Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
OWB600719 PS International Roaming
Hochgeladen von
Juan Carlos RCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
OWB600719 PS International Roaming
Hochgeladen von
Juan Carlos RCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
06.
April 2006 Security Level: Internal
WCDMA-PS
International
Roaming
www.huawei.com
WCDMA-PS Technical Support Department
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential
WCDMA-PS International Roaming
1. Introduction to Important Concepts of WCDMA-PS International Roaming
2. Basic Realization Process of International Roaming
• Typical Architectures of GPRS International Roaming
• Roaming land SGSN Requirements of GPRS International Roaming
• Use of DNS During GPRS International Roaming
• GPRS International Roaming APN-OI Selection
• Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for GPRS International
Roaming
3. Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of Unicom
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 2
Introduction to Important Concepts of PS International
Roaming
•VSGSN Visiting SGSN
•VGGSN Visiting GGSN
•HGGSN Home GGSN
•BG Border Gateway
•GRX GPRS Roaming Exchange
The GRX network is used to connect GPRS backbone networks and other GRX networks of
different operators to realize the interconnection and interworking between GPRS networks.
Different from the direct connection mode, the GRX network is an IP network professionally
operated and managed by the third party. The GRX network is responsible for the interconnection
between the GPRS networks of different operators. The GRX network is the core node of GPRS
roaming network. The GPRS network connecting with the GRX network can interconnect with the
GPRS network covered by the whole GPRS roaming network by the GRX network. Accordingly, a
GPRS operator can interconnect with one or a few GRX operators to realize the interconnection and
interworking with many GPRS operators at the network layer. At present, there are more than 20
GRX network operators all over the world. The operators connect most GPRS networks in the world.
•VPLMN Address allowed: Specifies whether the MS is allowed to use the APN in the domain of the
HPLMN only, or additionally the APN in the domain of the VPLMN.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 3
Introduction to Important Concepts of WCDMA-PS
International Roaming
• Local subscriber: the subscriber who subscribes in the local PLMN,
does not roam into another PLMN, and is activated at the local GGSN.
• Roaming subscriber: the subscriber who subscribes in the local PLMN,
roams into another PLMN, and is activated at the local GGSN.
• Visiting subscriber: the subscriber who subscribes in another PLMN,
roams into the local PLMN, and is activated by the local GGSN.
• Local subscriber + roaming subscriber = home subscriber of PLMN
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 4
WCDMA-PS International Roaming
1. Introduction to Important Concepts of WCDMA-PS International Roaming
2. Basic Realization Process of International Roaming
• Typical Architectures of GPRS International Roaming
• Roaming Land SGSN Requirements of GPRS International Roaming
• Use of DNS During GPRS International Roaming
• GPRS International Roaming APN-OI Selection
• Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for GPRS International
Roaming
3. Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of Unicom
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 5
Basic Realization Process of International Roaming
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 6
Basic Realization Process of International Roaming –
Typical Architecture 1
Routing within VPLMN: no control over subscribers’ activities
• The subscribers cannot use the
APN of homing land APN,
otherwise you cannot resolve
and get the accessed GGSN IP
address. For international
roaming, the subscription data
in HLR VPLMN Address
allowed must be TRUE.
+ efficient (direct) routing
+ There is no need for the
interconnection of DNS and
recursion resolution.
- HPMN has no control over the
call,
- dependent on TAP files for billing
-> no pre-paid billing possible
- no end to end QoS guarantied
- no Virtual Home Environment
(VHE)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 7
Basic Realization Process of International Roaming –
Typical Architecture 2
GSMA recommends GPRS routing via HPLMN
• Subscribers cannot use visited
land APN and GGSN, For
international roaming, the
subscription data in HLR
VPLMN Address allowed must
be FALSE.
+ HPLMN has full control over the
call
+ allows pre-paid billing
+ allows end to end QoS
+ Virtual Home Environment (VHE)
- Subscribers use the APN of
homing land to initiate services.
