Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Olive Oil
Hochgeladen von
Hamzah A. LaftaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Olive Oil
Hochgeladen von
Hamzah A. LaftaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The vegetable oil processing industry involves the extraction and processing of oils and fats from vegetable
sources. The extraction
processes are generally mechanical (boiling for fruits, pressing for seeds and nuts) or involve the use of solvent such as hexane.
Sesame seed has higher oil content (around 50%) than most of the known oilseeds. Sesame oil is generally regarded as high-priced
and high-quality oil.
1-health food for disease
prevention
2-Studies have also shown that
including sesame in the diet can
improve antioxidant capacity
3-Sesame oil is rich in fats, proteins,
carbohydrates, fiber and some
minerals
4-Other uses of sesame oil are that
it is used as a salad or cooking oil,
shortening margarine and soap,
paints, cosmetics, pesticide, and
perfumes
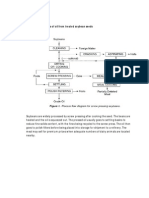
Fig. Process flow Diagram of the Sesame Oil Production
is a screw-type machine that presses oil seeds through a caged
After the seeds were roasted at
barrel-like cavity. Raw materials enter through the head box as different temperatures and
shown on Figure 1 and the waste products exit the other side. durations ,are then crushed to
increase the active surface, or
press the seed before it going to
solvent extraction (leaching) by
adding hexane or any solvent
like acetone to the sesame cake
after pressing. this operation can
extract the residual oil in the
cake.
Types of solvent
The right tube is the oil that extracted
Hexane is relatively inexpensive and produces a high oil yield, the by hexane, the left tube is the oil that
amount of hexane left in the edible oil is in the parts per million extracted using ethanol.
range. hexane has an aliphatic structure which makes it very
miscible with oil.
Ethanol are safer than hexane with lower toxicity and lower
flammability, However, the main constituents of sesame oil are
esters derived from glycerol and aliphatic saturated or unsaturated
fatty acids. The aliphatic structure gives alcohols such as ethanol
and isopropanol a limited solubility.
References:
1. Chelangat, Salome. “World's Leading Producers of Sesame Oil.” WorldAtlas, worldatlas.com. Updated 25 Aug 2017. Accessed 11 Dec 2017.
2. National Nutrient Database, ars.usda.gov. “Seeds, Sesame Seeds, Whole, Dried”. United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. Accessed 11
Dec 2017.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Essential Oils Vitality Guide: 33 Advanced Aromatherapy Tips and Tricks for Weight Loss, Stress Relief And Anti-Aging: Aromatherapy, Longevity, Organic Remedies SeriesVon EverandEssential Oils Vitality Guide: 33 Advanced Aromatherapy Tips and Tricks for Weight Loss, Stress Relief And Anti-Aging: Aromatherapy, Longevity, Organic Remedies SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vetiver Essential Oil Powerfully Grounding & Reassuring Oil Plus+ How to Use Guide & Recipes!: Healing with Essential OilVon EverandVetiver Essential Oil Powerfully Grounding & Reassuring Oil Plus+ How to Use Guide & Recipes!: Healing with Essential OilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Essential OilsDokument9 SeitenExtraction of Essential OilsBhaby ForevherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Esstential OilsDokument10 SeitenExtraction of Esstential Oilstessa mariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential oil in one titleDokument21 SeitenEssential oil in one titleعلي الطياريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrolytic Maceration and Cold Fat ExtractionDokument4 SeitenHydrolytic Maceration and Cold Fat ExtractionMardiyati AlwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnfleurageDokument4 SeitenEnfleuragenye nyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Medicinal Plants StudiesDokument10 SeitenJournal of Medicinal Plants StudiesCeleste MitchellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment # 4 Object: Requirement:: 1. Expression MethodDokument4 SeitenExperiment # 4 Object: Requirement:: 1. Expression Methodurooj latifNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLVENT EXTRACTION OF EDIBLE OILSDokument5 SeitenSOLVENT EXTRACTION OF EDIBLE OILSBartwell TazvingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil ExtractionDokument30 SeitenOil Extractionraisameh23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Essential Oil From FragrantDokument9 SeitenExtraction of Essential Oil From FragrantFakhar AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonus Infused OilsDokument4 SeitenBonus Infused OilsSubash DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volatile OilsDokument36 SeitenVolatile OilsGeillan Kim ManolidNoch keine Bewertungen
