Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Transformer Routine Test
Hochgeladen von
Farekh0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
151 Ansichten22 Seiten-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
151 Ansichten22 SeitenTransformer Routine Test
Hochgeladen von
Farekh-
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 22
IEC 60076 CONSISTS OF THE FOLLOWING PARTS,
UNDER THE GENERAL TITLE:
“POWER TRANSFORMERS”
Part 1: General
Part 2: Temperature rise
Part 3: Insulation levels, dielectric tests and external
clearances in air
Part 10: Determination of sound levels
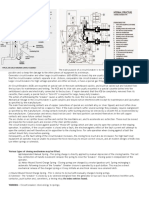
Visual Inspection
Insulation Resistance Test
Measurement of voltage ratio, vector group and
polarity displacement check
Winding Resistance Test at Ambient Temp.
Open Circuit Test (No Load Loss & I0)
Short Circuit Test (Load Loss & VZ)
Separate source AC withstand voltage test
Induced Potential Test
Protection Functional Check
Lightning Impulse Test
Determination of sound levels
Temperature Rise Test
OutLine Drawing suitability
Dimension suitability
Accessories completeness
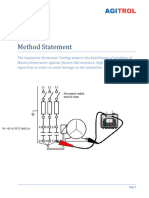
Measure the insulation resistance
between each terminals *:
HV – Body (ground)
LV – Body (ground)
HV – LV
At ambient temperature and corrected
to 20°C
*)1000 VDC, for 1 minute
Tool used: Megger® Insulation
Resistance Tester
Minimum Result for Transformer Insulation Resistance, and Temperature
Correction factor*
L-L Voltage Class Insulation Transformer Correction
(kV) Resistance Temperature Factor
(Mega Ohm)
1.2 32 15 0.73
2.5 68 20 1.0
5 135 25 1.3
8.66 230 30 1.8
15 410 35 2.5
25 670 40 3.3
34.5 930 45 4.5
46 1240 50 6.0
69 1860 55 8.1
Westinghouse: SUPERSEDES LL 47-600-100
Measure transformer turn/voltage ratio
between Primary and Secondary side
Calculation Value on relation:
Delta-Delta : Line Voltage HV
Line Voltage LV
Delta-Star : Line Voltage HV .
(Line Voltage LV / √3)
Star-Star : Line Voltage HV
Line Voltage LV
Star-Delta : (Line Voltage HV / √3)
Line Voltage LV
Maximum deviation tolerance was ±0,5%
Measuring by means of bridge method or voltage
drop method on principal tapping of each phase.
The no-load loss and the no-load current
shall be measured on one of the windings
at rated frequency and at a voltage
corresponding to rated voltage the
remaining winding or windings shall be left
open-circuited
Measure the impedance voltage and load loss
at rated frequency and rated current on
principal tap by applying to the high voltage
winding with the low voltage winding short-
circuited. The value of tests are corrected to
reference temperature (75° C)
The measurements shall be performed
quickly so that temperature rises do not cause
significant errors.
The test is intended to verify the AC withstand strength of the line and neutral
terminals and their connected windings to earth and other windings.
The separate source AC voltage test shall be made with single-phase
alternating voltage as nearly as possible on sine-wave form
The full test voltage shall be applied for 60 s between all terminals of
the winding under test connected together and all terminals of the remaining
windings, core, frame and tank or casing of the transformer, connected together
to earth.
The test is successful if no collapse of the test voltage occurs.
Line Voltage Class (kV) Applied Voltage (kV)
1.1 3
3.6 10
7.2 20
12 28
17.5 38
24 50
36 70
Table
Source
Transformer Under Test Step Up Transformer
The test is intended to verify the AC withstand strength
of each line terminal and its connected winding(s) to
earth and other windings, the withstand strength
between phases and along the winding(s) under test.
The test voltage across an untapped winding of the
transformer shall be as close as possible to twice the
rated voltage
When the test frequency exceeds twice the rated
frequency, the test time in seconds of the test shall be:
Transformer Frequency
T= 120 x (sec)
Generator Frequency
The test is successful if no collapse of the test voltage
occurs.
2x Nominal Voltage
at 350 Hz
The test is intended to verify the impulse withstand strength of
the transformer under test, when the impulse is applied to
its line terminals.
The impulse test sequence is applied to each of the line
terminals of the tested winding in succession, the other line
terminals of the winding shall be earthed directly.
The test sequence shall consist of one impulse of a voltage
between 50 % and 75 % of the full test voltage, and three
subsequent impulses at full voltage.