Interconnection is necessary
between GPRS networks.
- The recursion resolution of multi-
level DNS and the
interconnection between DNSs
are necessary.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 8
Basic Realization Process of International Roaming –
Typical Architecture 2: GRX Peering
• GRX peering allows
roaming between
operators connected to
different GRXs. Once a
GRX interconnects with
other GRXs, GPRS
operators are able to
communicate with all
other GPRS operators
and full global roaming
across an extensive and
linked network is
established.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 9
Basic Realization Process of International Roaming –
Typical Architecture 2: Realization Camel of Pre-Paid
International Roaming Service VPLMN SGSN IP
address is included in
VPLMN RAI information
should be included in IDP
• Mandatory requirement: APN for Create PDP context
request message
message
postpaid and prepaid subscribers
Active PDP context request Internet Initial DP
should be distinguished.
• Optional requirement: The IMSI or Home PLMN
Visit PLMN SCP
GGSN
MSISDN range for postpaid and SGSN
prepaid subscribers can be different.
APN and GGSN Prepaid Subscribers
• APN for domestic GPRS subscribers selection CDR
and roaming GPRS subscribers can be
the same.
• In Create PDP context message which DNS Server Billing system
sent from VPLMN SGSN, local GGSN
can get the VPLMN SGSN IP. By
searching the table of SGSNPLMN,
VPLMN MCCMNC code should be
found.
• After get the VPLMN MCCMNC code,
GGSN constructs the information
element of RAI and send this IE to SCP.
At this time, SCP receives the location
information for prepaid subscribers and
RAI shall be included in SCP CDR.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 10
GPRS International Roaming Realizes the
Requirements for Roaming Land VSGSN
•For the VSGSN of roaming land, configure the list of PLMNs where the
roaming is allowable. And ensure the service access of international
roaming subscribers.
•For the VSGSN of roaming land, configure correct SS7 data. And
ensure that the HLR signaling to the roaming subscriber home PLMN is
reachable.
•For the VSGSN of roaming land, configure a correct DNriserver. In
addition, according to the subscription data of subscriber and activation
request, construct a correct APN (APN NI+OI) to send it to DNS server,
and ensure that the subscriber activation is successful.
•The VSGSN of roaming land needs to realize the Gp interface, and
ensures that the route to the BG router is reachable.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 11
Use of DNS During GPRS International Roaming
• GPRS DNS is necessary in Intra-PLMN to realize the APN resolution
function within the local PLMN.
• All GRX providers will offer DNS routing.
• GRX provides the ROOT DNS function during GPRS international
roaming.
• The DNS between GPRS networks takes the DNS of GRX as the
ROOT to realize the recursion resolution of APN. In this way, roaming
subscribers can use the APN defined by homing land. By the DNS of
visited land, it is recursed to the DNS of GRX and the DNS of homing
land. After that, resolve the GGSN IP address of homing land, and
realize the activation.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 12
GPRS Internal Roaming APN-OI Selection
3 The APN from the single PDP context was selected APN OI: the string whose length is equal to or smaller than 36. APNOI
is made up of three LABELs. Between LABELs, “.” is used. At the end,
there must be “.gprs”. The characters of each LABEL can only be A – Z,
1 An APN was sent by the MS
a - z, 0 – 9, or the middle lin “-”. The configuration can be
implemented according to MNC & MCC, and the format is
User located
yes
“mncxxx.mccyyy.gprs”.
in HPLMN
no
no no HPLMN subscriber: HPLMN OI is the APNOI configured in SET
APN-OI in APN(R) APN-OI in APN(R) 3GSM/2GSM: the APNOI carried by an MS must be the HPLMN OI.
yes yes If MS is not configured with APNOI, select HPLMN OI (the APNOI
APN-OI is HPLMN
no
APN-OI is HPLMN
yes configured in SET 3GSM/2GSM).
