Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Classrom PPT For Topologies
Hochgeladen von
darsh0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
27 Ansichten8 SeitenTYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Originaltitel
CLASSROM PPT FOR TOPOLOGIES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PPTX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenTYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
27 Ansichten8 SeitenClassrom PPT For Topologies
Hochgeladen von
darshTYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PPTX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
Network Topology
• A network is the way computer system or network or equipment connected to
each other physically or logically.
• Physical Topology :It refers to placement of networks various components, device
location, cable installation.
• Logical Topology : It refers to data flow within the network graphically mapping
these links in geometric shape.
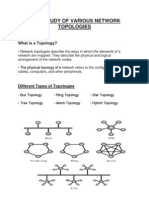
Types of Topologies
Ring Star Bus Mesh Tree
Topology Topology Topology Topology Topology
Ring topology
• In ring topology the nodes are
connected in the shape of a closed ring
so that each device is connected to two
other, one on either side.
• The ring works well where there is no
central-site computer system
• It is more reliable than a star network.
• The ring network requires more
complicated control software.
• Failure of one node results in the
failure of entire network.
Star Topology
• In star topology all the nodes are connected
to a central system called switch, which
forwards the data towards its final
destination. The switch controls the
communication on the network.
• It has minimal line cost and if any of the
local computer fails, the remaining remains
unaffected.
• The system crucially depends on the central
switch.
• If the central switch fails the entire network
goes down.
Bus Topology
•In a bus topology all the nodes are
connected to a central cable called
bus. A bus is a single continuous
cable. Transmission from any node
travels the length of the bus in both
direction and can be received by all
other nodes. The bus has terminator
at either ends which absorbs the
signal, removing it from the bus
•It is quite easy to set up, Failure of
one node does not effect the rest of
the network.
•It offers limited flexibility for
change.
•A signal on the bus must be strong
enough to reach the receiver.
Mesh topology
• A host is connected to one or more then 2 hosts.
• Fully connected network : all hosts have a point
to point connection to every other host in the
network.
•Partially connected network : not all host have
point to point connection to every other host.
•Data can be transmitted from different devices
simultaneously , even if one node fail there is
always an alternate present. So data transfer
doesn’t get affected.
•There are high chances
Tree topology
• It divides thenetwork in to multiple levels of
network. Mainly in LAN network is bifurcated into
3 types :
1) Highest layer is core layer.
2) Middle layer is distributive layer.
3) Lowest layer is access layer.
• It is scalable secondary nodes allow more
devices to be connected to a central node.
• Point to point connection of device, Having
different levels of the network makes it more
manageable hence easier fault identification
and isolation.
• Maintenance of the network may be an issue
when the network spans a great area.
• Since it is a variation of bus topology, if the
backbone fails, the entire network cripples.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Network TopologyDokument40 SeitenNetwork TopologyRez HabloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topologies PresentationDokument17 SeitenTopologies PresentationNaveen Bharath Reddy100% (1)
- Ansible Configuration Management - Second EditionDokument19 SeitenAnsible Configuration Management - Second EditionPackt PublishingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exstream01PrepApps PDFDokument147 SeitenExstream01PrepApps PDFAymen EL ARBINoch keine Bewertungen
- Django 1.2 ManualDokument1.077 SeitenDjango 1.2 ManualNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Fa Fit Class-Ix 4 Feb 2011Dokument113 SeitenFinal Fa Fit Class-Ix 4 Feb 2011TcvChauntraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsVon EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Commodore Power-Play 1982 Issue 03 V1 N03 WinterDokument78 SeitenCommodore Power-Play 1982 Issue 03 V1 N03 WinterSteven DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bca Project On Courier Management SystemDokument245 SeitenBca Project On Courier Management Systemnhnavneet85% (52)
- Types of Network TopologyDokument26 SeitenTypes of Network TopologyRoyan HabibieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument25 SeitenNetwork Topology421 Rushikesh Bhavsar IFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument25 SeitenNetwork TopologySSB WORLDNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Network TopologyDokument21 Seiten05 Network Topologyksav yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Lecture 03Dokument34 SeitenComputer Networks Lecture 03Farah QayoomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topologyies by SyedDokument19 SeitenTopologyies by SyedSyed hasan haiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 4Dokument31 SeitenLec 4Arslan Baloch AshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologiesDokument24 SeitenNetwork TopologiesArslanKamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks Computer NetworksDokument42 SeitenComputer Networks Computer Networksyashraj23Noch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument13 SeitenTopologyhadirehman488Noch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument37 SeitenTopologyMahbubul Islam KoushickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topology - Computer System ServicingDokument39 SeitenNetwork Topology - Computer System ServicingVhon Xander [Personal Channel]Noch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument7 SeitenTopologysbm2097Noch keine Bewertungen
