Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Antimicrobia Use
Hochgeladen von
goyeniran0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten7 Seitenantimicrobia use
Originaltitel
antimicrobia use
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenantimicrobia use
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
37 Ansichten7 SeitenAntimicrobia Use
Hochgeladen von
goyeniranantimicrobia use
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
Rational use of Antibiotic
• There is a need to improve rational use of
antibiotics in Africa.
• Antibiotics are life savers.
• No new antibiotic has been discovered in the
past few years.
• Antibiotics we have currently are limited in
stock.
• If depleted, there will be nothing left for us to
use
Factors contributing to irrational use of
antibiotics
• Irrational use is not helped by self-purchasing
of antibiotics which is common in Africa .
• Greater accessibility to antibiotics has
contributed to their irrational and excessive
use leading to increasing antimicrobial
resistance (AMR), a decline in effectiveness
and strain on health –care systems.
Examples of irrational use of
antibiotics
• Using longer courses than necessary
• Unnecessary use of combinations where a
single drug would be equally effective.
• Use of broad- spectrum antibiotics where a
narrow spectrum agent is indicated.
• Prophylactic use of antibiotic without any
proven benefit.
• Continuous use of parenteral antibiotics
instead of oral switch.
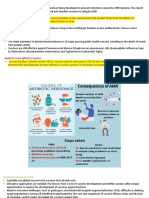
AMR outcomes
• Increase in mortality -It is estimated that AMR
infections currently causes approximately 50,000
deaths a year in Europe and US alone, increasing
to several hundred thousands when other
countries are included.
• The continual rise in AMR could result in infection
that are resistant to antibiotics becoming a
leading cause of death by 2050, with a clear link
between overuse of antibiotics and AMR
• Prolonged Hospital Stay.
• In some hospitals in Africa , antibiotics
account for up to 35% of medicine
expenditure.
• There are some concerns and issues with
antibiotic prescribing in Botswana for example
prescribing antibiotics for URTI which requires
just cough mixture
.
Factors that drive AMR
• Indiscriminate use of antibiotics e.g areas with
highest resistant rate also have highest
antimicrobial use
• Gene transfer between bacteria
• Travel
• Poor sanitation & hygiene
• Decrease in antibiotic development.
• These factors influence the development of AMR
jeopardizing the health of individual and society.
Way forward
• There have been combined activities in Botswana
to improve the use of antibiotics including the
development of antibiotic guideline and other
measures like strict policy however, research has
shown that guideline are not always followed.
• We need to document resistance patterns
• Plan future research activities since without such
studies planning is difficult.
• Development of infection control committee
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Rational Use of AntibioticsDokument5 SeitenRational Use of Antibioticsgoyeniran100% (1)
- Rational Drug Use - AntibioticsDokument4 SeitenRational Drug Use - AntibioticsgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Contributing To Irrational Use of AntibioticsDokument2 SeitenFactors Contributing To Irrational Use of AntibioticsgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Insight To Antibiotic ResistanceDokument25 SeitenNew Insight To Antibiotic Resistancefatma omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Resistance PresentationDokument10 SeitenAntibiotic Resistance PresentationGorrin MarquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Stewardship by Neha JaniDokument51 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardship by Neha Janinehah3943Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Antibiotic Stewardship and Antibiogram jxRqkQ9Dokument7 Seiten2 Antibiotic Stewardship and Antibiogram jxRqkQ9venkybyagari1129Noch keine Bewertungen
- AAW 2018 PowerPoint PresentationDokument60 SeitenAAW 2018 PowerPoint PresentationAgung RahmadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- S&W Antibiotics-2Dokument30 SeitenS&W Antibiotics-2sandykarmakar32Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics: Success and FailuresDokument43 SeitenAntibiotics: Success and Failurestummalapalli venkateswara raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Guardians: DR Brendan KennedyDokument26 SeitenAntimicrobial Guardians: DR Brendan KennedyDamianLove ChannelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Strategic Research Agenda of The Joint Programming Initiative On Antimicrobial Resistance - Why Is It Necessary?Dokument41 SeitenThe Strategic Research Agenda of The Joint Programming Initiative On Antimicrobial Resistance - Why Is It Necessary?JoseeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10. Concept