Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Govt. Engineering College Bikaner: A Power Point Persentation On Electro Cardio Gram
Hochgeladen von
Madan Dewasi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten11 Seitenthis is
Originaltitel
IJET-V2I6P11
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenthis is
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
11 Ansichten11 SeitenGovt. Engineering College Bikaner: A Power Point Persentation On Electro Cardio Gram
Hochgeladen von
Madan Dewasithis is
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
A
Power point persentation
On
ELECTRO CARDIO GRAM
2018-2019
Submitted to: Submitted by:
Mr. ravindra panchariya Madan lal dewasi
Department of EICE 15EEBEI026
B.Tech 4th year EICE
Govt. engineering college Bikaner
WHAT IS ECG ?
ECG stands for Electrocardiogram.
It refers to a test that is performed to check the
electrical activity of the heart.
The normal electrical activity indicates that the
heart is working normally.
ECG records the electrical impulses when the
heart is beating. These impulses are recorded
on a moving strip of paper or on a screen
it shows heart's electrical activity as line
tracings on paper.
What is ECG machine signal waves ?
The spikes and dips that appear in the tracings are called waves.
ECG has several types of waves to show fluctuation of heart
beating
Type of ECG machine waves
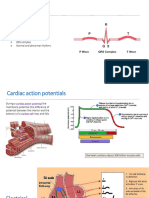
P Wave: It is the first upward movement of the ECG tracing. It
shows the electrical activity of the upper hear chambers.
QRS Complex: It consists of three waves that begin with a
downward deflection (Q) then a large upward deflection (R), and
then a downwards S wave. It shows the electrical activity of the
lower heart chambers.
ST Segment: It appears as a straight line when the ventricle
contracts without any electrical impulse.
T Wave: It is a modest upwards wave that represents ventricular
repolarization, i.e. when the lower heart chambers are preparing
for next muscle contraction.
How ECG works ?
Electrical impulse (wave of depolarisation) picked up by
placing electrodes on patient
The voltage change is sensed by measuring the current
change across 2 electrodes
a positive electrode and a negative electrode
If the electrical impulse travels towards the positive
electrode this results in a positive deflection
If the impulse travels away from the positive electrode this
results in a negative deflection
Electrodes and leads
Electrodes are the actual conductive pads attached to the
body surface.
Any pair of electrodes can measure the electrical potential
difference between the two corresponding locations of
attachment. Such a pair forms a lead.
Leads can also be formed between a physical electrode and
a virtual electrode, known as the Wilson's central terminal,
whose potential is defined as the average potential measured
by three limb electrodes that are attached to the right arm,
the left arm, and the left foot, respectively.
Commonly, 10 electrodes attached to the body are used to
form 12 ECG leads, with each lead measuring a specific
electrical potential difference
Continue..
Where to put electrode
The 10 electrodes in a 12-lead ECG are listed below.[21]
Electrode name Electrode placement
RA On the right arm, avoiding thick muscle.
LA In the same location where RA was placed, but on
the left arm.
RL On the right leg, lower end of inner aspect of calf
muscle. (Avoid bony prominences)
LL In the same location where RL was placed, but on
the left leg.
V1 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 and
5) just to the right of the sternum (breastbone).
V2 In the fourth intercostal space (between ribs 4 and
5) just to the left of the sternum.
V3 Between leads V2 and V4.
V4 In the fifth intercostal space (between ribs 5 and 6)
in the mid-clavicular line.
V5 Horizontally even with V4, in the left anterior axillary
line.
V6 Horizontally even with V4 and V5 in the mid-axillary
line.
Scope of ECG machine
ECG can detect various heart-related problems, some are listed
below;
A heart attack in the past (myocardial infarction)
Abnormal heart rhythms
Cause of unexplained chest pain
Enlargement of one side of the heart
Thickness of the walls of the heart chambers
Restricted blood supply to heart due to cholesterol deposits
To check the performance of implants like pacemaker
Thank you
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- REAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALDokument15 SeitenREAL Time ECG TRAINER MANUALSHANKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationVon EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Understanding An ECGDokument1 SeiteUnderstanding An ECGCecil-An DalanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg)Dokument12 SeitenElectrocardiogram (Ecg)Indranil SenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg PresentationDokument27 SeitenEcg Presentationanish3189Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Limb Leads (Frontal Plane)Dokument7 SeitenBipolar Limb Leads (Frontal Plane)jonna casumpangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 EcgDokument12 Seiten9 EcgTommy CharwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide TO: Noob'SDokument103 SeitenA Guide TO: Noob'SAgleema AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 1Dokument33 SeitenPresentation 1Даша КонстантиноваNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical TimeDokument14 SeitenElectrical TimeNithyaa SathishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)Dokument12 SeitenElectrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)श्रीकृष्ण हेङ्गजूNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS Physiology (Assignment) : Abu BakarDokument6 SeitenCVS Physiology (Assignment) : Abu BakarAbu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul EKGDokument101 SeitenModul EKGAjeng Dwik01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg Physio LectureDokument60 SeitenEcg Physio LectureAninze Chidera100% (1)