- Network & TopologiesDokument19 SeitenNetwork & TopologiesIsha bajpaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data ComDokument16 SeitenData ComsonuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Layout of Network TopologyDokument12 SeitenCommon Layout of Network TopologyJosh VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4-Network TopologiesDokument17 SeitenLecture 4-Network TopologiesNikhil GaddamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1Dokument62 SeitenModule 1SINGH NAVINKUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topology ProjectDokument14 SeitenTopology ProjectAbhishek Gupta33% (3)
- 03 Network Physical StructuresDokument17 Seiten03 Network Physical Structuresimam ghozaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument11 SeitenTopologymebanlnongbri5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit2 090714220454 Phpapp01Dokument31 SeitenUnit2 090714220454 Phpapp01vdevanaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies: 1-Bus TopologyDokument4 SeitenNetwork Topologies: 1-Bus TopologyIqra KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN Topolologies and Security Issues: by Alex GettDokument37 SeitenLAN Topolologies and Security Issues: by Alex GettMarvin SinuesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument24 SeitenNetwork TopologyVahough BhielhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and Networks: Course: BBA Subject: Introduction To Computer Unit: 4Dokument27 SeitenData Communication and Networks: Course: BBA Subject: Introduction To Computer Unit: 4220479Noch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 6 NewDokument9 SeitenGROUP 6 NewIcy MenaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologiesDokument43 SeitenNetwork Topologiesayunik615Noch keine Bewertungen
- Communication System: Network TopologiesDokument29 SeitenCommunication System: Network Topologiesyus11Noch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument17 SeitenTopologyPiush SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies NewDokument31 SeitenNetwork Topologies NewNEHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communications and Networking: Basic DefinitionsDokument36 SeitenData Communications and Networking: Basic DefinitionsnandhakumarmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network SecurityDokument41 SeitenNetwork Securityking.harlemchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network1Dokument33 SeitenComputer Network1kumarmeenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument66 SeitenChapter 3Bante TadeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking 1.2Dokument7 SeitenNetworking 1.2Echo greenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologyDokument18 SeitenNetwork TopologyArchanaa PadmavathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Topologies and Networking Standard: Unit 2Dokument25 SeitenNetwork Topologies and Networking Standard: Unit 2pratyay dhondNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 CCNDokument17 SeitenLecture 2 CCNNoor UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopologyDokument33 SeitenTopologyRanjan Dwivedi100% (1)
- Network TopologiesDokument43 SeitenNetwork TopologiesKunal Sah100% (1)
- Basic NetworksDokument14 SeitenBasic NetworksGilgamesh berserkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network TopologiesDokument11 SeitenNetwork TopologiesYashfa ShafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking TopologiesDokument4 SeitenNetworking Topologiessamriti100% (6)
- Network TopologyDokument15 SeitenNetwork TopologyKritika TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3Dokument60 SeitenLecture 3bayisadamisseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.classification and TopologiesDokument50 Seiten2.classification and TopologiesSami AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Topology 10Dokument11 SeitenComputer Network Topology 10家星Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic NetworkingDokument8 SeitenBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNM Chapter1Dokument15 SeitenCNM Chapter1Piyush PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cchapter 1 - Part IIDokument39 SeitenCchapter 1 - Part IIBezabh AbebawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NotesDokument17 SeitenComputer NotesMuhammad Bilal Hassan CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhDokument11 SeitenDr. Neha Gulati Assistant Professor University Business School Panjab University, ChandigarhNavneet NandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter12 Network TopologyDokument31 SeitenChapter12 Network Topologyhet shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCC Unit 4Dokument17 SeitenDCC Unit 4shobhitshendre986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4-Network