yes no
VPLMN subscriber: HPLMN OI is the assembly APN OI according to
no no
VPLMN Address APN-OI is VPLMN the MNC and MCC in IMSI. VPLMN OI is the APNOI configured in SET
Allowed
yes yes 3GSM/2GSM:
yes no VPLMN
VPLMN AP VPLMN Address Forbid Allow
Access Barred Allowed HPLMN
no yes
VPLMN AP
yes Forbid Case 1 Case 2
Access Barred
a
no
Allow Case 3 Case 4
b
Case 1 Case 2 Case 3 Case 4
yes The MS carries VPLMN OI. Reject V OI Reject V OI
HPLMN AP
Access Barred
no The MS carries HPLMN OI. Reject Reject H OI H OI
The MS carries other OI. Reject Reject Reject Reject
The MS does not carry OI. Reject V OI H OI V OI
H OI
c a Activate PDP
Context Reject
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 13
GPRS International Roaming APN-OI Selection
A c ce s s req u es te d Ac c e s s re q ue st ed A c c e ss r equ es te d
2 A default APN is to be
in H PL M N in V PL M N o nly in V PL M N f irs t
chosen by the SGSN
yes
User located a b c
in HPLMN
no
yes
VPLMN Address Allowed
no
In terro g ate D N S w ith Int errog a te D N S w ith I nte rrog ate D N S w ith
yes
VPLMN AP A PN + H PL M N - O I AP N + V PL M N - O I A P N + VP LM N -O I
Access Barred
no
no no
APN(SGSN) for APN(SGSN) for
PDP type known PDP type known
yes yes
s uc ce ss s u c ce s s
APN := APN := D N S res ult D N S re s ult
APN(SGSN) APN(SGSN)
f ail fa il
A c tiv ate P D P C re ate P D P
Activate PDP a
a b C ont ex t R ejec t C on te xt R equ es t
Context Reject
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 14
Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for
GPRS International Roaming – Concepts
1. NAT Server: according to the networking requirements, the root DNS in an international
office or the local PLMN must be open to the root DNS of GRX or the DNS of another
network (according to the recursion principle, it can only be open to GRX; in the
existing network, the DNS query situation exists too). The NAT technology is used
when DNS uses a private network address. For the networking of the DNS that directly
uses a public network address, do not consider the technology. In the design, in order
to save IP addresses of public networks, DNS should use a private network address.
2. Firewall Policy: The destination and source addresses of packets allowed by a firewall
must concern all the SGSN, GGSN, and DNS servers in the GPRS network. In addition,
the source and destination protocol ports consist of the following UDP ports: 3386
(GTPV0), 2152 (GTPV1), 2123 (GTPV1), and 53 (DNS).
3. GRE: In fact, the GRE protocol is a kind of encapsulation protocol. It provides a
mechanism to encapsulate the message of a kind of protocol into the message of
another kind of protocol. In this way, messages can be transmitted in a heterogeneous
network. At this time, the message transmission channel is called tunnel.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 15
Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for
GPRS International Roaming – Concepts
1. IPSec: IPSec realizes the protection of IP datagram or upper layer protocol by two security
protocols AH (Authentication Header) and ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload). AH
(Authentication Header) is the message authentication header protocol. It provides the following
functions: data source authentication, data integrality check, and avoiding message resending.
The ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) protocol provides all the functions of AH protocol (the
data integrity check does not include the IP header) and the encryption function for IP messages.
You can use only one protocol: AH or ESP. And you can use these two protocols at the same time.
The security service provided by IPSec needs the shared key. The Internet Key Exchange,IKE
protocol provides IPSec with the automatic negotiation exchange key. Establishing and
maintaining security alliance services can simplify the usage and management of IPSec. At
present, the existing network realizes IPSec in ESP+IKE mode.
