Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Cells: Structure and Organization: 7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi 1
Hochgeladen von
fabia afani0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten23 SeitenThe cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology or cellular biology. In this presentation you will learn about what is cell, how the cell work, and all about cell.
Originaltitel
1. Cell
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology or cellular biology. In this presentation you will learn about what is cell, how the cell work, and all about cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
32 Ansichten23 SeitenCells: Structure and Organization: 7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi 1
Hochgeladen von
fabia afaniThe cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology or cellular biology. In this presentation you will learn about what is cell, how the cell work, and all about cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 23
Cells :
Structure and Organization
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 1
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 2
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 3
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 4
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 5
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 6
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
HIERARCHY OF CELL MOLECULER ORGANIZATION
Cell Organelles Nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast,
golgi apparatus
Supramolecules Ribosome, enzyme complex,
contractile system, microtubles
Macromolecules Nucleic acid, protein, lipid,
polysaccharide
Building Block Nucleotide, amino acid,
monosaccharide, fatty acid, glycerol
Intermediate Pyruvic, malate, citrate,
Metabolic gliceraldehide-3-phosphat
Precursor from CO2, H2O, Nitrogen, ammonia
Environment
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 7
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 8
Kuliah Biokimia Dasar
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Prokaryotic Cell
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 9
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Cell wall present No cell wall present
Plastids inside of chloroplast No plastids
No lysosomes Lysosomes found
Some centrioles present Centrioles are always present
Large vacuoles hold cell matter If vacuoles are present they are small
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 10
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Bacteria Cell
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 11
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Animal Cell
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 12
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Plant Cell
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 13
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Plasma Membrane
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 14
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Plasma Membrane
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 15
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Mitochondrion
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 16
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 17
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
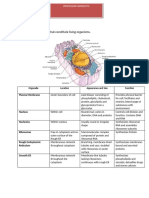
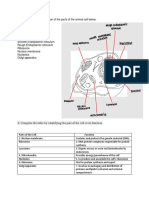
Cell Organization
Cell Part: Structure: Functions:
Plasma Membrane composed of a Serves as an external cell barrier;
membrane double layer of lipids acts in transport of substances
(phospholipids, cholesterol) into or out of the cell; externally
within which proteins are facing proteins act as receptors
embedded; proteins may (for hormones,
extend entirely through the neurotransmitters) and in cell-to-
lipid bilayer or protrude on cell recognition
only one face
Cell wall Depend on the organism Strengthen and give shape to the
cell
Cytoplasm Cellular region between the nuclear and plasma membranes;
consists of fluid cytosol, containing dissolved solutes, inclusions
(stored nutrients, pigments granules), and organelies, the
metabolic machinery of the cytoplasm.
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 18
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Cell Part: Structure: Functions:
Cytoplasmic organelles
−Mitochondria Rod-like, double-membrane Site of ATP synthesis;
structures; inner membrane powerhouse of the
folded into projections called cell
cristae
−Ribosome's Dense particles consisting of The sites of protein
two subunits, each synthesis
composed of ribosomal RNA
and proteins; free or attached
to rough ER
−Rough Membrane system enclosing a Makes proteins that are
endoplasmic cavity, the cistern a, and secreted from the cell;
reticulum coiling through the makes the cell's
cytoplasm; externally membrane
studded with ribosome's
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 19
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Cell Part: Structure: Functions:
−Smooth Membranous Site of lipid metabolism
endoplasmic system of
reticulum tubules; free of
ribosomes
−Golgi apparatus A stack of smooth Packages, modifies, and segregates
membrane sacs proteins for secretion from the cell
close to the and inclusion in lysosomes; sends
nucleus membranes from rough ER to their
destinations
−Lysosomes Membranous sacs Sites of intracellular digestion
containing acid
hydrolases
−Peroxisomes Membranous sacs The enzymes detoxify a number of
of oxidase toxic substances; the most
enzymes important enzyme, catalase, breaks
down hydrogen peroxide
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 20
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Cell Part: Structure: Functions:
−Microfilaments Fine filaments of the Involved in muscle contraction
contractile protein actin and other types of intracellular
movement; help form the cell's
cytoskeleton
−Intermediate Protein fibres; The stable cytoskeleton
filaments composition varies elements; resist tensile forces