The absence of significant differences between transients
recorded at reduced voltage and those recorded at full test
voltage constitutes evidence that the insulation has withstood
the test.
Test object with or without its auxiliary cooling plant, the
test object shall be on no-load and excited at the rated
voltage of sinusoidal or practically sinusoidal waveform
and rated frequency.
Equation to acquire sound level :
Where :
LW : Acoustic Noise Level
LpA : Noise Pressure level
S0 : Surface area of transformer under measure
S : Surface area of measurement
The accepted Sound level value is : dB
Definition: The difference between the temperature of the
part under consideration and the external cooling medium
Standard method for determination of steady-state
temperature rises on the test is equivalent in short-circuit
test connection.
The purpose of the test is to establish:
the top-liquid and average liquid temperature rises in a
steady-state condition with dissipation of total losses;
the average winding temperature rise at rated current for the
average liquid temperature rise as determined above;
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Maintenance of TrafoDokument4 SeitenMaintenance of TrafoNauval Bangbang Dwi PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tan-Delta TestDokument2 SeitenTan-Delta TestRakesh BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Furanic Compounds PDFDokument6 SeitenFuranic Compounds PDFAbdullah GhannamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineral Insulating OilDokument96 SeitenMineral Insulating OilnbhawyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slip Ring Motor Liquid Resistor Soft Starting System (HV-LRS) PDFDokument4 SeitenSlip Ring Motor Liquid Resistor Soft Starting System (HV-LRS) PDFLouie FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Transformer - For SwitchayrdDokument20 SeitenPower Transformer - For SwitchayrdSindhuKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gbu100 6649-0.0 PDFDokument24 SeitenGbu100 6649-0.0 PDFmarkgaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dielectric Breakdown Voltage TestingDokument2 SeitenDielectric Breakdown Voltage TestingAxel Mahya Avichena100% (2)
- Open Circuit and Short Circuit Test On PDFDokument12 SeitenOpen Circuit and Short Circuit Test On PDFkeerthimai100% (2)
- Maintenance Manual - TD-TSP-0004-2A PDFDokument19 SeitenMaintenance Manual - TD-TSP-0004-2A PDFSidhartha MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVRDokument42 SeitenAVRMaged Mounir100% (1)
- 7420p008 Uptimax Ni-CD BatteryDokument16 Seiten7420p008 Uptimax Ni-CD BatteryNazif HawariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer BushingDokument11 SeitenTransformer BushingNunna BaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motors and GeneratorsDokument8 SeitenMotors and GeneratorsHealthyCut FarmsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Protection and Transformer FaultDokument3 SeitenTransformer Protection and Transformer FaultThirumalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Types of Closing Mechanism May Be FittedDokument2 SeitenVarious Types of Closing Mechanism May Be FittedshahedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circuit Breaker - For SwitchayrdDokument9 SeitenCircuit Breaker - For SwitchayrdSindhuKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alfanar Co.: Site Test Report Ng-Sa Name of Substation: Dammam Housing 115/13.8KV Substation # 3 Aux - Relay (Rxmb1) TestDokument2 SeitenAlfanar Co.: Site Test Report Ng-Sa Name of Substation: Dammam Housing 115/13.8KV Substation # 3 Aux - Relay (Rxmb1) Testjayabal100% (1)
- SIP5 6MD85-86 V07.50 Manual C015-9 en PDFDokument1.216 SeitenSIP5 6MD85-86 V07.50 Manual C015-9 en PDFandreabautista1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unbalanced Fault Analysis Lec 8Dokument20 SeitenUnbalanced Fault Analysis Lec 8Bante TadeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Transducer - LTS 6-NPDokument2 SeitenCurrent Transducer - LTS 6-NPFadhil Tresna NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power TransformersDokument37 SeitenPower TransformersGanesuni HarishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tapcon Site ReportDokument2 SeitenTapcon Site Reportganeshapec8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement Insulation Resistance of Motors GeneratorsDokument5 SeitenMethod Statement Insulation Resistance of Motors Generatorssite.eng1100% (1)
- Presentation DGADokument63 SeitenPresentation DGAMuhammad Ahmed100% (2)
- Dielectric OilDokument2 SeitenDielectric OilMohammed Imran100% (1)