- OIL AND FAT Technology Lectures III - Crude Oil ProductionDokument55 SeitenOIL AND FAT Technology Lectures III - Crude Oil ProductionDavid Flores MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Extraction Processes: Screw Pressing, Solvent Extraction & Extruding-ExpellingDokument6 SeitenOil Extraction Processes: Screw Pressing, Solvent Extraction & Extruding-ExpellingNahid Akhter KathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 388 1574 2 PBDokument3 Seiten388 1574 2 PBAnz PaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 2 - Extraction of Coconut OilDokument9 SeitenExperiment No 2 - Extraction of Coconut OilChe PetarealNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument10 SeitenChemistryAswin AswinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Ilmiah Widya Teknik: Enfleurage Essential Oil From Jasmine and Rose Using Cold Fat AdsorbentDokument4 SeitenJurnal Ilmiah Widya Teknik: Enfleurage Essential Oil From Jasmine and Rose Using Cold Fat AdsorbentJakobus Benny SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT - IV 1. Processing of Fats and OilsDokument12 SeitenUNIT - IV 1. Processing of Fats and OilsHumera AdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patients With Asthma Benefit From Concomitant TherapyhhhDokument31 SeitenPatients With Asthma Benefit From Concomitant TherapyhhhNikolaos IoannoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Edible Oil Extraction EditDokument12 SeitenReport On Edible Oil Extraction EditVIPratik KOLINoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 Chapter 2Dokument35 Seiten08 Chapter 2Nur Aini IktikhafsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Make Cooking OilsDokument7 SeitenHow To Make Cooking OilsnightclownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Refining ProcessDokument16 SeitenOil Refining Processruman ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Chemical and BioengineeringDokument7 SeitenAddis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: School of Chemical and BioengineeringKidan ayenewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sunflower ProcessDokument7 SeitenSunflower ProcessJose David VillavicencioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry of Oils, Fats and Wax Processing: By: Alolod, Liezel Banuelos, Erika Grace Barrola, Marinel Lea GDokument20 SeitenChemistry of Oils, Fats and Wax Processing: By: Alolod, Liezel Banuelos, Erika Grace Barrola, Marinel Lea GMica Ella EstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easy ScentsDokument36 SeitenEasy ScentsLiliana VazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Candlenut Particels Size On The Result of Candlenut OilDokument9 SeitenThe Effects of Candlenut Particels Size On The Result of Candlenut Oilbudi darma maulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expression methodsDokument5 SeitenExpression methodsamama khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 SBT 720 Lecture 6-7Dokument23 SeitenUnit 1 SBT 720 Lecture 6-7star beautyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbal Cosmetics PharmacognosyDokument6 SeitenHerbal Cosmetics PharmacognosySanketraje JadhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Processesmainly Includes Rice Bran Oil Expelling, Extraction and RefiningDokument2 SeitenProcessesmainly Includes Rice Bran Oil Expelling, Extraction and RefiningmaniaeronauticalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary - EO Terminology - Ink FriendlyDokument8 SeitenGlossary - EO Terminology - Ink FriendlyMaría Garrido ContrerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHE 320 Term PaperDokument6 SeitenCHE 320 Term PaperModesola ShoroyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galenical PreperationDokument35 SeitenGalenical PreperationAhmed ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis and Performance of Four Stroke Diesel Engines by Using Polyalthia Longifolia, Annona Squamosa and Zizibus SeedsDokument31 SeitenAnalysis and Performance of Four Stroke Diesel Engines by Using Polyalthia Longifolia, Annona Squamosa and Zizibus Seedsk eswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Dragon Fruit Seed Oil With Other Edible Seed OilsDokument4 SeitenComparative Study of Dragon Fruit Seed Oil With Other Edible Seed OilsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lynea Schultz-Ela Aromatherapy: Consulting For The Natural Products IndustryDokument4 SeitenLynea Schultz-Ela Aromatherapy: Consulting For The Natural Products IndustryNilamdeen Mohamed ZamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Galenical PreperationsDokument35 SeitenGalenical Preperationsumart4843Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction - ChavezDokument3 SeitenExtraction - ChavezGabreille Rullamas ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Papers The Effects of Candlenut Particels Size On The Result of Candlenut OilDokument11 SeitenEnglish Papers The Effects of Candlenut Particels Size On The Result of Candlenut Oilbudi darma maulanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec1 Unit1Dokument28 SeitenLec1 Unit1ghoshna jyotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Of Life: Harnessing the Power of Nature for Everydey Well-BeingVon EverandOil Of Life: Harnessing the Power of Nature for Everydey Well-BeingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alleviate EnglishDokument2 SeitenAlleviate EnglishJeferson RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Making CreamDokument9 SeitenMaking CreamJai MurugeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oils-Volatile Oils: Dr. Sharififar 2012Dokument52 