acting on the cell
−Microtubles Cylindrical structures Support the cell and give it
composed of tubulin shape; involved in intracellular
proteins and cellular movements, form
centrioles
−Centrioles Paired cylindrical bodies, Organise a microtubule network
each composed of nine during mitosis to form the
triplets of microtubules spindle; form bases of cilia
and flagella
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 21
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Cell Part: Structure: Functions:
Nucleus Surrounded by the nuclear Control center of the cell;
membrane; contains fluid responsible for transmitting
nucleoplasm, nucleoli, genetic information and
and chromatin providing the instructions for
protein synthesis
−Nuclear Double bilipid membrane Separates the nucleoplasm from
membrane containing proteins; the cytoplasm and regulates
pierced by pores; passage of substances to
continuous with the and from the nucleus
cytoplasmic ER
−Nucleoli Dense spherical (non- Site of ribosome subunit
membrane-bounded) manufacture
bodies
−Chromatin Granular, threadlike material
composed of DNA and
histone proteins
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 22
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Next lecture:
pH and Buffer
7/9/2019 Kuliah Biokimia Dasar 23
Lab. Biokimia Nutrisi
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDokument6 SeitenCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- CytologyDokument20 SeitenCytologykaziba stephenNoch keine Bewertungen
- NatSci2 Chapter 3Dokument33 SeitenNatSci2 Chapter 3kayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5 FullDokument130 SeitenChap 5 Fullgaelle tannousNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument36 SeitenCellwnslthmangulad05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Dokument74 SeitenBiokim 4 - Bu Asih - sEL 2019Rizky NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyDokument3 SeitenLaboratory Report in Microbiology and ParasitologyynaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biological CellDokument23 SeitenThe Biological CellVivaMapwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 2 Cell Structure and FunctionDokument25 SeitenL 2 Cell Structure and Functionkaukab azimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Biol Lesson 7 Cell OrganellesDokument24 Seiten11 Biol Lesson 7 Cell Organellesfaiza purnomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDokument15 SeitenCell: The Basic Unit of LifeArslan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- CellDokument17 SeitenCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 - Tissues & Cells 2020Dokument32 SeitenTopic 2 - Tissues & Cells 2020Yan ZochowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsDokument65 SeitenThe Cell: Endomembrane System, Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Cytoskeleton and Extracellular ComponentsMeljean Kalaw CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsDokument3 SeitenList All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their FunctionsAira Shane MargesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDokument4 SeitenIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES Unit 3 - The CellDokument7 SeitenNOTES Unit 3 - The CellCarina LattoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles Structure & FunctionDokument4 SeitenCell Organelles Structure & FunctionDaniel ChinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleDokument3 SeitenWorksheet No. 1 - Cell OrganelleLaureen BarbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles and FunctionsDokument6 SeitenCell Organelles and FunctionsMia NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDokument4 SeitenCompare Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsJung Somin100% (1)
- Clinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsDokument10 SeitenClinical Hematology Cell Organelles and FunctionsEmmanuel Tristan OlarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell PhysiologyDokument11 SeitenCell PhysiologyjandaniellerasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemistryDokument4 SeitenBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Dokument6 SeitenExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDokument27 SeitenCell Structure and Cell OrganisationAzmaniza AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisDokument9 SeitenActivity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisEricka GenoveNoch keine Bewertungen
- CELLSDokument7 SeitenCELLSANGELO MOGRONoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana CellsDokument4 SeitenAna CellsDCRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant and Animal ScienceDokument10 SeitenPlant and Animal ScienceJason Alejandro Dis-ag IsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 5-4Dokument84 SeitenGroup 5-4googlegirl18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Notes 1Dokument10 SeitenBiochem Notes 1Coy NuñezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 49 Activity 1Dokument6 SeitenBio 49 Activity 1Theresa LambayonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDokument31 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Dokument46 Seiten1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)Dokument12 SeitenQuiz Fms 1 Questions and Answers 1. Describe The Organelle of The Cell (Cytoplasm and Its Components & The Functions of Each Organelles)deaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Label Parts and Functions of the Animal CellDokument2 SeitenLabel Parts and Functions of the Animal CellIsabella QuintosNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 345 S13 Continuity S14 (Chapter 5) S15 S16 S17 S18Dokument153 SeitenBIO 345 S13 Continuity S14 (Chapter 5) S15 S16 S17 S18gaelle tannousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsDokument18 SeitenBasic Unit of All Living Things: 3 Main RegionsRikki Mae BuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 104D MidtermsDokument27 SeitenChem 104D MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure ActivityDokument4 SeitenCell Structure ActivitysharksiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 1Dokument4 SeitenActivity 1sharksiedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDokument37 Seiten2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDokument6 SeitenCell Organelles and Their FunctionsVienne MonroidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell City Analogy 06Dokument2 SeitenCell City Analogy 06alek22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Botany Notes Part 2Dokument24 SeitenBotany Notes Part 2Rochenick MagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure and FunctionDokument32 SeitenCell Structure and Functionnaveedalikhoso365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellDokument12 SeitenInternal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellHACKER MANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDokument49 SeitenProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra StructureDokument8 SeitenMicrobio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra Structureapi-3743217100% (3)
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDokument39 SeitenLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell BiologyDokument30 SeitenCell BiologyHila Jagdish bhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction CellDokument48 SeitenIntroduction CellabdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDokument7 SeitenCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNoch keine Bewertungen
- PL4 Cell CompartmentsDokument11 SeitenPL4 Cell CompartmentsJake GopitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 LectureDokument13 SeitenModule 2 LectureJeal NochefrancaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cells F05Dokument31 SeitenCells F05Fetro Dola SyamsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Dokument34 SeitenIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANoch keine Bewertungen
- CellsDokument6 SeitenCellsaryam aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination Questions and Answers in BasDokument505 SeitenExamination Questions and Answers in Basdelton100% (1)
- Liposome Preparation Methods GuideDokument3 SeitenLiposome Preparation Methods GuideTheodøros D' SpectrøømNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 2 (Unfinished)Dokument22 SeitenUNIT 2 (Unfinished)青木ケイNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 NotesDokument12 Seiten1.4 Notesyara hazemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 General Biology 1Dokument23 SeitenModule 5 General Biology 1Glenn Capcap Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 4 Cell Transport ReviewerDokument7 SeitenTOPIC 4 Cell Transport Reviewerashhii ramosNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology 1 Lab: Modules 1 To 3Dokument22 SeitenGeneral Biology 1 Lab: Modules 1 To 3Naomi BelonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI 315 Midterm I NotesDokument44 SeitenBI 315 Midterm I Notes萩原 オードリーちゃんNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument20 SeitenBiologyAlecsD KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Biology Final Corrections PDFDokument109 Seiten9th Biology Final Corrections PDFashish varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prausnitz Derm Book Chapter 2012Dokument10 SeitenPrausnitz Derm Book Chapter 2012Valentina AdindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Lms in Medicine, Industry and Environmental BiotechnologyDokument634 SeitenBio Lms in Medicine, Industry and Environmental BiotechnologyHydraulique ScribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro to Zoology: Classification, Nutrition, EvolutionDokument13 SeitenIntro to Zoology: Classification, Nutrition, EvolutionRlan Gerard ManeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Slides - Fill in The BlanksDokument20 SeitenStudent Slides - Fill in The Blanksapi-663039855Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bbe+Tre 2021 C Ix p2 S&M Sample PaperDokument27 SeitenBbe+Tre 2021 C Ix p2 S&M Sample PaperasdhjkhhjksdfkjhjkhjhksfdjkhjkhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDokument5 SeitenAnimal Cells: The Building Blocks of LifePerry Sin67% (3)
- Membrane Potential: Dr. Arpana HazarikaDokument22 SeitenMembrane Potential: Dr. Arpana HazarikaDorin PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- NATS 1670 Recorded Lecture NotesDokument29 SeitenNATS 1670 Recorded Lecture NotescanaliphilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Processes and StructuresDokument157 SeitenBiology Processes and StructuresOmar SedkeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membran SelDokument62 SeitenMembran SelLena EnjelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SPM 2004 Paper 2Dokument12 SeitenBiology SPM 2004 Paper 2Sean100% (3)
- The Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaDokument176 SeitenThe Human Machine by RL Bijlani, SK ManchandaMUSKANNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsDokument24 SeitenANSWERS Worksheets Cell Structure FunctionsAnghel LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Van-Meer nrm2330Dokument13 SeitenVan-Meer nrm2330Oyindrila SamantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test Ch. 3 Cell Structure & FunctionDokument19 SeitenPractice Test Ch. 3 Cell Structure & Functionrofi modiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - Focusing Specimen Using The Compound MicroscopeDokument104 SeitenLesson 2 - Focusing Specimen Using The Compound Microscopehakuna matataNoch keine Bewertungen
- STC 222-1Dokument106 SeitenSTC 222-1Edeh Joshua100% (1)
- Common Mistakes-BiologyDokument8 SeitenCommon Mistakes-BiologyteahockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Dokument2 SeitenCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Mixed Matrix Membrane Development Progress and Prospect of Using 2D Nanosheet Filler For CO2 Separation and CaptureDokument28 SeitenMixed Matrix Membrane Development Progress and Prospect of Using 2D Nanosheet Filler For CO2 Separation and CaptureFikryNoch keine Bewertungen