of Essentail Drugs, Rational Use of Medicines and Prescription AuditDokument76 SeitenLecture 10. Concept of Essentail Drugs, Rational Use of Medicines and Prescription AuditSnehasish GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Description: Antibiotic ResistanceDokument2 SeitenProject Description: Antibiotic ResistanceVisha MainaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Clinical PhamacyDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Clinical Phamacypublic mailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Debate Pro Contra AntimicrobialDokument7 SeitenDebate Pro Contra Antimicrobialfitriani ikhsaniatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay About "The Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance in Developing Countries - Causes and Control Strategies"Dokument3 SeitenEssay About "The Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance in Developing Countries - Causes and Control Strategies"patricia diculescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMR Hindu July 2022 Special EditionDokument7 SeitenAMR Hindu July 2022 Special EditionAditya KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance (AMRDokument3 SeitenInsights into Antimicrobial Resistance (AMRJai GodaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANTIBIOTICS23Dokument94 SeitenANTIBIOTICS23RPMFA RPMFANoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline Antibiotic RationalDokument35 SeitenGuideline Antibiotic RationalIstianah EsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic StewardshipDokument6 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardshipkyliever100% (1)
- Antibiotic ResistanceDokument12 SeitenAntibiotic ResistanceSirwan SamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrational Use of Antibiotics PPT Final - 110919Dokument20 SeitenIrrational Use of Antibiotics PPT Final - 110919neha13t100% (2)
- Antimicrobial Stewardship Program BenefitsDokument31 SeitenAntimicrobial Stewardship Program BenefitsPrathusha Umakhanth100% (2)
- CMC Hospital Antibiotic Policy2012 PDFDokument43 SeitenCMC Hospital Antibiotic Policy2012 PDFO.r. Cadz100% (1)
- 8. PERAN APOTEKER - MDRDokument76 Seiten8. PERAN APOTEKER - MDRauliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Policy Guide for Medical CareDokument35 SeitenAntibiotic Policy Guide for Medical CareArpita Garg100% (2)
- Rational Use of AntibioticsDokument85 SeitenRational Use of AntibioticsAHMAD MAHIR BIN CHE RAHMATNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceDokument4 SeitenThe Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceAnto BijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSW Factsheet Cost InfetionsDokument2 SeitenGSW Factsheet Cost Infetionscharanmann9165Noch keine Bewertungen
- 222 317 1 SM PDFDokument4 Seiten222 317 1 SM PDFraraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading #1 Mission Critical - Preventing Antibiotic Resistance - Lesson 4Dokument2 SeitenReading #1 Mission Critical - Preventing Antibiotic Resistance - Lesson 4ynvrvy8vvxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combating Antibiotic Drug Resistance in PakistanDokument32 SeitenCombating Antibiotic Drug Resistance in PakistanSalman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AntibioticsDokument10 SeitenAntibioticsMurtdha ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consumer World Amr Awareness Week 2023 Power Point PresentationDokument29 SeitenConsumer World Amr Awareness Week 2023 Power Point PresentationSoha GalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic EfficacyDokument1 SeiteAntibiotic EfficacyELLA MAUREEN M DIMARUCUTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic in BacteriaDokument28 SeitenAntibiotic in BacteriaSanjetha ElangovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Antibiotic Awareness Week aims to increase awareness of antibiotic resistance (39Dokument4 SeitenWorld Antibiotic Awareness Week aims to increase awareness of antibiotic resistance (39Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Eco-EnvironmentDokument33 SeitenAntibiotic Resistant Bacteria in Eco-Environmentkedar karkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecec 03 00052Dokument4 SeitenEcec 03 00052Matiyas ZewdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Antibiotic Awareness Week 2019Dokument27 SeitenPhilippine Antibiotic Awareness Week 2019Lorenz L. Llamas IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- WHY WE MISUSE ANTIBIOTICS BY Dr.T.V.RaoDokument22 SeitenWHY WE MISUSE ANTIBIOTICS BY Dr.T.V.RaoTummalapalli Venkateswara RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- IFMSA Policy Proposal (Antimicrobial Resistance)Dokument7 SeitenIFMSA Policy Proposal (Antimicrobial Resistance)maimona abdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of AB For UTI Awareness PresentationDokument50 SeitenUse of AB For UTI Awareness PresentationAmnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Use and Resistance in ChildrenDokument15 SeitenAntibiotic Use and Resistance in ChildrenAnastasia PasaribuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Stewardship in OrthopedicsDokument17 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardship in Orthopedicsjomari dvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Op Amr FinalDokument2 SeitenOp Amr FinalJulio Andro ArtamulandikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotics? Boon or Bane?Dokument9 SeitenAntibiotics? Boon or Bane?Hao TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determinants Impacting The Use of Antibiotics Among Patients Visiting The Dental Clinic at Kampala International University Teaching Hospital in Bushenyi-Ishaka Municipality, WesteDokument15 SeitenDeterminants Impacting The Use of Antibiotics Among Patients Visiting The Dental Clinic at Kampala International University Teaching Hospital in Bushenyi-Ishaka Municipality, WesteKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Stewardship Program Promotes 5R ApproachDokument20 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardship Program Promotes 5R ApproachMing Yew TingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti-Microbial Resistance and PreventionDokument29 SeitenAnti-Microbial Resistance and Preventionmahamoud0% (1)
- The Pharmacist's Role in Preventing Antibiotic Resistance: Abstract and IntroductionDokument5 SeitenThe Pharmacist's Role in Preventing Antibiotic Resistance: Abstract and IntroductionDeginaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rational Use of Abx-ICUDokument46 SeitenRational Use of Abx-ICUYosef AssefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic PolicyDokument40 SeitenAntibiotic PolicyMona MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surveillance of Antibiotic Consumption: Hege Salvesen BlixDokument44 SeitenSurveillance of Antibiotic Consumption: Hege Salvesen BlixJust MahasiswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Elements Antibiotic Stewardship Appendix BDokument7 SeitenCore Elements Antibiotic Stewardship Appendix B19112281s3785Noch keine Bewertungen
- THESIS Collated CH 1-5Dokument34 SeitenTHESIS Collated CH 1-5Hanako AranillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amoxicillin Guide: Draw out your antibiotic weapon to defeat bacterial infections like pneumonia, STDs, urinary tract and skin infectionsVon EverandAmoxicillin Guide: Draw out your antibiotic weapon to defeat bacterial infections like pneumonia, STDs, urinary tract and skin infectionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (23)
- Natural Alternatives to Antibiotics: How you can Supercharge Your Immune System and Fight InfectionVon EverandNatural Alternatives to Antibiotics: How you can Supercharge Your Immune System and Fight InfectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug UseDokument7 SeitenDrug UsegoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Toelf Speaking Topics To Practise WithDokument3 SeitenSome Toelf Speaking Topics To Practise WithgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- AmrDokument2 SeitenAmrgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line GraphDokument13 SeitenLine GraphMikelAgberoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADR ReportingDokument3 SeitenADR ReportinggoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Medicine List: Why It's NeededDokument1 SeiteEssential Medicine List: Why It's NeededgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of EMLDokument1 SeiteAdvantages of EMLgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Medicine ListDokument1 SeiteEssential Medicine ListgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQDokument12 SeitenEthics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQsunshine151100% (1)
- Why ADR Reporting Is NecessaryDokument1 SeiteWhy ADR Reporting Is NecessarygoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Attitude 1Dokument12 SeitenBuilding Attitude 1goyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graph Sample For Ielts To ReadDokument11 SeitenGraph Sample For Ielts To ReadgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Prepare For IELTS - ListeningDokument10 SeitenHow To Prepare For IELTS - ListeningKim AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQDokument12 SeitenEthics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQsunshine151100% (1)
- FP Gee TheoryDokument67 SeitenFP Gee Theorym_hossamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQDokument12 SeitenEthics Codes For Any Pharmacists in Details. With MCQsunshine151100% (1)