2. BGP: BGP is an external gateway protocol (EGP). It is different from internal gateway protocols
(IGP) such as OSPF and RIP. Its respect is not to find and calculate a route, but control the
transmission of route and select the best route. At the time of route update, BGP sends only the
updated route. In this way, the bandwidths occupied because BGP broadcast routes are greatly
reduced. It is applicable when plenty of route information must be transmitted in the Internet. BGP
thoroughly solves the loop problem by the AS path information. BGP is easily expanded, and
applicable for the new development of network.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 16
Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for
GPRS International Roaming – Combination of IPSec
and GRE
• Use the IPSEC protocol to
encrypt the data messages
transmitted between HQ and
branches.
• When the HQ provides a branch
with voice and video multicasting
services, the transmission of
multicasting data stream must pass
through the Internet. In order to
assure the security, use the IPSEC
technology to encrypt the voice and
video multicasting data packets
transmitted in the Internet, and
assure the confidentiality, integrality,
and reality of the transmission. The
IPSEC protocol can only encrypt
and protect unicast messages.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 17
Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for
GPRS International Roaming – Combination of IPSec
and GRE
GRE Tunnel
IPSec Tunnel
Remote
Corporate
Internet office
intranet
network
Router A Router B
At the time of the interconnection between existing networks,
first realize GRE, and then realize IPSec, last realize the release of BGP dynamic routing table.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 18
WCDMA-PS International Roaming
1. Introduction to Important Concepts of WCDMA-PS International Roaming
2. Basic Realization Process of International Roaming
• Typical Architectures of GPRS International Roaming
• Roaming Land SGSN Requirements of GPRS International Roaming
• Use of DNS During GPRS International Roaming
• GPRS International Roaming APN-OI Selection
• Introduction to Key Interconnection Technologies for GPRS International
Roaming
3. Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of Unicom
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 19
Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of
Unicom – Functions of Proxy GGSN
• In order to realize the homing land access of the China Unicom GPRS
subscriber who roams outside China, a set of international GGSN agent
gateway devices will be constructed in Beijing and Guangzhou respectively
(first consider the local GGSN, and then consider the new construction).
• After the node of GGSN agent device is added, there is no influence on the
SGSN of roaming land country. It implements the APN decision and access
point selection according to related 3GPP standards too. After the SGSN
initiates the PDP data connection to GGSN, the GGSN agent does not
construct a PDP data connection channel with SGSN like the usual GGSN
devices. By analyzing and modifying the PDP data packet, the GGSN agent
further assists the visiting land SGSN and the homing land GGSN to set up the
data connection, and realize the homing land access requirements of
international roaming subscriber.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 20
Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of
Unicom – Subscriber Access Under Different Scenes
Scene 1: local service
Other PLMN 3
Scene 2: national roaming service
DNS Scene 3: international roaming
BSC/PCU
Proxy GGSN
SGSN service
DNS HLR
DNS HLR 2
SGSN
1
GPRS backbone
network
BSC/PCU
BSC/PCU SGSN GGSN Gi
GGSN
Gi
MMS Email MMS Email
Operator Services Farm Internet Internet Operator Services Farm
Corporate Intranet Corporate Intranet
ICP ISP ICP ISP
WAP Streaming
WAP Streaming
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 21
Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of
Unicom – Flow When A Subscriber Implements the
International Roaming
DNS
Proxy GGSN
Visit PLMN
2 3 4
BSC/PCU
5 GPRS
backbone
1 8
SGSN
network
6
7
GGSN
1. A subscriber initiates an activation request to VSGSN.
MMS Email
2. VSGSN queries the APN to DNS.
Internet Operator Services Farm
3. DNS returns the address of the APN (it is Proxy GGSN here). Corporate Intranet
ICP ISP
4. VSGSN sends the request to Proxy GGSN. WAP Streaming
5. Proxy GGSN analyzes the activation request, and sends the
regenerate request to homing land HGGSN.