SeitenEssential Oils-Volatile Oils: Dr. Sharififar 2012كهلان البريهيNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooking OilDokument6 SeitenCooking OilMAGOMU DAN DAVIDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oil ExtractionDokument2 SeitenEssential Oil ExtractionAbdul MajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Spill Cleanup LabDokument3 SeitenOil Spill Cleanup LabMadison BoatlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oils For Beginners: Aromatherapy and Essential Oils for Weight Loss, Natural Remedy, Stress Relief, Body Massage and BeautyVon EverandEssential Oils For Beginners: Aromatherapy and Essential Oils for Weight Loss, Natural Remedy, Stress Relief, Body Massage and BeautyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLID-LIQUID EXTRACTIONDokument4 SeitenSOLID-LIQUID EXTRACTIONHarshal Agrawal100% (1)
- Chem ProjectDokument17 SeitenChem ProjectSora RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Oil Extraction TechniquesDokument10 SeitenEssential Oil Extraction Techniquestele6100% (1)
- Extraction of Essential Oil From AniseedDokument5 SeitenExtraction of Essential Oil From AniseedKrishna GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatherapy GuideDokument26 SeitenAromatherapy Guideglucy5670100% (11)
- Unit Processing MethodsDokument12 SeitenUnit Processing MethodsIsabella DonatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluidization: Unit OperationDokument5 SeitenFluidization: Unit OperationHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid - Presentation1.pptx Lecture - 11 - Fixed-Fluidized BedsDokument17 SeitenFluid - Presentation1.pptx Lecture - 11 - Fixed-Fluidized BedsHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch2 PDFDokument30 Seitench2 PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cool Staff 1Dokument1 SeiteCool Staff 1Hamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polymer Chemistry:: Styrene Butadiene Rubber Marieam MouyedDokument2 SeitenPolymer Chemistry:: Styrene Butadiene Rubber Marieam MouyedHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polysulfone: HistoricalDokument4 SeitenPolysulfone: HistoricalHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- حميد سجينه PDFDokument8 Seitenحميد سجينه PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- طيف فلاح بتروكيمياويات PDFDokument4 Seitenطيف فلاح بتروكيمياويات PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimize Acetone Production Process from Isopropyl AlcoholDokument8 SeitenOptimize Acetone Production Process from Isopropyl AlcoholHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch2 PDFDokument30 Seitench2 PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Is PE Made: Polyethylene Plastic Production ProcessDokument3 SeitenHow Is PE Made: Polyethylene Plastic Production ProcessHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- مستند بلا The Application of Ethylene Propylene Rubber Production PDFDokument3 Seitenمستند بلا The Application of Ethylene Propylene Rubber Production PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenol Production via Sulphonation ProcessDokument2 SeitenPhenol Production via Sulphonation ProcessHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polybutadiene Rubber Properties and UsesDokument3 SeitenPolybutadiene Rubber Properties and UsesHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoplastic Elastomers: Geoffrey Holden, in Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, 2011Dokument4 SeitenThermoplastic Elastomers: Geoffrey Holden, in Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, 2011Hamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood-Plastic Composites Based On Recycled and Virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)Dokument13 SeitenDimensional Stability and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood-Plastic Composites Based On Recycled and Virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)Hamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report By: Taha Mushtaq Talib 3 Class Oil&gas RefiningDokument5 SeitenReport By: Taha Mushtaq Talib 3 Class Oil&gas RefiningHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimensional Stability and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood-Plastic Composites Based On Recycled and Virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)Dokument13 SeitenDimensional Stability and Mechanical Behaviour of Wood-Plastic Composites Based On Recycled and Virgin High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)Hamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- مستند بلا The Application of Ethylene Propylene Rubber Production PDFDokument3 Seitenمستند بلا The Application of Ethylene Propylene Rubber Production PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polybutadiene Report PDFDokument9 SeitenPolybutadiene Report PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vinyl Acetate Production: Chemical CharacterizationDokument3 SeitenVinyl Acetate Production: Chemical CharacterizationHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polybutadiene Report PDFDokument9 SeitenPolybutadiene Report PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Description: Figure 1: Molecular Structure of High Impact