TopologyDokument32 SeitenLecture 4-Network Topologyjasmhmyd205Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture2 3 PDFDokument53 SeitenLecture2 3 PDFS SabbirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jsunil Tutorial: Scanned by CamscannerDokument6 SeitenJsunil Tutorial: Scanned by CamscannerdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample PapersDokument11 SeitenSample PapersdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porting Objective-C To Java: by Theresa Ray of Tensor Information Systems, IncDokument9 SeitenPorting Objective-C To Java: by Theresa Ray of Tensor Information Systems, Incjanardhan6429Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lakshya Talent Search Examination (LTSE-X)Dokument16 SeitenLakshya Talent Search Examination (LTSE-X)darshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lakshya Talent Search Examination (LTSE-X)Dokument16 SeitenLakshya Talent Search Examination (LTSE-X)darshNoch keine Bewertungen
- QNPoster1 BenefitsDokument1 SeiteQNPoster1 BenefitsdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse CircularDokument2 SeitenCbse CirculardarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse CircularDokument2 SeitenCbse CirculardarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- QNPoster3 Reasons PDFDokument1 SeiteQNPoster3 Reasons PDFdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Readme PDFDokument5 SeitenReadme PDFdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comedk Information Brochure 2019 VF PDFDokument31 SeitenComedk Information Brochure 2019 VF PDFdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Pattern SchemeDokument2 SeitenTraffic Pattern SchemedarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indigo Cadet Pilot Program: The CourseDokument2 SeitenIndigo Cadet Pilot Program: The CoursedarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eligibility Clauses To Claim For Government SeatsDokument5 SeitenEligibility Clauses To Claim For Government SeatsdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCC Basic ScienceDokument10 SeitenNCC Basic ScienceantharmukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- C# Compiler ErrorsDokument3 SeitenC# Compiler ErrorsKyle DalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 IT135-8Dokument3 SeitenWeek 3 IT135-8Jerwin Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- X-Sending and Receiving IDOCs Using A Single Stac... SCN PDFDokument4 SeitenX-Sending and Receiving IDOCs Using A Single Stac... SCN PDFbekirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xde SDKDokument4 SeitenXde SDKvijaykrsainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporte de SSDDokument7 SeitenReporte de SSDDaniel Vasquez CuevasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring RADIUS: in This ChapterDokument32 SeitenConfiguring RADIUS: in This ChapteraliahmadqjNoch keine Bewertungen
- WMM Specification 1-1Dokument36 SeitenWMM Specification 1-1Murali Thangaraj0% (1)
- SMSC Emi Ucp Interface 4.5Dokument89 SeitenSMSC Emi Ucp Interface 4.5mircammNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8MP Starlight Motorized IR Bullet Camera: TC-C38TS Spec: I8/A/E/Y/M/H/2.7-13.5mm/V5.0Dokument4 Seiten8MP Starlight Motorized IR Bullet Camera: TC-C38TS Spec: I8/A/E/Y/M/H/2.7-13.5mm/V5.0Wael Gab AllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ES2402 16P 2C User Manual PDFDokument97 SeitenES2402 16P 2C User Manual PDFPaul Ramos CarcaustoNoch keine Bewertungen
- DVD R155 ManualDokument75 SeitenDVD R155 ManualGeforcerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument2 SeitenGujarat Technological UniversityKrunal ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Programming: Engr. Waqar AhmedDokument20 SeitenMobile Programming: Engr. Waqar AhmedSajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swconfig50 Getting StartedDokument360 SeitenSwconfig50 Getting StartedJose Gerardo Pineda GalindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- FortiADC GLB Deployment GuideDokument23 SeitenFortiADC GLB Deployment GuideKunalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jayashree Type ConversionDokument5 SeitenJayashree Type ConversionBoobalan RNoch keine Bewertungen
- P063Dokument3 SeitenP063ZoYa MunirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cognitive TPG A760 Two-Color Thermal/Impact Hybrid Printer BrochureDokument2 SeitenCognitive TPG A760 Two-Color Thermal/Impact Hybrid Printer BrochureJohnny BarcodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Battlecard Microsoft PDFDokument1 SeiteBattlecard Microsoft PDFgutinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of New Bharat Fiber Unlimited Broadband Combo 100GB CUL ' Plan in All The Circles (Except A&N Circle) - W.E.F 05/02/2020 To 31/03/2020Dokument1 SeiteIntroduction of New Bharat Fiber Unlimited Broadband Combo 100GB CUL ' Plan in All The Circles (Except A&N Circle) - W.E.F 05/02/2020 To 31/03/2020rcpawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM Notes and Domino 9 Whats NewDokument6 SeitenIBM Notes and Domino 9 Whats NewSanthosh PcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mendeley Tutorial 2018Dokument67 SeitenMendeley Tutorial 2018Bagas Dyakso DarmojoNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTE Int RecDokument3 SeitenLTE Int RecSK Basak BDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Video ProcessingDokument3 SeitenVideo ProcessingBanafsheh RezaeianNoch keine Bewertungen