6. Homing land HGGSN sends the activation response to the SGSN.
7. VSGSN allows the activation initiated by an MS subscriber.
8. The MS implements the data service.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 22
Introduction to the International Roaming Scheme of
Unicom – Details
• The precondition of this scheme is that the route between SGSN and home GGSN is reachable.
• Roaming land SGSN must support and accept the activation response message whose GGSN address changes.
• The GGSN of international gateway office finds out the real APN according to the activation PDP
message, and judges whether the PROXY function is enabled under APN. If the function is
enabled, according to the carried MSISDN, check whether the number is in the configured number
segment. If it is matchable, you can find the home GGSN address. If the home GGSN address
found is not the Gn interface address of the board or the Gn interface address of another SPU
board of the device, encapsulate the GTP message and the carried IP/UDP header into a
complete IP message. And deliver the message to the bottom layer for route forwarding. At the
same time, deliver a sign to ask the bottom layer not carry out the SEQ modification.
• If the home GGSN address found is the Gn interface address of another SPU board of the device,
use the recommendation function to recommend the message to the mapping board for the
activation. If the address found is the Gn interface address of this board, directly implement the
normal activation flow.
• If you cannot find out the home GGSN, it indicates that the GGSN processes according to a
normal activation message. If the activation request is not matched to the MSISDN relationship
table, the subscriber cannot be PROXY, directly implement the related activation processing on the
board.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 23
References
• GPRS International Roaming and Application Wang Nanbin
• GRE Tunnel Technologies Introduction and Application Wang Yibin
41478
• Combined Application of IPSec and GRE Song Yufeng
• International Roaming Charging Solution for Prepaid Subscribers
Dong Fangshuo
• WGGSN GGSN9811 V800R002C05 Attribute Design Specifications
• 3GPP 23060
• 3GPP 29060
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential Page 24
06.April 2006 Security Level: Internal
Thank You
www.huawei.com
www.huawei.com
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. HUAWEI Confidential
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- In in Mobile - CamelDokument62 SeitenIn in Mobile - CamelManish Das100% (1)
- GPRS Roaming - Connectivity & ScenariosDokument18 SeitenGPRS Roaming - Connectivity & ScenariosManish Bansal100% (1)
- Learn SoRDokument8 SeitenLearn SoRRasheedKhouliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mmtel Architecture Overview: C2 GeneralDokument49 SeitenMmtel Architecture Overview: C2 GeneralClaudiu CiobanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMS BasicDokument11 SeitenSMS Basicsrsnth100% (1)
- Intelligent Networks (In) and CAMELDokument11 SeitenIntelligent Networks (In) and CAMELnaggu1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMS Service Centralization and Continuity Guidelines 9 May 2012Dokument14 SeitenIMS Service Centralization and Continuity Guidelines 9 May 2012eru5Noch keine Bewertungen
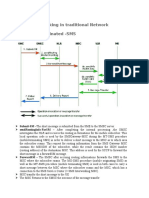
- 1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSDokument7 Seiten1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSdilipsharma04Noch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Call Path CourseDokument75 SeitenGSM Call Path CourseHeraa FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G SMS FlowDokument37 Seiten2G SMS FlowShaharyar KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMSC Call FlowsDokument12 SeitenSMSC Call FlowsAnkit Raina100% (1)
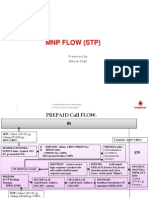
- Mobile Number Portability in IndiaDokument28 SeitenMobile Number Portability in IndiaphanivyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMS Signaling: Sebastian Schumann Slovak TelekomDokument49 SeitenIMS Signaling: Sebastian Schumann Slovak TelekomAshish ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VOIP SIP PardeepDokument85 SeitenVOIP SIP PardeepViswanathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Signaling Connection Control Part SCCPDokument12 Seiten2 Signaling Connection Control Part SCCPMohamed AbushamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camel PPSDokument82 SeitenCamel PPSmugeshpv90Noch keine Bewertungen