- Everything About ECGDokument4 SeitenEverything About ECGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECGDokument15 SeitenECGJegathese BaskerNoch keine Bewertungen
- MASTERING ECG LEADS - Bipolar Limb LeadsDokument4 SeitenMASTERING ECG LEADS - Bipolar Limb LeadsSharan MurugaboopathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Signals PDFDokument14 SeitenECG Signals PDFTohfatul JinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGDokument76 SeitenElectrocardiography: An Introduction To The ECGInnocent Clifford MaranduNoch keine Bewertungen
- EcgDokument7 SeitenEcgMohammed EhabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Base of The ElectrocardiogramDokument15 SeitenBase of The ElectrocardiogramPutri AfisiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electrocardiogram: Ecg: by Gaurishi Agarwal, 32Dokument17 SeitenThe Electrocardiogram: Ecg: by Gaurishi Agarwal, 32Gaurishi AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Made Easy by Mallareddy SripujaDokument46 SeitenECG Made Easy by Mallareddy Sripujagrreddy836100% (3)
- Auskultation. ECG - LastDokument5 SeitenAuskultation. ECG - LastAndreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Leads: Bipolar Limb Leads (I, II, and Unipolar Limb Leads (aVRDokument11 SeitenECG Leads: Bipolar Limb Leads (I, II, and Unipolar Limb Leads (aVRFelipe GallardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram12 LeadsDokument28 SeitenElectrocardiogram12 LeadsshyluckmayddpNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrocardiographyDokument13 SeitenElectrocardiographymuditanatomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecure-6 The Heat & Electrocardiogram (ECG)Dokument72 SeitenLecure-6 The Heat & Electrocardiogram (ECG)Noor AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg + Ventricular Tachycardia and FibrillationDokument9 SeitenEcg + Ventricular Tachycardia and Fibrillationsakkiyy154Noch keine Bewertungen
- ميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Electrocardiography ميكحلا دادعإ لكوع نسح يلع رمتسملا ميلعتلا مسق فارشإ ضيرمتلا ةرئاد يبطلا رصان عمجمDokument7 Seitenميحرلا نمحرلا الله مسب Electrocardiography ميكحلا دادعإ لكوع نسح يلع رمتسملا ميلعتلا مسق فارشإ ضيرمتلا ةرئاد يبطلا رصان عمجمأبوأحمد الحكيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- NMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsDokument4 SeitenNMTEC 211-ECG Lab InstructionsRisleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ElectrophysiologyDokument18 SeitenBasic ElectrophysiologyCarlo Domingo LadieroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg 111029102429 Phpapp01Dokument103 SeitenEcg 111029102429 Phpapp01Vickry WahidjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECGDokument62 SeitenECGSanju TanwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- LdfısjlısDokument52 SeitenLdfısjlısChristine HudginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief Introduction To The Standard 12-Lead ECG (EKG)Dokument29 SeitenA Brief Introduction To The Standard 12-Lead ECG (EKG)Lazar BoskovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of ECGDokument53 SeitenBasic Principles of ECGSmita Jain100% (1)
- ECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasVon EverandECG/EKG Interpretation: An Easy Approach to Read a 12-Lead ECG and How to Diagnose and Treat ArrhythmiasBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Elektrokardiogramm) Is A Graphic Produced by An ElectrocardiographDokument5 SeitenElektrokardiogramm) Is A Graphic Produced by An ElectrocardiographReverie ManalaysayNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Kupe - ECGDokument14 SeitenDR Kupe - ECGIrfan ZiadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic: Biophysical Basics of Electrocardiography and Blood Pressure Measurement Techniques Time: 2 HoursDokument5 SeitenTopic: Biophysical Basics of Electrocardiography and Blood Pressure Measurement Techniques Time: 2 Hoursnamar13766Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Read An Electrocardiogram (ECG) - Part One: Basic Principles of The ECG. The Normal ECGDokument84 SeitenHow To Read An Electrocardiogram (ECG) - Part One: Basic Principles of The ECG. The Normal ECGshaine htetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg PresentationDokument42 SeitenEcg PresentationAnwar SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial CentreDokument90 SeitenECG Interpretation: DR S J Bhosale DM, FPCC (Canada) Associate Professor Tata Memorial Centrevaishali TayadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conquering The ECGDokument25 SeitenConquering The ECGPankaj PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenLab Manualg8248418302Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECG All LeadsDokument25 SeitenECG All LeadsVIJAYKUMAR ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture-10 Electrocardiography PDFDokument28 SeitenLecture-10 Electrocardiography PDFSurya VootlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential LineDokument15 SeitenElectrocardiogram (Ecg) : Base Line or Isopotential Linegyspsunshine girlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg PlacementDokument7 SeitenEcg PlacementOliver Bagarinao100% (1)
