panangbigbig Ken Panangisurat Kadagiti Numero Manipud 0 Aginggana 100Dokument4 SeitenPanangbigbig Ken Panangisurat Kadagiti Numero Manipud 0 Aginggana 100EVANGELINE DARRASNoch keine Bewertungen
- P CLS14 Powertec Compact Leg Sled ManualDokument15 SeitenP CLS14 Powertec Compact Leg Sled ManualElizabeth GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science - 11 - Q1 - 13 - Use of The Other Ingredients in Cleaning Agents 08082020Dokument18 SeitenPhysical Science - 11 - Q1 - 13 - Use of The Other Ingredients in Cleaning Agents 08082020gwynceNoch keine Bewertungen