PolystyreneDokument4 SeitenGeneral Description: Figure 1: Molecular Structure of High Impact PolystyreneHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Is PE Made: Polyethylene Plastic Production ProcessDokument3 SeitenHow Is PE Made: Polyethylene Plastic Production ProcessHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- مستند بلا عنوانDokument4 Seitenمستند بلا عنوانHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polybutadiene Rubber Properties and UsesDokument3 SeitenPolybutadiene Rubber Properties and UsesHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- طيف فلاح بتروكيمياويات PDFDokument4 Seitenطيف فلاح بتروكيمياويات PDFHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoplastic Elastomers: Geoffrey Holden, in Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, 2011Dokument4 SeitenThermoplastic Elastomers: Geoffrey Holden, in Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, 2011Hamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited - PetroDokument4 SeitenEdited - PetroHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranem Ahmed SabryDokument3 SeitenRanem Ahmed SabryHamzah A. LaftaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressing Cavity Pump Overhaul GuideDokument5 SeitenProgressing Cavity Pump Overhaul Guidesdsds-54Noch keine Bewertungen
- Standardization Parameters For Production of Tofu Using WSD-Y-1 MachineDokument6 SeitenStandardization Parameters For Production of Tofu Using WSD-Y-1 MachineAdjengIkaWulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect 17 Amp Freq RespDokument22 SeitenLect 17 Amp Freq RespBent777Noch keine Bewertungen
- SmartRunway SmartLandingDokument39 SeitenSmartRunway SmartLandingMikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Khasi Community of MeghalayaDokument3 SeitenKhasi Community of MeghalayaMidhat FatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebrosur Silk Town PDFDokument28 SeitenEbrosur Silk Town PDFDausNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomyDokument10 SeitenCricothyroidotomy and Needle CricothyrotomykityamuwesiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMRAD - G1 PepperDokument13 SeitenIMRAD - G1 PepperRomero, Ken Angelo B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Is Revalida ExamDokument11 SeitenIs Revalida ExamRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radar PPNDokument5 SeitenRadar PPNSawaf MfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebook Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior An Introduction To Psychopharmacology 2Nd Edition Prus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDokument62 SeitenEbook Drugs and The Neuroscience of Behavior An Introduction To Psychopharmacology 2Nd Edition Prus Test Bank Full Chapter PDFeffigiesbuffoonmwve9100% (10)
- YOKOGAWADokument16 SeitenYOKOGAWADavide ContiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nakshatra Exaltation DebilitationDokument3 SeitenNakshatra Exaltation DebilitationBhanu Pinnamaneni100% (1)
- QUESTION A2 and A3 Examples PDFDokument24 SeitenQUESTION A2 and A3 Examples PDFDemian VeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFDokument102 SeitenManual Del GVMapper v3 3 PDFguanatosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of PID controllersDokument4 SeitenDesign of PID controllersFseha GetahunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dorian Auto production model with either-or constraints optimizationDokument1 SeiteDorian Auto production model with either-or constraints optimizationyanurarzaqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business PlanDokument63 SeitenBusiness PlanKristine BalanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- UPSC IFS Botany Syllabus: Paper - IDokument3 SeitenUPSC IFS Botany Syllabus: Paper - IVikram Singh ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ninoy Aquino Parks and Wildlife CenterDokument7 SeitenNinoy Aquino Parks and Wildlife CenterNinia Richelle Angela AgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016Dokument19 SeitenSynopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016AmAnDeepSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQDokument4 SeitenFunction and Euqations - Quantitative Aptitude Questions MCQAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsDokument7 Seiten37th APSDC Scientific PresentationsSatyendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Herbs and Foods Used As Galactogogues PDFDokument4 SeitenCommon Herbs and Foods Used As Galactogogues PDFHadi El-MaskuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shanidham - In-Shanidham Pacify Lord ShaniDokument3 SeitenShanidham - In-Shanidham Pacify Lord ShanisubramanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vincent Hoa's English 101 PortfolioDokument24 SeitenVincent Hoa's English 101 PortfoliovincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- BELL B40C - 872071-01 Section 2 EngineDokument38 SeitenBELL B40C - 872071-01 Section 2 EngineALI AKBAR100% (1)
- ABB 3HAC050988 AM Arc and Arc Sensor RW 6-En PDFDokument238 SeitenABB 3HAC050988 AM Arc and Arc Sensor RW 6-En PDForefat1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basler Electric 87T - Great InfoDokument3 SeitenBasler Electric 87T - Great InfoMrNoch keine Bewertungen