- Controlled Switching of High-Voltage Circuit-BreakersDokument8 SeitenControlled Switching of High-Voltage Circuit-BreakersBaris GurbuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 BCD 1 B 28Dokument12 Seiten7 BCD 1 B 28pedro perezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Tan Delta and Resistivity Test - OTDDokument5 SeitenOil Tan Delta and Resistivity Test - OTDAnand MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active and Reactive PowerDokument2 SeitenActive and Reactive PowerEr Mohammad SadiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNV Earthing Rule Pag.36Dokument1 SeiteDNV Earthing Rule Pag.36CHOCAMAN1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drying Out Process For TransformerDokument4 SeitenDrying Out Process For TransformerAradhana Ray100% (1)
- Lock Rotor ProtectionDokument3 SeitenLock Rotor ProtectionTonoTonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easypact Cvs 2011engDokument84 SeitenEasypact Cvs 2011engthiago_gomes7953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityDokument37 SeitenPower Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied Universityrodruren01Noch keine Bewertungen
- Field Procedure For Overhauling Job of Power Transformer: Voltamp Transformers LTDDokument2 SeitenField Procedure For Overhauling Job of Power Transformer: Voltamp Transformers LTDSwarup NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meggering Insulation Resistance Testing of Dry-Type Power TransformerDokument3 SeitenMeggering Insulation Resistance Testing of Dry-Type Power TransformerSugeng SumarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning ProtectionTechniques For Roof-Top PV SystemsDokument27 SeitenLightning ProtectionTechniques For Roof-Top PV SystemspowerpuffgalsxgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ehv Circuit BreakersDokument12 SeitenEhv Circuit BreakersBoreda RahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Topic On: Circuit Breaker-IDokument25 SeitenSeminar Topic On: Circuit Breaker-IParameshwar TummetiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS-4 HV TestingDokument1 SeiteSS-4 HV TestingSoumya BhowmickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection SchemesDokument20 SeitenProtection SchemesMohamed Wahid100% (1)
- REF Fuse Application GuideDokument17 SeitenREF Fuse Application GuidemuskanumeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protection FundamentalsDokument28 SeitenProtection Fundamentalsteektak1100% (1)
- NZ7 ATSE (CB Class)Dokument17 SeitenNZ7 ATSE (CB Class)Rahmat Nur IlhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- REM615 Appl 756885 ENlDokument168 SeitenREM615 Appl 756885 ENlwilsonpamintuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Report: Measurement of Turns RatioDokument2 SeitenTest Report: Measurement of Turns RatioJRC TestingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Oil & Its EvolutionDokument7 SeitenTransformer Oil & Its EvolutionShrikanth SolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Group TestDokument16 SeitenVector Group Testvda0% (1)
- AVR DECS200 Instalation and CommissioningDokument1 SeiteAVR DECS200 Instalation and CommissioningralphholingsheadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Tester - Oil Breakdown Voltage (BDV) Tester - Power ElectronicalDokument2 SeitenOil Tester - Oil Breakdown Voltage (BDV) Tester - Power Electronicalmustafa1805100% (1)
- New GIS SPEC For 220kV 132kV & 66kV Ammended Type Test 10yrs May 2018 PDFDokument37 SeitenNew GIS SPEC For 220kV 132kV & 66kV Ammended Type Test 10yrs May 2018 PDFp_kashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type VTT 11, 12: Definite Time Delay RelayDokument6 SeitenType VTT 11, 12: Definite Time Delay RelayArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityVon EverandKnowledge is "Real Power": Introduction to Power QualityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Testing Method of StatmentDokument11 SeitenTransformer Testing Method of Statmentsite.eng1100% (1)
- Pamphlet On Maintenance and Overhauling of Lightning ArresterDokument10 SeitenPamphlet On Maintenance and Overhauling of Lightning ArresterAjay Kumar PoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing of TransformerDokument37 SeitenTesting of TransformerVikas GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformer Test ProceduresDokument28 SeitenTransformer Test ProceduresGonzalesCha100% (25)