- Project 2 Electrocardiography: Practical TasksDokument16 SeitenProject 2 Electrocardiography: Practical TasksFahad ShahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical 2: Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : by - Mohamad Azmir Bin Azizan Medical Lab Technologist Faculty of Medicine UitmDokument19 SeitenPractical 2: Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : by - Mohamad Azmir Bin Azizan Medical Lab Technologist Faculty of Medicine UitmraburtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Electrode PlacementDokument4 SeitenECG Electrode PlacementMannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- E.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentDokument36 SeitenE.C.G Machine: by Er.U.Karthik Premkumar, H.O.D - Biomedical Engineering DepartmentAch ThungNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Seminar On ECGDokument16 SeitenA Seminar On ECGVibha C PrabhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg Engl Large 126Dokument125 SeitenEcg Engl Large 126Andreea-Sânziana StanciuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Von EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Cardiograph yDokument2 SeitenElectro Cardiograph yNi Putu NitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg PrsentationDokument33 SeitenEcg Prsentationtehillahkabwe100Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12electrocardiogram Part 1Dokument18 Seiten12electrocardiogram Part 1Jaydave PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia Critique Paper 1Dokument4 SeitenMultimedia Critique Paper 1api-345838334Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revise Chap 12Dokument14 SeitenRevise Chap 12RACHEL DAMALERIONoch keine Bewertungen
- As 4587-1999 Water Mist Fire Protection Systems - System Design Installation and CommissioningDokument10 SeitenAs 4587-1999 Water Mist Fire Protection Systems - System Design Installation and CommissioningSAI Global - APAC100% (1)
- Student Teacher InterviewDokument3 SeitenStudent Teacher InterviewLauren ColeNoch keine Bewertungen
- UA5000 V100R019C06 Hardware Description 05 PDFDokument563 SeitenUA5000 V100R019C06 Hardware Description 05 PDFdabouzia slahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Council of Medical ResearchDokument6 SeitenIndian Council of Medical Researchram_naik_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Avenger 220 Cruise Street BS IVDokument79 SeitenAvenger 220 Cruise Street BS IVShubham AatopartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Michael J. Flynn - Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness, 1972Dokument13 SeitenMichael J. Flynn - Some Computer Organizations and Their Effectiveness, 1972earthcrosserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adient Managment CSRDokument68 SeitenAdient Managment CSRClaudia PEÑANoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Publishing ProcessDokument1 SeiteJournal Publishing Processmohamedr55104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mcs Text BookDokument309 SeitenMcs Text Bookkancha_basu2447100% (1)
- (English) Time and The Brain - The Illusion of Now - Hinze Hogendoorn - TEDxUtrechtUniversity (DownSub - Com)Dokument14 Seiten(English) Time and The Brain - The Illusion of Now - Hinze Hogendoorn - TEDxUtrechtUniversity (DownSub - Com)Диана ТатарчукNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thing in Itself Kantian: AnstoßDokument1 SeiteThing in Itself Kantian: Anstoßwhynotbequiet23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Akruti Marathi MultiFont Engine ReadmeDokument22 SeitenAkruti Marathi MultiFont Engine Readmenmshingote2779% (38)
- ECM 206 Site VisitDokument36 SeitenECM 206 Site VisitAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (2)
- Staffing ProcessDokument18 SeitenStaffing ProcessEbtesam EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Perceived Threat of Covid-19 and T.I (Reference Article)Dokument10 Seiten1-Perceived Threat of Covid-19 and T.I (Reference Article)Hassan NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urban Problems and SolutionsDokument12 SeitenUrban Problems and SolutionsJohn Lloyd Agapito50% (2)
- (Revised) Dale Carnegie-How To Win Friends and Influence People-Simon and Schuster (1981)Dokument12 Seiten(Revised) Dale Carnegie-How To Win Friends and Influence People-Simon and Schuster (1981)TomasUreñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr./Ar. Jocelyn A. Rivera-Lutap, Fuap, FriaDokument1 SeiteDr./Ar. Jocelyn A. Rivera-Lutap, Fuap, FriaShanaia BualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Leaflet Seawater ElectrochlorinationDokument4 SeitenProduct Leaflet Seawater Electrochlorinationgkdora574Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle CRM On DemandDokument2 SeitenOracle CRM On Demandajazahmednet3946Noch keine Bewertungen
- ROV Inspection and Intervention VesselDokument2 SeitenROV Inspection and Intervention VesselAhmad Reza AtefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet - StatisticsDokument3 SeitenWorksheet - StatisticsGabriel Ch MendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intellectual Property Rights: Indian PerspectiveDokument20 SeitenIntellectual Property Rights: Indian PerspectiveFateh Singh RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Placement Training Program: Sample Profiling (All About You)Dokument2 SeitenPre-Placement Training Program: Sample Profiling (All About You)RISHAV RAJ GUPTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4 Chapter 4 - CorrosionDokument2 SeitenTutorial 4 Chapter 4 - CorrosionHafizatul AqmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NC1 AC Contactor, 9 95A: Contactors ContactorsDokument2 SeitenNC1 AC Contactor, 9 95A: Contactors ContactorsYamendra GurungNoch keine Bewertungen
- 136 OsgoodeDokument8 Seiten136 Osgoodejawaid6970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Painting and Weathering Unlocked PDFDokument91 SeitenPainting and Weathering Unlocked PDFWrensEye100% (6)