- Practice Topics (IBT TOEFL Independent Speaking)Dokument2 SeitenPractice Topics (IBT TOEFL Independent Speaking)Bindita ChaudhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Line GraphDokument8 SeitenWriting Line GraphgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Speaking Topics from AIPPG.comDokument2 SeitenIELTS Speaking Topics from AIPPG.comTrang TranNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOEFL Speaking QuestionDokument4 SeitenTOEFL Speaking QuestiongoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOEFL Speaking Question 2Dokument10 SeitenTOEFL Speaking Question 2goyeniran100% (1)
- TOEFL Speaking Question 1Dokument25 SeitenTOEFL Speaking Question 1goyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ielts SamplesDokument2 SeitenIelts SamplesgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- International sporting events ease tensions but not a cure-allDokument3 SeitenInternational sporting events ease tensions but not a cure-allgoyeniranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Guidelines For NarcoticsDokument4 SeitenClinical Guidelines For NarcoticsClara VerlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gharbis Classification of Hydatid Cyst PDFDokument60 SeitenGharbis Classification of Hydatid Cyst PDFPalwasha MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic StewardshipDokument6 SeitenAntibiotic Stewardshipkyliever100% (1)
- Motivation Letter - EmboDokument1 SeiteMotivation Letter - EmboFebby NurdiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pe 2 Week 6Dokument2 SeitenPe 2 Week 6Nicoleigh ArnejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blunt Trauma AbdomenDokument41 SeitenBlunt Trauma AbdomenSanthanu SukumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Paul Hospital of Tuguegarao, Inc.: Monthy Unit Performance ReportDokument3 SeitenSt. Paul Hospital of Tuguegarao, Inc.: Monthy Unit Performance ReportDani CawaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of EpidemiologyDokument9 SeitenInternational Journal of Epidemiologycooky maknaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Emergencies in The Dental Practice Poster: Revised and UpdatedDokument8 SeitenMedical Emergencies in The Dental Practice Poster: Revised and UpdatedMelissa Gabriela Sánchez SaucedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wash in School ProgramDokument12 SeitenWash in School ProgramSDO MedicalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 852-Article Text-1782-1-10-20221103Dokument11 Seiten852-Article Text-1782-1-10-20221103ritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Paper: On Joint ReplacementDokument144 SeitenWhite Paper: On Joint ReplacementCosme MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial PMR Pahang 2010 English (p1)Dokument9 SeitenTrial PMR Pahang 2010 English (p1)abdfattah50% (2)
- CAz Clinic Poliserozita UMFDokument16 SeitenCAz Clinic Poliserozita UMFMariaIoanaCoroiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- YEAR 2019 Region: VI Province / City: Iloilo Municipality: Dumangas Barangay: TamboboDokument3 SeitenYEAR 2019 Region: VI Province / City: Iloilo Municipality: Dumangas Barangay: Tamboboc lazaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liposomal Drug Delivery SystemDokument15 SeitenLiposomal Drug Delivery SystemsyeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student's Handbook 2014Dokument52 SeitenStudent's Handbook 2014Ahmed MawahibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chairside Diagnostic Kit - Dr. PriyaDokument25 SeitenChairside Diagnostic Kit - Dr. PriyaDr. Priya PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical Insufficiency:: Miscarriage Early (Premature)Dokument2 SeitenCervical Insufficiency:: Miscarriage Early (Premature)Ardelean EmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG Management of Dementia (2nd Edition)Dokument162 SeitenCPG Management of Dementia (2nd Edition)umiraihana1Noch keine Bewertungen
- TP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1Dokument2 SeitenTP-L3-402 Nursing Admin Checklist 5.1عبيدة محمد ابو عابدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progyluton-26 1DDokument16 SeitenProgyluton-26 1DUsma aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Terminal Illness in ChildrenDokument8 SeitenManagement of Terminal Illness in Childrenraneen reazNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Chronic Pain and FatigueDokument6 SeitenNCP Chronic Pain and FatigueMary Rose Bell Arias100% (1)
- Salvia, DivornumDokument1 SeiteSalvia, Divornumeab7686Noch keine Bewertungen
- DiabetesDokument515 SeitenDiabetesPaola Rivera DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesDokument5 SeitenDCA-Coalition Insulin GuidelinesNabihah BarirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invitae - TRF938 Invitae FVT VUS OrderFormDokument2 SeitenInvitae - TRF938 Invitae FVT VUS OrderFormMs.BluMoon SageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hahn El 2016Dokument9 SeitenHahn El 2016ka waiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI BookshelfDokument23 SeitenShwachman-Diamond Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelfgrlr0072467Noch keine Bewertungen