- TransformerDokument9 SeitenTransformerVikas GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOC026.53.00796 8edDokument108 SeitenDOC026.53.00796 8edFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiang Helori PDFDokument1 SeiteTiang Helori PDFFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex-Linear LED Light FittingsDokument8 SeitenEx-Linear LED Light FittingsFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- KIL - LAL SERIES - Linear LightingDokument6 SeitenKIL - LAL SERIES - Linear LightingFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Champ LMV HID LuminairesDokument8 SeitenChamp LMV HID LuminairesFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- L Industrial Lighting Products: Table V/Effective Ceiling ReflectanceDokument2 SeitenL Industrial Lighting Products: Table V/Effective Ceiling ReflectanceFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- CoreLine Highbay PhilipsDokument3 SeitenCoreLine Highbay PhilipsFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Lighting Crouse Hinds PDFDokument356 SeitenIndustrial Lighting Crouse Hinds PDFFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Lighting Crouse Hinds PDFDokument356 SeitenIndustrial Lighting Crouse Hinds PDFFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zone ConceptDokument14 SeitenZone ConceptFarekhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abb Acs550 VFD ManualDokument192 SeitenAbb Acs550 VFD ManualPavan Kumar100% (2)
- Installation and Operating InstructionsDokument8 SeitenInstallation and Operating Instructionsronalde90Noch keine Bewertungen
- 50 HZ Vs 60hzDokument4 Seiten50 HZ Vs 60hzerson1981Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lista Chint Sep 18Dokument10 SeitenLista Chint Sep 18Daygo BarcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alpha 4 8 12 Eng ManuaaliDokument44 SeitenAlpha 4 8 12 Eng Manuaaliza3amNoch keine Bewertungen
- Display Na BAA01 - ManualDokument55 SeitenDisplay Na BAA01 - ManualTomislav DjidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacitors LMVPFCDokument56 SeitenCapacitors LMVPFCأمين توات الجزائريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installaton Manual FPRADokument30 SeitenInstallaton Manual FPRAjcardenas55Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preventive MaintenanceDokument31 SeitenPreventive MaintenanceNeeraj Singh100% (1)
- Sirona Orthophos XG Dental X-Ray - Maintenance Instructions PDFDokument58 SeitenSirona Orthophos XG Dental X-Ray - Maintenance Instructions PDFomar kassarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sdmo Telys 1 Control Panel ManualDokument40 SeitenSdmo Telys 1 Control Panel ManualGONZALO100% (1)
- Axpert MKS-MKS+ 1-5KVA Manual 20160301 PDFDokument36 SeitenAxpert MKS-MKS+ 1-5KVA Manual 20160301 PDFishtiaq3any1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protonix Fortuner Home & Industrial InvertersDokument2 SeitenProtonix Fortuner Home & Industrial InvertersPrem Chaudhary IndiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grundfosliterature DDEDokument24 SeitenGrundfosliterature DDEIvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDokument4 SeitenMODEL: SC330 Industrial Range Powered by Cummins: Diesel Generating Set 400/230 V - 50 HZ - 3phaseDefly GustiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siemens Indoor Air Quality Controller QPA84 - enDokument4 SeitenSiemens Indoor Air Quality Controller QPA84 - enStruja StrujićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dse4510 Mkii Dse4520 Mkii Operator ManualDokument116 SeitenDse4510 Mkii Dse4520 Mkii Operator ManualMário GuelreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Media Player PRN45HDDokument112 SeitenMedia Player PRN45HDslakojNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 PDFDokument70 Seiten3 PDFHerbin AryantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 MW Onix Solar Project Report PDFDokument13 Seiten1 MW Onix Solar Project Report PDFankit100% (2)
- HEYER ECONA - User Manual Rev. 1.1 EN 0817Dokument99 SeitenHEYER ECONA - User Manual Rev. 1.1 EN 0817JhonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sl20 Cg20 Parts Manual Ph7 Opl Pn-450222 (Rev-2) 042803Dokument29 SeitenSl20 Cg20 Parts Manual Ph7 Opl Pn-450222 (Rev-2) 042803naokito AkemiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADokument38 SeitenAMarius FloreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bidi-Switch: Power Switch Bidirectional InterfaceDokument9 SeitenBidi-Switch: Power Switch Bidirectional InterfaceSupuran RichardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VT6290 Manual PDFDokument68 SeitenVT6290 Manual PDFAmaury LoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.4.TEC100IndoorNew ComplianceDokument51 Seiten6.4.TEC100IndoorNew CompliancesumanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYGECO - Notice SB 0MAN052 H - ENGDokument20 SeitenHYGECO - Notice SB 0MAN052 H - ENGmarius tothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sircal Instruments (UK) LTD: MP-2000 Rare Gas Purifier Operating & Servicing ManualDokument31 SeitenSircal Instruments (UK) LTD: MP-2000 Rare Gas Purifier Operating & Servicing ManualPavel Vancu57% (7)
- Service Manual: Microwave OvenDokument40 SeitenService Manual: Microwave Ovenbram samyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course "EEM 2 DC Machines": WWW - Lucas-Nuelle - deDokument17 SeitenCourse "EEM 2 DC Machines": WWW - Lucas-Nuelle - desifuszNoch keine Bewertungen