- ATI Call FlowDokument39 SeitenATI Call FlowVivek ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camel Call FlowDokument0 SeitenCamel Call FlowVenky KondepudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-02 Short Message ServiceDokument21 Seiten01-02 Short Message ServiceUmar MiskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleDokument87 SeitenGSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Basic PrincipleObaid RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Call FlowDokument11 SeitenIn Call FlowPrathyusha VijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telecordia IMS Presentation ConceptsDokument45 SeitenTelecordia IMS Presentation ConceptsballavNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMSC 1Dokument52 SeitenSMSC 1Manivannan LoganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Dokument49 SeitenCDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Clarence W HayesNoch keine Bewertungen
- HLR Data BarringDokument2 SeitenHLR Data BarringSamSameleviNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Terminating Call FlowDokument4 SeitenGSM Terminating Call Flowxxxhere100% (3)
- Presentation of 3GPP Charging Management-Sep 2004Dokument46 SeitenPresentation of 3GPP Charging Management-Sep 2004khubaib_maharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tac2 Workshop GSM Network: Call FlowDokument26 SeitenTac2 Workshop GSM Network: Call FlowAdinda Dendi IsnandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAMEL Feature1Dokument34 SeitenCAMEL Feature1elson brito juniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Protocol Stack - V2 26-08Dokument21 Seiten3G Protocol Stack - V2 26-08rizwanbhatt0% (1)
- Need For Global Title TranslationDokument5 SeitenNeed For Global Title TranslationKalaarangan100% (2)
- Fe MGWDokument34 SeitenFe MGWAmin100Noch keine Bewertungen
- MNP CAll FlowDokument13 SeitenMNP CAll Flowsurjeetyadav2014100% (1)
- SMPP+ Between SMSC and INDokument6 SeitenSMPP+ Between SMSC and INChethan VmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Flow Diameter To OCSDokument5 SeitenService Flow Diameter To OCSLiren AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSMA - Concept and Benefit For IPXDokument12 SeitenGSMA - Concept and Benefit For IPXbennyngNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Roaming GuideDokument76 SeitenInternational Roaming Guidevijrag_bit100% (1)
- Signaling in Telecommunication NetworksVon EverandSignaling in Telecommunication NetworksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Location Update DescriptionDokument12 SeitenLocation Update Descriptionpradeepkumarverma07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Huawei Csoftx3000 Signaling ProtocolsDokument23 SeitenHuawei Csoftx3000 Signaling Protocolsaajayagarwal80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tekelec SS7 GuideDokument24 SeitenTekelec SS7 GuideNaftal MassingueNoch keine Bewertungen
- TekelecDSR Presentation GSIFDokument24 SeitenTekelecDSR Presentation GSIFAntonio Albo MarotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access Barring AnalysisDokument3 SeitenAccess Barring Analysismathur_mayurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 International RoamingDokument10 Seiten13 International RoamingMahesh Kumar NigamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session 1 Session Fundamentals of NPDokument17 SeitenSession 1 Session Fundamentals of NPinm7ripeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMPP SMS Call FlowDokument1 SeiteSMPP SMS Call Flowkataz2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3GPP Charging PrinciplesDokument55 Seiten3GPP Charging Principlesf2zubacNoch keine Bewertungen
- IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandIP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkVon EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- SIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionVon EverandSIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsVon EverandBackhauling / Fronthauling for Future Wireless SystemsKazi Mohammed Saidul HuqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7.7.3 Configuring IS-IS Over Frame Relay: AlternateDokument8 SeitenLab 7.7.3 Configuring IS-IS Over Frame Relay: AlternateKishore Reddy KandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final KPI Target RevisionDokument1 SeiteFinal KPI Target RevisionIndrajeet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationDokument20 SeitenLab Report - Cisco Router ConfigurationfelipebrazilNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC)Dokument17 SeitenInternational Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC)AIRCC - IJCNCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Routing V10 enDokument46 SeitenRouting V10 ensybaritzNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Configure BGPDokument24 SeitenHow To Configure BGPGilles de WitteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Requirements and TechnologyDokument28 SeitenChapter 2 Requirements and Technologyrhouma rhouma100% (1)
- Ospf Lab GuidDokument3 SeitenOspf Lab Guidfalaad64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Copy ofDokument19 SeitenCopy ofNickhil RevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSRP Vs VRRP Vs GLBPDokument2 SeitenHSRP Vs VRRP Vs GLBPChristinah KenosiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSFB and Csfb-RimDokument23 SeitenCSFB and Csfb-Rimpanya prachachitNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITT420 - Exercise 1Dokument5 SeitenITT420 - Exercise 1Noor SalbiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- EX - No 8. Simulation of Distance Vector/Link State RoutingDokument2 SeitenEX - No 8. Simulation of Distance Vector/Link State RoutingHaru HarshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory-: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Is A Routing Protocol For Internet Protocol (IP)Dokument4 SeitenTheory-: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Is A Routing Protocol For Internet Protocol (IP)Saugat TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subnetting Ip V4 Kelas C: Contoh SoalDokument6 SeitenSubnetting Ip V4 Kelas C: Contoh Soalcokie24Noch keine Bewertungen
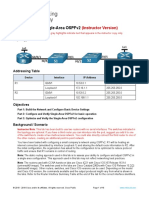
- 2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMDokument16 Seiten2.7.2 Lab - Configure Single-Area OSPFv2 - ILMMario Alberto Saavedra MeridaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIG-IP Advanced Routing Troubleshooting GuideDokument96 SeitenBIG-IP Advanced Routing Troubleshooting Guideปลาชุม ชุมพลNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virus Port MikrotikDokument2 SeitenVirus Port MikrotikKhodor AkoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- CiscoPress CCNP Enterprise Advanced Routing ENARSI 300 410 OfficialDokument1.157 SeitenCiscoPress CCNP Enterprise Advanced Routing ENARSI 300 410 Officialxmywayx5316Noch keine Bewertungen
- PRTG Report 2101 - A. Disponibilidad (Ping) - Created 2021-06-02 09-54-16 (2021-05-01 00-00 - 2021-05-31 00-00) UTCDokument2 SeitenPRTG Report 2101 - A. Disponibilidad (Ping) - Created 2021-06-02 09-54-16 (2021-05-01 00-00 - 2021-05-31 00-00) UTCSander SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Training For FM From HuaweiDokument102 Seiten3G Training For FM From HuaweiMuhammed YousriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timesheet - Raja Arif Ramoza 211016 - 07112016Dokument16 SeitenTimesheet - Raja Arif Ramoza 211016 - 07112016Afrilianti liaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE OverviewDokument44 SeitenLTE OverviewRavi SVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Survey of Wormhole Attack in Wireless Sensor NetworksDokument10 SeitenSurvey of Wormhole Attack in Wireless Sensor NetworksCSIT iaesprimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Router Manager User Manual EnglishDokument426 SeitenRouter Manager User Manual EnglishtotopgNoch keine Bewertungen
- U900 Activation RF Kpi Analysis - Cluster2 - 28 - May 2014Dokument20 SeitenU900 Activation RF Kpi Analysis - Cluster2 - 28 - May 2014Sana UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lte Blind HoDokument7 SeitenLte Blind Homanish_chaturvedi_19Noch keine Bewertungen
- GNS3 - OSPF Lab - Part 1: Learning ObjectivesDokument5 SeitenGNS3 - OSPF Lab - Part 1: Learning ObjectivesJe RelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6. - Dynamic Routing ProtocolDokument5 SeitenLab 6. - Dynamic Routing ProtocolChandra Prakash MeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RAN14.0 Introduction v11Dokument171 SeitenRAN14.0 Introduction v11Swandito HaryoyudantoNoch keine Bewertungen